Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Chemistry II Equation Sheet
Uploaded by
adilb24032000Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Chemistry II Equation Sheet
Uploaded by
adilb24032000Copyright:
Available Formats
General Chemistry II Equation Sheet
Think about how to set up the problem first, then apply the needed principles and formulas.
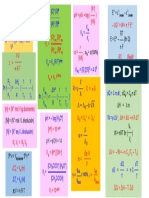
Phase Changes Acids and Bases
∆Tb = iKb m Kw = [H3 O+ ][OH − ] = Ka × Kb
∆Tf = iKf m pOH = − log[OH − ]
π = iM RT [OH − ] = 10−pOH
c = kP pH + pOH = pKa + pKb = 14.00 (at 25◦ C)
c1 c2 [A− ]
p1 = p2 pH = pKa + log [HA]
◦ [BH + ]
Psolution = χsolvent Psolvent pOH = pKb + log [B]
◦ ◦ [H3 O+ ]eq
∆P = Psolvent − Psolution = χsolute Psolvent % ionization [HA]0
× 100%
pKa = − log(Ka )
Cells pKb = − log(Kb )
E = E◦ − RT
nF ln(Q) Ka = 10−pKa
E = E◦ − 0.0592
n log(Q) (at 25◦ C) Kb = 10−pKb
∆G = −nF Ecell
∆G◦ = −nF Ecell
◦ Equilibria
◦ = RT [C]c [D]d
Ecell nF ln(K) Qc = [A]a [B]b
◦ = [C]c [D]d
Ecell 0.0592V
n log(K) (at 25◦ C) Kc = [A]a [B]b
d
PD ·PCc
USE ONE: Qp = PA ·PBb
a
d
◦ = E◦ ◦ PD ·PCc
Ecell cathode(red.) − Eanode(red.) Kp = PA ·PBb
a
◦ = E◦
Ecell ◦ Kp = Kc [R × T ]∆n
cathode(red.) + Eanode(ox.)
∆G = ∆G◦ + RT ln(Q)
Thermodynamics ∆G◦ = −RT ln(K)
∆G = ∆H − T ∆S rate = k[A]x [B]y
−∆Hsys Ea
∆Ssurr = T k = Ae− RT
∆Suniv = ∆Ssys + ∆Ssurr ln( kk21 ) = Ea 1
R ( T2 − 1
T1 )
◦ ◦ ◦ ln(2)
∆Srxn = ΣSproducts + ΣSreactants half life = k (1st order reactions only)
∆G◦rxn = Σ∆G◦products + Σ∆G◦reactants [A]t = −kt + [A]o
ln([A]t ) = −kt + ln([A]o )
1 1
Concentrations [A]t
= kt + [A]o
molessolute
molality = mass
solvent(kg)
molessolute
% by mass = masssolute +masssolvent × 100%
molessolute 6
parts per million = masssolute +masssolvent × 10
molessolute 9
parts per billion = masssolute +masssolvent × 10
Burdge, J., & Overby, J. (2018). Chemistry: Atoms First. McGraw-Hill Education.
