Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IM Que Ans
Uploaded by
Parmar SanjayOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IM Que Ans
Uploaded by
Parmar SanjayCopyright:
Available Formats
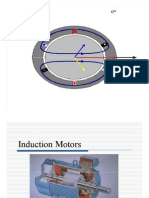
1 – explain the construction of stator of Squirrel Cage and Slip Ring rotor.
The stator in a squirrel cage induction motor is a stationary part that surrounds the rotor. It typically
consists of a laminated iron core with evenly spaced slots to hold the stator windings. The stator
windings are made of copper or aluminum conductors, and they are arranged in a way to create a
rotating magnetic field when energized.
The winding configuration can be either a single-phase or three-phase setup, depending on the motor
design. In a three-phase motor, there are usually three sets of windings spaced 120 degrees apart. These
windings are connected to the power supply, and when alternating current flows through them, a
rotating magnetic field is produced.
The rotor, often referred to as the squirrel cage, is placed inside the stator. It consists of laminated iron
cores with conductive bars or rods arranged in a circular cage-like structure. When the stator produces a
rotating magnetic field, it induces currents in the rotor conductors, creating a secondary magnetic field.
The interaction between the stator and rotor magnetic fields results in the generation of torque, causing
the rotor to turn and drive the motor.
The rotor of slip ring motor consists of a cylindrical core with steel laminations. Besides this, the rotor
has parallel slots to accommodate 3-phase windings. The windings in these slots are arranged at 120
degrees to each other. This arrangement can reduce noise and avoid irregular pausing of a motor.
4 - What do you mean by speed control of induction motor. State various methods of speed control.
Induction motor speed control is a process of manipulating currents in an induction motor to regulate
speed OR changing the supply voltage until the torque required by the load is developed at the desired
speed
Speed Control Methods of Induction Motor -From the stator side
>Voltage Control Method
>Frequency Control Method
>Pole Changing Method
>Stator Resistance Method
From the rotor side
>Rotor Resistance Control Method
>Slip Power Recovery Method
>Cascading (or) Tandem connection
5 – Explain any one method of speed control.
Pole Changing Speed Control
This method of speed control of induction motor can only be applied to the squirrel cage induction
motor. The number of poles in the rotor of a slip ring induction motor is fixed, whereas the squirrel cage
rotor can be adapted to any number of poles. The poles of the induction motor can be changed in two
ways.
>Multiple winding sets
>Consequent pole changing
In the first method, we use multiple winding sets of stator windings designed for different sets of poles.
While in operation, any one of them can be connected according to the speed requirements of the user,
and the other sets will keep in open. We know that
Ns=120f/P
As the number of poles increases, the speed will be reduced. This method can only vary the speed in
steps, and it is expansive as it involves multiple stator windings.
In the method of consequent pole changing, we can obtain another set of poles by reversing the coils.
This method can only give two sets of speeds.
Cascading or Tandem Connection
In this method of speed control of induction motor, we need two induction motors, one is essentially a
slip ring induction motor, and the other is either a slip ring induction motor or a squirrel cage induction
motor. Both machines will be mechanically coupled; the first motor is a slip ring induction motor which
feeds the second one through its slip rings.
(Figure)
The speed of the slip-ring induction motor is
Ns1=120 f/P1
The speed of the second motor is
Ns2=120s1f/P2
In this method, four different speeds are possible. They are
120 f/P1+P2 in cumulative cascading
120 f/P1−P2 in differential cascading
120 f/P1 (When motor-1 only operating)
120 f/P2 (When motor-2 only operating)
In differential cascading, the number of poles in both motors should not be equal
6 – Power flow phasor diagram
In a 3-phase induction motor, the stator winding is connected to 3-phase supply and the rotor winding is
short-circuited. The energy is transferred magnetically from the stator winding to the short-circuited,
rotor winding. Therefore, an induction motor may be considered to be a transformer with a rotating
secondary (short-circuited). The stator winding corresponds to transformer primary and the rotor finding
corresponds to transformer secondary. In view of the similarity of the flux and voltage conditions to
those in a transformer, one can expect that the equivalent circuit of an induction motor will be similar to
that of a transformer.
8 – explain and draw torque slip characteristics
The torque slip curve for an induction motor gives us the information about the variation of torque with
the slip. The slip is defined as the ratio of difference of synchronous speed and actual rotor speed to the
synchronous speed of the machine. The variation of slip can be obtained with the variation of speed that
is when speed varies the slip will also vary and the torque corresponding to that speed will also vary.
