Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Y9SciLW Full Answers For Web-Pages-27
Uploaded by
justforlessons130 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageThe document describes three experiments to distinguish between physical and chemical changes:
1. The first experiment examines changes in color for various substances when heated and cooled or after water is added. It determines whether the color change is physical or chemical based on reversibility.
2. The second experiment examines the color of limestone powder before and after heating using universal indicator. Although the appearance stays the same, the indicator color changes from green to blue, showing the substance changed from neutral to basic.
3. Since new substances are formed during the chemical change but not the physical changes, the limestone experiment demonstrates a chemical change occurred when it was heated.
Original Description:
Original Title
Y9SciLW Full Answers for Web-pages-27
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes three experiments to distinguish between physical and chemical changes:
1. The first experiment examines changes in color for various substances when heated and cooled or after water is added. It determines whether the color change is physical or chemical based on reversibility.
2. The second experiment examines the color of limestone powder before and after heating using universal indicator. Although the appearance stays the same, the indicator color changes from green to blue, showing the substance changed from neutral to basic.
3. Since new substances are formed during the chemical change but not the physical changes, the limestone experiment demonstrates a chemical change occurred when it was heated.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageY9SciLW Full Answers For Web-Pages-27
Uploaded by
justforlessons13The document describes three experiments to distinguish between physical and chemical changes:
1. The first experiment examines changes in color for various substances when heated and cooled or after water is added. It determines whether the color change is physical or chemical based on reversibility.
2. The second experiment examines the color of limestone powder before and after heating using universal indicator. Although the appearance stays the same, the indicator color changes from green to blue, showing the substance changed from neutral to basic.
3. Since new substances are formed during the chemical change but not the physical changes, the limestone experiment demonstrates a chemical change occurred when it was heated.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Answers 27
Description of Name(s) of any new substance(s) How the change can be
the change formed by the change reversed
19. Milk going sour Sour milk contains lactic acid and other It’s impossible to make sour milk fresh
substances. again.
20. Picking up nails None. Pull the nails off again.
with a magnet
21. Rusting Rust (an oxide coating). In a blast furnace – not easy.
Results
1. 1, 2, 5, 6, 8, 11, 12, 14, 15, 16, 18, 20.
2. 3, 4, 7, 9, 10, 13, 17, 19, 21.
Conclusions
1. The first list of changes in the results are physical changes.
2. The second list of changes in the results are chemical changes.
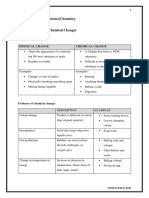
Reversible and irreversible changes (page 108)
Results
Colour before Colour when Colour after Colour after
Substance heating hot cooling water added
Zinc oxide White Yellow White White
Copper carbonate Green Black Black Black
Copper sulfate Blue White White Blue
Conclusions
1. This colour change is a physical change because the change reversed on cooling.
2. This colour change is a chemical change because the change did not reverse on cooling / the change was
permanent.
3. This colour change is a physical change because the change reversed on adding water.
Detecting chemical changes (page 109)
Results table
Colour of the Universal Indicator
Appearance of the limestone after mixing with limestone powder
Before heating White powder Green
After heating White powder Blue
Conclusions
1. The powder’s appearance stays the same.
2. The powder changes from neutral to basic.
Therefore, since new substances are formed, the change must be chemical.
