Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A5 Morphology of Flowering Plants
Uploaded by
KevinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A5 Morphology of Flowering Plants
Uploaded by
KevinCopyright:
Available Formats
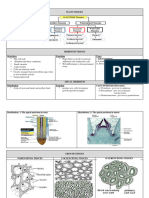
FRUIT STEM
SEED TYPES
• Simple → Mango • Ascending part of axis bearing
• Feature of flowering plants. • After fertilisation, ovules develop branches, leaves, flowers, fruits.
• Compound → lamina dividived Pinnately
• Fruit is mature / ripened ovary into seeds. • Devlops from plumule of seed
• Compound → Neem, palmately
(develops after fertilization) • Seed has seed coat & embryo. • Bears nodes & internodes
• Compound → Silk, Cotton
• Fruit wall → Pericarp • Embryo has radicle, embryonal axis • Has buds – terminal & auxillary.
• Pericarp divided into outer epicarp & cotyledons.
& inner endocarp & middle mesocarp • One cotyledon – Monocot seeds
• Drupe → fruit of coconut & mango (Wheat, Maize) PHYLLOTAXY
• Parthenocarpic fruits that develop • Two cotyledons – Dicot seeds (Gram • Alternate – leaf at each node in
without fertilisation of ovary & Pea). alternate manner ROOT
• Opposite – leaf at each node in opposite
• Elongation of Radicle in plans forms
manner
primary root. Lateral roots from
• Whorled – More than 2 leaves at a node
primary root form secondary.
& form a whorl.
• Tertiary roots.
FAMILIES
• FABACEAE – also called papilionoidae
(sub family of Leguminosae). Pulses, Oil.
• FLORAL FORMULA– %♀K (5) C 1+2+(2)A(a)+1 G1 ROOT SYSTEMS
• SOLANACEAE– “Potato family” tomato,
brinjal, potato, chilli. • Primary roots & its branches form
• FLORAL FORMULA– ⊕♀K(5) C(5) A(5) G(2) Tap root system .e.g mustard
• LILIACEAE– “Lily family” (Tulips) • Roots coming from base of the stem
Characteristic family of Monocots. form fibrous root system. E.g wheat
• Formal formula– Br⊕♀ P(3+3) A 3+3 G (3) • Roots arising from other than radicle
→ adventitious roots. E.g Grass etc.
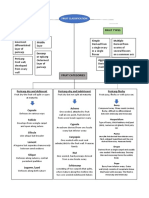
MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTS
INFLORESCENCE
• Inflorescence – Arrangement of MODIFICATION OF ROOTS
flowers on floral axis. • Strong Roots Turnip carrot
• Floral meristem is modified shoot • Prop roots → Banyan tree (hanging
apical meristem roots)
• Racemose inflorescence – main axis • Stilt roots → Palm (support)
grows; flowers in acropetal manner • Pneumatophores → Mangroves (for oxygen
(soybean) / respiration)
• Cymose inflorescence – main axis • Nodulated Roots → Pea (for nitrogen fixation)
terminates flowers in basipetal
order (Tulip)
AERIAL
LEAF
• Stem tendril for • Lateral,
climbing – cucumber flattened
REGIONS OF ROOT
• Flower – reproductive unit of • Stem thorn for protection structure on stem • Root cap → protects the apex of Root.
Calyx Corolla Androecium Gynoecium
angiosperms. → Citrus that develops at node. • Region of meristematic activity →
• Flower arranged on thalamus • Outermost • Next to Calyx • Inner to Corolla • Innermost whorl • Phylloclade – for grow new cells.
• 3 main parts → leaf
whorl • Petals • Stamens • Carpel/ Pistil photosynthesis – opuntia • Region of elongation → lengthening of root
base, Petiole, lamina
• Sepals • Brightly • Male Reproductive • Female • Cladode – leaf–like • Region of maturation → cells
On the basis • Hypogynous – Overy • Performs photosynthesis
• Green coloured Part Reproductive part structure – Asparagus differentiates & mature
of position of highest • Protect the • Attract insects • Stamen has another • Corpel has stigma,
ovary w.r.t • Perigynous – all flower for pellination & filament style & ovary
TYPES OF FLOWER
all whorls whorls same level.
