Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIOLOGY - Ecology, Respiration and Photosynthesis
BIOLOGY - Ecology, Respiration and Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
Vicky BerolskyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOLOGY - Ecology, Respiration and Photosynthesis
BIOLOGY - Ecology, Respiration and Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
Vicky BerolskyCopyright:
Available Formats
ECOLOGY
4.1 species, communities and ecosystems:
Species: groups of organisms that can interbreed to produce fertile offspring
Population: Members of a species may be reproductively isolated in separate groups
Community: is formed by populations of different species living together and interacting with
each other
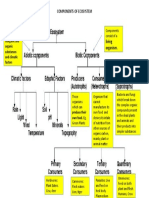
Ecosystem: A community forms an ecosystem by its interactions with the abiotic
environment
Habitat: the natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism.
Biotic factor: a living thing, as an animal or plant, that influences or affects an ecosystem
Abiotic factor: a nonliving condition or thing, as climate or habitat, that influences or affects
an ecosystem and the organisms in it
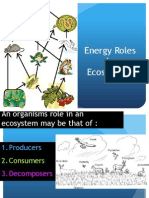
Autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition:
Autrophic nutrition is meant that some organisms make their own carbon compounds
from carbon dioxide and other simple substances, it means self-feeding
Heterotrophic is meant that some organisms obtain their carbon compounds from other
organisms
Type of Definition Type of Examples
heterotroph digestion
(internal or
external)
Consumer Feed off other organisms Internal Paramecium
Detritivore Obtain organic nutrients Internal Earthworms
from detritus by internal
digestion
Saprotroph Heterotrophs that obtain External Bacteria and
organic nutrients from fungi
dead organic matter by
external digestion
4.2 Climate change
Greenhouse gases: carbon dioxide and vapour are the most significant greenhouse
gasses.
You might also like
- IB Biology Chapter 4 Ecology Revision NotesDocument30 pagesIB Biology Chapter 4 Ecology Revision NotesDana PorterNo ratings yet
- Page 122 Food ChainsDocument1 pagePage 122 Food ChainsMohit sadhNo ratings yet
- Bio PresentationDocument10 pagesBio Presentationgodin6696No ratings yet
- 6.1 Types of NutritionDocument11 pages6.1 Types of NutritionNoor Hidayah SambliNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Written Report in EcologyDocument5 pagesGroup 5 Written Report in EcologyAnn CelineNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - 4 EnviSciDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 2 - 4 EnviSciKristine Mhae GabrielNo ratings yet
- Booklet 4.1Document18 pagesBooklet 4.1Seo Young YOONNo ratings yet
- Autotrophic, Heterotrophic and Saprophytic NutritionDocument3 pagesAutotrophic, Heterotrophic and Saprophytic NutritionAshwariya BarsateeNo ratings yet
- EnviEng MRII 0894 PDFDocument47 pagesEnviEng MRII 0894 PDFDaniel MalapitanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1Vyan Anand (Admn. No : 7366)No ratings yet
- BionutritionDocument48 pagesBionutritionHesandi PeirisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The EcosystemDocument1 pageChapter 2 - The Ecosystembmmr.071791No ratings yet
- CH 15 (Our Environment)Document10 pagesCH 15 (Our Environment)Rajvir tradaNo ratings yet
- EcologyDocument19 pagesEcology2022303299No ratings yet
- 4.1 Species, Communities and Ecosystems: DefinitionsDocument10 pages4.1 Species, Communities and Ecosystems: DefinitionsAnuradha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Env 664 RDGHDocument1 pageEnv 664 RDGHaman dhillonNo ratings yet
- Energy - Ecosystem (4 Files Merged)Document190 pagesEnergy - Ecosystem (4 Files Merged)Turuvit Subramanian 19BLA1065No ratings yet
- Ecology II Part B - Ecological Interactions - Food Chains Food Webs 2017Document38 pagesEcology II Part B - Ecological Interactions - Food Chains Food Webs 2017Shahriar HaqueNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems ServicesDocument9 pagesEcosystems ServicesRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Dynamic of EcosystemsDocument7 pagesDynamic of EcosystemszinNo ratings yet
- Functioning EcosystemDocument4 pagesFunctioning Ecosystemofurumchinyere9No ratings yet