You might also like
- Chemistry Cheat Sheet-1Document1 pageChemistry Cheat Sheet-1r3birthvalNo ratings yet
- Exam3 EquationsheetDocument1 pageExam3 EquationsheetNguyễn Minh AnhNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Equilibria FormulasDocument1 pageThermodynamics and Equilibria FormulasKitkatNo ratings yet
- UIL Chemistry Reference Materials: 1 EquationsDocument2 pagesUIL Chemistry Reference Materials: 1 EquationsAnonymous BsqwX1jsNo ratings yet
- Fórmulas QuímicaDocument1 pageFórmulas Químicaalvarokiller2.0No ratings yet
- 5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics: Mit OpencoursewareDocument7 pages5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics: Mit OpencoursewarecaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium in Ideal Gas MixturesDocument6 pagesChemical Equilibrium in Ideal Gas MixturesMia Nur AliaNo ratings yet
- C Sol Ch-06 EquilibriumDocument10 pagesC Sol Ch-06 Equilibriummysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- R 0.08206 L Atm Mol: Constants and FormulaeDocument1 pageR 0.08206 L Atm Mol: Constants and FormulaeKevin DziubaNo ratings yet
- CH E 441 Ex1 Spring 05Document6 pagesCH E 441 Ex1 Spring 05Jhon Barzola PalominoNo ratings yet
- PV=nRT equation and acid-base equilibrium expressionsDocument1 pagePV=nRT equation and acid-base equilibrium expressionsDaniel FeymanNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Equations, Constants and TablesDocument4 pagesFinal Exam Equations, Constants and Tablessammy alanNo ratings yet
- Practice Final ExamDocument18 pagesPractice Final ExamAttri BezbaruahNo ratings yet
- Rumus Dan Persamaan Yang Dapat Digunakan (Soal Farmakokinetika)Document1 pageRumus Dan Persamaan Yang Dapat Digunakan (Soal Farmakokinetika)asriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9. Kinetics: Rates of Chemical ReactionsDocument11 pagesChapter 9. Kinetics: Rates of Chemical ReactionsAtiya SultanaNo ratings yet
- Useful chemistry and physics formulasDocument1 pageUseful chemistry and physics formulasJemarey de RamaNo ratings yet
- KP Expressions for Chemical EquilibriaDocument2 pagesKP Expressions for Chemical Equilibriacessarine relevoNo ratings yet
- 5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics: Mit OpencoursewareDocument7 pages5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics: Mit OpencoursewarecaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Kinetics and reaction ratesDocument6 pagesKinetics and reaction ratesArasuNo ratings yet
- Elementary Reaction SolutionDocument10 pagesElementary Reaction SolutionJocelyn Grisel García GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 38Document5 pagesLecture 38Hagere EthiopiaNo ratings yet
- Formulae and Periodic TableDocument2 pagesFormulae and Periodic TableVal Thi VanNo ratings yet
- Chem EquiDocument8 pagesChem EquiJeremy CNo ratings yet
- Kinetika Kimia s1Document28 pagesKinetika Kimia s1Umiia RuhunussaNo ratings yet
- CHM1311A - Gas Laws, Thermochemistry, Kinetics, Equilibria DataDocument4 pagesCHM1311A - Gas Laws, Thermochemistry, Kinetics, Equilibria DataAhhhhhhhhhhhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Energy Balance: I Ki PiDocument13 pagesChapter 4: Energy Balance: I Ki PiAhmed Qutb AkmalNo ratings yet
- ch15 PDFDocument29 pagesch15 PDFHafidz RafiqiNo ratings yet
- T T W Q Q W T T SA W Flux T T W Flux T T J J CM: Carnot Efficiency 1 T TDocument7 pagesT T W Q Q W T T SA W Flux T T W Flux T T J J CM: Carnot Efficiency 1 T TJowel MercadoNo ratings yet
- ApformdataDocument2 pagesApformdataspatters123No ratings yet
- Equilibrium, Acids & BasesDocument14 pagesEquilibrium, Acids & BaseswildplayersgamingNo ratings yet
- Constants and Key Equations in Chemicall ReactionDocument5 pagesConstants and Key Equations in Chemicall ReactionFrancisca BrazNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 FormulaDocument4 pagesExam 2 FormulaRishabh NayakNo ratings yet
- Inter:: nf n ± V ε n n n f n n n y=Ca Ca y= Ca Ca y= Ca CaDocument1 pageInter:: nf n ± V ε n n n f n n n y=Ca Ca y= Ca Ca y= Ca Casergio rodriguezNo ratings yet
