Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ch10 Workbook ON Science 9
Uploaded by
mllupoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch10 Workbook ON Science 9
Uploaded by
mllupoCopyright:
Available Formats
COMPLETE AND RETURN IT TO MR.
LLUPO ON THE DAY OF THE CHAPTER TEST
Chapter 10 Workbook NAME: ___________________________________________
Section 10.1 Review - Exploring Static Charges
Multiple Choice
1. Which of the following is a positively charged 4. When an ebonite rod is rubbed with animal fur, the rod
particle? becomes negatively charged. Why?
a. anion a. Positive charges are transferred from the fur to the rod.
b. proton b. Negative charges are transferred from the rod to the fur.
c. neutron c. Negative charges are created on the surface of the rod.
d. atom d. Negative charges are transferred from the fur to the rod.
e. electron e. Positive charges are transferred from the rod to the fur.
2. What charge does an object have if it has excess 5. A glass rod is rubbed with a cotton cloth. Which statement
electrons? is true?
a. positive a. The glass rod will become negatively charged.
b. negative b. The glass rod will become positively charged.
c. neutral c. The cotton will have a neutral charge.
d. none of the above d. The cotton will become positively charged.
e. not enough information is given e. Both will remain neutral.
3. Which of the following statements is true? 6. Compared with polyester, nylon will
a. A positively charged atom has more neutrons a. lose electrons more easily
than protons. b. lose electrons with more difficulty
b. A positively charged atom has more protons c. lose protons more easily
than neutrons. d. lose protons with more difficulty
c. A positively charged atom has more protons e. not enough information given
than electrons.
d. A positively charged atom has more electrons 7. Which of the following statements is true?
than protons. a. Electrons are able to move easily in a conductor.
e. A positively charged atom has no electrons. b. Electrons are able to move easily in an insulator.
Use the table below to answer questions 4 to 6. c. Electrons are tightly held by a conductor.
d. Protons are able to move easily in an insulator.
Electrostatic Series of Some Common Materials e. Protons are the charge carried in a conductor.
Glass
Weak 8. Which of the following materials is a good conductor?
Human hair a. glass
Nylon b. wood
Wool c. copper
d. fur
Fur
e. rubber
Silk
Cotton
Lucite (a clear plastic)
Polyester
Foam
Strong
Ebonite
142 MHR • Unit 4 The Characteristics of Electricity 978-0-07-031851-9
Section 10.1 Review - Exploring Static Charges
Multiple Choice
9. What is electricity? 13. Which of the following is not true?
a. a form of energy that results from the a. Lightning bolts are giant sparks caused by the
interaction of electrons build-up of static charge.
b. a form of energy that results from the b. Static cling causes plastic wrap to stick to your
interaction of neutrons lunch.
c. a form of energy that results from the c. People who work on computers must reduce the
interaction of atoms net static charges on objects to avoid damaging
d. a form of resistance that results from the sensitive circuits.
interaction of charged particles d. Static cling is never useful.
e. static charge caused by friction e. Static charges must be reduced in many
situations to protect people and equipment.
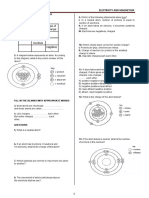
Use the diagram on the right
to answer questions 10 and 11. 14. How does a clothes dryer generate static charges on
the clothes?
10. Which atomic model does a. The current providing the heat in the dryer
the atom represent? generates static charge by induction.
a. Thomson model b. The materials tumble and rub against each other
b. Bohr model as the dryer drum rotates.
c. Rutherford model c. Charging by friction occurs in a clothes dryer.
d. Bohr-Rutherford model d. B and C
e. Dalton model e. A clothes dryer does not generate static charges
on the clothes.
