Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer in Avionics
Uploaded by
sulitstephanie0070 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesThis document provides information about aircraft electrical systems and their components. It discusses the following:
1) Current, voltage, resistance, and Ohm's law which are fundamental electrical concepts.
2) Aircraft have different electrical sources like batteries, which can be lead-acid or nickel-cadmium, and ground power units that provide electricity while the aircraft is on the ground.
3) The electrical generating system uses alternators to generate alternating current and generators that can produce both alternating and direct current from mechanical energy.
Original Description:
Notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information about aircraft electrical systems and their components. It discusses the following:
1) Current, voltage, resistance, and Ohm's law which are fundamental electrical concepts.
2) Aircraft have different electrical sources like batteries, which can be lead-acid or nickel-cadmium, and ground power units that provide electricity while the aircraft is on the ground.
3) The electrical generating system uses alternators to generate alternating current and generators that can produce both alternating and direct current from mechanical energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesReviewer in Avionics
Uploaded by
sulitstephanie007This document provides information about aircraft electrical systems and their components. It discusses the following:
1) Current, voltage, resistance, and Ohm's law which are fundamental electrical concepts.
2) Aircraft have different electrical sources like batteries, which can be lead-acid or nickel-cadmium, and ground power units that provide electricity while the aircraft is on the ground.
3) The electrical generating system uses alternators to generate alternating current and generators that can produce both alternating and direct current from mechanical energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
AVIONICS braking or damping mechanism in a circuit to
avoid over current in the load
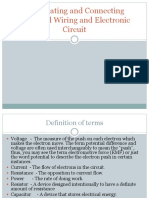
WHAT IS CURRENT
VOLTAGE
Electric current is the movement of electrons
It is an electrical pressure that causes the
through a wire. Electric current is measured in
electron to move through a conductor
amperes (amps) and refers to the number of
measured in volts (V
charges that move through the wire per
second
What causes current flow?
- Current flow takes place whenever most of
the electron movement in a material is in one
direction.
- This movement is from a (-) charge to a (+)
charge and occurs only as long as a
difference in charge exists and that
difference in charge is called the
POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE.
- EMF or Electromotive Force is the energy
per unit charge that maintains the
POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE.
Direct Current (DC)
ETHYMOLOGY OF ELECTRICAL
- Direct current is a method in which electricity
PARAMETERS UNIT
always flows in a certain direction, as
Alessandro Volta (Volt)
compared to the flow of a river. It refers to
- It is a widely known fact that the Volt is the
the flow of electricity obtained from batteries,
unit of electromotive force and that it is
solar cells, etc.
named after Alessandro Volta who was an
Alternating Current (AC)
Italian scientist and pioneer of electrical
- Alternating current (AC) is a method in which
science
the positive and negative sides are
- What is a less well known fact about the
constantly switched periodically and the
history of Volta is that he invented the first
direction of the flow of electricity changes
primary battery and in doing so he moved
accordingly. This is the flow of electricity
electrical science from the electrostatic era
obtained from a generator or outlet. The
into electrodynamic age
electricity produced at power plants and sent
André-Marie Ampère (Ampere)
to homes is also transmitted as alternating
- André-Marie Ampère was a French physicist
current.
and scientist who discovered
electromagnetism. He helped describe the
way to measure the flow of electricity. The
ampere, which is the unit for measuring
electric current, was named after him
Georg Simon Ohm (Ohm)
- Georg Simon Ohm was a German physicist,
best known for his “Ohm’s Law”, which
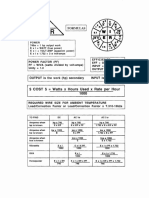
RESISTANCE states that the current flow through a
It is an electrical physical quantity that opposes conductor is directly proportional to the
the electrical measured in ohms (Ω). potential difference (voltage) and inversely
NOTE: proportional to the resistance. The physical
- Electrical resistance is analogous to friction unit of electrical resistance, the Ohm (Ω),
in a mechanical system. They both convert was named after him.
energy to heat and dissipate it to the OHM’S LAW
surrounding environment, so electrical What is Ohm’s Law?
resistance can sometimes be thought of as a
- Ohm's Law is used to describe the Assembled with electrodes (plates) that
relationship between voltage, current and have been fully charged and dried. The
resistance in an electrical circuit defined by electrolyte is added to the battery when it
the algebraic equation V=IR is placed in service, and battery life begins
when the electrolyte is added. An aircraft
storage battery consists of 6 or 12 lead-
acid cells connected in series.
o Valve-Regulated (Sealed Batteries)
Contain all electrolyte absorbed in glass-
mat separators with no free electrolyte.
