Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Probability Distribution
Probability Distribution
Uploaded by
Vignesh R0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesThe document discusses probability distributions and the normal distribution. It provides details on the normal curve being a symmetrical and bell-shaped distribution centered around the mean. It notes that approximately 68% of values in a normal distribution are within one standard deviation of the mean, 95% are within two standard deviations, and 99.7% are within three standard deviations.
Original Description:
Statatics
Original Title
Probability distribution
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses probability distributions and the normal distribution. It provides details on the normal curve being a symmetrical and bell-shaped distribution centered around the mean. It notes that approximately 68% of values in a normal distribution are within one standard deviation of the mean, 95% are within two standard deviations, and 99.7% are within three standard deviations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesProbability Distribution
Probability Distribution
Uploaded by
Vignesh RThe document discusses probability distributions and the normal distribution. It provides details on the normal curve being a symmetrical and bell-shaped distribution centered around the mean. It notes that approximately 68% of values in a normal distribution are within one standard deviation of the mean, 95% are within two standard deviations, and 99.7% are within three standard deviations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Probability distribution
Normal curve
● Probability distribution
● A probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the
probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes for an experiment.
It is a mathematical description of a random phenomenon in terms of its
sample space and the probabilities of events (subsets of the sample space).
● Normal curve
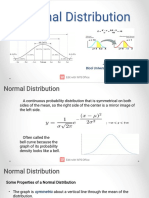
● The normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that is
symmetrical on both sides of the mean, so the right side of the center is a
mirror image of the left side. ... The normal distribution is often called the
bell curve because the graph of its probability density looks like a bell.
Normal curve based on a probable occurance of an event when that
probability depends on chance, when each event has an equal chances of
occuring that is occurance of the event must be equally, likely and must be
mutually independent.
● Normal probability distribution
• About 68% of values drawn from a normal distribution are within
one standard deviation σ away from the mean; about 95% of the
values lie within two standard deviations; and about 99.7% are
within three standard deviations.[6] This fact is known as the
68-95-99.7 (empirical) rule, or the 3-sigma rule.
● Principles of normal probability curve
• Normal curve is based upon the probable occurance of an
event.
• Each event has an equal chances of occuring.
• The occurrence of the event must be equally and likely
must be mutually independent curve.
• The normal curve or normal distribution closely
resembles the binomial distribution.
• The occurrence of the event must depend purely upon
chance.
• A large number of observations must be made to get the
normal curve.
• There is only one maximum point in the normal curve.
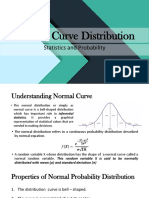
● Properties of normal probability curve
• Normal curve is also called as normal probability curve, bell
shaped curve and gassian curve and curve of error.
• There is high concentration of score in central of normal curve.
• The normal curve is sloping towards the end.
• The mean, mode and median are all equal. The curve is
symmetric at the center (i.e. Around the mean, μ). Exactly half of
the values are to the left of center and exactly half the values are
to the right. The total area under the curve is 1.
•The Gaussian distribution belongs to the family of stable
distributions which are the attractors of sums of independent,
identically distributed distributions whether or not the mean or
variance is finite. Except for the Gaussian which is a limiting case,
all stable distributions have heavy tails and infinite variance.