11. Which of the following is true for the atomic
model shown? 15. What is a conductivity tester?
a. An atom consists of three types of particles: a. a device to distinguish between an insulator and
protons, neutrons, and electrons. a conductor
b. The nucleus contains the protons, the neutrons, b. a battery connected to two contact points and a
and the electrons. light bulb
c. Negatively charged electrons are relatively far c. a device to detect static charge
from the nucleus. d. a device to distinguish between a semiconductor
d. A, B, and C are true. and a conductor
e. A and C are true. e. A and B
12. Which of the following is not true about sparks 16. Why must a fuel truck be grounded before it can be
from electrostatic discharge? fuelled?
a. Sparks can cause explosions at grain elevators. a. to limit the build-up of static electricity, which
b. Sparks are not dangerous in any way. could spark and cause an explosion
c. Sparks can damage sensitive electronics. b. to keep the truck perfectly still
d. Sparks can ignite gases used for anesthesia in an c. to reduce the friction between the tires and the
operating room. pavement
e. Sparks can damage pacemakers. d. static charge builds up on the rubber tires
e. it is not necessary to ground a fuel truck
MHR • Unit 4 The Characteristics of Electricity 143
Section 10.1 Review - Exploring Static Charges
Written Answer Answer the following questions in your notebook.
17. Why are dust particles attracted to a newly polished car?
18. What is a semiconductor?
19. What does grounding mean?
20. Copy the following diagram into your notebook. Draw arrows to show the direction of electron flow when a
negatively charged object is grounded.
21. Why are electrical equipment and the people working on the equipment grounded?
22. On a dry winter day, you walk on a carpet and then touch a doorknob. If the doorknob is metal, you feel a shock. If
the doorknob is made of wood, you do not feel a shock. Why?
23. Explain charging by friction.
24. Why are the handles of screwdrivers often made of plastic or rubber?
144 MHR • Unit 4 The Characteristics of Electricity 978-0-07-031851-9
Section 10.1 Review - Exploring Static Charges
Written Answer
Answer the following questions in your notebook. Use the following diagram to answer questions 25 to 27.
25. In part A, what charge do the girl’s hair and the plastic comb have?
26. In part B, what charge do the girl’s hair and the plastic comb have?
27. Explain why the hair and comb are no longer neutral in part B.
28. List two conclusions explained by the Bohr-Rutherford model of the atom.
29. Describe how an anti-static sheet for a clothes dryer works.
30. Why is static charge a concern in an operating room?
31. Why are insulating materials, such as rubber footwear and woolen materials, not allowed in an operating room?
32. Why do some fuel trucks have chains that touch the road?
MHR • Unit 4 The Characteristics of Electricity 145
Section 10.2 Review - Charging by Contact and by Induction
Multiple Choice
1. A pith ball electroscope is negatively charged after 5. If the electroscope is given a permanent charge by
coming in contact with a charged rod. Which induction using the rod below, what will the charge on
statement best describes what happens? the electroscope be?
a. The electrons move from the pith ball to the a. positive
charged rod. b. neutral
b. The electrons move from the charged rod to the c. negative
pith ball. d. no charge
c. The protons move from the pith ball to the e. none of the above
charged rod.
d. The protons move from the charged rod to the
pith ball.
e. The neutrons move from the pith ball to the rod.
2. What happens when a neutral object is charged by
contact?
a. The neutral object gains the same type of charge
as the charging object.
6. A negatively charged ruler is brought near a suspended
b. The neutral object gains the opposite type of
ball. The ball is repelled by the ruler. What can you
charge as the charging object. conclude from this observation?
c. It depends on what the object is made of. a. The ball is neutral.
d. The neutral object remains neutral. b. The ball is positively charged.
e. The neutral object makes the charging object c. The ball is negatively charged.
neutral. d. The ball is either neutral or positively charged.
e. not enough information is given
3. Why are tiny bits of paper attracted to a charged
rubber rod? 7. Two suspended balloons repel each other when they
a. Paper is positively charged. are brought close together. What can you conclude
b. The paper becomes temporarily oppositely about the balloons?
charged by induction. a. They have opposite charges.
c. Paper is negatively charged. b. They have the same charge.
d. The paper acquires a net positive charge by c. One balloon is neutral, and the other balloon is
induction. positively charged.
e. Rubber and paper always attract each other. d. One balloon is neutral, and the other balloon is
negatively charged.
