Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Documento Sin Título
Uploaded by
gladys0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Documento sin título
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesDocumento Sin Título
Uploaded by
gladysCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Grammar:
The description of the sequence, ordering, rules, structure, of a language to
determine what is good or wrong, regular or irregular, common or not common
in a language
Patterning:
The property that allows us to know the regular combination and ordering of
words in a phrase or sentence.
Approaches
Prescriptive approach:
Based on the Latin rules and Latin frameworks, to indicate the proper use of a
language.
Descriptive approach:
Gathering of language samples, describe the patterning of language behavior
and use to show the structure and use of each language.
Parts of speech: Classification of words.
Agreement: Concordance.
A verb is a word or group of words that is used in a sentence to indicate that
something happens or exists.
Types of verbs
● Auxiliary Verbs: commonly known as helping verbs are used to support the
main verb to describe an action. Amit is jogging regularly to reduce fat.
● Main Verbs: expresses or describes the principal action being done by the
subject. He was trembling in the cold weather.”
● Transitive verbs: there has to be an object.“The principal discussed the
indiscipline issue with the teachers.”
● Intransitive verbs: the object is not required.
● Complex-transitive verbs in English include believe, consider, declare, elect,
find, judge, keep, know, label, make, name, presume, pronounce, prove,
drive, rate, regard, and think.
An adjective is a word that modifies or describes a noun.
Types of adjectives
● Attributive adjectives: The adjectives that precede the noun or pronoun.
Pretty girl
● Predicative adjectives: Adjectives that occur after a linking verb.The girl is
pretty.
● Comparative adjectives: are used to compare two things Prettier, taller,
shorter, more beautiful.
● Superlative adjectives: are used to compare three or more things. highest,
shortest, most beautiful, nastiest.
● Interrogative Adjectives What, which, and whose, when they are used with
nouns to ask questions, are called Interrogative Adjectives. Whose book is
this?
● Proper Adjectives Adjectives formed from proper nouns are called Proper
Adjectives. Ex. British, Chinese etc. The British professor is teaching in the
class.
A determiner is a type of a word that sits before a noun or a noun phrase.
Types of determiners
● Articles indicate the specificity or definiteness. Articles can be classified into
two categories called definite articles (the) and indefinite articles (a, an).
● Possessive determiners indicate the possession or ownership. My, your, his,
her, its, our, their, and whose are the possessive determiners in the English
language.
● Quantifiers indicate the quantity. Cardinal numbers (one, two, three, etc.) and
indefinite adjectives (e.g., many, much, most, several, some) belong to this
category.
● Demonstrative determiners indicate the specificity and position of the noun.
This, that, these and those belong to this category.
Constituent Analysis: A type of analysis to show how small constituents go
together to form larger constituents.
Constituents: are words (elements) group together to form phrases.
Types of diagrams
Boxes: simply show the distribution of constituents.How many words? How many
phrases? Which phrases?
Diagram: Shows the types of forms that can be substituted at different levels of the
structure.
Labeled and bracketed analysis: Each constituent is distinguished using [ ] +
Labels of Parts of Speech. It shows: Labeled constituents. Hierarchical organization
of constituents.Sentence Level - Phrase Level Word Level.
The following comprehensive project aims to approach Descriptive Grammar
through three methods: Structural Analysis, Constituent analysis and Labeled and
Bracketed analysis. The first method is based on Parts of Speech where words are
classified according to the type (noun, verb, adjective…) and agreement, where
language characteristics (number, gender, voice, time, person) are described. The
second method shows the way in which small constituents (words/elements) group
together to create larger constituents (phrases), and the third method indicates the
hierarchical organizations of the constituents, starting from the complete sentence to
then identifying the group of phrases, the parts of speech of those groups of phrases
and others single elements. The same study sample will be used that combines groups
of phases that allow to put in practice the three different analyses, where, as in the
first part of the project, the grammatical and functional characteristics of each element
are specified.
Proofed (April 27, 2019). Vocabulary Tips: Is “Thank You” One Word or Two? Proofed.
