Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Internal Transport and Circulation
Uploaded by
JYNEST CUIZONOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Internal Transport and Circulation
Uploaded by
JYNEST CUIZONCopyright:
Available Formats
INTERNAL TRANSPORT AND CIRCULATION not be able to breathe, feed itself, bring nutrients to its
different parts, and maintain homeostasis (stable state) of its
Objective: Explain how materials are transported around the internal environment.
body, especially in mammals
Internal transport in plants uses xylem and phloem.
In biology, an internal transport system enables an organism to Open circulatory systems: Systems in which a body cavity
move particles into its body and within its body. This system or hemocoel contains most of the circulating fluid, as in
also enables the organism to remove the unwanted particles insects.
from within its body. Without such system, the organism will The pumping action of a heart drives fluid forward
not be able to breathe, feed itself, bring nutrients to its through an aorta, then through a series
different parts, and maintain homeostasis (stable state) of its of arteries. No veins exist; used blood seeps
internal environment. into sinuses that drain into the hemocoel.
Internal transport in plants uses xylem and phloem. Closed circulatory systems: Systems in which blood is
contained everywhere in vessels, as in all vertebrates.
Open circulatory systems: Systems in which a body cavity
or hemocoel contains most of the circulating fluid, as in The heart may have 2 to 4 chambers. The heartbeat
insects. originates from a pacemaker at the sinoatrial
The pumping action of a heart drives fluid forward node. Highest pressure, at maximum contraction, is
through an aorta, then through a series called systole; lowest pressure is called diastole.
of arteries. No veins exist; used blood seeps
into sinuses that drain into the hemocoel. In mammals, the right atrium pumps oxygen-poor
blood from the body's tissues into the right
Closed circulatory systems: Systems in which blood is ventricle, which pumps it through the pulmonary
contained everywhere in vessels, as in all vertebrates. arteries into the lungs. The left atrium meanwhile
pumps oxygen-rich blood from the lungs into the left
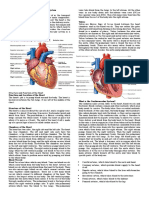
The heart may have 2 to 4 chambers. The heartbeat ventricle, which pumps it through the aorta for
originates from a pacemaker at the sinoatrial distribution throughout the body.
node. Highest pressure, at maximum contraction, is
called systole; lowest pressure is called diastole. Arteries carry blood from the heart to the body's
tissues.
In mammals, the right atrium pumps oxygen-poor
blood from the body's tissues into the right
ventricle, which pumps it through the pulmonary Veins return the blood from the body's tissues back to
arteries into the lungs. The left atrium meanwhile the heart. Valves in veins prevent the blood from
pumps oxygen-rich blood from the lungs into the left flowing backward.
ventricle, which pumps it through the aorta for
distribution throughout the body.
Vertebrate blood is always red because of the oxygen-
carrying pigment hemoglobin, carried in red blood
Arteries carry blood from the heart to the body's
cells (erythrocytes).
tissues.
Thus, the circulatory system transport materials throughout the
Veins return the blood from the body's tissues back to
body. Nutrients, water, and oxygen are transported to the
the heart. Valves in veins prevent the blood from
billions of body cells and wastes such as carbon dioxide are
flowing backward.
carried away or removed from the body.
Vertebrate blood is always red because of the oxygen-
carrying pigment hemoglobin, carried in red blood
cells (erythrocytes).
Thus, the circulatory system transport materials throughout the
body. Nutrients, water, and oxygen are transported to the
billions of bodies cells and wastes such as carbon dioxide are
carried away or removed from the body.