VENATION
• Epigynous – Overy MODIFICATION OF PARTS UNDERGROUND
inferior • Arrangement
• Gamosepalous • Gamopetalous • Stamens united as • Carpels fused • Bulb → Onion of veins
On the basis • Bracteate (Sepals united) (petals united) one bundle (syncarpous) (storage) • Reticulate → network
of Bracts • Ebracteate • Polysepalous • Polypetalous (Monadelphous) • Carpels free • Rhizome →ginger (storage) of veins
(Sepals free) (petals free) • Two bundle – (Apocarpous) • Corm → Colocasia • Parallel → Veins are
Presence of • Bisexual (both present) • Tuber → Potato (stroge) parallel
(Diadelphous)
stamen &
carpel
• Unisexual (only one) AESTIVATION • More than two pLACENTATION
• Arrangement of sepals or bundles • Arrangement of
petals in a floral bud (polyadelphous) ovules in ovary MODIFICATIONS
On the basis of • Actinomorphic (radial • Epipetalous - SUB–AERIAL
• Valvate – no overlapping of • Marginal – pea • Tendril → Pea
symmetry symmetry) Stamen fused with
whorls. • Axile – China Rose • Offset → pistia,
• Zygomorphic (Bilateral petal • Spine → opuntia
• Twisted – overlapping occurs • Parietal – Mustard Eicchornia
symmetry) • Epiphyllous – • Stolon → Strawberry • Flesh leaves → Onion
• Imbricate – Overlapping present • Free central – • Succulent → Aloe
but not in particular direction stamen attached prime rose • Runner → Oxalis
On the basis of • Trimerous • Sucker → Chrysanthemum • Phyllode → Acacia
• Vexillary – One large petal to perianth • Basal – Sunflower
no. of floral • Tetramerous banana (Vegetative • Insectivorous → Venus –
appendages • Pentamerous overlaps other Marigold Propagation) fly trap.
anand_mani16 DR. Anand Mani https://www.anandmani.com/ https://discord.io/anandmani t.me/anandmani001
You might also like
- Diversity AnimalsDocument20 pagesDiversity AnimalsnithinjothimuruganNo ratings yet
- Weed ID and Emerging WeedsDocument76 pagesWeed ID and Emerging WeedsMuhammad KhaidirNo ratings yet
- 2 Reading Materials FBS011 Plant Morphology 2 (Flowers, Fruits, Seeds) - 1Document73 pages2 Reading Materials FBS011 Plant Morphology 2 (Flowers, Fruits, Seeds) - 1Alainie AMINOLAHNo ratings yet
- BIOL 100 Plant Form and FunctionDocument9 pagesBIOL 100 Plant Form and FunctionNiña Jean Tormis AldabaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Unit 31Document31 pagesModule 1 Unit 31Jane MontecalvoNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity Pt1Document7 pagesPlant Diversity Pt1Johann Richardson de VegaNo ratings yet
- Bio ch1 Premium NOtesDocument20 pagesBio ch1 Premium NOtesreal sahilNo ratings yet
- Plant Parts and FunctionsDocument63 pagesPlant Parts and FunctionsmacybnzNo ratings yet
- Poaceae - The Grasses: Wisconsin Flora "Wordle"Document15 pagesPoaceae - The Grasses: Wisconsin Flora "Wordle"Cipta Adi NugrahaNo ratings yet
- BIO13 December 7, 2022 by Franchez Cassandra B. EscanderDocument24 pagesBIO13 December 7, 2022 by Franchez Cassandra B. EscanderFranchez Cassandra EscanderNo ratings yet
- Roots Stem and LeavesDocument1 pageRoots Stem and Leavesyvone iris salcedoNo ratings yet
- Grass Introduction (M Baynes) PDFDocument11 pagesGrass Introduction (M Baynes) PDFNovaaa RukmanaNo ratings yet
- Gymnosperms PDFDocument4 pagesGymnosperms PDFElvis Alexis PoouNo ratings yet
- BIOL1012 Module 5 - Part 1 Morphology, Internal Structure and Growth of PlantsDocument79 pagesBIOL1012 Module 5 - Part 1 Morphology, Internal Structure and Growth of PlantsKayla CoxNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPDocument10 pagesExperiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPMirahmad FadzlyNo ratings yet
- Plant-Kingdom Part 2Document3 pagesPlant-Kingdom Part 2Vidushi KapoorNo ratings yet
- Botany PPT 1Document60 pagesBotany PPT 1SidNo ratings yet
- Morphology 2023Document159 pagesMorphology 2023sbamofficalNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity 2024Document47 pagesPlant Diversity 2024pieterhansconsultantNo ratings yet
- Cucumber Murano F1Document1 pageCucumber Murano F1greatgeniusNo ratings yet
- Flowering, Non-FloweringDocument2 pagesFlowering, Non-FloweringAmalia LyachNo ratings yet