You might also like
- Induction MotorDocument12 pagesInduction MotorsacchashuddhoNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument9 pagesDC MachinesRishan AkalankaNo ratings yet
- Induction Synchronous MotorsDocument35 pagesInduction Synchronous MotorsDeandre LaingNo ratings yet
- History: AC Motor Electromagnetic Induction Slip Rings Commutators Slip-Ring AC Motors Polyphase FrictionDocument8 pagesHistory: AC Motor Electromagnetic Induction Slip Rings Commutators Slip-Ring AC Motors Polyphase FrictionegyptonNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument89 pagesThree Phase Induction MotorTHE ROCKNo ratings yet
- 3phase Induction Motor (Sukhpreet)Document17 pages3phase Induction Motor (Sukhpreet)Ankesh KunwarNo ratings yet
- Presentation On 3 Phase MotorDocument14 pagesPresentation On 3 Phase MotorPushkar PanditNo ratings yet
- Taken From Course Structure 3 Phase Induction MachinesDocument18 pagesTaken From Course Structure 3 Phase Induction MachinesSyed Ahmed MasoodNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction MotorsDocument22 pagesThree Phase Induction MotorsSabiha MahbubNo ratings yet
- Induction Motors Unit 3Document26 pagesInduction Motors Unit 3babu KaroliNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument114 pagesInduction MotorNesarkiran BagadeNo ratings yet
- Skip To ContentDocument17 pagesSkip To Contentkidanemariam teseraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Induction MotorsDocument34 pagesLecture 6 - Induction Motorsswamy_satya20004521No ratings yet
- Single Phase MotorDocument32 pagesSingle Phase MotorsnzaimahNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Machines and SCDocument6 pagesSynchronous Machines and SCivancho04mNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines-II Units-III & IV Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesElectrical Machines-II Units-III & IV Questions and AnswersJoseph Harindranath100% (2)
- Construction of Three Phase Induction MotorDocument18 pagesConstruction of Three Phase Induction MotorRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Ac MotorsDocument17 pagesAc MotorsPineappleJamNo ratings yet
- Electrical MotorDocument23 pagesElectrical MotorAnik73% (11)
- CHAPTER 8 Induction MotorDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 8 Induction MotorDhanashree ParanjapeNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Navigation SearchDocument8 pagesInduction Motor: Navigation SearchSoni Mishra TiwariNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Citations VerificationDocument11 pagesInduction Motor: Citations VerificationChamika Dilshan WickramawardenaNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument43 pagesInduction MotorJanine Jade SetiasNo ratings yet
- Em Lab ReportDocument8 pagesEm Lab ReportRaees MughalNo ratings yet
- Part II - AC MotorsDocument30 pagesPart II - AC MotorsYan Liang HaoNo ratings yet
- Government College University LahoreDocument8 pagesGovernment College University LahoreAreeba NasirNo ratings yet
- A.C. MachineDocument32 pagesA.C. MachinehayikNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument8 pagesInduction MotorNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- EMlabreport (Final) 1Document9 pagesEMlabreport (Final) 1Areeba NasirNo ratings yet
- What Are The Speed Control Method of Induction MotorsDocument12 pagesWhat Are The Speed Control Method of Induction MotorsRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Bee052 Electrical Machine Modeling and AnalysisDocument28 pagesBee052 Electrical Machine Modeling and Analysissunny g.100% (1)
- EE 205 Lecture 29Document17 pagesEE 205 Lecture 29Akshat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Development of Equivalent Circuit of Induction MotorDocument11 pagesStep by Step Development of Equivalent Circuit of Induction MotornandhakumarmeNo ratings yet
- TP2-Satya PrakashDocument13 pagesTP2-Satya Prakashm_azhagarNo ratings yet
- Ee 2403 Special Electrical MachinesDocument21 pagesEe 2403 Special Electrical MachinesSurya KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Ac Motors: An AC Motor Is An Driven by AnDocument18 pagesAc Motors: An AC Motor Is An Driven by AnBalamuni PsaNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Inductionmachine 110625084515 Phpapp01Document25 pagesChapter3 Inductionmachine 110625084515 Phpapp01Ibrahim HussainNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesInduction Motor: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaadhikari_pradeepNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument13 pagesInduction MotorJobin VargheseNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of Induction MotorDocument26 pagesSpeed Control of Induction MotorrajasekaranNo ratings yet
- RameshDocument12 pagesRameshKurapati Siddarth100% (1)
- Induction Motors: Submitted BY P.Durga Prasad 09A25A0205Document15 pagesInduction Motors: Submitted BY P.Durga Prasad 09A25A0205Suresh JillellaNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Asynchronous and Synchronous MotorsDocument6 pagesThe Difference Between Asynchronous and Synchronous MotorsShiva Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ece3414.7induction Machines IDocument18 pagesEce3414.7induction Machines IwillycanNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: This Article Does NotDocument24 pagesInduction Motor: This Article Does Notyashraj786100% (1)
