Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study #3
Uploaded by
James Emman Clemente0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views8 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views8 pagesDrug Study #3
Uploaded by
James Emman ClementeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Pharmacology
Using the Drug Handbook, make a drug study of the different agents affecting the Upper Respiratory System and the Lower Respiratory System.
A. Drugs Affecting Upper Respiratory Tract
Classification Generic Name Pharmacodynamics Indications Nursing Considerations
Decongestants Pseudoephedrine Sympathomimetic Temporary relief of Assessment & Drug Effects
(Sudafed) effects, causes nasal congestions Monitor HR and BP, especially in those with a
vasoconstriction in caused by the history of cardiac disease. Report tachycardia or
Mucous common cold, hay hypertension.
membranes of fever, sinusitis; Patient & Family Education
nasal passages promotion of nasal Avoid taking it within 2 h of bedtime because drug
resulting in their and sinus drainage; may act as a stimulant.
shrinkage, which relief of eustachian Discontinue medication and consult physician if
promotes drainage tube congestion. extreme restlessness or signs of sensitivity occur.
and improvement in Consult physician before concomitant use of OTC
ventilation. medications; many contain ephedrine or other
sympathomimetic amines and might intensify
action of pseudoephedrine.
Do not breast feed while taking this drug without
consulting physician.
Mucolytics Acetylcysteine Splits links in the Mucolytic adjunctive BASELINE ASSESSMENT
(Mucomyst) mucoproteins therapy for Mucolytic: Assess pretreatment respirations for rate,
contained in the abnormal, viscid, or depth, rhythm. IV antidote: Obtain baseline LFT, PT/INR
respiratory mucus inspissated mucous and drug screen. For use as antidote, obtain
secretions, secretions in acute acetaminophen level to determine need for treatment with
decreasing the and chronic acetylcysteine.
viscosity of the bronchopulmonary INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
secretions; protects disorders; to lessen If bronchospasm occurs, discontinue treatment, notify
liver cells from hepatic injury in physician; bronchodilator may be added to therapy.
acetaminophen cases of Monitor rate, depth, rhythm, type of respiration
effects. acetaminophen (abdominal, thoracic). Observe sputum for color,
toxicity. consistency, and amount. IV antidote: Administer within 8
hrs of acetaminophen ingestion for maximal hepatic
protection; ideally, within 4 hrs after immediate-release
and 2 hrs after liquid acetaminophen formulations.
PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
• Slight, disagreeable sulfuric odor from solution may be
noticed during initial administration but disappears quickly.
• Adequate hydration is important part of therapy.
• Follow guidelines for proper coughing and deep
breathing techniques.
• Auscultate lung sounds.
Expectorants Guaifenesin Enhances reflex Guaifenesin is an Assessment & Drug Effects
(Robitussin) outflow of expectorant that is Monitor for therapeutic effectiveness. Persistent
respiratory tract indicated for cough may indicate a serious condition requiring
fluids by irritation of providing temporary further diagnostic work.
gastric mucosa. symptomatic relief Notify physician if high fever, rash, or headaches
Aids in from congested develop.
expectoration by chests and coughs Patient & Family Education
reducing which may be due to Increase fluid intake to help loosen mucus; drink
adhesiveness and a cold, bronchitis, at least 8 glasses of fluid daily.
surface tension of and/or other Contact physician if cough persists beyond 1 wk.
secretions. breathing illnesses. Contact physician if high fever, rash, or headache
develops.
Do not breast feed while taking this drug.
Antihistamines Diphenhydramine Competitively Symptomatic relief of BASELINE ASSESSMENT
(Benadryl) blocks the effects of perennial and If pt is having acute allergic reaction, obtain history of
histamine at seasonal rhinitis, recently ingested foods, drugs, environmental exposure,
histamine-1 vasomotor rhinitis, and emotional stress. Monitor B/P rate; depth, rhythm,
receptor sites; has allergic conjunctivitis, type of respiration; quality, rate of pulse. Assess lung
atropine-like urticaria, and sounds for rhonchi, wheezing, and rales.
antipruritic and angioedema; also INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
sedative effects. used for treating Monitor B/P, esp. in elderly (increased risk of
motion sickness and hypotension). Monitor children closely for paradoxical
parkinsonism and as reaction. Monitor for sedation.
a night time sleep aid PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
and to suppress • Tolerance to antihistaminic effect generally does not
coughs. occur; tolerance to sedative effect may occur.