You might also like
- Worksheet ProbabilityDocument6 pagesWorksheet Probabilityela garcia100% (2)
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Probability and Statistics, Revised EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Probability and Statistics, Revised EditionNo ratings yet
- API 580 - RBI Question BankDocument30 pagesAPI 580 - RBI Question BankSabarni Mahapatra100% (3)
- StatProb LAS Week2 Normal Distribution PDFDocument9 pagesStatProb LAS Week2 Normal Distribution PDFMark Cidric Roquero IINo ratings yet
- Statistics in PsychologyDocument15 pagesStatistics in PsychologyNehaNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument3 pagesNormal DistributionSangeetha SumamNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument27 pagesStatisticsBernice Mikaela IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution Nov 2021 - FinalDocument36 pagesNormal Distribution Nov 2021 - FinalmussaNo ratings yet
- Midterm ExamDocument2 pagesMidterm ExamMelissa Nazar0% (1)
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W8Document6 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q4 - W8kotarobrother23No ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument32 pagesNormal DistributionJanahNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution:: - Probability - Characteristics and Application of Normal Probability Curve - Sampling ErrorDocument21 pagesNormal Distribution:: - Probability - Characteristics and Application of Normal Probability Curve - Sampling ErrorsanthiyasandyNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument3 pagesNormal DistributionMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Uzmah Jan-07 - 031532Document9 pagesUzmah Jan-07 - 031532Saqib MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionsDocument27 pagesNormal DistributionsArianne Trish MaggayNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument37 pagesProbabilityAmeena MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Normal CurveDocument13 pagesNormal CurveJaycer De MesaNo ratings yet
- 02.4 Probability - CPDDocument23 pages02.4 Probability - CPDRomel DecenillaNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument25 pagesNormal DistributionMina BhattaNo ratings yet
- Math VillafuerteDocument12 pagesMath VillafuertejeffreysonbelenNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument21 pagesNormal DistributionJewi MoreteNo ratings yet
- Frequency DistributionDocument35 pagesFrequency DistributionVivek AgrahariNo ratings yet
- Normal Curve Distribution: Statistics and ProbabilityDocument9 pagesNormal Curve Distribution: Statistics and ProbabilityJet Carillo ToledoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 11 Normal Probability DistributionsDocument51 pagesWEEK 11 Normal Probability DistributionsEvelyn VelascoNo ratings yet
- 4 Normal and Binomial Distribution 2021Document45 pages4 Normal and Binomial Distribution 2021Haikal DinieNo ratings yet
- STAT PROB Week 5 Sy 2020 2021Document19 pagesSTAT PROB Week 5 Sy 2020 2021hinatashoyo111706No ratings yet
- Nature, Properties and Applications of The Normal CurveDocument4 pagesNature, Properties and Applications of The Normal CurveChaeri ParkNo ratings yet
- SP-Q3 Note#5 Normal Random VariableDocument2 pagesSP-Q3 Note#5 Normal Random VariablePaulo Amposta CarpioNo ratings yet
- Week#7 SIM (Normal Distribution)Document27 pagesWeek#7 SIM (Normal Distribution)Mr.JoJINo ratings yet
- Normal and Exponential Distribution: by Abhijeet SalunkeDocument21 pagesNormal and Exponential Distribution: by Abhijeet SalunkeAsh KNo ratings yet
- Basic StatisticsDocument106 pagesBasic StatisticsSudhanshu Kumar Satyanveshi100% (1)
- Normal DistributionDocument25 pagesNormal DistributionPauline Anne LopezNo ratings yet
- 5-Introduction To The Normal Distribution (Bell Curve)Document9 pages5-Introduction To The Normal Distribution (Bell Curve)Zeeshan AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 5-Introduction To The Normal Distribution (Bell Curve)Document9 pages5-Introduction To The Normal Distribution (Bell Curve)Zeeshan AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution Undergrad 2022Document41 pagesNormal Distribution Undergrad 2022gerwadakasumuni2121No ratings yet
- The Normal Distribution: Density CurvesDocument3 pagesThe Normal Distribution: Density CurvesnaackeiltNo ratings yet
- Stat 3Document12 pagesStat 3Von Edrian PaguioNo ratings yet
- StatsDocument3 pagesStatsdream is my husbandNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument19 pagesNormal DistributionreiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Riezel PepitoNo ratings yet
- Prob and Stats, Nov 5: The Normal Probability Distribution Book Sections: N/ADocument22 pagesProb and Stats, Nov 5: The Normal Probability Distribution Book Sections: N/AShanna Mae TarusanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Riezel PepitoNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 UNIT 3.doxDocument12 pagesPaper 2 UNIT 3.doxTulika SarkarNo ratings yet
- The Normal Distribution: ConceptsDocument17 pagesThe Normal Distribution: ConceptsJay Ian GeronaNo ratings yet
- Niepid: Research Methods Normal DistributionDocument6 pagesNiepid: Research Methods Normal Distributionsucess psychologyNo ratings yet