- 5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics: Mit OpencoursewareDocument7 pages5.60 Thermodynamics & Kinetics: Mit OpencoursewarecaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Decrease volume or increase pressure rightDocument29 pagesDecrease volume or increase pressure righthertianaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium: 2.1. Some DefinitionsDocument24 pagesChemical Equilibrium: 2.1. Some DefinitionsNguyễn Quốc HưngNo ratings yet
- CM150-2 Exercise 3 (MODULE 3)Document6 pagesCM150-2 Exercise 3 (MODULE 3)owl lawletNo ratings yet
- 6.0 Chemical EquilibriumDocument105 pages6.0 Chemical EquilibriumTasya KassimNo ratings yet
- Chem 1220 Assignment 1Document2 pagesChem 1220 Assignment 1KathiNo ratings yet
- Q02-Chem - 1023 - Final - ExamDocument5 pagesQ02-Chem - 1023 - Final - ExamRodríguez Rito AméricaNo ratings yet
- SÍMBOLOS A UTILIZAR TRANSFERENCIA DE CALOR Y MECÁNICA DE FLUIDOSDocument60 pagesSÍMBOLOS A UTILIZAR TRANSFERENCIA DE CALOR Y MECÁNICA DE FLUIDOSAlonso GalvisNo ratings yet
- 6.2 Equilibrium Constants 1718Document28 pages6.2 Equilibrium Constants 1718Ainaa NajwaaNo ratings yet
- Understanding jet engine thermodynamicsDocument7 pagesUnderstanding jet engine thermodynamicsChafey MuNo ratings yet
- ZnCl2 production kinetics and mass balanceDocument4 pagesZnCl2 production kinetics and mass balanceYoe CavanaNo ratings yet
- Test-Ii Chemistry: Part-I Section-I Single Correct Choice Type 1. (D)Document19 pagesTest-Ii Chemistry: Part-I Section-I Single Correct Choice Type 1. (D)pro7No ratings yet
- Neraca Massa Energi Reaktor SlakerDocument9 pagesNeraca Massa Energi Reaktor Slakeroshin sinar hati siahaanNo ratings yet
- Second Semester Stage 2Document99 pagesSecond Semester Stage 2Watch DogsNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet - Quiz 1Document1 pageData Sheet - Quiz 1Dylan HamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium Part III-1 PDFDocument6 pagesChemical Equilibrium Part III-1 PDFEstivenson Vasquez CNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics (CHE 303) : Kfupm - Edu.saDocument95 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics (CHE 303) : Kfupm - Edu.sai 3l3jNo ratings yet
- Draft Equations File For 2020Document6 pagesDraft Equations File For 2020Subhajit MondalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Chemical EquilibriumDocument74 pagesChapter 6 Chemical Equilibriumnoor syahirahNo ratings yet
- Calculations in Advanced Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesCalculations in Advanced Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicsJohnNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic equations and state modelsDocument3 pagesThermodynamic equations and state modelsKeith Danae SuquibNo ratings yet
- 2-1 Chemical Equilibrium 2-09-2019Document114 pages2-1 Chemical Equilibrium 2-09-2019carlos lara rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document9 pagesTask 1Julius CagampangNo ratings yet
- original (2)Document4 pagesoriginal (2)yigaf49105No ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium ConstantsDocument81 pagesChemical Equilibrium ConstantsPHƯƠNG ĐẶNG YẾNNo ratings yet
- Lec 5chemical EquilibriumDocument25 pagesLec 5chemical Equilibriuma.alsayed6805No ratings yet
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Membrane Separation ProcessesDocument14 pagesMembrane Separation ProcessesPRAJWAL RASTOGINo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 Chem 140Document3 pagesExperiment 6 Chem 140Clandy CoNo ratings yet
- E 1452 - 92 Standard Practice For Preparation of Calibration Solutions For Spectrophotometric and For Spectroscopic Atomic Analysis PDFDocument3 pagesE 1452 - 92 Standard Practice For Preparation of Calibration Solutions For Spectrophotometric and For Spectroscopic Atomic Analysis PDFBryanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analytical Chemistry and Its Importance of Pharmaceutical FieldDocument9 pagesQuantitative Analytical Chemistry and Its Importance of Pharmaceutical Fieldcyper zoonNo ratings yet