• Avoid tasks that require alertness, motor skills until
response to drug is established.
• Dry mouth, drowsiness, dizziness may be an expected
response to drug.
• Avoid alcohol.
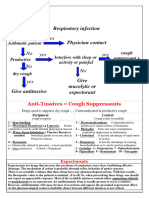
Antitussives Dextromethorpha Depresses the Control of non- Examination and Evaluation
n cough center in the productive cough. Assess frequency and nature of cough, lung
medulla to control Temporarily relieves sounds, and amount and type of sputum
cough spasms. coughing spasm. produced. Document whether this drug is
effective in reducing cough.
Assess dizziness that might affect gait, balance,
and other functional activities. Report balance
problems and functional limitations to the
physician, and caution the patient and
family/caregivers to guard against falls and
trauma.
Patient/Client-Related Instruction
Caution patient to avoid taking more than the
recommended dose or taking alcohol or other
CNS depressants concurrently with this
medication; fatalities have occurred.
Instruct patient to cough effectively: sit upright
and take several deep breaths before attempting
to cough.
Advise patient to minimize cough by avoiding
irritants, such as cigarette smoke, fumes, and
dust. Humidification of environmental air, frequent
sips of water, and sugarless hard candy may also
decrease the frequency of dry, irritating cough.
Advise patient that any cough lasting more than 1
wk or accompanied by fever, chest pain,
persistent headache, or skin rash warrants
medical attention.
Instruct patient or family/caregivers to report other
problematic side effects such as severe or
prolonged nausea or sedation.
B. Drugs Affecting Lower Respiratory Tract
Classification Generic Name Pharmacodynamics Indications Nursing Considerations
Bronchodilators Albuterol Stimulates beta2- Salbutamol is BASELINE ASSESSMENT
Sympathomimetics adrenergic receptors indicated for the Assess lung sounds, pulse, B/P, color,
in lungs, resulting in symptomatic relief characteristics of sputum noted. Offer emotional
relaxation of and prevention of support (high incidence of anxiety due to difficulty
bronchial smooth bronchospasm due to in breathing and sympathomimetic response to
muscle (little effect on bronchial asthma, drug).
HR). chronic bronchitis, INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
Therapeutic Effect: reversible obstructive Monitor rate, depth, rhythm, type of respiration;
Relieves airway disease, and quality and rate of pulse; ECG; serum potassium,
bronchospasm and other chronic glucose; ABG determinations. Assess lung
reduces airway bronchopulmonary sounds
resistance. disorders in which for wheezing (bronchoconstriction), rales.
bronchospasm is a PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
complicating factor, • Follow guidelines for proper use of inhaler.
and/or the acute • A healthcare provider will show you know to
prophylaxis against properly prepare and use your medication. You
exercise-induced must demonstrate correct preparation and
bronchospasm and injection techniques before using medication.
other stimuli known to
induce
bronchospasm.
Bronchodilators Atropine Competitively blocks To decrease Assessment & Drug Effects
Parasympatholytics acetylcholine secretions before Monitor vital signs. HR is a sensitive
muscarinic receptor surgery, treatment of indicator of patient's response to atropine.
sites, blocking the parkinsonism, Be alert to changes in quality, rate, and
effects of the restoration of cardiac rhythm of HR and respiration and to
parasympathetic rate and arterial changes in BP and temperature.
nervous system. pressure following Initial paradoxical bradycardia following IV
vagal stimulation, atropine usually lasts only 1–2 min; it
relief of bradycardia most likely occurs when IV is
and syncope due to administered slowly (more than 1 min) or
hyperactive carotid when small doses (less than 0.5 mg) are
sinus reflex, relief of used. Postural hypotension occurs when
pylorospasm, patient ambulates too soon after
relaxation of the parenteral administration.