INTERNAL TRANSPORT AND CIRCULATION
Objective: Explain how materials are transported around the
body, especially in mammals
In biology, an internal transport system enables an organism to
move particles into its body and within its body. This system
also enables the organism to remove the unwanted particles
from within its body. Without such system, the organism will
You might also like
- Transport in HumansDocument6 pagesTransport in HumansJason Ng100% (5)
- Circulation and Transportation in Gen - Bio 2 For Grade 11 STEMDocument60 pagesCirculation and Transportation in Gen - Bio 2 For Grade 11 STEMDead Eye100% (1)
- Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument22 pagesCardiovascular DiseaseSunday JamesNo ratings yet
- Chest PainDocument31 pagesChest PainMarwan GamaleldinNo ratings yet
- امتحان مهم كاردياك سيرجاريDocument15 pagesامتحان مهم كاردياك سيرجاريIbrahim Barham50% (2)
- Obstetric Highlights Elmar P. Sakala PDFDocument47 pagesObstetric Highlights Elmar P. Sakala PDFwalt65No ratings yet
- Tof and PdaDocument47 pagesTof and PdaskerstinNo ratings yet
- Genzoo Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesGenzoo Circulatory SystemAbram TicmanNo ratings yet
- Bio T4 DLP KSSM Chapter 10Document133 pagesBio T4 DLP KSSM Chapter 10fadilahNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2a CirculationDocument8 pagesWEEK 2a Circulationdoodle dangerNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemRob NoconNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesCirculatory SystemMaybelyn Rivera PagkatotohanNo ratings yet
- Sistem Peredaran Darah ResumeDocument10 pagesSistem Peredaran Darah Resumeilham ramNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument5 pagesBiologykingninNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12, BioDocument26 pagesChapter 12, BioRylee LNo ratings yet
- Zo 503 Comparative Physiology by DR - PoornimaDocument20 pagesZo 503 Comparative Physiology by DR - PoornimaAbhishek Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- 1-2.transport in Ani & Pl. WK 1,2Document9 pages1-2.transport in Ani & Pl. WK 1,2sunoyebimpeNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORTATION 10 Class NotesvvpDocument3 pagesTRANSPORTATION 10 Class NotesvvpSD card 32 gbNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory SystemBobong blyatNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORTATIONDocument9 pagesTRANSPORTATIONAnonymousNo ratings yet
- The Tiger in The ZooDocument4 pagesThe Tiger in The ZoolijethaNo ratings yet
- Animals Gas Exchange Fluid Transport and CirculationDocument2 pagesAnimals Gas Exchange Fluid Transport and CirculationVeñegas ArielNo ratings yet
- Comparative Anatomy of Circulation in Annelid, Arthopoda and MolluscsDocument4 pagesComparative Anatomy of Circulation in Annelid, Arthopoda and MolluscsNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Life Processes Part IIDocument9 pagesLesson 6 Life Processes Part IIjokerbladed19No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory SystemGennelle GabrielNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Vascular TissueDocument8 pagesCirculatory System Vascular TissueDrSachin SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Chapter 4Document61 pagesBiology 2 Chapter 4Malas Nak TaipNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesCirculatory SystemKhawar HussainNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals 1Document6 pagesTransport in Animals 1makah2711No ratings yet
- Human SystemsDocument46 pagesHuman SystemsShankarayNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument41 pagesCirculatory SystemMerned Lopez100% (1)
- Transportation 1 PDFDocument9 pagesTransportation 1 PDFNakshatra PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Presidium Indirapuram Students Handout-3 Grade X (Biology) Chapter: Life Processes Topic: TransportationDocument8 pagesPresidium Indirapuram Students Handout-3 Grade X (Biology) Chapter: Life Processes Topic: TransportationSaniya nebNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesCardiovascular SystemMayim LouiseNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument6 pagesThe Circulatory SystemShamel BebitaNo ratings yet
- Heart and CirculationDocument12 pagesHeart and CirculationEizelle Zabyne VerzosaNo ratings yet
- g3. TransportationDocument30 pagesg3. TransportationKaycee Louchel OccenaNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - Transport of Food and Minerals in Animals and PlantsDocument5 pagesLife Processes - Transport of Food and Minerals in Animals and PlantsmasaminathanNo ratings yet
- Campbell Chapter 42 NotesDocument17 pagesCampbell Chapter 42 NotesRyan LiuNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemMark ArceNo ratings yet
- Grade7 Bio Chapter10 Transportation - CW&HWDocument6 pagesGrade7 Bio Chapter10 Transportation - CW&HWTanushree RNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesWeek 2 Circulatory SystemCarl Brian L. MonteverdeNo ratings yet
- Transport and Circulation in Plants and AnimalsDocument17 pagesTransport and Circulation in Plants and AnimalsTekomiNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and CirculationDocument31 pagesBody Fluids and CirculationAdrinne Jamie Danao DavidNo ratings yet
- Life Process Part 2 2Document32 pagesLife Process Part 2 2Anin BertNo ratings yet
- Transportation in Plants and AnimalsDocument12 pagesTransportation in Plants and AnimalsRaman -No ratings yet
- L5 NotesDocument9 pagesL5 Notes17 ERMINO, Nicole AngelaNo ratings yet
- M.SC 1 Sem Paper 2Document18 pagesM.SC 1 Sem Paper 2Anju yadavNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Circulatory System FinalDocument51 pagesGroup 7 Circulatory System FinalAngel Faith FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Biology 11Document52 pagesChapter 12 Biology 11ax1leNo ratings yet