Retrieved from https://getproofed.com/writing-tips/thank-you-one-word-or-two
You might also like
- From Word to Sentence: A Guide to Grammar, Usage, and Sentence StyleFrom EverandFrom Word to Sentence: A Guide to Grammar, Usage, and Sentence StyleNo ratings yet
- Revision Editing ChecklistDocument2 pagesRevision Editing Checklistsell hassNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument4 pagesEnglish GrammarBlue MoonNo ratings yet
- QUESTIONSSSDocument6 pagesQUESTIONSSSAlexaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document16 pagesLecture 3kundyz083No ratings yet
- Tugas English For Spesific PurposeDocument16 pagesTugas English For Spesific PurposeTaniaClaraNo ratings yet
- Summary 4th Meeting (Gina Adriani P Lanang A12223011)Document3 pagesSummary 4th Meeting (Gina Adriani P Lanang A12223011)gina adrianiNo ratings yet
- English 10 - 2nd GradingDocument69 pagesEnglish 10 - 2nd GradingKARYLLE LYRA CONSEBITNo ratings yet
- Learn Adjectives As Part of Speech For Bank 2Document11 pagesLearn Adjectives As Part of Speech For Bank 2waseemNo ratings yet
- Теор Грамма Ответы На ВопросыDocument85 pagesТеор Грамма Ответы На ВопросыSophieNo ratings yet
- Seminar 7Document8 pagesSeminar 7milenalarin8No ratings yet
- Unit 3 - SyntaxDocument11 pagesUnit 3 - SyntaxSofia SanchezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.2. Part-Of-Speech TheoriesDocument15 pagesLecture 2.2. Part-Of-Speech TheoriesGulziya MaratkyzyNo ratings yet
- Literature Review VerbsDocument6 pagesLiterature Review Verbsafmzfxfaalkjcj100% (1)
- Grammar GNS 101 - 045314Document23 pagesGrammar GNS 101 - 045314Juicy LipsNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument66 pagesGrammarWirun Cherngchawano100% (1)
- Linguistic Aspect: Tenses, Aspects, Simple Sentences, Compound Sentences, Complex SentencesDocument2 pagesLinguistic Aspect: Tenses, Aspects, Simple Sentences, Compound Sentences, Complex SentencesNesha Siti NurwulanNo ratings yet
- Discourse AnalysisDocument105 pagesDiscourse Analysismeymirah100% (5)
- ReadWrite Q1 W1 & 2 Pattern of Written Text & Evaluate Written Text OkDocument69 pagesReadWrite Q1 W1 & 2 Pattern of Written Text & Evaluate Written Text OkKookieTaeWins LoveConquersNo ratings yet
- Why Clauses-Lexico GrammarDocument16 pagesWhy Clauses-Lexico GrammarAmalia Rahma FirdausNo ratings yet
- Donasco - Stylistics, Discourse Analysis and Speech ActsDocument36 pagesDonasco - Stylistics, Discourse Analysis and Speech ActsHanah Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- GrammaireDocument15 pagesGrammaireYun LaraNo ratings yet
- Blacky Words From TKT Book, Eval. Lenguas ExtranjerasDocument11 pagesBlacky Words From TKT Book, Eval. Lenguas Extranjerasariannyencarnacion077No ratings yet
- Reading and Writing Skills Quarter 3 - Module 1: Patterns of Development in Writing Across DisciplinesDocument38 pagesReading and Writing Skills Quarter 3 - Module 1: Patterns of Development in Writing Across DisciplinesJelaii AguilarNo ratings yet
- Verbal AbilityDocument10 pagesVerbal AbilityUtkarsh DalmiaNo ratings yet
- Syntactic Categories: Aura Satya Pinasti 1801050043 6BDocument2 pagesSyntactic Categories: Aura Satya Pinasti 1801050043 6BAura SatyaNo ratings yet
- Inglese 2Document28 pagesInglese 2Roberta GambinoNo ratings yet
- Paper-Review BlancaDocument5 pagesPaper-Review BlancaSumayaNo ratings yet
- Kel 3.ADJECTIVESDocument9 pagesKel 3.ADJECTIVESDaviq Surya FarhanNo ratings yet
- VocabstrategiesDocument5 pagesVocabstrategiesapi-198070564No ratings yet