spasm of biliary and Patient & Family Education
ureteral colic and Follow measures to relieve dry mouth:
bronchospasm, adequate hydration; small, frequent
control of crying and mouth rinses with tepid water; meticulous
laughing episodes mouth and dental hygiene; gum chewing
associated with brain or sucking sugarless sourballs.
lesions, relaxation of Note: Drug causes drowsiness, sensitivity
uterine hypertonicity, to light, blurring of near vision, and
management of temporarily impairs ability to judge
peptic ulcer, control of distance. Avoid driving and other activities
rhinorrhea associated requiring visual acuity and mental
with hay fever, alertness.
antidote for Discontinue ophthalmic preparations and
cholinergic overdose, notify physician if eye pain, conjunctivitis,
and poisoning from palpitation, rapid pulse, or dizziness
various mushrooms. occurs.
Do not breast feed while taking this drug
without consulting physician.
Bronchodilators Theophylline Directly relaxes Symptomatic relief or Assessment & Drug Effects
Methylxanthines
bronchial smooth prevention of Monitor vital signs. Improvement in
muscle, causing bronchial asthma and respiratory status is the expected
bronchodilation and reversible outcome.
increasing vital bronchospasm Observe and report early signs of
capacity; also associated with possible toxicity: Anorexia, nausea,
increases force of chronic bronchitis and vomiting, dizziness, shakiness,
diaphragmatic emphysema. restlessness, abdominal discomfort,
muscle. irritability, palpitation, tachycardia, marked
hypotension, cardiac arrhythmias,
seizures.
Monitor for tachycardia, which may be
worse in patients with severe cardiac
disease. Conversely, theophylline toxicity
may be masked in patients with
tachycardia.
Patient & Family Education
Take medication at the same time every
day.
Avoid charcoal-broiled foods (high in
polycyclic carbon content); may increase
theophylline elimination and reduce the
half-life as much as 50%.
Limit caffeine intake because it may
increase incidence of adverse effects.
Cigarette smoking may significantly lower
theophylline plasma concentration.
Corticosteroids Prednisone Inhibits accumulation Prednisone is BASELINE ASSESSMENT
of inflammatory cells indicated as an anti- Question medical history as listed in Precautions.
at inflammation sites, inflammatory or Obtain baselines for height, weight, B/P, serum
phagocytosis, immunosuppressive glucose, electrolytes. Check results of initial tests
lysosomal enzyme drug for allergic, (tuberculosis [TB] skin test, X-rays, ECG).
release/synthesis, dermatologic, INTERVENTION/EVALUATION
release of mediators gastrointestinal, Monitor B/P, serum electrolytes, glucose, results
of inflammation. hematologic, of bone mineral density test, height, weight in
Therapeutic Effect: ophthalmologic, children. Be alert to infection (sore throat, fever,
Prevents/suppresses nervous system, vague symptoms); assess oral cavity daily for
cell-mediated renal, respiratory, signs of Candida infection. Monitor for symptoms
immune reactions. rheumatologic, of adrenal insufficiency, immunosuppression.
Decreases/prevents infectious, endocrine, PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
tissue response to or neoplastic • Report fever, sore throat, muscle aches, sudden
inflammatory conditions as well as weight gain, swelling, loss of appetite, or fatigue.
process. in organ transplant. • Avoid alcohol, minimize use of caffeine.
• Report symptoms of elevated blood sugar levels
Mast Cell Cromolyn Synthetic asthma- For the management Assessment & Drug Effects
Stabilizer Sodium prophylactic agent of patients with Withhold drug and notify physician if any
with unique action. bronchial asthma. of the following occur; angioedema or
Inhibits release of Also used in the bronchospasm.
bronchoconstrictors— treatment of vernal Monitor for exacerbation of asthmatic
histamine and SRS-A keratoconjunctivitis, symptoms including breathlessness and
(slow-reacting vernal conjunctivitis, cough that may occur in patients
substance of and vernal keratitis. receiving cromolyn during corticosteroid
anaphylaxis) from withdrawal.
sensitized pulmonary For patients with asthma, therapeutic
mast cells, thereby effects may be noted within a few days
suppressing an but generally not until after 1–2 wk of
allergic response. therapy.
