Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Keraangka English
Uploaded by
Rifqi Aulia DestiansyahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Keraangka English
Uploaded by
Rifqi Aulia DestiansyahCopyright:
Available Formats
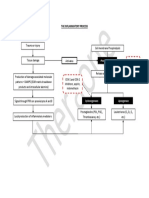
Primary injury (Acute compression)
ACTH4-10
Administration
Acute phase Vascular damage
Ion imbalance
Accumulation of
neurotransmitters
Free radical formation
Lipid peroxidation
Inflammatory
Edema
Cell death (Necrosis)
Excess levels of Damage to phospholipid
Ca2+ in cell membranes
mitochondria NADPH oxidase via
electron transport chain
Formation Formation of free Formation of esterified
superoxide arachhidonic acid arachhidonic acid
COX-1, COX-2
Lipid
peroxidation
Prostalglandin G2 Hydrolysis
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
Secondary Injuries
PG endoperoxide
+ OH+ synthase
15(S)-PGF2a
Unsaturated lipid radical Prostalglandin H2
Lipid hydroperoxides
15(S)-8-iso-
Peroxylradicals Thromboxane PGF2a
(F2 isoprostan)
Malondialdehyde PGE2
PGF2a
PGD2
4-hydroxyl-2-nonenal
Subacute Cell death (Apoptosis)
phase Demyelination of axons
Wallerian degeneration
Axonal dieback
Matrix remodeling
Evolution of glial scar cells
Chronic Formation of cystic cavity
phase Progressive axonal dieback
Maturation of glial scar cells
You might also like
- Jigs and FixturesDocument85 pagesJigs and FixturesMudassar KhanNo ratings yet
- Weekly Training Schedule - Samples: Warmup SMR (Foam Roll, LAX Ball,) 5-10 Rolls or 30sec EachDocument6 pagesWeekly Training Schedule - Samples: Warmup SMR (Foam Roll, LAX Ball,) 5-10 Rolls or 30sec Eachogalloza100% (2)
- List of AbbreviationsDocument3 pagesList of Abbreviationsjuwita latiefahNo ratings yet
- ICU One Pager Lactic AcidosisDocument1 pageICU One Pager Lactic AcidosisNicholas Helmstetter100% (1)
- 12 Week Fat Destroyer - Complete Fat Loss Workout & Diet Program - Muscle & StrengthDocument19 pages12 Week Fat Destroyer - Complete Fat Loss Workout & Diet Program - Muscle & StrengthAli100% (1)
- 18 - Lipid MetabolismDocument26 pages18 - Lipid Metabolismcheckmate100% (1)
- The Hidden Power of Siu Nim TauDocument6 pagesThe Hidden Power of Siu Nim TauLucianLukas100% (5)
- Operation and Maintenance Manual For Urban Water Utilities PDFDocument182 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual For Urban Water Utilities PDFKrischaEverNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual Professional: Digital Control Unit Cem7Document98 pagesInstruction Manual Professional: Digital Control Unit Cem7sonnguyen273100% (1)
- Trypanosomiasis & LeishmaniasisDocument50 pagesTrypanosomiasis & LeishmaniasisMardoni Efrijon75% (4)
- Biomaterials Based Sensors Recent Advances and ApplicationsDocument416 pagesBiomaterials Based Sensors Recent Advances and Applicationshenry.a.peraltaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineers Licensure Examination Results Released in Four (4) Working DaysDocument41 pagesElectrical Engineers Licensure Examination Results Released in Four (4) Working DaysRapplerNo ratings yet
- HIE PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHIE PathophysiologyRNo ratings yet
- Draft Kerangka Teori 30 Juli 2018 - Rev2Document3 pagesDraft Kerangka Teori 30 Juli 2018 - Rev2debby nirmasariNo ratings yet
- Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle: DR Imran SiddiquiDocument10 pagesTricarboxylic Acid Cycle: DR Imran Siddiquiapi-19824406No ratings yet
- MicroBio Lec Transes 8 9Document7 pagesMicroBio Lec Transes 8 9Kai BarsanaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Effect of NSAIDs and Antiemetics OnlyDocument26 pagesSystemic Effect of NSAIDs and Antiemetics OnlyNicco MarantsonNo ratings yet
- Review Article Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Lipid Peroxidation in Apoptosis, Autophagy, and FerroptosisDocument14 pagesReview Article Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Lipid Peroxidation in Apoptosis, Autophagy, and FerroptosislakjdlkaNo ratings yet
- ASB0204 Chap 7 - CidDocument42 pagesASB0204 Chap 7 - CidZulhelmiNo ratings yet
- Asgn 1Document3 pagesAsgn 1PARVATHY ANILNo ratings yet
- Parkinsons SinalizaçãoDocument2 pagesParkinsons SinalizaçãotamaraNo ratings yet