- Probability Distributions-Sarin BDocument20 pagesProbability Distributions-Sarin BsarinNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ii. Lesson 1 The Normal Dist. TableDocument3 pagesChapter Ii. Lesson 1 The Normal Dist. Tablealiciatomada123No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 State ArmanDocument9 pagesAssignment 2 State ArmanM.NadeemNo ratings yet
- Illustrating Normal CurveDocument11 pagesIllustrating Normal CurveDan MonevaNo ratings yet
- Probability in A NutshellDocument3 pagesProbability in A NutshellLdvdMiixNo ratings yet
- Normal Probability DistributionDocument14 pagesNormal Probability Distributiontorresalexanderscott14No ratings yet
- Normal Probability DistributionDocument8 pagesNormal Probability DistributionッCarlosanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Normal Probability CurveDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of Normal Probability CurveDavid LalbiakdikaNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument45 pagesNormal Distributionvishal yadavNo ratings yet
- Continuous Probability DistributionDocument53 pagesContinuous Probability Distributionanola prickNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument9 pagesNormal DistributionDeeksha ManojNo ratings yet
- Day 02-Random Variable and Probability - Part (I)Document34 pagesDay 02-Random Variable and Probability - Part (I)Sparsh VijayvargiaNo ratings yet
- ch06-ProbDistribs RandomVarsDocument11 pagesch06-ProbDistribs RandomVarsHerman HermanNo ratings yet
- SP MidtermsDocument4 pagesSP MidtermsClarkson GodinezNo ratings yet
- Statistics:Data Management: Section 1: The Normal Distribution Section 2: Simple Linear RegressionDocument10 pagesStatistics:Data Management: Section 1: The Normal Distribution Section 2: Simple Linear RegressionhellloitismeNo ratings yet
- The Standard Normal Probability Distribution: ObjectivesDocument15 pagesThe Standard Normal Probability Distribution: ObjectivesJason BigataNo ratings yet
- STATFINALeditDocument69 pagesSTATFINALeditregine balonzoNo ratings yet
- Normal Random VariablesDocument33 pagesNormal Random VariablesJestoni MaravillasNo ratings yet
- Statistics 2Document121 pagesStatistics 2Ravi KNo ratings yet
- Random Processes For Engineers 1st Hajek Solution ManualDocument18 pagesRandom Processes For Engineers 1st Hajek Solution ManualJustine Lotthammer100% (39)
- Mod 2 1 Concepts of Individual Decision MakingDocument23 pagesMod 2 1 Concepts of Individual Decision MakingStevenSeilmontNo ratings yet
- Yule-Simon DistributionDocument4 pagesYule-Simon Distributionmaddy555No ratings yet
- Possibility and Probability Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesPossibility and Probability Lesson PlanVíctor González MedinaNo ratings yet
- The Poisson DistributionDocument9 pagesThe Poisson Distributionsyedah1985No ratings yet
- Probability Distribution: Binomial Poisson NormalDocument45 pagesProbability Distribution: Binomial Poisson NormalSalihah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Api 201b QAAEMDocument7 pagesApi 201b QAAEMtucchelNo ratings yet
- Probability: By: Hina Gul Mba 2 Semester Dec. 1, 2009Document19 pagesProbability: By: Hina Gul Mba 2 Semester Dec. 1, 2009Hina KhanNo ratings yet
- Judgment Under UncertaintyDocument10 pagesJudgment Under UncertaintyAlejita SanchezNo ratings yet
- Probability and StatisticsDocument2 pagesProbability and StatisticsKristine Mae CainongNo ratings yet
- G Quantitative-Techniques Final-Presentation PDFDocument62 pagesG Quantitative-Techniques Final-Presentation PDFSteffanie GranadaNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics For EngineersDocument25 pagesProbability and Statistics For Engineersjhon wickNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Probability TheoryDocument71 pagesUnit 1 - Probability TheoryRajdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Statistics 100A Homework 4 Solutions: Ryan RosarioDocument8 pagesStatistics 100A Homework 4 Solutions: Ryan RosarioPei JingNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4 (Pass - Quizchapter4) (Page 1 of 2)Document1 pageQuiz 4 (Pass - Quizchapter4) (Page 1 of 2)co caNo ratings yet
- Probabaility Prob-Sta-Week-4Document26 pagesProbabaility Prob-Sta-Week-4Shezzy KhanNo ratings yet
- DLL Math 6 q4 - Week 8Document8 pagesDLL Math 6 q4 - Week 8Raprap SilaoNo ratings yet
- SDE IntroDocument3 pagesSDE IntroAtul RaiNo ratings yet
- Bahria University, Karachi Campus Department of Business StudiesDocument3 pagesBahria University, Karachi Campus Department of Business StudiesOmar ShNo ratings yet
- 2014 Mahler ST SampleDocument171 pages2014 Mahler ST SampleHandoyoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Review of Probability and Basic StatisticsDocument90 pagesUnit 1 Review of Probability and Basic StatisticsBrennan BarnettNo ratings yet
- c02 ProbabilityDocument6 pagesc02 Probabilityobisesan phillipNo ratings yet
- Bayes' TheoremDocument9 pagesBayes' TheoremDeeksha ManojNo ratings yet
- Max Weber On "Lifestyle"Document7 pagesMax Weber On "Lifestyle"AnneThraxNo ratings yet
- Types of Risk:: Comparison Chart Key Differences ConclusionDocument3 pagesTypes of Risk:: Comparison Chart Key Differences Conclusiondipabali chowdhuryNo ratings yet