Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Psychrometrics
Uploaded by
lokesh.bitra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageOriginal Title
psychrometrics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pagePsychrometrics
Uploaded by
lokesh.bitraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Psychrometrics 6.
13
Fig. 3 Schematic Solution for Example 2
Fig. 5 Schematic Solution for Example 3
Fig. 4 Schematic of Device for Cooling Moist Air
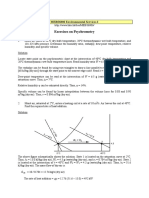
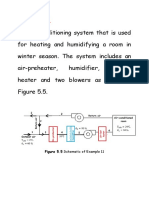
Solution: Figure 3 schematically shows the solution. State 1 is located
on the saturation curve at 2°C. Thus, h1 = 13.0 kJ/kg (dry air), W1 =
4.3 g (water)/kg (dry air), and v1 = 0.784 m3/kg (dry air). State 2 is
located at the intersection of t = 40°C and W2 = W1 = 4.3 g (water)/kg
(dry air). Thus, h2 = 51.6 kJ/kg (dry air). The mass flow of dry air is
Fig. 6 Adiabatic Mixing of Two Moist Airstreams
·
m da = 10 ⁄ 0.784 = 12.76 kg ⁄ s (dry air)
From Equation (42),
1q2 = m· da [ ( h 1 – h 2 ) – ( W 1 – W 2 ) h w2 ] (44)
1q2 = 12.76 ( 51.6 – 13.0 ) = 492 kW
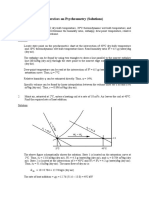
Example 3. Moist air at 30°C dry-bulb temperature and 50% rh enters a
Moist Air Cooling and Dehumidification cooling coil at 5 m3/s and is processed to a final saturation condition at
10°C. Find the kW of refrigeration required.
Moisture condensation occurs when moist air is cooled to a tem-
Solution: Figure 5 shows the schematic solution. State 1 is located at
perature below its initial dew point. Figure 4 shows a schematic the intersection of t = 30°C and φ = 50%. Thus, h1 = 64.3 kJ/kg (dry
cooling coil where moist air is assumed to be uniformly processed. air), W1 = 13.3 g (water)/kg (dry air), and v1 = 0.877 m3/kg (dry air).
Although water can be removed at various temperatures ranging State 2 is located on the saturation curve at 10°C. Thus, h2 = 29.5 kJ/kg
from the initial dew point to the final saturation temperature, it is (dry air) and W2 = 7.66 g (water)/kg (dry air). From Table 2, hw2 =
assumed that condensed water is cooled to the final air temperature 42.11 kJ/kg (water). The mass flow of dry air is
t2 before it drains from the system.
·
For the system of Figure 4, the steady flow energy and material m da = 5 ⁄ 0.877 = 5.70 kg ⁄ s (dry air)
balance equations are
From Equation (44),
· · ·
m da h 1 = m da h 2 + 1q2 + m w h w2 1q2 = 5.70 [ ( 64.3 – 29.5 ) – ( 0.0133 – 0.00766 )42.11 ]
m· da W 1 = m· da W 2 + m· w = 197 kW
Adiabatic Mixing of Two Moist Airstreams
Thus,
A common process in air-conditioning systems is the adiabatic
· · mixing of two moist airstreams. Figure 6 schematically shows the
m w = m da ( W 1 – W 2 ) (43) problem. Adiabatic mixing is governed by three equations:
You might also like
- Chapter 08Document15 pagesChapter 08Jap Ibe86% (7)
- Cooling Towers (Excellent Collection)Document55 pagesCooling Towers (Excellent Collection)moh khNo ratings yet
- Psychometric Exercises 1Document5 pagesPsychometric Exercises 1elimnasrNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual Fluid Mechanics 5th EdiDocument8 pagesSolutions Manual Fluid Mechanics 5th EdiАпцгдк Ьфш БгднчллNo ratings yet
- Catalog Trane Pakage 5-10 TR 410aDocument162 pagesCatalog Trane Pakage 5-10 TR 410anafoukh0% (1)
- امثلةعلى الدورة الشتويةDocument7 pagesامثلةعلى الدورة الشتويةkarrar AilNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Psychrometric Chart and Air ConditioDocument20 pages2.3 Psychrometric Chart and Air ConditioRey Niño GarciaNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric ChartDocument50 pagesPsychrometric ChartVishal Mehta100% (2)
- CHAPTER 2 Psychrometry and Air-ConditioningDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 2 Psychrometry and Air-ConditioningMdnor Rahim0% (1)
- Mech3005 Exercise01 SolutionDocument4 pagesMech3005 Exercise01 SolutionKarla CeaNo ratings yet
- Frost On Air-Cooling EvaporatorsDocument7 pagesFrost On Air-Cooling EvaporatorsVladimir KojicNo ratings yet