- Stepper MotorDocument18 pagesStepper MotorLasantha Abeykoon67% (3)
- Introduction To Induction Motor: Experiment 11Document4 pagesIntroduction To Induction Motor: Experiment 11Apna VeerNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor: Stator ConstructionDocument9 pagesInduction Motor: Stator ConstructionMohamed IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 InductionmachineDocument25 pagesChapter3 InductionmachineAbhijitNo ratings yet
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationFrom EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseFrom EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseNo ratings yet
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- VPF FormDocument1 pageVPF FormParmar SanjayNo ratings yet
- EE 1st Unit Test Schedule Sem 4 Sem 6 Even 2023-24Document1 pageEE 1st Unit Test Schedule Sem 4 Sem 6 Even 2023-24Parmar SanjayNo ratings yet
- SeatingArrangement EEDocument1 pageSeatingArrangement EEParmar SanjayNo ratings yet
- MCQ Ee247Document9 pagesMCQ Ee247Parmar SanjayNo ratings yet
- Akulon TC 185 Material SpecsDocument2 pagesAkulon TC 185 Material SpecsAli ZaibNo ratings yet
- Applications - Flash - Method Programa ComsolDocument8 pagesApplications - Flash - Method Programa Comsolivan fernandezNo ratings yet
- The Practical For Welding Engineer PDFDocument11 pagesThe Practical For Welding Engineer PDFRian Suari Aritonang0% (1)
- Timeline of Atomic TheoryDocument1 pageTimeline of Atomic TheoryHyung AynNo ratings yet
- Multiple Chioce Questions ThermoDocument8 pagesMultiple Chioce Questions ThermoRose Belle A. GarciaNo ratings yet
- 5 Lead-Tin Phase Diagrams Using Cooling CurvesDocument2 pages5 Lead-Tin Phase Diagrams Using Cooling CurvesOliver TabellNo ratings yet
- FuselageDocument13 pagesFuselageprashanth_anNo ratings yet
- Modeling Heat Treatment of Steel PartsDocument8 pagesModeling Heat Treatment of Steel PartssakthistoryNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification - LV Control Cable - WP4Document10 pagesTechnical Specification - LV Control Cable - WP4nnNo ratings yet
- The Use of Silicone Materials in Close Proximity PDFDocument4 pagesThe Use of Silicone Materials in Close Proximity PDFLBNo ratings yet
- 64290bc8ffe07d0018482b6a - ## - AITS 06 Question PaperDocument29 pages64290bc8ffe07d0018482b6a - ## - AITS 06 Question Papervision xeroxNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structures-II - U1 - L1 - T8 - Analysis of Unsymmetrical Bending of Beams - Neutral Axis MethodDocument9 pagesAircraft Structures-II - U1 - L1 - T8 - Analysis of Unsymmetrical Bending of Beams - Neutral Axis Methodsarathkumar sebastinNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: A Fundamental Approach: June 2012Document26 pagesStrength of Materials: A Fundamental Approach: June 2012Abi DemNo ratings yet
- Approximate Hardness Conversion Chart For Copper No 102 To 142 InclusiveDocument1 pageApproximate Hardness Conversion Chart For Copper No 102 To 142 Inclusivenhan leNo ratings yet
- 8.6 Factors Affecting Standard Electrode Potential (SEP)Document8 pages8.6 Factors Affecting Standard Electrode Potential (SEP)cintiaNo ratings yet
- Members in Compression - IVDocument38 pagesMembers in Compression - IVFatin FalconNo ratings yet
- Circular Column Design Based On ACI 318-19: Input Data & Design SummaryDocument5 pagesCircular Column Design Based On ACI 318-19: Input Data & Design SummaryJEEVENDRANNo ratings yet
- The Uses of Metal Matrix Composites in Bicycles: Kerry BissetDocument17 pagesThe Uses of Metal Matrix Composites in Bicycles: Kerry BissetKerry BissetNo ratings yet
- Design of Pre Stressed Concrete ElementsDocument54 pagesDesign of Pre Stressed Concrete ElementsRoshani JavaliNo ratings yet
- RT Relevant DiscontinuitiesDocument70 pagesRT Relevant Discontinuitiesabdo50% (2)
- Edgar Dutra Zanotto: Is Glass A Liquid or Is It Not? While Teaching MaterialsDocument4 pagesEdgar Dutra Zanotto: Is Glass A Liquid or Is It Not? While Teaching MaterialsValécia DantasNo ratings yet
- Telemacanique K-Line ContactorsDocument48 pagesTelemacanique K-Line ContactorsBra BicabaNo ratings yet
- Borehole Stability Analysis in Deepwater Shallow Sediments: Yan ChuanliangDocument7 pagesBorehole Stability Analysis in Deepwater Shallow Sediments: Yan ChuanliangJose Leo MissionNo ratings yet
- Fe2o3 Trên CNTDocument96 pagesFe2o3 Trên CNTlumineurNo ratings yet
- Index: Modern Diffraction Methods, First Edition. Edited by Eric J. Mittemeijer and Udo WelzelDocument10 pagesIndex: Modern Diffraction Methods, First Edition. Edited by Eric J. Mittemeijer and Udo WelzelalkimiaNo ratings yet
- 21 - Acoustic EmissionDocument7 pages21 - Acoustic EmissionMarcoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document9 pagesExperiment 1Shaun Loo50% (2)
- VDM® Alloy 625 - Nickel Iron Alloy - MatmatchDocument4 pagesVDM® Alloy 625 - Nickel Iron Alloy - MatmatchRaznovrsni KutakNo ratings yet
- Creep TestingDocument26 pagesCreep Testingsamurai7_77No ratings yet
- 243-wikarta-KULIAH V VII BEAM Gaya Internal Diagram Gaya Geser Dan MomenDocument22 pages243-wikarta-KULIAH V VII BEAM Gaya Internal Diagram Gaya Geser Dan Momenikhsan nurfauziNo ratings yet