Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elastic Limit 11111111111111111111111111
Uploaded by
Khushi SalgaonkarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elastic Limit 11111111111111111111111111
Uploaded by
Khushi SalgaonkarCopyright:
Available Formats
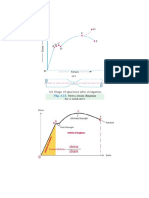
Elastic limit:- Point E represent the elastic limit Even if the specimen is stressed beyond point P and
upto E. it will regain its initial size and shape when the load is removed. This indicases that the material is
in elastic stage upto point E. Therefore E is called elastic limit.
Proportional limit:: Within proportional limit stress is directly proportional to strain Hence, the
material will regain its original shape after unloading. The stress corresponding to the load is known as
limit of proportionality.
Ultimate tensile Strength: After yield point y plastic deformation increases. The material becomes
stranger due to strain hardening and higher and higher load is required to deform the material finally the
load and stress reaches a maximum value as given by point U. The stress corresponding to paint U is
called yield strength.
Yield Stress (Point Y):: The loading beyond E cause plastic deformation and material start yielding.
During this stage it is not possible to recover the initial size and shape of the material on removal of load
it is seen from the diagram beyond point E strain increases at faster rate up to y- The stress corresponding
to yield point y is called yield strength.
Stress Concentration: Whenever a machine component changes the shape of its cross-section, the
simple stress distribution no longer holds good and the neighbourhood of the discontinuity is different.
This irregularity in the stress distribution caused by abrupt changes of form is called stress concentration.
concentration can not be totally eliminated but it may be reduced to some extent. A device or concept
that is useful in assisting a design engineer to visualize the presence of stress concentration and how it
may be mitigated is that of stress flow lines, as shown in Fig. The mitigation of stress concentration means
that the stress flow lines shall maintain their spacing as far as possible.
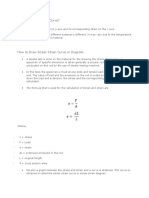
Factor of Safety
It is defined, in general, as the ratio of the maximum stress to the working stress.
Factor of safety = Maximum stress /Working or design stress
In case of ductile materials e.g
Factor of safety = Yield point stress /Working or design stress
In case of brittle materials
Factor of safety = Ultimate stress or design stress
Selection of Factor of Safety
1. The reliability of the properties of the material and change of these properties during service ;
2. The reliability of test results and accuracy of application of these results to actual machine parts ;
3. The reliability of applied load ;
4. The certainty as to exact mode of failure ;
5. The extent of simplifying assumptions ;
6. The extent of localised stresses ;
You might also like
- Stress-Strain DiagramDocument10 pagesStress-Strain DiagramSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain CurveDocument7 pagesStress Strain Curvekihal zohirNo ratings yet
- True Stress - True Strain Curve: Part One: AbstractDocument2 pagesTrue Stress - True Strain Curve: Part One: AbstractSoham DeNo ratings yet
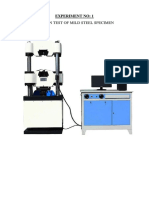
- Experiment No. 11: Aim: To Draw Stress-Strain Diagram For A Mild Steel Specimen Under Tensile Test. TheoryDocument2 pagesExperiment No. 11: Aim: To Draw Stress-Strain Diagram For A Mild Steel Specimen Under Tensile Test. Theorysumanroyal123No ratings yet
- Theory of Tensile Test Engineering Essay PDFDocument8 pagesTheory of Tensile Test Engineering Essay PDFgraNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Mechanical PropertiesDocument51 pagesUnit-1 Mechanical PropertieskameshvvNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document30 pagesUnit 1lakshmi narayanaNo ratings yet
- What Is Stress Strain Curve?Document3 pagesWhat Is Stress Strain Curve?Prabu CholanNo ratings yet
- Material Properties ReportDocument8 pagesMaterial Properties ReportazizsaafanNo ratings yet
- Simple Stress and StrainDocument16 pagesSimple Stress and StrainAvinash DharwadkarNo ratings yet
- Stress and Strain - Class 1Document21 pagesStress and Strain - Class 1Ahmad AliyuNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain RealtionshipDocument35 pagesStress Strain RealtionshipKhalid YousafNo ratings yet
- Stress and Strain: Elastic ModulusDocument10 pagesStress and Strain: Elastic Moduluslaura sageNo ratings yet
- Stresses in Machine MemberDocument18 pagesStresses in Machine MemberK ULAGANATHANNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Mechanical ReportDocument6 pagesStrength of Materials - Mechanical ReportAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Solids and Structural MechanicsDocument15 pagesSolids and Structural MechanicsBONFACE MUGUNANo ratings yet
- Stresses in Machine ElementsDocument18 pagesStresses in Machine ElementsthirumalaikumaranNo ratings yet