4. A charged conductor is brought near an uncharged e. Both balloons are neutral.
insulator. Which of the following statements
is true? 8. Which of the following applies to a neutral object?
a. Both objects will repel each other. i. It is attracted to a positive surface.
b. Both objects will attract each other. ii. It is attracted to a negative surface.
c. Neither object exerts an electric force. iii. It has the same number of protons as electrons.
d. The objects will repel each other only if the
conductor has a negative charge. a. i and ii only
e. The objects will attract each other only if the b. i and iii only
conductor has a positive charge. c. ii and iii only
d. i, ii, and iii
e. none of the above
146 MHR • Unit 4 The Characteristics of Electricity 978-0-07-031851-9
Section 10.2 Review - Charging by contact and by Induction
Multiple Choice
9. What does the law of electric charges state? 13. The rod is negatively charged and the pith ball is
a. Unlike charges and like charges both attract. neutral. Which of the following statements is true?
b. Unlike charges and like charges both repel. a. The left side of the pith ball will become
c. Like charges attract and unlike charges repel. negatively charged.
d. Like charges repel and unlike charges attract. b. The left side of the pith ball will become
e. Electrons attract each other and neutrons repel positively charged.
each other. c. The pith ball will be attracted to the rod.
d. The pith ball will be repelled by the rod.
10. Which phrase best describes the electric field of a e. B and C are true.
positive charge?
a. points outward 14. What happens to the pith ball if the rod touches it?
b. points inward a. The pith ball becomes positively charged.
c. is circular around the charge b. The pith ball becomes negatively charged.
d. moves all positive charges away c. The pith ball stays uncharged.
e. A and D d. The charge on the pith ball alternates between
positive and negative.
11. Which phrase best describes the electric field of a e. The charge on the pith ball alternates between
negative charge? negative and neutral.
a. points outward
b. points inward 15. What is true about the leaves of an electroscope?
c. is circular around the charge a. made of a metal
d. moves all negative charges away b. are conducting
e. B and D c. separate when a charged object touches the
electroscope
12. Which of the following methods of charging gives d. fall together when grounded
the same charge as the charging object? e. All of the above are true.
a. friction
b. induction 16. What is true about the electric field of a charge?
c. contact a. increases as the distance from the charge
d. A and B increases
e. B and C b. decreases as the distance from the charge
increases
Use the diagram below to answer questions 13 and 14. c. does not change
d. is the area around the charge where its effect is
felt
e. B and D
MHR • Unit 4 The Characteristics of Electricity 147
Section 10.2 Review - Charging by Contact and by Induction
Written Answer
17. In what direction will a positive charge move when placed in the electric field surrounding another positive charge?
18. Refer to the diagram below. A positively charged rod is brought near two fixed and neutral spheres. How are the
spheres charged if they are separated while the rod is kept in position?
19. What is the function of an electroscope?
20. When a neutral object is charged by induction, what charge does it become?
21. What is the difference between charging by friction and charging by contact? In your answer, explain the difference
in terms of electron transfer.
22. What type of charges move through a conductor?
23. How is the electric force between two charged objects related to the amount of charge on each object?
24. How is the electric force between two charged objects related to the distance between them?
148 MHR • Unit 4 The Characteristics of Electricity 978-0-07-031851-9
Section 10.2 Review - Charging by Contact and by Induction
Written Answer
25. What determines the amount of net charge on an object?
26. Use the following diagram to explain what happens to the pith ball, and why.
27. What is the test for charge?
28. How do you determine whether an object has a neutral charge?
29. How can an electroscope be used to find out whether an object is neutral or charged?
30. Name one difference between the electric force and the force of gravity.
31. What is one similarity between the electric force and the force of gravity?
32. Name the three elements of an electroscope, and explain why they are made of metal.
MHR • Unit 4 The Characteristics of Electricity 149
Section 10.3 Review - Charges at Work
Multiple Choice
1. What path does lightning follow? 6. The device in the following diagram is an electrostatic
a. straight precipitator. What is an electrostatic precipitator?