- HO 14 Krebs CycleDocument8 pagesHO 14 Krebs CycleNo RefundNo ratings yet
- PhotobioreactorsDocument15 pagesPhotobioreactorsSir TemplarNo ratings yet
- Ciclo de Krebs Cadena Respiratoria Fosforilación OxidativaDocument47 pagesCiclo de Krebs Cadena Respiratoria Fosforilación OxidativaMARIA FERNANDA MORALES MURUETANo ratings yet
- 2 GlycolysisDocument43 pages2 GlycolysisAbdul RaufNo ratings yet
- 5BBB0223 Metabolic Integration PSW1 ExplanationDocument25 pages5BBB0223 Metabolic Integration PSW1 ExplanationW BNo ratings yet
- Riboflavina Mecanismo LehningerDocument2 pagesRiboflavina Mecanismo LehningerkpsantanaNo ratings yet
- The Inflammatory Process: Phospholipase ADocument1 pageThe Inflammatory Process: Phospholipase ACharles Jebb Belonio JuanitasNo ratings yet
- A14 Respiration in PlantDocument1 pageA14 Respiration in PlantBhaskar WakadeNo ratings yet
- Note 26 Jan 2024Document17 pagesNote 26 Jan 2024hs87s6smtnNo ratings yet
- Biochem Vitamins MineralsabsbbzDocument9 pagesBiochem Vitamins MineralsabsbbzYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step 1 First Aid 2021-101-230Document130 pagesUSMLE Step 1 First Aid 2021-101-230mariana yllanesNo ratings yet
- Pharmacodynamic-Kinetic Drugs LeukemiaDocument71 pagesPharmacodynamic-Kinetic Drugs LeukemiaLulu Windra FerdinaNo ratings yet
- Review Article: The Sources of Reactive Oxygen Species and Its Possible Role in The Pathogenesis of Parkinson's DiseaseDocument10 pagesReview Article: The Sources of Reactive Oxygen Species and Its Possible Role in The Pathogenesis of Parkinson's DiseaselathifatulNo ratings yet
- Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras PCP and HallucinogensDocument36 pagesPsych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras PCP and Hallucinogensgigidurul1111No ratings yet
- Metabolic Acidosis - Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders - Merck Manuals Professional EditionDocument2 pagesMetabolic Acidosis - Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders - Merck Manuals Professional Editionmaulidanabilah5No ratings yet
- KEMU Guide by Sheraz Ali SOLVEDDocument133 pagesKEMU Guide by Sheraz Ali SOLVEDdrmoazzinivyNo ratings yet
- Fermentation: ... When There Is No External Terminal Electron Acceptor!Document15 pagesFermentation: ... When There Is No External Terminal Electron Acceptor!rahullakhmaniNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and TCA Cycle Enzymes and EC Reference NumbersDocument1 pageGlycolysis and TCA Cycle Enzymes and EC Reference NumbersDr. SHIVA AITHALNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument79 pagesBiomolecules9929raoyadav6No ratings yet
- Jamiel James Arceno Biochemisty Bsn1BDocument2 pagesJamiel James Arceno Biochemisty Bsn1BjamielNo ratings yet
- Figure 1: The Common Mutation Sites in The Retinoblastoma Protein (PRB) - PRB Is Protein Made UpDocument8 pagesFigure 1: The Common Mutation Sites in The Retinoblastoma Protein (PRB) - PRB Is Protein Made UpSanthiya KunasegaranNo ratings yet
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument13 pagesPentose Phosphate PathwayRith Hengmeng (Study Smart)No ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument5 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYLEIGHNo ratings yet
- Zinc Overview PDFDocument11 pagesZinc Overview PDFLê Nguyễn Hoàng Anh100% (1)
- Chapt07 Lecture 2015F-3Document65 pagesChapt07 Lecture 2015F-3PaulNo ratings yet
- 14 NSAIDS LastDocument46 pages14 NSAIDS LastMewael TesfamichaelNo ratings yet
- Pros Tag Land InsDocument16 pagesPros Tag Land InsTinaxNo ratings yet
- Reactive Oxygen Species: Dr. Septi Handayani, M.SiDocument55 pagesReactive Oxygen Species: Dr. Septi Handayani, M.SiDenyNo ratings yet
- L5 The Citric Acid Cycle (CAC)Document21 pagesL5 The Citric Acid Cycle (CAC)Cheng FuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cell & Molecular Biology: Cellular Respiration (II) Photosynthesis (I)Document13 pagesIntroduction To Cell & Molecular Biology: Cellular Respiration (II) Photosynthesis (I)Puron RahmanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and Coenzymes 2019Document1 pageEnzymes and Coenzymes 2019Rishu SinghNo ratings yet