Has no intrinsic Patient & Family Education
bronchodilator, Throat irritation, cough, and hoarseness
antihistaminic, or can be minimized by gargling with water,
vasoconstrictor drinking a few swallows of water, or by
properties, thus only sucking on a lozenge after each
of value when taken treatment.
prophylactically. Talk to your physician about what to do in
the event of an acute asthmatic attack.
Cromolyn is of no value in acute asthma.
Cromolyn does not eliminate the
continued need for therapy with
bronchodilators, expectorants, antibiotics,
or corticosteroids, but the amount and
frequency of use of these medications
may be appreciably reduced.
You might also like
- Local Anesthesia Made Easy: Complete Guide on How to make your Local Anesthetic Procedure a Success (Including a List of Anesthetic Equipment and their Uses)From EverandLocal Anesthesia Made Easy: Complete Guide on How to make your Local Anesthetic Procedure a Success (Including a List of Anesthetic Equipment and their Uses)No ratings yet
- Differentiating Anesthesia Equipment: Identify and Understand Anesthesia Equipment in 1 Hour (Including the most popular manufacturers and suppliers to buy Anesthesia Equipment)From EverandDifferentiating Anesthesia Equipment: Identify and Understand Anesthesia Equipment in 1 Hour (Including the most popular manufacturers and suppliers to buy Anesthesia Equipment)No ratings yet
- AtroventDocument2 pagesAtroventKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Drug Action and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument38 pagesDrug Action and Nursing ResponsibilitiesSnehal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DrugDocument5 pagesDrug Study Drugjl frusaNo ratings yet
- Flovent (Fluticasone)Document3 pagesFlovent (Fluticasone)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Agents: Dextromethorphan, Diphenhydramine, Guaifenesin, Albuterol, and BudesonideDocument30 pagesRespiratory Agents: Dextromethorphan, Diphenhydramine, Guaifenesin, Albuterol, and BudesonideLindy JaneNo ratings yet
- NURS 2516 Clinical Medications Worksheets: Nursing Process-AssessmentDocument1 pageNURS 2516 Clinical Medications Worksheets: Nursing Process-AssessmentAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Guaifenesin Elixir PACKAGE INSERTDocument5 pagesGuaifenesin Elixir PACKAGE INSERTEllie Marie RoyalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For Postpartum MothersDocument5 pagesDrug Study For Postpartum MothersnnicakoNo ratings yet
- DilaudidDocument2 pagesDilaudidAdrianne Bazo100% (2)
- Respiratory Drugs GuideDocument56 pagesRespiratory Drugs GuideIra G. Delos Santos100% (1)
- Pharmacology PDFDocument20 pagesPharmacology PDFMichelle SatairapanNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - CopdDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY - CopdMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- Ipratroprium Drug CardDocument3 pagesIpratroprium Drug CardXiaoDuckyNo ratings yet
- New Singulair MontelukastDocument1 pageNew Singulair MontelukastCassie100% (2)
- Atrovent (Ipratropium)Document1 pageAtrovent (Ipratropium)E100% (2)
- SinacDocument2 pagesSinacENo ratings yet
- Albuterol SalbutamolDocument2 pagesAlbuterol SalbutamolPePpER29No ratings yet
- Respiratory DrugsDocument19 pagesRespiratory DrugsBryan MedranoNo ratings yet
- AtroventDocument1 pageAtroventSheri490100% (1)
- AlbuterolDocument1 pageAlbuterolCassieNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Drugs GuideDocument56 pagesRespiratory Drugs GuideShang MacarayonNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Review For FinalsDocument9 pagesPharmacology Review For FinalsJaya ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology HandoutsDocument9 pagesNursing Pharmacology HandoutsVince LeonidaNo ratings yet