- Animal Organ SystemDocument139 pagesAnimal Organ SystemMilyn Mae PalganNo ratings yet
- The Human Body Systems: (Zoology Lecture)Document46 pagesThe Human Body Systems: (Zoology Lecture)शंकराय नमोNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory SystemMarnel DincolNo ratings yet
- Transportation Notes Class 10thDocument10 pagesTransportation Notes Class 10thKrishna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemSaadNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument12 pagesTransport in AnimalsJedidiah DickNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemLili M.No ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemLili M.No ratings yet
- Excellup Class TenDocument3 pagesExcellup Class TenHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- What Is An Open Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesWhat Is An Open Circulatory SystemBarus LaubawisNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System in ManDocument54 pagesThe Circulatory System in ManStudent ResearchNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter - 1 (Part - 2)Document7 pagesBiology Chapter - 1 (Part - 2)aaronNo ratings yet
- Transportation - Life Processes Class 10 Notes: Transportation in Human Beings: The Circulatory System Is Responsible ForDocument4 pagesTransportation - Life Processes Class 10 Notes: Transportation in Human Beings: The Circulatory System Is Responsible ForGeetanjali jadhavNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument30 pagesCirculatory SystemIra Lavigne De VillaNo ratings yet
- Co WorksheetsDocument2 pagesCo WorksheetsJYNEST CUIZONNo ratings yet
- Q3 W2 Cpar CuizonDocument14 pagesQ3 W2 Cpar CuizonJYNEST CUIZONNo ratings yet
- TriviaDocument2 pagesTriviaJYNEST CUIZONNo ratings yet
- Ucsp ST-3Document4 pagesUcsp ST-3JYNEST CUIZONNo ratings yet
- Ucsp ST-1Document4 pagesUcsp ST-1JYNEST CUIZONNo ratings yet
- Ucsp ST-4Document4 pagesUcsp ST-4JYNEST CUIZONNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document1 pageActivity 3JYNEST CUIZONNo ratings yet
- Quiz Cassava Final!Document12 pagesQuiz Cassava Final!JYNEST CUIZONNo ratings yet
- V Coconut Oil LabelDocument2 pagesV Coconut Oil LabelJYNEST CUIZONNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document1 pageActivity 2JYNEST CUIZONNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document1 pageActivity 1JYNEST CUIZONNo ratings yet
- Angina Pectoris 2Document47 pagesAngina Pectoris 2inyanji.barasaNo ratings yet
- 199 Questions-Fcps Part 1 Medicine Paper - PDF 16 November 2011-By PimaDocument13 pages199 Questions-Fcps Part 1 Medicine Paper - PDF 16 November 2011-By PimaServantof Islam100% (5)
- Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (S-ICD)Document6 pagesSubcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (S-ICD)Narendra KumarNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument594 pagesJurnalVeveyNo ratings yet
- Oral and Dental Management in Children With Tetralogy of FallotDocument4 pagesOral and Dental Management in Children With Tetralogy of FallotRisyaRahmadaniNo ratings yet
- Pnle Exam Part 1Document14 pagesPnle Exam Part 1bNo ratings yet
- Ebook Diastology Clinical Approach To Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction 2E Dec 2 2020 - 0323640672 - Elsevier PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument68 pagesEbook Diastology Clinical Approach To Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction 2E Dec 2 2020 - 0323640672 - Elsevier PDF Full Chapter PDFmelissa.osbeck548100% (26)
- Slide One: IV Therapy Module A.2 "Anatomy and Physiology" ScriptDocument9 pagesSlide One: IV Therapy Module A.2 "Anatomy and Physiology" ScriptEko MojoNo ratings yet
- Treadmill Spacer 3501 Treadmill InstructionsDocument28 pagesTreadmill Spacer 3501 Treadmill InstructionsChris TwiggerNo ratings yet
- Rat Dissection Protocol - Intro BiologyDocument10 pagesRat Dissection Protocol - Intro BiologyValar Mathei PadmanadhanNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction and Heart Failure Practice Quiz (70 Questions)Document44 pagesMyocardial Infarction and Heart Failure Practice Quiz (70 Questions)Melodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Ebook Echocardiography With SimulationsDocument91 pagesEbook Echocardiography With SimulationsAbdul WaheedNo ratings yet
- Electrical Burn of The Upper Extremity: Interesting Case SeriesDocument4 pagesElectrical Burn of The Upper Extremity: Interesting Case SeriesZza MufidahNo ratings yet
- (CVS) Heart BlockDocument4 pages(CVS) Heart Blockapi-3769252No ratings yet
- Bio 123 PDFDocument32 pagesBio 123 PDFP NagNo ratings yet
- Set 2 Bioenergetics Grades 4 6Document22 pagesSet 2 Bioenergetics Grades 4 6Diva NoorzaiNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Rhythms Edu 505 - Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesCardiac Rhythms Edu 505 - Lesson Planleslye2No ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)Document11 pagesCoronary Artery Disease (CAD)Abi AntonyNo ratings yet
- How Does Exercise Affect Heart Rate Alvin PDFDocument13 pagesHow Does Exercise Affect Heart Rate Alvin PDFapi-134712575No ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument16 pagesHeart FailureRavin DebieNo ratings yet
- Resume Sheetal KanwarDocument3 pagesResume Sheetal KanwarLingam YoniNo ratings yet
- Zanki Step 2 - Cardiovascular SystemDocument129 pagesZanki Step 2 - Cardiovascular SystemChunlei WangNo ratings yet
- Workshop #5 Internal Medicine IIDocument77 pagesWorkshop #5 Internal Medicine IIhevinpatelNo ratings yet
- Accuvix A30 ReferenceDocument230 pagesAccuvix A30 Referencem_rebelo5808No ratings yet
- ESCAPE Study - JAMA 2005Document9 pagesESCAPE Study - JAMA 2005MICHAEL AMARILLO CORREANo ratings yet