b. curved
c. circular
d. jagged
e. perfectly horizontal
2. Which of the following is not true about lightning?
a. The rubber tires on a car will protect you from a
lightning strike.
b. Lightning usually strikes the highest object in
an area.
c. A lightning strike carries a very large electric
current.
d. Lightning takes the path of least resistance a. a type of cleaner
between a cloud and the ground. b. a device that removes unwanted particles
e. A lightning strike can injure an unprotected c. a device that removes unwanted liquid droplets from
person. a flow of gas
d. a device to reduce pollution
3. Which of the following is true about a lightning e. all of the above
rod?
a. It is a metal sphere or point.
7. For what purpose is a Van de Graaff generator used?
b. It is attached to the highest part of a building. a. to accumulate and transfer electrons
c. It is connected to the ground. b. to charge objects
d. It provides a low-resistance path for the electric c. as an insulator
current to the ground. d. to accumulate and transfer neutrons
e. All of the above are true. e. A and D
4. Where is a person most likely to be hit by 8. What is true about the element that is used in copiers,
lightning? printers, and scanners?
a. in a field a. It is light sensitive.
b. in a boat b. The element is selenium.
c. in a house c. The element is copper.
d. in a car d. It is heat sensitive.
e. A and B e. A and B are true.
5. What is a positive ion?
a. an atom with a deficiency of electrons
b. an atom with an excess of electrons
c. a neutral atom with more neutrons
d. an atom with no charge
e. none of the above
150 MHR • Unit 4 The Characteristics of Electricity 978-0-07-031851-9
Section 10.3 Review - Charges at Work
Written Answer
9. Name three practical uses of electric charges.
10. When do lightning strikes occur most frequently in Canada?
11. Why does a piece of paper that has just emerged from a photocopier stick to clothes?
12. Why is electrostatic spray painting a good environmental and economic choice?
Use the diagram below to answer questions 13 to 15.
13. Where is the charge generated on a Van de Graaff generator?
14. Where is the charge collected on a Van de Graaff generator?
15. By what method does the charging take place in a Van de Graaff generator?
16. What property of selenium makes it useful in a photocopier?
MHR • Unit 4 The Characteristics of Electricity 151
Chapter 10 Review - Static Charges and Energy
Multiple Choice
1. When is there a repulsive force between two Use the following diagram to answer questions 6 and 7.
charged objects?
a. when their charges are of unlike sign
b. when the objects have the same number of
protons
c. when their charges are of like sign
d. when they have the same number of electrons
e. when they have the same number of charges
2. When is there an attractive force between two
charged objects? The following observations were made on the pith balls
a. when their charges are of unlike sign in the diagram.
b. when the objects have the same number of i. Ball A attracts B, and ball A repels C.
protons ii. Ball D attracts B, and ball D has no effect on E.
c. when their charges are of like sign iii. A negatively charged rod attracts both A and E.
d. when they have the same number of electrons
e. when they have the same number of charges 6. Which of the following statements is true?
a. A, B, and C are charged, but D and E are not
3. When there is an equal amount of positive and charged.
negative charge on an object, how is the object b. A and B are not charged, but C, D, and E are
charged? charged.
a. positively charged c. All of them are charged.
b. negatively charged d. Only D and E are charged.
c. neutral e. A, B, and D are charged.
d. supercharged
e. none of the above 7. Which of the following statements could be true?
a. A and C are positively charged.
4. A negatively charged rod is brought near one end b. D and E are neutral.
of an uncharged metal bar. What will the charge be c. B is negatively charged.
of the metal bar farthest from the charged rod? d. All of the above could be true.
a. positive e. A and C
b. negative
c. neutral 8. During charging by induction, the charged object exerts
d. alternating between positive and negative a force on the protons and electrons in a solid neutral
e. alternating between positive and neutral object, but only the electrons move. Why?
a. The protons are induced to remain still.