- Producers, Consumers & DecomposersDocument1 pageProducers, Consumers & Decomposerssantanu40580No ratings yet
- Types of NutritionDocument17 pagesTypes of NutritionAshley RamnarayanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document5 pagesLesson 2angelina cajuraoNo ratings yet
- Nama: Fatimatus Suhroh NPM: 1911060305 Kelas: Biologi E: Ecosystems and Human InterferencesDocument4 pagesNama: Fatimatus Suhroh NPM: 1911060305 Kelas: Biologi E: Ecosystems and Human Interferencesdwi rahmaNo ratings yet
- Puputok Na Ugat Ko Sa Ulooo AAAAHHHHHH Genbio MidtermsDocument9 pagesPuputok Na Ugat Ko Sa Ulooo AAAAHHHHHH Genbio Midtermscassyleen03No ratings yet
- Ecology and EcosystemDocument13 pagesEcology and EcosystemKush TejaniNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument6 pagesEcosystemconnect.amairaNo ratings yet
- 06 Full X Food and Humans 2023 (Students)Document19 pages06 Full X Food and Humans 2023 (Students)wvcs2gz9bbNo ratings yet
- Modes of Nutrition: Source: General Biology 2 by M.A.O. JavierDocument2 pagesModes of Nutrition: Source: General Biology 2 by M.A.O. JavierIrish cambri0% (1)
- ECOSYSTEM PPT Final PGDocument56 pagesECOSYSTEM PPT Final PGShovana DeyNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Theory Class 10Document11 pagesNutrition Theory Class 10TarunNo ratings yet
- 6.1types of NutritionDocument15 pages6.1types of NutritionIMELDA80% (5)
- Energy-Roles-In-Ecosystems-Notes-7 12bDocument10 pagesEnergy-Roles-In-Ecosystems-Notes-7 12bapi-218158367No ratings yet
- Instructors: See Notes Section Below This SlideDocument52 pagesInstructors: See Notes Section Below This Slidea1silver948No ratings yet
- Food ChainsDocument7 pagesFood ChainsAbhijitNo ratings yet
- Components of An Ecosystem-Lesson 2 Power Point.1Document9 pagesComponents of An Ecosystem-Lesson 2 Power Point.1jamieprudhommeNo ratings yet
- Components of An Ecosystem-Lesson 2 Power PointDocument9 pagesComponents of An Ecosystem-Lesson 2 Power PointjamieprudhommeNo ratings yet
- Class 10: ContentDocument120 pagesClass 10: ContentNitin KumarNo ratings yet
- A.A Basic Concepts of EcologyDocument67 pagesA.A Basic Concepts of Ecologyrieann leonNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: 6.1 Understanding Types of NutritionDocument18 pagesNutrition: 6.1 Understanding Types of NutritionAileen PoLyNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 EcologyDocument73 pagesCHP 2 EcologySIMBA The Lion KingNo ratings yet
- What Are Three Categories of Organisms in The Ecosystem?Document3 pagesWhat Are Three Categories of Organisms in The Ecosystem?carlNo ratings yet
- 2 WEEK 6 EcosystemDocument28 pages2 WEEK 6 EcosystemNina Angela CateNo ratings yet
- Heterotrophic Nutrition Final 2018Document37 pagesHeterotrophic Nutrition Final 2018Otole dickensNo ratings yet
- Myp3 Scavenger HuntDocument2 pagesMyp3 Scavenger Huntminajaved5No ratings yet
- Q4 STEM General Biology 2 Week 2Document4 pagesQ4 STEM General Biology 2 Week 2Bernard D. Fajardo Jr.No ratings yet
- 1.introduction MicrobialProcesesDocument42 pages1.introduction MicrobialProcesesCasper BilgisayarNo ratings yet
- Envi SciDocument23 pagesEnvi SciJeanelle Ledesma MarabutNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiologyHesothaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants PART 1Document11 pagesNutrition in Plants PART 1Sarika AhujaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Ecology Claass 1Document51 pagesPresentation On Ecology Claass 1Soumyajit NandiNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument86 pagesEcosystemvishalNo ratings yet
- Envi SciDocument4 pagesEnvi SciJohn Fernand RacelisNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering Introduction PDFDocument84 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Introduction PDFChilton John DuatNo ratings yet
- Module 1 (Ii) - 2Document15 pagesModule 1 (Ii) - 2ermiasNo ratings yet
- Components of EcosystemDocument1 pageComponents of EcosystemShreya DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document70 pagesChapter 1nidNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology of Terpenoid Production from Microbial Cell FactoriesFrom EverandBiotechnology of Terpenoid Production from Microbial Cell FactoriesNo ratings yet