- 8902 Solutions AndrewsDocument13 pages8902 Solutions Andrewsfrancesco62% (13)
- Psychometric ChartDocument50 pagesPsychometric Chartjunior alfredoNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric Chart NotesDocument50 pagesPsychrometric Chart NotesMohammed MudassirNo ratings yet
- Unit7 B MKMDocument11 pagesUnit7 B MKMSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-5: Typical Air-Conditioning ProcessesDocument10 pagesLecture-5: Typical Air-Conditioning Processesabrar alhadadNo ratings yet
- Ibrahim Dincer, Tahir Abdul Hussain Ratlamwala Auth. Integrated Absorption Refrigeration Systems Comparative Energy and Exergy Analyses PDFDocument280 pagesIbrahim Dincer, Tahir Abdul Hussain Ratlamwala Auth. Integrated Absorption Refrigeration Systems Comparative Energy and Exergy Analyses PDFahaddi58100% (2)
- AT12 MabaoDocument17 pagesAT12 MabaoMichael Alex MabaoNo ratings yet
- Psycrometric ProcessDocument33 pagesPsycrometric Processmdalt9180No ratings yet
- Phase Equilibrium in Mixtures: International Series of Monographs in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandPhase Equilibrium in Mixtures: International Series of Monographs in Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- TraduucionDocument10 pagesTraduucionJefferson Fabian TipanluisaNo ratings yet
- Exercises On Psychrometry (Solutions)Document4 pagesExercises On Psychrometry (Solutions)nirbhay pandeyNo ratings yet
- Example1. Air at 12°C DBT and 85% RH Is To Be Brought To 36°C DBT and 23.2°C WBTDocument33 pagesExample1. Air at 12°C DBT and 85% RH Is To Be Brought To 36°C DBT and 23.2°C WBTAhmed QasimNo ratings yet
- Lecture (8) HDocument9 pagesLecture (8) HAmir alturkNo ratings yet
- A Stream of Warm Air With A DryDocument3 pagesA Stream of Warm Air With A DryRey Niño GarciaNo ratings yet
- Mixing: (RA) From Conditioned Space As Shown in Fig. 40Document3 pagesMixing: (RA) From Conditioned Space As Shown in Fig. 40Nicolai CeloNo ratings yet
- Psychometry Air Conditioning EditDocument33 pagesPsychometry Air Conditioning EditlewisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-2Document48 pagesChapter 3-2AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric-CalculationDocument5 pagesPsychrometric-CalculationAmmarul NafikNo ratings yet
- The Psychrometric Chart: Theory and Application: Perry Peralta NC State UniversityDocument50 pagesThe Psychrometric Chart: Theory and Application: Perry Peralta NC State UniversityAlaeddin Guner RodopNo ratings yet
- 9.thermo Psychometry Objective by RajputDocument3 pages9.thermo Psychometry Objective by RajputMuruganantham MajesticNo ratings yet
- Revised ManuscriptDocument23 pagesRevised Manuscriptapi-3728640No ratings yet
- PeraltaDocument51 pagesPeraltafortes_76635895No ratings yet
- Tutorial 9v18sol PDFDocument4 pagesTutorial 9v18sol PDFSohayb GattousNo ratings yet
- Exercises of Ch3 (w6) - AnswerDocument3 pagesExercises of Ch3 (w6) - AnswerNguyễn Nam AnhNo ratings yet
- PSYCHROMETRIC GraphDocument31 pagesPSYCHROMETRIC GraphEnemona ShellengNo ratings yet
- Problem Set For HydroDocument9 pagesProblem Set For HydroogulNo ratings yet
- Btech Me 3 Sem Thermodynamics Kme 301 2023Document2 pagesBtech Me 3 Sem Thermodynamics Kme 301 2023darrelle1010No ratings yet
- H 23.5 KJ/KG Dry AirDocument1 pageH 23.5 KJ/KG Dry AirChe AguilarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document6 pagesChapter 8Paulo AzañeroNo ratings yet
- Revised ManuscriptDocument23 pagesRevised Manuscriptapi-3728640No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document16 pagesChapter 3Laurence Lee AdventoNo ratings yet
- Bogor Workshop Drying ProblemsDocument13 pagesBogor Workshop Drying ProblemsMeggy AraoNo ratings yet
- Evaporation Examples: (1) Energy Balance MethodDocument3 pagesEvaporation Examples: (1) Energy Balance MethodJack HaamboteNo ratings yet
- Evaporation Examples: (1) Energy Balance MethodDocument3 pagesEvaporation Examples: (1) Energy Balance MethodcarieNo ratings yet