5. When a neutral metal sphere is charged by contact b. Only electrons can move in the solid.
with a positively charged glass rod, what happens c. The force is not strong enough to move the
to the sphere? protons.
a. The sphere loses electrons. d. The electrons are repelled by the protons, causing
b. The sphere gains electrons. the electrons to move.
c. The sphere loses protons. e. None of the above.
d. The sphere gains protons.
e. The sphere gains negative charge.
152 MHR • Unit 4 The Characteristics of Electricity 978-0-07-031851-9
Chapter 10 Review - Static Charges and Energy
Written Answer
9. Name two good conductors of electricity.
10. Name two good insulators.
11. How is an electroscope grounded?
12. Name four practical applications that use electrostatic principles.
13. When do you sometimes feel an electric shock? Use electron flow in your answer.
14. What is the purpose of a ground, and where is it connected?
15. While combing your hair, what type of comb should you use? Explain your reasoning.
16. What is the main difference between charging by induction and charging by contact?Refer to the following
diagram in your answer.
MHR • Unit 4 The Characteristics of Electricity 153
Chapter 10 Review - Static Charges and Energy
Written Answer
17. If you were wearing cotton socks and dragged your feet over a wool carpet, both your socks and the carpet
would become charged. What charge would each one get, and why?Refer to the electrostatic series table in
Section 10.1.
18. Assume you rub a material with fur and the material becomes charged. Explain how you could use a negatively
charged ebonite rod or a positively charged glass rod to determine the type of charge on the material.
19. No matter how hard you rub two objects made of the same material together, it is not possible to charge them.
Explain why.
20. Match the condition in the left column with the action in the right column.
With a negatively charged electroscope,
Actions
what happens when …
a. you bring a positive rod near the sphere on the i. The leaves move farther apart and remain there.
top of the electroscope?
b. you touch a very negative rod to the sphere on ii. There is no change in the position of the leaves
the top of the electroscope? detected.
c. you touch a copper wire connected to a water iii. The leaves temporarily move closer together.
pipe to the sphere on the top?
d. you bring a neutral rod near the sphere on the iv. The leaves fall back and hang vertically, indicating
top of the electroscope? no charge.
21. What is thunder?
22. Why do you always see lightning before you hear the thunder?
23. Explain the properties of conductors and insulators in terms of electrons.
24. Copy the following diagram into your notebook. Draw arrows to represent the magnitude and direction of the
electric fields.