Questions
1. Acidic.
2. CO2
You might also like
- Form 2 Chemistry Physical and Chemical Changes PDFDocument6 pagesForm 2 Chemistry Physical and Chemical Changes PDFivanna pierreNo ratings yet
- Virtual Lab Physical or Chemical ChangeDocument2 pagesVirtual Lab Physical or Chemical ChangeAustin Williams83% (6)
- Chem1200A Lab Experiment 2Document4 pagesChem1200A Lab Experiment 2Amy BalicagNo ratings yet
- Unit Standard Number Unit Standard Title Demonstrate Knowledge of Chemical Change. Element RangeDocument5 pagesUnit Standard Number Unit Standard Title Demonstrate Knowledge of Chemical Change. Element Rangeapi-3826124No ratings yet
- Physical N Chemical ChangesDocument16 pagesPhysical N Chemical Changessarahudi100% (4)
- Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab Reportivan glenn baldomerostNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Part 5Document10 pagesChemistry - Part 5BALA GANESHNo ratings yet
- Clas 10 Chemistry ch-1 April Day 1Document4 pagesClas 10 Chemistry ch-1 April Day 1gourav kaliaNo ratings yet
- Matter and It's PropertiesDocument6 pagesMatter and It's PropertiesUlysses Carcido AraoNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Act 7Document5 pagesData Sheet Act 7Altricia Nicolle LadoresNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Changes: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument14 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StylealoobhujiaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Experiment 2: Understand The Changes in Terms of Chemical and Physical PropertiesDocument2 pagesLab Report: Experiment 2: Understand The Changes in Terms of Chemical and Physical PropertiesAriful IslamNo ratings yet
- Physical Change and Chemical ChangeDocument50 pagesPhysical Change and Chemical ChangeAebee AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Physical & Chemical Changes-Class 7Document4 pagesPhysical & Chemical Changes-Class 7satyam.nigam1552No ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Changes Lab ReportDocument5 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes Lab ReportWilliam CarriereNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report BiochemistryDocument6 pagesLaboratory Report BiochemistryMuhammad Haziq Fikri Bin Mohd Nazri J22A0134No ratings yet
- Mpah Tg5 U10 AnswersDocument2 pagesMpah Tg5 U10 AnswersDita KusumaNo ratings yet
- OVERMUGGED 2023 Sec 2 Science - Worksheet (Question)Document30 pagesOVERMUGGED 2023 Sec 2 Science - Worksheet (Question)Danisha MutiaraNo ratings yet
- Document Copy 2Document3 pagesDocument Copy 2jodycarlisaNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Changes: Hashim, Sha-Yna Fatma O. Alih, Kathly AnnDocument5 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes: Hashim, Sha-Yna Fatma O. Alih, Kathly AnnAlih KathlyannNo ratings yet
- Prac3 Mthetheleli 221040133Document4 pagesPrac3 Mthetheleli 221040133Mthetheleli NxeleNo ratings yet
- Classification of Matter and Its PropertiesDocument8 pagesClassification of Matter and Its PropertiesBarachiel Vedua100% (1)
- UntitledDocument36 pagesUntitledGirija KushwahNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical ChangeDocument22 pagesPhysical and Chemical ChangeSharmaine C. TABADANo ratings yet
- Experiment #1 - Food TestDocument5 pagesExperiment #1 - Food TestZachary MedwinterNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Property WorksheetDocument2 pagesPhysical and Chemical Property WorksheetTshanna RobertsNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Property WorksheetDocument2 pagesPhysical and Chemical Property WorksheetTshanna RobertsNo ratings yet
- 647bfb2b3d4f0-Changes in Matter Part 1 2Document8 pages647bfb2b3d4f0-Changes in Matter Part 1 2Erandi Kusala AmarasiriNo ratings yet
- Sci7 - Ch2 - L4 - MatterDocument43 pagesSci7 - Ch2 - L4 - Mattertchr keiNo ratings yet
- Copia de Chemical and Physical ChangesDocument14 pagesCopia de Chemical and Physical ChangesJuan Fernando Zapata GarciaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Chemical Equilibrium CHM420Document9 pagesExperiment 5 Chemical Equilibrium CHM420najwa nabilaNo ratings yet
- EASEOHSP II - Chemistry Module 15 Changes That Matter Undergoes PDFDocument24 pagesEASEOHSP II - Chemistry Module 15 Changes That Matter Undergoes PDFMantikar IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Changes Class 7 ScienceDocument17 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes Class 7 Sciencesanyam nayakNo ratings yet