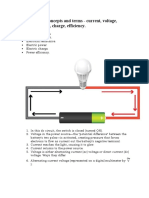
Types of Simple Circuit The electrochemical reactions for VRLA
- Series Circuit batteries are the same as flooded
o A circuit is said to be connected in series batteries, except for the gas
recombination mechanism that is
when the same current flows through all the
predominant in VRLA batteries.
components in the circuit.
- Nickel-Cadmium Batteries
o Formula:
o Consists of a metallic box, usually stainless
steel, plastic-coated steel, painted steel, or
titanium containing a number of individual
cells. These cells are connected in series to
obtain 12 volts or 24 volts. NiCd cells
installed in an aircraft battery are typical of
the vented cell type
- Parallel Circuit Ground Power Unit (GPU)
o A circuit is said to be parallel when the - Usually consist of a generator powered by a
electric current has multiple paths to flow diesel engine but may found in other
through. The components that are a part of configurations. It can be either a fixed or
the parallel circuits will have a constant mobile unit which can be connected to the
voltage across all ends electrical system of an aircraft while on the
o Formula: ground to provide either 120V AC or 28V DC
power.
ELECTRICAL GENERATING SYSTEM
Alternator
- A device that turns mechanical energy into
electricity as an AC (alternating current). A
magnet in an alternator rotates, creating a
current to distribute energy
- AC Output
Generator
- Can also convert mechanical energy into
electrical energy, but are capable of
producing both AC and DC. A rotor inside
AIRCRAFT ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
the generator rotates and the rotation of this
An aircraft electrical system is a self-contained rotor builds up electricity, creating a
network of components that generate, transmit, magnetic field, resulting in the creation of the
distribute, utilize and store electrical energy needed energy to spin the armature.
ELECTRICAL SOURCES - AC Output
Batteries - DC Output
- Lead Acid Batteries EMERGENCY ELECTRICAL GENERATING
o Dry Charged Cell (Flooded or Wet SYSTEM
Batteries) Auxiliary Power Unit
- A small jet engine which is normally located - Designed with the zero point in the center of
in the tail cone of the aircraft but, in some the face and a negative or positive indication
cases, is located in an engine nacelle or in on either side. It is used to monitor the
the wheel well. It can be used, as required, performance of the aircraft electrical system
to provide an additional source of electrical showing if the alternator/generator is
power in the event of the loss of an engine producing an adequate supply of electrical
generator. It can also be used as a source of power. When the pointer is on the plus side,
bleed air for starter assist for an inflight it shows the charging rate of the battery. A
engine relight. minus indication means more current is
Ram Air Turbine (RAT) being drawn from the battery than is being
- A small turbine that is installed in an aircraft replaced
and used as an alternate or emergency Voltage Regulator
hydraulic or electrical power source. The - Controls the rate of charge to the battery by
RAT generates power from the airstream. In stabilizing the generator or alternator
emergency cases the RAT will power vital electrical output. As a general rule, the
systems such as flight controls or flight- generator/alternator voltage output should be
critical instrumentation, navigation and higher than the battery voltage
communication equipment. Some RATs
produce only hydraulic power which in turn is
used to power an electrical generator.
ELECTRICAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
Fuse
- Is an electrical safety device that operates to
provide overcurrent protection of an electrical
circuit. Its essential component is a metal
wire or strip that melts when too much
current flows through it, thereby stopping or
interrupting the current. It is a sacrificial
device; once a fuse has operated it is an
open circuit, and must be replaced or
rewired, depending on its type.
Circuit Breaker
- An electrical safety device designed to
protect an electrical circuit from damage
caused by an overcurrent or short circuit. Its
basic function is to interrupt current flow to
protect equipment and to prevent the risk of
fire. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and
then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can
be reset (either manually or automatically) to
resume normal operation.