154 MHR • Unit 4 The Characteristics of Electricity 978-0-07-031851-9
Chapter 10 Review - Static Charges and Energy
Written Answer
25. Explain how lightning is formed.
26. Explain, step by step, how a sphere can be negatively charged by induction using a charged rod.
27. Identify the two factors that affect the force between two charges.
28. You are caught in a thunderstorm. Should you take cover under a tree? Explain your answer.
29. Silver is an excellent conductor, yet it is rarely used in common applications. Why?
30. Match each definition in Column A to the correct term in Column B.
Column A Column B
a. method that transfers charges to Earth i. electroscope
b. equipment that can detect static charge ii. induction
c. method of charge transfer when combing your hair iii. contact
d. method of charge transfer that can produce sparks iv. grounding
e. method of charge transfer when an object is touched v. friction
31. How are electric sparks produced?
32. What method of charge transfer is involved when a spark is formed?
MHR • Unit 4 The Characteristics of Electricity 155
You might also like
- Ch11 Workbook ON Science 9Document14 pagesCh11 Workbook ON Science 9mllupoNo ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument9 pagesStatic ElectricityEssraa KhamisNo ratings yet
- Summative Test For Physics 2Document3 pagesSummative Test For Physics 2Ford MiloNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure (Grade 8) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeaching PDFDocument1 pageAtomic Structure (Grade 8) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeaching PDFnick2107067% (3)
- HLP Physics 9 July Ethan Tristan 9 Habakkuk 8Document5 pagesHLP Physics 9 July Ethan Tristan 9 Habakkuk 8margaretta yunitaNo ratings yet
- Physics Assessment - Easy 2Document9 pagesPhysics Assessment - Easy 2MARICEL MIRANDANo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Section 1Document2 pagesChapter 16 Section 1Hassan SobhyNo ratings yet
- Electronics Engineering Board ChallengeDocument109 pagesElectronics Engineering Board ChallengeEarlJaysonAlvaranNo ratings yet
- Final RevisionDocument9 pagesFinal Revisionhelomen321No ratings yet
- Science SOL 4.3 - Electricity: Lightning Is Caused by Static ElectricityDocument3 pagesScience SOL 4.3 - Electricity: Lightning Is Caused by Static ElectricityKrishnaKumar PodagatlapalliNo ratings yet
- Types of ChargingDocument50 pagesTypes of ChargingShannen Abegail FernandezNo ratings yet
- EEreviewerDocument80 pagesEEreviewerE-4296CASTILLOasistNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity Class 8Document21 pagesStatic Electricity Class 8proodoot50% (2)
- Class - 8 Physics Chapter - 8 Electricity Exercise SolutionsDocument5 pagesClass - 8 Physics Chapter - 8 Electricity Exercise SolutionsArpan BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Subatomic Physics Test 13-14 2Document10 pagesChapter 22 - Subatomic Physics Test 13-14 2Srood SalarNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Workbook On Science 9Document14 pagesCh5 Workbook On Science 9mllupoNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits VI CLASSDocument7 pagesElectricity and Circuits VI CLASSsrinav sNo ratings yet
- Midterm ExamDocument3 pagesMidterm Exambernadeth barajasNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Physics Penguin PDFDocument19 pagesWorksheet Physics Penguin PDFjleodennisNo ratings yet
- Physics SummativeDocument4 pagesPhysics SummativeAerian BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity - QuizizzDocument7 pagesStatic Electricity - QuizizzRico YupitaNo ratings yet
- 1 Objectives Practice Set 1Document8 pages1 Objectives Practice Set 1verlashNo ratings yet
- Dep ElectronicsDocument2 pagesDep ElectronicsNathalie Garmeles MiñosaNo ratings yet
- Gibilisco AnswersDocument54 pagesGibilisco AnswersIan Von ArandiaNo ratings yet
- Electrics CombinedDocument80 pagesElectrics CombinedfernandocharithNo ratings yet
- Quarterly Test in g9 Science 2nd Grading PDFDocument1 pageQuarterly Test in g9 Science 2nd Grading PDFAJ Alagban100% (1)