- Vicodin Drug Study Que Fransis A.Document3 pagesVicodin Drug Study Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsDocument1 pageNURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsCassieNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology EssentialsDocument13 pagesNursing Pharmacology EssentialsMajestic RavenNo ratings yet
- Drug Benzocaine LozengeDocument1 pageDrug Benzocaine LozengeSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Module 14 - Drugs-affecting-the-Respiratory-System-3Document48 pagesModule 14 - Drugs-affecting-the-Respiratory-System-3weissNo ratings yet
- Albuterol InhailerDocument1 pageAlbuterol InhailerAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Ineffective Breathing PatternDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary System Comprehensive Examination Answers and RationalesDocument4 pagesPulmonary System Comprehensive Examination Answers and RationalesNursyNurseNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TheophyllineDocument1 pageDrug Study Theophyllinevaldez.adler.lNo ratings yet
- Levalbuterol XopenexDocument2 pagesLevalbuterol XopenexCassie100% (1)
- انواع السعال واختيار الدواء المناسبDocument3 pagesانواع السعال واختيار الدواء المناسبOmer AlsameiNo ratings yet
- Restoring Fluid Balance Through RehydrationDocument11 pagesRestoring Fluid Balance Through RehydrationMicah MagallanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology HandoutsDocument10 pagesNursing Pharmacology HandoutsMICHAELA TIMBOLNo ratings yet
- Viii. Medications: Generic Name: Actions: AssessmentDocument4 pagesViii. Medications: Generic Name: Actions: AssessmentJohn Alex Maramba MelencioNo ratings yet
- Morphine (Astramorph) PCADocument2 pagesMorphine (Astramorph) PCAAdrianne Bazo100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyZek Comidoy100% (1)
- Pines City Colleges Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPines City Colleges Drug StudyShannon CabfitNo ratings yet
- Antihistamine BlockersDocument12 pagesAntihistamine Blockersyra capiliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology HandoutsDocument8 pagesNursing Pharmacology HandoutsDexie MaeNo ratings yet
- EpinephrineDocument1 pageEpinephrineRaymundo MalijanNo ratings yet
- OxycodoneDocument2 pagesOxycodoneENo ratings yet
- Nalbuphine (Nubain)Document2 pagesNalbuphine (Nubain)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- TramadolDocument7 pagesTramadolFlauros Ryu JabienNo ratings yet
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- NCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!From EverandNCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Yunnan Baiyao Guide: Yunnan Baiyao Stops Bleeding, Relieves Pain, Improves Blood Flow, Treats Cancer in Dogs and Other AilmentsFrom EverandYunnan Baiyao Guide: Yunnan Baiyao Stops Bleeding, Relieves Pain, Improves Blood Flow, Treats Cancer in Dogs and Other AilmentsNo ratings yet
- Alternative and Non-Prescription Medicines: A Practical GuideFrom EverandAlternative and Non-Prescription Medicines: A Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- The Essential Guide to Cephalexin: Usage, Precautions, Interactions and Side Effects.From EverandThe Essential Guide to Cephalexin: Usage, Precautions, Interactions and Side Effects.No ratings yet
- Drug Study #2Document47 pagesDrug Study #2James Emman ClementeNo ratings yet
- Drugs PharmaDocument5 pagesDrugs PharmaJames Emman ClementeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Agents Used Thyroid and Glucose Metabolism - ClementeDocument18 pagesDrug Study On Agents Used Thyroid and Glucose Metabolism - ClementeJames Emman ClementeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CNS StimulantsDocument10 pagesDrug Study CNS StimulantsJames Emman ClementeNo ratings yet
- Acid-Fast StainingDocument2 pagesAcid-Fast StainingJames Emman ClementeNo ratings yet