Bus Bar
- Used as a terminal in the aircraft electrical
system to connect the main electrical system
to the equipment using electricity as a source
of power. This simplifies the wiring system
and provides a common point from which
voltage can be distributed throughout the
system. Electrical power is supplied to the
various electrically energized components in
an aircraft via these common points.
Ammeter
You might also like
- Chapter 1 Electricity Theory PDFDocument29 pagesChapter 1 Electricity Theory PDFRosalie Vertudes0% (1)
- Basic Electricity Lesson 02Document17 pagesBasic Electricity Lesson 02Sandra Barnett CrossanNo ratings yet
- Method of Statement For Micropile 01Document7 pagesMethod of Statement For Micropile 01NedyHortetlNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ElectricityDocument12 pagesIntroduction To ElectricityRomel PanisNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectricityDocument11 pagesBasic ElectricityFrancess Mae AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Basic Principles of ElectricityDocument53 pagesBasic Principles of ElectricityRaghu NadhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ElectricityDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Electricityreynaldo palacase100% (1)
- Ee 003 Lecture11Document39 pagesEe 003 Lecture11JC LoplopNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electricity 1.1Document23 pagesIntroduction To Electricity 1.1August DuqueNo ratings yet
- Session 2-1 - Introduction To Electricity and Electrical SystemsDocument59 pagesSession 2-1 - Introduction To Electricity and Electrical SystemsCeino Rey QuimintanNo ratings yet
- Control Valve PW200/ 220-7Document48 pagesControl Valve PW200/ 220-7Teknik Makina100% (2)
- Util 313 Module 1Document34 pagesUtil 313 Module 1Jonnel FuertezNo ratings yet
- A Historical Overview of Basic Electrical Concepts For Field Measurement TechniciansDocument3 pagesA Historical Overview of Basic Electrical Concepts For Field Measurement TechniciansManuel Philip ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Chap123 JazDocument12 pagesChap123 JazJasmine MonesNo ratings yet
- Circuits ReviewerDocument5 pagesCircuits ReviewerMatthew JordanNo ratings yet
- Lec - Basics of ElectronicsDocument40 pagesLec - Basics of Electronicszaheerduaa27No ratings yet
- ElectricalDocument26 pagesElectrical3re0oooNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals OF ElectricityDocument37 pagesFundamentals OF ElectricityMarvin Sarmiento TalimonganNo ratings yet
- Ohm'S Law: Name: Chura Cachi Jose Manuel Semester: Second Career: Industrial Electricity Matter: EnglishDocument9 pagesOhm'S Law: Name: Chura Cachi Jose Manuel Semester: Second Career: Industrial Electricity Matter: EnglishJorel LopezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Electrical TermsDocument34 pagesLesson 1 Electrical TermsVeah Mae TacotacoNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument7 pagesEnergyMike OrdonioNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity: Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of ElectricityDocument5 pagesStatic Electricity: Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of ElectricitydsscharanNo ratings yet
- PHYS101L LabReport9Document13 pagesPHYS101L LabReport9Leidee Charmellie SerranoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Introduction To Electricity Copy For StudentsDocument31 pagesLESSON 3 Introduction To Electricity Copy For Studentsixearth84No ratings yet
- UNIT I NotesDocument34 pagesUNIT I NotesKarthikeyan VNo ratings yet
- Electricity Is The Set ofDocument2 pagesElectricity Is The Set ofSam Axel BenedictoNo ratings yet
- Elementary Electrical EngineeringDocument28 pagesElementary Electrical EngineeringLopez, Paolo AdonisNo ratings yet