- Tensile TestDocument12 pagesTensile Testmeysam1215100% (3)
- Stress and Strain: Elastic ModulusDocument20 pagesStress and Strain: Elastic Moduluslaura sageNo ratings yet
- SOM Write Up1Document34 pagesSOM Write Up1KUNKRINo ratings yet
- HOME ASSIGNMENT 2 (AutoRecovered)Document15 pagesHOME ASSIGNMENT 2 (AutoRecovered)ATIF KHANNo ratings yet
- Stress-Strain Curve 3. Short Term Mechanical PropertiesDocument183 pagesStress-Strain Curve 3. Short Term Mechanical PropertieskhagendrakryadavNo ratings yet
- AttaDocument5 pagesAttaSaeed AyeenNo ratings yet
- Assig 1Document6 pagesAssig 1world vibesNo ratings yet
- Stress-Strain CurveDocument8 pagesStress-Strain Curvedani chNo ratings yet
- MM 1Document6 pagesMM 1Rana Naveed0% (1)
- Mechanical Properties of Materials - MechaniCalcDocument11 pagesMechanical Properties of Materials - MechaniCalcharieduidNo ratings yet
- Stress and StrainDocument42 pagesStress and StrainPaul James Thadhani100% (5)
- Young S Modulus (E) : Ratio Between Tensile Stress and Tensile Strain or Compressive Stress and Compressive StrainDocument14 pagesYoung S Modulus (E) : Ratio Between Tensile Stress and Tensile Strain or Compressive Stress and Compressive StrainJitendra GangwarNo ratings yet
- Creep & Stress ConcenbtrationDocument6 pagesCreep & Stress ConcenbtrationvrajendraupadhyayNo ratings yet
- Topic Cover: Stress and StrainDocument42 pagesTopic Cover: Stress and StrainVinaasha BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- MD-I Lecture 04Document21 pagesMD-I Lecture 04Uzair NaeemNo ratings yet
- Lezione 25-05-2022Document9 pagesLezione 25-05-2022Lorenzo CampanellaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - TENSION TEST OF MILD STEEL SPECIMENDocument10 pagesExperiment 1 - TENSION TEST OF MILD STEEL SPECIMENSamiha Maysoon Nooria100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Static and Fatigu Design FundamentalsDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Static and Fatigu Design FundamentalsEDWARD T CHENJERAINo ratings yet
- Le 09 em Ja Fa22Document20 pagesLe 09 em Ja Fa22Muhammad Ashnab ZahidNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements Design Against Fluctuating LoadsDocument39 pagesDesign of Machine Elements Design Against Fluctuating LoadsAwan AJaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Stress Strain DiagramDocument26 pagesAssignment Stress Strain DiagramShivani MedhekarNo ratings yet
- Unit.2 Part.1Document48 pagesUnit.2 Part.1Narender NarruNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document63 pagesChap 3snupisnupNo ratings yet
- Stress-Strain Curve 3. Short Term Mechanical PropertiesDocument183 pagesStress-Strain Curve 3. Short Term Mechanical PropertiesManprita BasumataryNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document13 pagesExperiment 2الشهاب ناروتوNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4. Stresses On StructuresDocument5 pagesLESSON 4. Stresses On StructuresAdarsh bhatNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test: (Selection and Testing of Materials (PE-ME 701E) Continuous Assessment 2 (CA 2)Document9 pagesTensile Test: (Selection and Testing of Materials (PE-ME 701E) Continuous Assessment 2 (CA 2)Prabhat RoutNo ratings yet
- Lec 8Document11 pagesLec 8kottapalli krishna chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint PresentationDocument65 pagesPowerPoint PresentationMRIDUL SINGLANo ratings yet
- Stress Concentration Final PDFDocument14 pagesStress Concentration Final PDFSomdeep DuttaNo ratings yet
- Rheological Properties (Terminology)Document18 pagesRheological Properties (Terminology)adNo ratings yet
- Simple Stress and StrainsDocument15 pagesSimple Stress and StrainsSharad JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.Document52 pagesChapter 1.Dnyaneshwar AkhareNo ratings yet
- Portal Frame PDFDocument7 pagesPortal Frame PDFeidalinNo ratings yet
- University of Technology Chemical Engineering Oil and Refining BranchDocument13 pagesUniversity of Technology Chemical Engineering Oil and Refining Branchجعفر ذيابNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain CurveDocument2 pagesStress Strain CurveVignesh VickyNo ratings yet
- The Tension and Compression TestDocument3 pagesThe Tension and Compression Testnabila putriNo ratings yet
- Med 1Document32 pagesMed 1Engr Imtiaz Hussain GilaniNo ratings yet
- Anexo VI: Tensile PropertiesDocument5 pagesAnexo VI: Tensile PropertiesPsNo ratings yet
- Machine Design - IntroductionDocument47 pagesMachine Design - IntroductionGanesh DongreNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document54 pagesLecture 1nofal AdreesNo ratings yet
- Laboratory (EXP 2 - Tensile) 1Document14 pagesLaboratory (EXP 2 - Tensile) 1Sri KartikeayanNo ratings yet