- DC Electronics Chapter2 PDFDocument112 pagesDC Electronics Chapter2 PDFfabrice mellantNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Review Question For Grade 9 Unit 3Document5 pagesChemistry Review Question For Grade 9 Unit 3mtadesse158No ratings yet
- Gibilisco MCQ in Basic Physical Concept ECE Board ExamDocument4 pagesGibilisco MCQ in Basic Physical Concept ECE Board ExamXyNo ratings yet
- Quarterly Test in g9 Science 2nd Grading PDF Chemical Polarity Covalent Bond 7Document1 pageQuarterly Test in g9 Science 2nd Grading PDF Chemical Polarity Covalent Bond 7Elijah CapatiNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Science 8Document2 pagesSummative Test Science 8Edgardo BalistoyNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Grade 9Document2 pagesAtomic Structure Grade 9Ratna PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 Module 1Document14 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Module 1yinyang21rawrNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 1 Answer Key PartialDocument8 pagesQUIZ 1 Answer Key Partialmikelandrew30No ratings yet
- Some Natural Phenomena Textbook Q-ADocument3 pagesSome Natural Phenomena Textbook Q-AharipriyaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual p6 105 ELECTRICITYDocument7 pagesConceptual p6 105 ELECTRICITYmean comiaNo ratings yet
- Notes Physics Grade 8 ElectrostaticsDocument8 pagesNotes Physics Grade 8 ElectrostaticsRejo Raghuvaran100% (2)
- Electronics 1aDocument6 pagesElectronics 1amary_nailynNo ratings yet
- DLL 1stDocument2 pagesDLL 1stFrician Bernadette MuycoNo ratings yet
- Third Periodic ExamDocument1 pageThird Periodic ExamJunnel MaravillaNo ratings yet
- 13-Electric Force-FieldDocument2 pages13-Electric Force-FieldMiya GomezNo ratings yet
- MCQ Radiology 2017 Answer الصحDocument2 pagesMCQ Radiology 2017 Answer الصحM.AhmedNo ratings yet
- Physics Ss1 Edidot - 081647Document6 pagesPhysics Ss1 Edidot - 081647Raymy ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Physics Assessment - AverageDocument18 pagesPhysics Assessment - AverageMARICEL MIRANDANo ratings yet
- 1) Gen - Physics 2-Module 1Document6 pages1) Gen - Physics 2-Module 1Ma. Alyzandra G. LopezNo ratings yet
- Cadaloria High School: Schools Division Office of IsabelaDocument3 pagesCadaloria High School: Schools Division Office of IsabelaRichwellPanganibanSolivenNo ratings yet
- Cebu Technological University: AST 111 Fundamentals of Electrical and ElectronicsDocument2 pagesCebu Technological University: AST 111 Fundamentals of Electrical and ElectronicsDominic Libradilla100% (1)
- MessageDocument3 pagesMessageabdulrahmanmohammad242kbsNo ratings yet
- 9 Physics Activity Book 2020-2021Document40 pages9 Physics Activity Book 2020-2021Mobile gamerNo ratings yet
- Q3L1 - Electric Charge & Electric ForceDocument32 pagesQ3L1 - Electric Charge & Electric Forcerhenzmarielle.pasionNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions From Electrostatics and Current ElectricityDocument2 pagesMultiple Choice Questions From Electrostatics and Current ElectricitySandhya73% (49)
- 2 Des, Jovan 9 LaurenDocument4 pages2 Des, Jovan 9 LaurenFaber O.MNo ratings yet
- Electrics and Electricals Oxford QuestionsDocument83 pagesElectrics and Electricals Oxford QuestionsbadboynashtaNo ratings yet
- Ee111 Final Exam (2019-2020)Document3 pagesEe111 Final Exam (2019-2020)Abdul Halil AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 1ST Quarter Exam. Eim W - Ket To CorrectionsDocument7 pages1ST Quarter Exam. Eim W - Ket To CorrectionsTeacher Ronel SDO NavotasNo ratings yet
- General-Physics-2 Q3 M1 Electric-ChargeDocument8 pagesGeneral-Physics-2 Q3 M1 Electric-ChargeArian Avner De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- OBE Elecs 1 Midterm Examination - v1 Answer KeyDocument9 pagesOBE Elecs 1 Midterm Examination - v1 Answer KeyRaymond Joseph MeimbanNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab - Ionic and Molecular CompoundsDocument20 pagesBiochem Lab - Ionic and Molecular CompoundsAngeli Robyn OngNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1From EverandTheoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- ch1 Physics 12 Study GuideDocument16 pagesch1 Physics 12 Study GuidemllupoNo ratings yet