- Foundation of ElectricityDocument26 pagesFoundation of ElectricityRaven TarroquinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1Venkat TakkellaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Relationship in Circuit TheoryDocument11 pagesFundamental Relationship in Circuit TheoryEugenio Tabilog IIINo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument9 pagesElectrostaticsJannice Anne SantosNo ratings yet
- Bu 2 ReviewerDocument13 pagesBu 2 Reviewercristian borjeNo ratings yet
- Famusudo Catharine OluwaseunfunmiDocument15 pagesFamusudo Catharine OluwaseunfunmiAkinola AyomideNo ratings yet
- Voltage Load Resistance Dual Current Source: Added/subtracted in Series Must Be Same in ParallelDocument8 pagesVoltage Load Resistance Dual Current Source: Added/subtracted in Series Must Be Same in ParallelDuck520No ratings yet
- Electron Theory and Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesElectron Theory and Ohm's LawGABUAT, KIRK STEVEN P.No ratings yet
- Electricity Hand OutsDocument3 pagesElectricity Hand OutsKayser Jeff FernandezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ElectricityDocument16 pagesIntroduction To ElectricityWilson AgustinNo ratings yet
- Electricity 1Document86 pagesElectricity 1Jm MagnoNo ratings yet
- Q4-L5 - Electric Currents, Circuits, & Ohm's Law (For Notes)Document22 pagesQ4-L5 - Electric Currents, Circuits, & Ohm's Law (For Notes)rhenzmarielle.pasionNo ratings yet
- 276 - BE8251 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering - UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS and MEASUREMENTS NotesDocument42 pages276 - BE8251 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering - UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS and MEASUREMENTS NotesBalaNo ratings yet
- Eletric CurrentDocument13 pagesEletric Currentcalew17036No ratings yet
- Basic CircuitsDocument15 pagesBasic Circuitskayem14No ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument85 pagesElectricityapi-2851792610% (1)
- Chapter 4 Electricity and MagnetismDocument126 pagesChapter 4 Electricity and MagnetismCziara JustineNo ratings yet
- Intro To Electric Circuits: GLAS WiringDocument20 pagesIntro To Electric Circuits: GLAS WiringShaunNo ratings yet
- Utilities 1 ReviewerDocument11 pagesUtilities 1 ReviewerESCARO, JOSHUA G.No ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Concepts and TermsDocument18 pagesBasic Electrical Concepts and TermsMark Jerwin SacapañoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Elements of Lift Technology Ed 3Document51 pagesElectrical Elements of Lift Technology Ed 3Fiorella Amer CarrNo ratings yet
- Principles of ElectricityDocument25 pagesPrinciples of ElectricityKeziah LafortezaNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument32 pagesOhm's LawDezz Balleta-BonaNo ratings yet
- Telecommunications Wiring Clyde N Herrick 3rd Edition Chapter 1 PDFDocument24 pagesTelecommunications Wiring Clyde N Herrick 3rd Edition Chapter 1 PDFguimaNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Electrical Circuits: On Completion of This Module, You Will Be Able ToDocument11 pagesModule 3: Electrical Circuits: On Completion of This Module, You Will Be Able ToMustapha IsaadNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectricityDocument11 pagesBasic Electricitybeckam88No ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument9 pagesElectricityGuevara, Blez M.No ratings yet
- Basic Electrical TheoryDocument6 pagesBasic Electrical TheoryMohd Ziaur Rahman RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document61 pagesLecture 1jackdrejeNo ratings yet