- Unit 4rac - Prob.sol - Docx 1Document3 pagesUnit 4rac - Prob.sol - Docx 1sai pranayNo ratings yet
- Mining Water Tank - It Is Used To Stored Water For Mining Operation Infrastructure and Is AlsoDocument11 pagesMining Water Tank - It Is Used To Stored Water For Mining Operation Infrastructure and Is AlsoKrizzia LeyesaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Properties of Moist Air: StructureDocument15 pagesUnit 6 Properties of Moist Air: StructurearjunmechsterNo ratings yet
- Examples (Psychrometric Chart) Continues Sunum PDFDocument23 pagesExamples (Psychrometric Chart) Continues Sunum PDFAysu KirazNo ratings yet
- Chap 10 SolnDocument20 pagesChap 10 Solngarbage94No ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Understanding Membrane Distillation and Osmotic DistillationFrom EverandUnderstanding Membrane Distillation and Osmotic DistillationNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- The Quantum Mechanical Three-Body Problem: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandThe Quantum Mechanical Three-Body Problem: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 40CCF Zen CassetteDocument2 pages40CCF Zen CassetteErwin MaldoNo ratings yet
- SACDocument3 pagesSACthehoang12310No ratings yet
- (9F) Exergy Analysis of R1234ze (Z) As MGN Temperature Heat Pump Woeking Fluid With Multi-Stage CompressionDocument10 pages(9F) Exergy Analysis of R1234ze (Z) As MGN Temperature Heat Pump Woeking Fluid With Multi-Stage CompressionDaniel DimaNo ratings yet
- Gambar Instalasi Ac - Daikin InverterDocument4 pagesGambar Instalasi Ac - Daikin Inverterfathjaya lestariNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Product RatingsDocument1 pageCertificate of Product RatingsFernando PascualNo ratings yet
- S.No NameDocument6 pagesS.No NameTHOMASNo ratings yet
- Hvac Assignment: Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient, Compressor, Effects of Bend On DuctDocument29 pagesHvac Assignment: Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient, Compressor, Effects of Bend On DuctNeerajaNo ratings yet
- Heat and Flow NotesDocument92 pagesHeat and Flow NotesAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- System Component SelectionDocument6 pagesSystem Component SelectionhtanhNo ratings yet
- Cbx26uh 060Document12 pagesCbx26uh 060Alberto Nava RodriguezNo ratings yet
- IES VE Revit Plugin GuideDocument18 pagesIES VE Revit Plugin GuideHarry CrowleyNo ratings yet
- PDF Uts Termodinamika DDDocument6 pagesPDF Uts Termodinamika DDSABER FARHANNo ratings yet
- Rheem Furnace ManualDocument12 pagesRheem Furnace Manualmatt12manyNo ratings yet
- IP and SI Psych Charts STPDocument2 pagesIP and SI Psych Charts STPJacob DaigerNo ratings yet
- SkyAir - Cooling Only - NU (FHC, FH-NU)Document149 pagesSkyAir - Cooling Only - NU (FHC, FH-NU)quynhd4dcnNo ratings yet
- 2013 Trane High Wall R410aDocument4 pages2013 Trane High Wall R410aRonald ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Aprilaire 700 ManualDocument20 pagesAprilaire 700 ManualbuicNo ratings yet
- Realisasi Preventive AcDocument6 pagesRealisasi Preventive AcSafar FXNo ratings yet
- Exchanger Tubes-Ms Block - Exchanger.exchanger TubeDocument33 pagesExchanger Tubes-Ms Block - Exchanger.exchanger Tubevijay vickyNo ratings yet
- Dupont Refrigerants: R-22 ReplacementsDocument4 pagesDupont Refrigerants: R-22 ReplacementsEzsilvasilva SilvaNo ratings yet
- EDP Assignment 1 95Document9 pagesEDP Assignment 1 95NicKillNo ratings yet
- TROX TRS-R-R5 - 825x225Document1 pageTROX TRS-R-R5 - 825x225Mohammed Tausif AhmedNo ratings yet
- Heat Load Calculation ExampleDocument5 pagesHeat Load Calculation ExampleJoshua RanjithNo ratings yet
- DVM S EcoDocument8 pagesDVM S EcodanielNo ratings yet
- Tekmar Thermostat 557 p9335 03Document2 pagesTekmar Thermostat 557 p9335 03api-221502147No ratings yet
- Auy54luas - Aoy54ljbyl - TechnicalDocument33 pagesAuy54luas - Aoy54ljbyl - TechnicalViorel CioataNo ratings yet