- Plant Structures GrowthDocument6 pagesPlant Structures GrowthIshana KapilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter I (The Plant Body)Document45 pagesChapter I (The Plant Body)Pyae SoneNo ratings yet
- Botany: Stems ReviewerDocument2 pagesBotany: Stems Reviewera yellow flowerNo ratings yet
- Reproduction 3 - Flowering and Non-FloweringDocument27 pagesReproduction 3 - Flowering and Non-Floweringrenato.minaNo ratings yet
- Q2 SCI - Week 5-Modes of Reproduction in Flowering and Non FloweringDocument31 pagesQ2 SCI - Week 5-Modes of Reproduction in Flowering and Non FloweringBUENA ROSARIONo ratings yet
- MEP4 Unit 2.2 Group of PlantsDocument28 pagesMEP4 Unit 2.2 Group of PlantsDayann Ella CruzNo ratings yet
- Pbs100 - PPT 9 - FlowersDocument112 pagesPbs100 - PPT 9 - FlowersMayMenderoNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: - CharacteristicsDocument20 pagesKingdom Plantae: - CharacteristicsJunaedi Ahmad AlzNo ratings yet
- Botany Gymnosperm-22Document29 pagesBotany Gymnosperm-22Ali Hamza ZahidNo ratings yet
- Fruit ClassificationDocument1 pageFruit ClassificationMuhd Azhar ZuhairyNo ratings yet
- Things To Know About Gymnosperms (Botany)Document4 pagesThings To Know About Gymnosperms (Botany)PerrieNo ratings yet
- The Weed Story: Prepared and Presented by Carla Bucknor and Timon WilliamsonDocument18 pagesThe Weed Story: Prepared and Presented by Carla Bucknor and Timon Williamsonspiderone13No ratings yet
- Fruits & Seed Dispersal (Rev Sp12)Document5 pagesFruits & Seed Dispersal (Rev Sp12)anjali vermaNo ratings yet
- Botany ReproductionDocument5 pagesBotany ReproductionJAKE BENZYN TENo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants Mind MapsDocument4 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants Mind Mapsjai maa Durga aadi parashaktiNo ratings yet
- If We Take Care of Plants Then We Get Fruits, Vegetables, and Vitamins. Plants That We GrowDocument1 pageIf We Take Care of Plants Then We Get Fruits, Vegetables, and Vitamins. Plants That We GrowCristina BisqueraNo ratings yet
- 2.3b PLANT TISSUESDocument6 pages2.3b PLANT TISSUES2023820042No ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument6 pagesMorphologyxajela2259No ratings yet
- 514 Plant PropagationDocument19 pages514 Plant Propagationricabaloyo2002No ratings yet
- Roots Reviewer PDFDocument4 pagesRoots Reviewer PDFGAILE MEIZTY MOSADANo ratings yet
- Chapter BotanyDocument62 pagesChapter BotanyArockia RajaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document14 pagesLecture 1nanalat952No ratings yet
- Reproduction: Fertilisation in PlantsDocument18 pagesReproduction: Fertilisation in PlantsNoza WahabNo ratings yet
- 2 Types of Seed Plants: - AngiospermsDocument25 pages2 Types of Seed Plants: - Angiospermsklmax1024No ratings yet
- Plant Structure, Growth, and Development: RootsDocument9 pagesPlant Structure, Growth, and Development: RootsHerlin MabalaNo ratings yet
- Kenya Highland Seed Catalogue - KHS SEED CATALOGUEDocument2 pagesKenya Highland Seed Catalogue - KHS SEED CATALOGUEOliver KiburiNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantDocument41 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantAbhinandan PatilNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Study Notes1Document80 pagesCBSE Class 12 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Study Notes1Fasil PattaraNo ratings yet
- 514 Plant PropagationDocument19 pages514 Plant PropagationGilbert Herrera MorenteNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 5. GymnospermaeDocument30 pagesKuliah 5. GymnospermaeErry MaryaniNo ratings yet
- Botany NotesDocument9 pagesBotany NotesLoeyNo ratings yet
- 07-Avo-Variety AvocadoDocument13 pages07-Avo-Variety AvocadosimohammedNo ratings yet
- Gymnosperms and AngiospermsDocument38 pagesGymnosperms and AngiospermsMeah PachecoNo ratings yet
- OrnamentalsDocument15 pagesOrnamentalsChona KiwasNo ratings yet
- Lamiaceae (Mint) Family FeaturesDocument1 pageLamiaceae (Mint) Family FeaturesEva TuáNo ratings yet
- BotanyDocument14 pagesBotanyCyrill Mae MagallonNo ratings yet