- Hand Out Mata Kuliah-SyntaxDocument16 pagesHand Out Mata Kuliah-SyntaxArief BaskoroNo ratings yet
- Questions for the Exams (Копия)Document4 pagesQuestions for the Exams (Копия)KanykeiNo ratings yet
- Eapp 11Document22 pagesEapp 11Regine FuentesNo ratings yet
- What Is Genre?Document10 pagesWhat Is Genre?Poco M3No ratings yet
- 6 PRESENTING GRAMMAR IN THE CLASSROOM IN THE 21stDocument37 pages6 PRESENTING GRAMMAR IN THE CLASSROOM IN THE 21stRomalaine Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Loaded Word Use For Persuasive Writing 8 Grade Mini-Lesson by Taylor Anne WeaverDocument2 pagesLoaded Word Use For Persuasive Writing 8 Grade Mini-Lesson by Taylor Anne WeaverTaylorNo ratings yet
- Module 6. Varieties of DiscourseDocument32 pagesModule 6. Varieties of DiscourseGrigoryNo ratings yet
- TKT Kal Part 3 Grammar Determiners and Pronouns PDFDocument9 pagesTKT Kal Part 3 Grammar Determiners and Pronouns PDFRachel Maria Ribeiro100% (1)
- English ReviewerDocument7 pagesEnglish Reviewerreyvier09elnarNo ratings yet
- Eggins 1994Document5 pagesEggins 1994thanhtamnguyen76100% (1)
- Sulisna Juharti Wd. Hesran Nurhayani Muhamat ImawanDocument21 pagesSulisna Juharti Wd. Hesran Nurhayani Muhamat ImawanJuharti JutiNo ratings yet
- 3.paragraph Development 1 - NIKDocument22 pages3.paragraph Development 1 - NIKChan BaekminNo ratings yet
- 20/20 Good: Learning Activity 1.1Document9 pages20/20 Good: Learning Activity 1.1Carmen BazurtoNo ratings yet
- Functional GrammarDocument4 pagesFunctional GrammarShyamal Kanti DasNo ratings yet
- Diction ParagraphDocument2 pagesDiction Paragraphapi-264701954No ratings yet
- Grammatical and Lexical CategoriesDocument10 pagesGrammatical and Lexical CategoriesMeenah PeixesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document71 pagesLesson 3Antonette RecopertoNo ratings yet
- Sentence AnalysisDocument32 pagesSentence AnalysisPantho BaruaNo ratings yet
- Unidad 1: What Is Formal Grammar?Document8 pagesUnidad 1: What Is Formal Grammar?IvánNo ratings yet
- Structural WordsDocument10 pagesStructural Wordstalitha sevrillaNo ratings yet
- Eggins 1994Document9 pagesEggins 1994Clases Particulares de InglésNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SyntaxDocument12 pagesIntroduction To SyntaxAmir SohailNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument25 pagesEnglishIvy BacallaNo ratings yet
- Happy LaiaDocument2 pagesHappy LaiaEdita laiaNo ratings yet
- Reflection About Pedagogical GrammarDocument4 pagesReflection About Pedagogical GrammarCitlaliNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive English Grammar Guide: From Basics to Competitive ExcellenceFrom EverandComprehensive English Grammar Guide: From Basics to Competitive ExcellenceNo ratings yet
- Applied Linguistics: A Genre Analysis Of: Research Articles Results and Discussion Sections in Journals Published in Applied LinguisticsFrom EverandApplied Linguistics: A Genre Analysis Of: Research Articles Results and Discussion Sections in Journals Published in Applied LinguisticsNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive English Learning: Your All-in-One Guide for ESL SuccessFrom EverandComprehensive English Learning: Your All-in-One Guide for ESL SuccessNo ratings yet
- Product PlanDocument25 pagesProduct Planapi-594514169No ratings yet
- Essential Question and Enduring Understanding TutorialDocument28 pagesEssential Question and Enduring Understanding TutorialAureliano BuendiaNo ratings yet