- Column ChromatographyDocument2 pagesColumn ChromatographymaggumsxNo ratings yet
- Silicycle Sample Preparation BrochureDocument64 pagesSilicycle Sample Preparation BrochurennNo ratings yet
- TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE OF THE PHILIPPINES ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY PROBLEM SETDocument1 pageTECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE OF THE PHILIPPINES ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY PROBLEM SETKaizerNo ratings yet
- Aspen Separation Unit-OpsDocument25 pagesAspen Separation Unit-Opsedwin dableoNo ratings yet
- Quality Controlof Herbs Determinationof Amino Acidsin Althaea Matricariaand TaraxacumDocument5 pagesQuality Controlof Herbs Determinationof Amino Acidsin Althaea Matricariaand TaraxacumMuraleetharan_BNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases, Buffers & Salts ExplainedDocument26 pagesAcids, Bases, Buffers & Salts ExplainedHossiana J MoNo ratings yet
- 3 - Modified Buffers Biochem Lab 1 With WorksheetDocument4 pages3 - Modified Buffers Biochem Lab 1 With WorksheetkatherinecalmaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies: HPLC Method For SimultaneousDocument10 pagesJournal of Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies: HPLC Method For SimultaneousJosé Carlos Solís SuárezNo ratings yet
- Zetasizer Pro and Zetasizer Ultra: Advance With ConfidenceDocument20 pagesZetasizer Pro and Zetasizer Ultra: Advance With ConfidencesannintkdNo ratings yet
- Nickel Experiment XWDocument4 pagesNickel Experiment XWKhairul Anwar Abd HamidNo ratings yet
- Ultracentrifuge - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesUltracentrifuge - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShailendra YadavNo ratings yet
- MSC ChemistryDocument54 pagesMSC ChemistryShivam Vinoth100% (1)
- Solvent ExtractionDocument12 pagesSolvent Extractionalihus9598No ratings yet
- Determination of Total, Temporary and Permanent Hardness in Water Sample Using EDTA MethodDocument8 pagesDetermination of Total, Temporary and Permanent Hardness in Water Sample Using EDTA MethodNaresh kumarNo ratings yet
- Chap 04 Acids and BasesDocument22 pagesChap 04 Acids and BasesavNo ratings yet
- Chem 28 SyllabusDocument11 pagesChem 28 SyllabusDianne TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Chem Assignment Notes 1Document8 pagesGrade 10 Chem Assignment Notes 1habiba buttNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry and Its Branches - Print - QuizizzDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry and Its Branches - Print - QuizizzandieNo ratings yet
- Articulo MentolDocument4 pagesArticulo Mentoljuan_k5950No ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Common Ion Effect and Buffers: Answers To QuestionsDocument3 pagesExperiment 4 Common Ion Effect and Buffers: Answers To QuestionsCamille GrefaldiaNo ratings yet
- Che 152. Separation Processes Handout 1.1. Countercurrent Multistage Distillation With Reflux: Ponchon-Savarit Method Multiple Equilibrium StagesDocument11 pagesChe 152. Separation Processes Handout 1.1. Countercurrent Multistage Distillation With Reflux: Ponchon-Savarit Method Multiple Equilibrium StagesBor OtNo ratings yet
- New India Assurance Co. Ltd. and other company contactsDocument2,539 pagesNew India Assurance Co. Ltd. and other company contactsShreyas07100% (2)
- Batch and continuous distillation column typesDocument6 pagesBatch and continuous distillation column typesOmer IbrahimNo ratings yet
- ANJAC Science Instrumentation Centre ChargesDocument4 pagesANJAC Science Instrumentation Centre Charges16 Malola KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Liquid Chromatography - Normal Phase: P Jandera, Univerzita Pardubice, Pardubice, Czech RepublicDocument12 pagesLiquid Chromatography - Normal Phase: P Jandera, Univerzita Pardubice, Pardubice, Czech RepublicEuderDiasNo ratings yet
- Asid, Bes Dan GaramDocument6 pagesAsid, Bes Dan GaramTENGKU AHMAD NAQIUDDIN BIN TENGKU NADZUAN MoeNo ratings yet