- Pathways Toward Deterioration in COVID-19Document83 pagesPathways Toward Deterioration in COVID-19Mercedes BouterNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and MicroelementsDocument94 pagesVitamins and MicroelementsDrRanjeet Kumar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Mellékvese Szteroid HormonszintéziseDocument1 pageMellékvese Szteroid HormonszintézisePéterfi IstvánNo ratings yet
- Bio - CO 6Document2 pagesBio - CO 6Jae Bert UbisoftNo ratings yet
- Reperfusion InjuryDocument11 pagesReperfusion InjuryjujuNo ratings yet
- CoEnzymes 2Document2 pagesCoEnzymes 2k8rbwkpgn7No ratings yet
- 8 IRI 0604 Fix6 - 4 - 06Document71 pages8 IRI 0604 Fix6 - 4 - 06api-19916399No ratings yet
- Cumene Process DesignDocument16 pagesCumene Process Designendang dian lestariNo ratings yet
- DRB 13-14 - Metabolic Pathways Dan EngeeneringDocument43 pagesDRB 13-14 - Metabolic Pathways Dan EngeeneringItsAndrioNo ratings yet
- Revisi TerakhirDocument14 pagesRevisi TerakhirSyaiful RizalNo ratings yet
- First Aid CVS - PharmacologyDocument9 pagesFirst Aid CVS - PharmacologyMohammed HalimyNo ratings yet
- Introduction BCHN 222 2022Document39 pagesIntroduction BCHN 222 2022Francisca ManyisaNo ratings yet
- Review Cellular-RespirationDocument2 pagesReview Cellular-RespirationechaNo ratings yet
- PATHWAYS SummaryDocument5 pagesPATHWAYS Summaryslu.veniegasmb.1144No ratings yet
- I. 1° Structure Determination of A Polypeptide General StepsDocument6 pagesI. 1° Structure Determination of A Polypeptide General StepsAllyson CarlosNo ratings yet
- Syok Pada AnakDocument28 pagesSyok Pada AnakTaufik Abidin100% (1)
- Metallotherapeutic Drugs and Metal-Based Diagnostic Agents: The Use of Metals in MedicineFrom EverandMetallotherapeutic Drugs and Metal-Based Diagnostic Agents: The Use of Metals in MedicineNo ratings yet
- Eden For Grown-Ups: Toward A New Ethic of Earth, of Sex, and of CreationDocument7 pagesEden For Grown-Ups: Toward A New Ethic of Earth, of Sex, and of CreationNYU Press86% (7)
- RA-05-Office SafetyDocument5 pagesRA-05-Office Safetyamritha n krishnaNo ratings yet
- Mto Shear ScriptDocument7 pagesMto Shear ScriptAustria, Gerwin Iver LuisNo ratings yet
- Venkat Guntipally An Accomplished IT ProfessionalDocument8 pagesVenkat Guntipally An Accomplished IT ProfessionalVenkat GuntipallyNo ratings yet
- Honey: A Reservoir For Microorganisms and An Inhibitory Agent For MicrobesDocument7 pagesHoney: A Reservoir For Microorganisms and An Inhibitory Agent For MicrobesVidianka RembulanNo ratings yet
- PEM Self Clinching Nuts CL SeriesDocument12 pagesPEM Self Clinching Nuts CL SeriesAce Industrial SuppliesNo ratings yet
- Academic PressureDocument7 pagesAcademic PressureJohn Mark MontillaNo ratings yet
- Descripcion CodigoDocument90 pagesDescripcion Codigolorena barbaranNo ratings yet
- Design of EW CircuitDocument8 pagesDesign of EW Circuitpatrick.harris881No ratings yet
- Dkg-329 User ManualDocument43 pagesDkg-329 User ManualKỹ Sư TđhNo ratings yet
- TroxerutinDocument3 pagesTroxerutincarlosNo ratings yet
- Lubrication RegimesDocument3 pagesLubrication RegimesfyhufhNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Strategic Management Concepts 13th Edition DavidDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Strategic Management Concepts 13th Edition DavidShawnMatthewsedjq100% (48)
- DigSilent Training Program - RwandaDocument5 pagesDigSilent Training Program - RwandaBUNANI CallixteNo ratings yet
- Faults and EarthquakesDocument32 pagesFaults and EarthquakesArdoKimayKimArdoNo ratings yet
- R7310202 Electrical MeasurementsDocument2 pagesR7310202 Electrical MeasurementssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- PCT - 1351913 Eatnon ManualDocument326 pagesPCT - 1351913 Eatnon Manualmartha BernalNo ratings yet
- Calculation: Model Name Kostor Silhouette Color Prod Code PO O/S / Midsole Last Mold #Document8 pagesCalculation: Model Name Kostor Silhouette Color Prod Code PO O/S / Midsole Last Mold #Like StefiNo ratings yet
- JTlecture 01 PrintDocument17 pagesJTlecture 01 PrintJae-Soo ChangNo ratings yet
- 201203230432504f6bfcf272d31Document38 pages201203230432504f6bfcf272d31Bqdcc6No ratings yet