- Click On 1 4 Leaflet PDFDocument88 pagesClick On 1 4 Leaflet PDFEseniya TishkinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To You Are Not Addicted To Cigarette Smoking You Are Starving: How The Magic Mineral Prevents The Desire To Smoke - . .Document17 pagesIntroduction To You Are Not Addicted To Cigarette Smoking You Are Starving: How The Magic Mineral Prevents The Desire To Smoke - . .tshkrel100% (1)
- Rules of DebateDocument2 pagesRules of DebateTom MendiolaNo ratings yet
- A Literature Review On Indonesia'S Deradicalization Program For Terrorist PrisonersDocument18 pagesA Literature Review On Indonesia'S Deradicalization Program For Terrorist PrisonersShaheen AzadNo ratings yet
- Caribbean Studies IADocument18 pagesCaribbean Studies IAansa_france100% (1)
- Avid Vocabulary Word BankDocument17 pagesAvid Vocabulary Word Bankapi-243081850No ratings yet
- Demonio - A QuedaDocument4 pagesDemonio - A QuedaAnderson AugustoNo ratings yet
- Dekada 70 and The Patriot: A Film Analysis ofDocument3 pagesDekada 70 and The Patriot: A Film Analysis ofCHARLIES CutiesNo ratings yet
- 12A & 80G ProcedureDocument4 pages12A & 80G ProcedurekshripalNo ratings yet
- Torture Is A Pre-Psychotic SyndromeDocument140 pagesTorture Is A Pre-Psychotic SyndromeBradford S. WeeksNo ratings yet
- PROM-12395-002 1114007 BRO QIAstat-Dx 0518 SPREAD WWDocument3 pagesPROM-12395-002 1114007 BRO QIAstat-Dx 0518 SPREAD WWTaty ElejaldeNo ratings yet
- Menominee Tribe v. United StatesDocument13 pagesMenominee Tribe v. United Statesfirst lastNo ratings yet
- Flymaster NAV Manual EN v2 PDFDocument52 pagesFlymaster NAV Manual EN v2 PDFRoberto PlevanoNo ratings yet
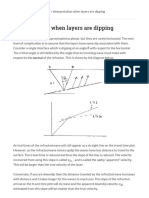
- Interpretation When Layers Are Dipping - Geophysics For Practicing Geoscientists 0.0Document5 pagesInterpretation When Layers Are Dipping - Geophysics For Practicing Geoscientists 0.0abd_hafidz_1No ratings yet
- Whats Important WorkbookDocument2 pagesWhats Important WorkbookCerchez IulianaNo ratings yet
- Impression Management For LawyersDocument27 pagesImpression Management For Lawyersrulenso passmoreNo ratings yet
- LP QuartilesDocument3 pagesLP QuartilesTheKnow04No ratings yet
- Hip Rafter Layout BasicsDocument5 pagesHip Rafter Layout BasicseeNo ratings yet
- The Nights - Chords Easy - Avicii (Version 1) - Guitar Chords, TabsDocument2 pagesThe Nights - Chords Easy - Avicii (Version 1) - Guitar Chords, TabslabNo ratings yet
- Improving Students' Speaking Proficiency in EFL Classes Through Oral Presentation TechniqueDocument132 pagesImproving Students' Speaking Proficiency in EFL Classes Through Oral Presentation TechniqueYasmine Hacini100% (1)
- Manga EvolutionDocument2 pagesManga EvolutionardhaNo ratings yet
- AI Lecture72006Document39 pagesAI Lecture72006BGSLCNo ratings yet
- Rorschach Audio: Ghost Voices and Perceptual Creativity by Joe BanksDocument8 pagesRorschach Audio: Ghost Voices and Perceptual Creativity by Joe BanksyoutreauNo ratings yet
- Principle of TotalityDocument23 pagesPrinciple of TotalityMarggie Salao50% (6)
- Ethics PaperDocument126 pagesEthics PaperDarshanSinghS100% (1)
- Chemotherapy Agents in Periodontal Treatment 2Document5 pagesChemotherapy Agents in Periodontal Treatment 2shathaNo ratings yet
- Dress Sexy For My FuneralDocument20 pagesDress Sexy For My Funeralbrlrek0010% (1)
- Durga Anand Sanipilli: Obile Mail Nandsanipilli Gmail COMDocument3 pagesDurga Anand Sanipilli: Obile Mail Nandsanipilli Gmail COMDurgaAnandNo ratings yet