- Dengue (Lab Report)Document3 pagesDengue (Lab Report)James Emman ClementeNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument1 pageCarbohydratesJames Emman ClementeNo ratings yet
- Heal Yourself NaturallyDocument204 pagesHeal Yourself NaturallyKanjaFit100% (8)
- Helminths Questions: Jenna KellyDocument21 pagesHelminths Questions: Jenna Kellylouie john abilaNo ratings yet
- NeutrophiliaDocument10 pagesNeutrophiliamaria martinezNo ratings yet
- Choose The Correct Answer For Questions (1 - 90)Document12 pagesChoose The Correct Answer For Questions (1 - 90)حمزة الفنيني100% (3)
- False Localising SignsDocument46 pagesFalse Localising SignsVarun B RenukappaNo ratings yet
- 2022 Masingue P.Latour Rev Neurol Genetic Analysis in HereditaryDocument20 pages2022 Masingue P.Latour Rev Neurol Genetic Analysis in HereditaryLéo VidoniNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure (Congestive Heart Failure) FINALDocument6 pagesHeart Failure (Congestive Heart Failure) FINALKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- Medical History TemplateDocument4 pagesMedical History TemplateBrijesh KukretiNo ratings yet
- Magnesium sulfate medicationDocument2 pagesMagnesium sulfate medicationAndrea ANo ratings yet
- Standardized Lumbar Puncture ProcedureDocument5 pagesStandardized Lumbar Puncture ProcedureAgeng RestiNo ratings yet
- The Orthopedic History and Physical Exam GuideDocument28 pagesThe Orthopedic History and Physical Exam GuideAgriya Shresth100% (1)
- 11.0 Pediatrics Flashcards Oct 2023Document13 pages11.0 Pediatrics Flashcards Oct 2023Shane Laika Bay DugayNo ratings yet
- CDM CasesDocument24 pagesCDM CasesmalcomxNo ratings yet
- Pterygium - EyeWikiDocument1 pagePterygium - EyeWikiPaudel SujanNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument19 pagesCase Study: Acute GlomerulonephritisKuruma Maricar SorianoNo ratings yet
- Virology Compilation For Final Exam GuideDocument51 pagesVirology Compilation For Final Exam GuideJenny Rose PangdaoNo ratings yet
- Wawa - Sistem Saraf PusatDocument38 pagesWawa - Sistem Saraf PusatnuhaNo ratings yet
- Examining A Case: Carbamazepine-Triggered Drug Reaction With Eosinophilia and Systemic SymptomsDocument2 pagesExamining A Case: Carbamazepine-Triggered Drug Reaction With Eosinophilia and Systemic SymptomsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Tatsumi 1997Document9 pagesTatsumi 1997dad dzd adaNo ratings yet
- Role of Jalauka in Diabetic Foot UlcerDocument12 pagesRole of Jalauka in Diabetic Foot UlcerMinakshi Gulshan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Filariasis Parasite Infection and TransmissionDocument60 pagesFilariasis Parasite Infection and TransmissionDanielle Pecson100% (1)
- Gingival Tissue Management Methods for Dental RestorationsDocument20 pagesGingival Tissue Management Methods for Dental RestorationsSriram PugalenthiNo ratings yet
- Entamoeba histolytica Causes AmoebiasisDocument46 pagesEntamoeba histolytica Causes AmoebiasisAlfia Nikmah100% (3)
- MR Dokter Sang (Appendiks & CKR)Document15 pagesMR Dokter Sang (Appendiks & CKR)AgungKezumaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument42 pagesEndocrine System Multiple Choice QuestionswanderagroNo ratings yet
- Mortality Report April 25th 2019Document12 pagesMortality Report April 25th 2019ramotNo ratings yet
- The Original Prevention of Sickness PamphletDocument88 pagesThe Original Prevention of Sickness PamphletGeorge Singleton100% (4)
- 2016 Brain Bee Competitions Questions - DoDocument10 pages2016 Brain Bee Competitions Questions - DoughNo ratings yet
- Ackerman - Histologic Diagnosis of Inflammatoy Skin Diseases - Third EditionDocument2,066 pagesAckerman - Histologic Diagnosis of Inflammatoy Skin Diseases - Third EditionSamanthaNo ratings yet
- AlzheimersDocument6 pagesAlzheimersAlfred DizonNo ratings yet