- Brown and Beige Minimalist Vintage Scrapbook Self-Introduction PresentationDocument26 pagesBrown and Beige Minimalist Vintage Scrapbook Self-Introduction PresentationRhusella Adrianne de GraciaNo ratings yet
- Five Simple Grafting Techniques Best Suited for Most Exotic Fruit PlantsFrom EverandFive Simple Grafting Techniques Best Suited for Most Exotic Fruit PlantsNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/22omarNo ratings yet
- Natsci002 End Term A.Y. 2019 - 2020 Ma. Victoria V. Manzan, RN, MN Florence Joy F. Octaviano, RN, ManDocument6 pagesNatsci002 End Term A.Y. 2019 - 2020 Ma. Victoria V. Manzan, RN, MN Florence Joy F. Octaviano, RN, ManJanice Gentile AlisonNo ratings yet
- MCQ Class 7 Reproduction in PlantsDocument12 pagesMCQ Class 7 Reproduction in Plantssakshamgarg0711No ratings yet
- 4 Morphology of Flowering Plants: SolutionsDocument12 pages4 Morphology of Flowering Plants: SolutionsIhtisham Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 28Document9 pagesCbjescpu 28bprkupraveenNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Book3Document114 pagesAgricultural Book3donald eliyaNo ratings yet
- PollinationDocument22 pagesPollinationNAVEEN DHIMAN100% (1)
- Macrocosm Mesocosm and Microcosm The PerDocument16 pagesMacrocosm Mesocosm and Microcosm The PerUday DokrasNo ratings yet
- FlowersDocument56 pagesFlowerszhelyazkova.milaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Biology 11Document46 pagesChapter 14 Biology 11ax1leNo ratings yet
- Rajkumar Biology Unit - 6 by RajatDocument32 pagesRajkumar Biology Unit - 6 by RajatayonavobrownNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument11 pagesPlant ReproductionRagavNarayanan0% (1)
- Chapter 2 Bilogy Holiday HomeworkDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Bilogy Holiday HomeworkAayush RastogiNo ratings yet
- QS AnswersDocument8 pagesQS AnswersJorifNo ratings yet
- American Society of Plant Taxonomists Is Collaborating With JSTOR To Digitize, Preserve and Extend Access To Systematic Botany MonographsDocument63 pagesAmerican Society of Plant Taxonomists Is Collaborating With JSTOR To Digitize, Preserve and Extend Access To Systematic Botany MonographsJuan David Rodriguez HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Biology 11 Unit 8 Assignment 1 What Are The Functions of The Parts of The Flower Virtual LabDocument3 pagesBiology 11 Unit 8 Assignment 1 What Are The Functions of The Parts of The Flower Virtual Labapi-32345376750% (2)
- It SicenceDocument2 pagesIt Sicenceedgdel03No ratings yet
- Flower DissectionDocument3 pagesFlower DissectionEmilyn BenamirNo ratings yet
- Structure of PlantsDocument17 pagesStructure of PlantsJillian Lao100% (5)
- Botlab Flowers Fruits Fruits Seed Dispersal 1Document6 pagesBotlab Flowers Fruits Fruits Seed Dispersal 1Charles GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Pass The Psa 2Nd Edition Edition Will Brown Download PDF ChapterDocument51 pagesPass The Psa 2Nd Edition Edition Will Brown Download PDF Chapterangie.martinez997100% (6)
- LTSC Handbook 2014 Low Res-April8 PDFDocument146 pagesLTSC Handbook 2014 Low Res-April8 PDFblinking02No ratings yet
- Flora of Presidency of MadrasDocument1,679 pagesFlora of Presidency of MadrasAnantha Krishna K SNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction QuestionsDocument3 pagesPlant Reproduction Questionsjustinchu1505No ratings yet
- Flower Anatomy 1Document36 pagesFlower Anatomy 1Iram Tahir100% (1)
- Art Integrated Test Class 4 Anita Pandey (Responses)Document4 pagesArt Integrated Test Class 4 Anita Pandey (Responses)Anita PandeyNo ratings yet
- Angiosperms PPT RevisedDocument55 pagesAngiosperms PPT RevisedJohn Philip Neri Besedillas100% (2)
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument13 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsAdhithyan MNo ratings yet
- Revision of WrightiaDocument22 pagesRevision of WrightiaRaine BugayongNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Flower Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesParts of A Flower Lesson PlanToni Gutz50% (2)