- ch1 NEW Physics 12 Study GuideDocument16 pagesch1 NEW Physics 12 Study GuidemllupoNo ratings yet
- Answers Physics 12 Study GuideDocument3 pagesAnswers Physics 12 Study GuidemllupoNo ratings yet
- ScienceSkills AssignmentDocument7 pagesScienceSkills AssignmentmllupoNo ratings yet
- Phys Sol Ch03Document120 pagesPhys Sol Ch03Peggy DominicoNo ratings yet
- Eclass Program Information and Login InstructionsDocument1 pageEclass Program Information and Login InstructionsmllupoNo ratings yet
- Ch8 Workbook ON Science 9Document14 pagesCh8 Workbook ON Science 9mllupoNo ratings yet
- Ch2 Workbook On Science 9Document14 pagesCh2 Workbook On Science 9mllupoNo ratings yet
- Ch9 Workbook ON Science 9Document16 pagesCh9 Workbook ON Science 9mllupoNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Hcd-Cpz1Document80 pagesService Manual: Hcd-Cpz1boroda2410No ratings yet
- ElectricianSemIICITSQB PDFDocument82 pagesElectricianSemIICITSQB PDFmarvin2008No ratings yet
- Hypertac Cid Series ConnectorsDocument3 pagesHypertac Cid Series Connectorsdilnair99No ratings yet
- Wireless PowerDocument31 pagesWireless Poweral_1989No ratings yet
- Straatman Solar SystemsDocument8 pagesStraatman Solar SystemsMNo ratings yet
- EE19BTECH11021Document20 pagesEE19BTECH11021abhiNo ratings yet
- 973B - Hi - Tech Smart Key - Handbook - 01 - 08 - 09 PDFDocument64 pages973B - Hi - Tech Smart Key - Handbook - 01 - 08 - 09 PDFNguyễn Chánh Sĩ100% (6)
- Configuration 3 TDJ-172718DEI-65FT2v01Document1 pageConfiguration 3 TDJ-172718DEI-65FT2v01ДмитрийNo ratings yet
- Changeover & by Pass SwitchesDocument12 pagesChangeover & by Pass Switcheshemant kumarNo ratings yet
- 3.5/4.5 Digit Process/Temperature Indicators, Controllers: V V V V VDocument2 pages3.5/4.5 Digit Process/Temperature Indicators, Controllers: V V V V VSahityan PalanichamyNo ratings yet
- Electronics: A Review On Small Power Rating PV Inverter Topologies and Smart PV InvertersDocument26 pagesElectronics: A Review On Small Power Rating PV Inverter Topologies and Smart PV InvertersPadmavathi RNo ratings yet
- Generador Cummins HV824C (Ads-510)Document2 pagesGenerador Cummins HV824C (Ads-510)foroNo ratings yet
- Utilitech PQS45UT 500-Watt Portable Work Light ManualDocument20 pagesUtilitech PQS45UT 500-Watt Portable Work Light ManualMatthew LeingangNo ratings yet
- IEEE Guide For The Selection of Monitoring For Circuit BreakersDocument80 pagesIEEE Guide For The Selection of Monitoring For Circuit BreakersJoel Cruz CondoriNo ratings yet
- SM Tec8300Document90 pagesSM Tec8300m.torresNo ratings yet
- Nabl 500 PDFDocument124 pagesNabl 500 PDFFundary ShopNo ratings yet
- Activity4 Group1Document17 pagesActivity4 Group1NicoNo ratings yet
- TRENDCOM ManualDocument14 pagesTRENDCOM ManualAndrés Ain-ActiveNo ratings yet
- HBS86H Hybrid Stepper Servo Drive ManualDocument22 pagesHBS86H Hybrid Stepper Servo Drive ManualPhúc Phan TiếnNo ratings yet
- 20.8.2020 Class-1Document21 pages20.8.2020 Class-1abhi shekNo ratings yet
- TV Trouble Shooting Manual: Information Source 5Document9 pagesTV Trouble Shooting Manual: Information Source 5Rapelang SepekaNo ratings yet
- Fermentation Monitor 5100 - EnglishDocument33 pagesFermentation Monitor 5100 - EnglishXian KrispNo ratings yet
- CityRover Workshop ManualDocument645 pagesCityRover Workshop ManualTheCityRover100% (17)
- Educate - Empower: EnhanceDocument9 pagesEducate - Empower: Enhancenaufal hakimNo ratings yet
- Ladder DiagramDocument17 pagesLadder DiagramItsMeRyanCNo ratings yet
- True, Reactive and Apparent PowerDocument14 pagesTrue, Reactive and Apparent PowerTuhin HandaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS)Document28 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS)Musa MagaulaNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: KDL-V32XBR2 KDL-V32XBR2Document75 pagesService Manual: KDL-V32XBR2 KDL-V32XBR2aquiles armandoNo ratings yet
- Oper For Cooling UnitDocument32 pagesOper For Cooling Unitsourabh naikyaNo ratings yet
- EEE418 Embedded SystemDocument13 pagesEEE418 Embedded SystemABDULLAH AL BAKINo ratings yet