- Look at The Picture On The Side.: Think-Pair-ShareDocument26 pagesLook at The Picture On The Side.: Think-Pair-ShareCharo Nudo PongasiNo ratings yet
- Intro To Electric Circuits: GLAS WiringDocument20 pagesIntro To Electric Circuits: GLAS WiringKrishna BoreddyNo ratings yet
- Css 06 Tcew 01 IntroDocument18 pagesCss 06 Tcew 01 IntroavinmanzanoNo ratings yet
- Ohm Law Lecture OneDocument22 pagesOhm Law Lecture OneMoiz KhanNo ratings yet
- MEM - Project Pump and TurbineDocument22 pagesMEM - Project Pump and TurbineAbhi ChavanNo ratings yet
- NCERT PUNCH Chemistry Class 11 Complete Book Flattened SignedDocument304 pagesNCERT PUNCH Chemistry Class 11 Complete Book Flattened Signedsd0806787No ratings yet
- Gas Cylinder Rules 2022Document2 pagesGas Cylinder Rules 2022manoharandaNo ratings yet
- CB500X 42mkpa200 0Document130 pagesCB500X 42mkpa200 0Miguel LamarosaNo ratings yet
- 6ctaa8 3-G2Document5 pages6ctaa8 3-G2Anas BasarahNo ratings yet
- EM15 Series User Manual-V1 0 7Document162 pagesEM15 Series User Manual-V1 0 7nicolasNo ratings yet
- Tom Henry - Electrical Formulas and Calculations (2005 National Electrical Code - Nfpa 70 - Nec)Document14 pagesTom Henry - Electrical Formulas and Calculations (2005 National Electrical Code - Nfpa 70 - Nec)Delmar FerrerNo ratings yet
- Energy Impact of Connected and Automated Vehicles: Aymeric Rousseau Dominik KarbowskiDocument21 pagesEnergy Impact of Connected and Automated Vehicles: Aymeric Rousseau Dominik KarbowskiJaja OcochatNo ratings yet
- Systemair ASP600 CENTRIFUGAL FAN SWSIDocument4 pagesSystemair ASP600 CENTRIFUGAL FAN SWSIerickNo ratings yet
- WFM - WT - Burner BoomDocument2 pagesWFM - WT - Burner BoomAndrey RogozhaNo ratings yet
- Lb-Xp12-350-Pd-En-V1.3-201912 - EquivalenteDocument2 pagesLb-Xp12-350-Pd-En-V1.3-201912 - EquivalenteDaniel Oliveira Freitas RochaNo ratings yet
- GCP - Technintegral - Rev00 - 21.07.2021Document60 pagesGCP - Technintegral - Rev00 - 21.07.2021edwinNo ratings yet
- Frn0001c2s2a Frn0002c2s2a Frn0004c2s2a Frn0006c2s2a Frn0010c2s2a Frn0012c2s2a Frn0020c2s2a Frn0025c2s2a Frn0033c2s2a FRDocument263 pagesFrn0001c2s2a Frn0002c2s2a Frn0004c2s2a Frn0006c2s2a Frn0010c2s2a Frn0012c2s2a Frn0020c2s2a Frn0025c2s2a Frn0033c2s2a FRKhanh Nguyen DuyNo ratings yet
- Physics 4PH 2P January 2021 Marking SchemeDocument13 pagesPhysics 4PH 2P January 2021 Marking Schemevtxv1vidNo ratings yet
- Fault Analysis: Prof. M Venkateswara RaoDocument39 pagesFault Analysis: Prof. M Venkateswara RaoagarwaalaaaaNo ratings yet
- First Air Fas4 Parts ListDocument14 pagesFirst Air Fas4 Parts ListrobertNo ratings yet
- Sensor BticinoDocument12 pagesSensor BticinoRobertNo ratings yet
- Scci - Irr PT Bukit Asam - Maret 2021Document9 pagesScci - Irr PT Bukit Asam - Maret 2021wahyusetyawanNo ratings yet
- Equipment Layout ListDocument10 pagesEquipment Layout Listnas_mech8208No ratings yet
- Extension PT. SIS 2017Document1 pageExtension PT. SIS 2017David SummerNo ratings yet
- rz1 K en 50267 Xlpe LSZH Flexible CableDocument5 pagesrz1 K en 50267 Xlpe LSZH Flexible CableFerAK47aNo ratings yet
- Online Summer Project 1Document71 pagesOnline Summer Project 1Shivani Nileshbhai PatelNo ratings yet
- Laporan Mingguan Edit - 3Document45 pagesLaporan Mingguan Edit - 3Anisa BudianiNo ratings yet
- تقرير تأكل (Anodic Protection)Document10 pagesتقرير تأكل (Anodic Protection)ياسر نوفل ورد100% (1)
- RENR7695Document2 pagesRENR7695ait mimouneNo ratings yet
- Squirrel Cage Induction Motor Preventive MaintenaceDocument6 pagesSquirrel Cage Induction Motor Preventive MaintenaceNishantPareekNo ratings yet
- DTW Design Operation ManualDocument43 pagesDTW Design Operation ManualShaaroo Warra RabbiiNo ratings yet
- Safety Contactors: Product SelectionDocument4 pagesSafety Contactors: Product SelectionAlan OgataNo ratings yet