- MaximDocument9 pagesMaximKhushi SalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court and The Constitutional ProcessDocument34 pagesSupreme Court and The Constitutional ProcessKhushi SalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- 45 Days ChallengeDocument2 pages45 Days ChallengeKhushi SalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Mineral ResourcesDocument7 pagesMineral ResourcesKhushi SalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- De Concentration 123Document4 pagesDe Concentration 123Khushi SalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument8 pagesEcosystemKhushi SalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Lifestyle & Medical DetailsDocument6 pagesLifestyle & Medical DetailsKhushi SalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- MultidisciplinaryDocument6 pagesMultidisciplinaryKhushi SalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- M Gowda A GowdaDocument3 pagesM Gowda A GowdaKhushi SalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Table of Contents O1Document2 pagesTable of Contents O1Khushi SalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Indian National CongressDocument7 pagesIndian National CongressKhushi SalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- De Concentration 123Document4 pagesDe Concentration 123Khushi SalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Ground Architecture (Mourad Medhat)Document146 pagesGround Architecture (Mourad Medhat)Aída SousaNo ratings yet
- John Hopkins Evidence Table - Systematic ReviewDocument2 pagesJohn Hopkins Evidence Table - Systematic Reviewsandy ThylsNo ratings yet
- Of Personality Traits of Only and Sibling School Children in BeijingDocument14 pagesOf Personality Traits of Only and Sibling School Children in BeijingMuhammad Hamza AsgharNo ratings yet
- 1991 - Defect Chemistry of BaTiO3Document20 pages1991 - Defect Chemistry of BaTiO3Beh NaatNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting and Capital Budgeting and Risk Analysis Risk AnalysisDocument16 pagesCapital Budgeting and Capital Budgeting and Risk Analysis Risk AnalysisHaris FendiarNo ratings yet
- Summative 1Document4 pagesSummative 1Nean YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Enterpreneurship Assignment 2Document8 pagesEnterpreneurship Assignment 2Khusbu JaiswalNo ratings yet
- EED516-Assignment 1 - S1 2023Document2 pagesEED516-Assignment 1 - S1 2023RETRO GAMERSNo ratings yet
- Spying From Space - Constructing America's Satellite Command and Control Systems (PDFDrive)Document230 pagesSpying From Space - Constructing America's Satellite Command and Control Systems (PDFDrive)MohammadNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Perylsa CompletoDocument221 pagesCatalogo Perylsa CompletoAlvaro Diaz0% (1)
- The Research Problem: The Key Steps in Choosing A TopicDocument5 pagesThe Research Problem: The Key Steps in Choosing A TopicJoachim San JuanNo ratings yet
- INT PL 2020 Web 01-20 PDFDocument320 pagesINT PL 2020 Web 01-20 PDFAndriana Vilijencova100% (1)
- The First-Fourth Books of The HitopadésaDocument116 pagesThe First-Fourth Books of The HitopadésaMiguel RosaNo ratings yet
- Module 14-Area ComputationsDocument5 pagesModule 14-Area ComputationsGerovic Parinas50% (2)
- Basic Program Structure in C++: Study Guide For Module No. 2Document9 pagesBasic Program Structure in C++: Study Guide For Module No. 2Ji YoungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Leukocyte Migration and Inflammation - The IS Relies Upon The Continual Circulation of Leukocytes Through The BodyDocument12 pagesChapter 15 - Leukocyte Migration and Inflammation - The IS Relies Upon The Continual Circulation of Leukocytes Through The BodyEmad ManniNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Grammar Lesson PlanDocument26 pagesAssignment 2 Grammar Lesson PlanKesia Kerspay100% (1)
- HVS Hotel Cost Estimating Guide 2021Document124 pagesHVS Hotel Cost Estimating Guide 2021pascal rosasNo ratings yet
- Can Snails Become Habituated To A StimulusDocument2 pagesCan Snails Become Habituated To A StimulusSachitra Wijethunga100% (1)
- Which Will Weigh The Least Without AnswerDocument7 pagesWhich Will Weigh The Least Without AnswerumeshNo ratings yet
- 2022 Cement Lime Manufacturing Ehs Guidelines enDocument39 pages2022 Cement Lime Manufacturing Ehs Guidelines enSamiNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary Report Julio13Document8 pagesExecutive Summary Report Julio13exxgineNo ratings yet
- Pradeep Kshetrapal - Genius Physics (Class 12) - For IIT-JEE and CBSE 2 - Libgen - LiDocument338 pagesPradeep Kshetrapal - Genius Physics (Class 12) - For IIT-JEE and CBSE 2 - Libgen - Lisujan subediNo ratings yet
- History of Computer ReviewerDocument10 pagesHistory of Computer ReviewerNeil Andrew Aliazas78% (9)
- Communicative English Lab Manual 1643268175Document24 pagesCommunicative English Lab Manual 1643268175Dimple BhatiNo ratings yet
- Evolis User ManualDocument28 pagesEvolis User ManualIonmadalin1000No ratings yet
- ResumeDocument3 pagesResumeSaharsh MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Fuses f150Document7 pagesFuses f150ORLANDONo ratings yet
- Solved Consider Again The Demand Function For Corn in Formula 1Document1 pageSolved Consider Again The Demand Function For Corn in Formula 1M Bilal SaleemNo ratings yet