- CHY 40.1 Formal Laboratory Report PDFDocument9 pagesCHY 40.1 Formal Laboratory Report PDFSugar Rey Rumart RemotigueNo ratings yet
- Physical Changes and Chemical ChangesDocument3 pagesPhysical Changes and Chemical Changess2014290No ratings yet
- NCERT - Class7 Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument6 pagesNCERT - Class7 Physical and Chemical ChangesSyed Kashif HasanNo ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument18 pagesChem ReviewerMariz del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Tabaldo, Raynanact.5 Physical, ChemicalDocument5 pagesTabaldo, Raynanact.5 Physical, ChemicalRaynan TabaldoNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS Science Quarter 4 Module 3Document3 pagesANSWERS Science Quarter 4 Module 3Chelsea Nicole La ViñaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The IonsDocument2 pagesAnalysis of The IonsJoanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerNo ratings yet
- Set I Physical and Chemical Changes VII-Answer KeyDocument5 pagesSet I Physical and Chemical Changes VII-Answer KeyPranav JNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument4 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsClement MwapeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Chemical EquilibriumDocument22 pagesExperiment 4: Chemical EquilibriumCess MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Reactions: For Class 10Document30 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Reactions: For Class 10HimanshuNo ratings yet
- Act5 AnswersDocument7 pagesAct5 AnswersOmar AdilNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Day 2Document52 pagesWeek 3 Day 2Precilla HalagoNo ratings yet
- Bread Making Teacher ChartDocument2 pagesBread Making Teacher ChartAnnisa ZulfahNo ratings yet
- Matter Quiz With AnswersDocument8 pagesMatter Quiz With AnswersRalph Edward LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document10 pagesChapter 14Linn TanNo ratings yet
- Chemical or Physical Change Worksheet-2Document2 pagesChemical or Physical Change Worksheet-2fakhar.0917No ratings yet
- Year 8 Chapter 1 How Plants GrowDocument32 pagesYear 8 Chapter 1 How Plants GrowNicholas Leong100% (1)
- CC pg4Document1 pageCC pg4api-292408320No ratings yet
- May 7 Grade 5 Chemical Reactions Offline ENGDocument5 pagesMay 7 Grade 5 Chemical Reactions Offline ENGngulubetsereletso89No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument4 pagesChapter 2: Physical and Chemical ChangesNaqvi play'sNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Physical and Chemical Changes 1Document45 pagesCH 6 Physical and Chemical Changes 1Khoa Hoa Nguyen Thi Thu TrangNo ratings yet
- 5 Indicators of A Chemical ChangeDocument13 pages5 Indicators of A Chemical ChangeFelix AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- IodinDocument7 pagesIodinMizni Zaharanil HilmiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 7 - Physical and Chemical Changes 1Document5 pagesExperiment No. 7 - Physical and Chemical Changes 1Airame Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Year 8 ReactionsDocument3 pagesYear 8 ReactionsCally ChewNo ratings yet
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1991From EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1991Philip M. WeintraubNo ratings yet
- Y9SciLW Full Answers For Web-Pages-2Document1 pageY9SciLW Full Answers For Web-Pages-2justforlessons13No ratings yet
- Y9SciLW Full Answers For Web-Pages-54Document1 pageY9SciLW Full Answers For Web-Pages-54justforlessons13No ratings yet
- Y9SciLW Full Answers For Web-Pages-44Document1 pageY9SciLW Full Answers For Web-Pages-44justforlessons13No ratings yet
- Y9SciLW Full Answers For Web-Pages-35Document1 pageY9SciLW Full Answers For Web-Pages-35justforlessons13No ratings yet
- Y9SciLW Full Answers For Web-Pages-49Document1 pageY9SciLW Full Answers For Web-Pages-49justforlessons13No ratings yet
- Y9SciLW Full Answers For Web-Pages-4Document1 pageY9SciLW Full Answers For Web-Pages-4justforlessons13No ratings yet
- Y9SciLW Full Answers For Web-Pages-6Document1 pageY9SciLW Full Answers For Web-Pages-6justforlessons13No ratings yet