0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views13 pagesFinite State Machine Design Essentials
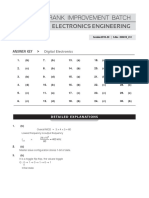
1) The document discusses various finite state machine approaches including Moore and Mealy models, state diagrams, and examples of state machines for an abb sequence detector, mod-5 counter, and frequency detector.
2) It also covers topics like underspecification, overspecification, metastability, clock gating, glitches, pulse detection, and edge detection circuits.
3) Examples are provided to illustrate Moore to Mealy and Mealy to Moore conversions, synchronous and asynchronous counters, and the use of flip-flops, synchronizers, and oneshot circuits.
Uploaded by
PABBATHI BALAJICopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views13 pagesFinite State Machine Design Essentials
1) The document discusses various finite state machine approaches including Moore and Mealy models, state diagrams, and examples of state machines for an abb sequence detector, mod-5 counter, and frequency detector.
2) It also covers topics like underspecification, overspecification, metastability, clock gating, glitches, pulse detection, and edge detection circuits.
3) Examples are provided to illustrate Moore to Mealy and Mealy to Moore conversions, synchronous and asynchronous counters, and the use of flip-flops, synchronizers, and oneshot circuits.
Uploaded by
PABBATHI BALAJICopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd