Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Report OXYGENATION
Report OXYGENATION
Uploaded by
hornejas.elissa.20210 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageOxygen is essential for cellular function and survival, while carbon dioxide must be eliminated to maintain acid-base balance. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the atmosphere and blood through four key processes: ventilation through breathing, alveolar-capillary gas exchange via diffusion, transport of gases between tissues and lungs, and movement of gases between systemic capillaries and tissues. Impairment of these respiratory functions can significantly impact a person's ability to breathe, circulate gases, and perform daily activities.
Original Description:
Original Title
report OXYGENATION
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentOxygen is essential for cellular function and survival, while carbon dioxide must be eliminated to maintain acid-base balance. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the atmosphere and blood through four key processes: ventilation through breathing, alveolar-capillary gas exchange via diffusion, transport of gases between tissues and lungs, and movement of gases between systemic capillaries and tissues. Impairment of these respiratory functions can significantly impact a person's ability to breathe, circulate gases, and perform daily activities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageReport OXYGENATION
Report OXYGENATION
Uploaded by
hornejas.elissa.2021Oxygen is essential for cellular function and survival, while carbon dioxide must be eliminated to maintain acid-base balance. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the atmosphere and blood through four key processes: ventilation through breathing, alveolar-capillary gas exchange via diffusion, transport of gases between tissues and lungs, and movement of gases between systemic capillaries and tissues. Impairment of these respiratory functions can significantly impact a person's ability to breathe, circulate gases, and perform daily activities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
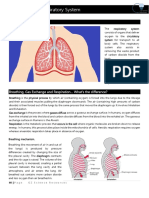
OXYGENATION
Oxygen, a clear, odorless gas that constitutes
approximately 21% of the air we breathe, is necessary
for proper functioning of all living cells. The absence of
oxygen can lead to cellular, tissue, and organism death.
Cellular metabolism produces carbon dioxide, which
must be eliminated from the body to maintain normal
acid–base balance. Delivery of oxygen and removal of
carbon dioxide require the integration of several
systems including the hematologic, cardiovascular, and
respiratory systems. The respiratory system provides the
essential first process in this integrated system, that is,
movement and transfer of gases between the
atmosphere and the blood (Patton & Tibodeau, 2010).
Impaired function of the system can significantly affect
our ability to breathe, transport gases, and participate in
everyday activities.
Respiration is the process of gas exchange between the
individual and the environment and involves four
components:
1. Ventilation or breathing, the movement of air in and
out of the lungs as we inhale and exhale
2. Alveolar-capillary gas exchange, which involves the
diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the
alveoli and the pulmonary capillaries
3. Transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the
tissues and the lungs
4. Movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide between
the systemic capillaries and the tissues.
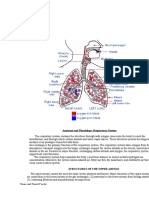
The structure of the respiratory system facilitates gas
exchange and protects the body from foreign matter
such as particulates and pathogens. The four processes
of the respiratory system include pulmonary ventilation,
alveolar gas exchange, transport of oxygen and carbon
dioxide, and systemic diffusion.
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology CopdDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology CopdAssenav May100% (3)
- Case Study CopdDocument7 pagesCase Study CopdIrveen Joy RamirezNo ratings yet
- Reapiratiry System 1Document4 pagesReapiratiry System 1vela7bNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Insufficiency.Document54 pagesOxygen Insufficiency.Josephine George JojoNo ratings yet
- Wepik The Breath of Life Exploring The Wonders of The Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesWepik The Breath of Life Exploring The Wonders of The Respiratory SystemJia TabioloNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory SystemChikuta ShingaliliNo ratings yet
- MEJIA, Michelle Erika F. BSN Iii-B NCM103 (RESPIDocument1 pageMEJIA, Michelle Erika F. BSN Iii-B NCM103 (RESPIMichelle ErikaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology LecturesDocument37 pagesRespiratory Physiology LectureswiasonNo ratings yet
- Lec 17 Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesLec 17 Circulatory SystemEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Respiratory: Keyword: Respiration, Respiratory, OxygenDocument8 pagesRespiratory: Keyword: Respiration, Respiratory, Oxygensiti syahirahNo ratings yet
- Case MiDocument1 pageCase MiMariecar GarazaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Syste3Document2 pagesRespiratory Syste3JhoyceNo ratings yet
- Respiration & BreathingDocument18 pagesRespiration & BreathingKristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument25 pagesRespiratory SystemAnonymous 5hYhEkINo ratings yet
- I.Title Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument23 pagesI.Title Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseJessel VinluanNo ratings yet
- Res (Iratory SystemDocument2 pagesRes (Iratory SystemJosielyn ValladolidNo ratings yet
- Bab Iii Tinjauan PustakaDocument28 pagesBab Iii Tinjauan PustakaLela Nazila ItuSayaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen InsufficiencyDocument24 pagesOxygen InsufficiencyRatna VimalNo ratings yet
- Notes On The Respiratory SystemDocument1 pageNotes On The Respiratory SystemNessa GNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Plants and AnimalsDocument7 pagesGas Exchange in Plants and AnimalsMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Pastel Illustration Computer UI English Class Education PresentationDocument30 pagesPastel Illustration Computer UI English Class Education PresentationElaiza marie VenusNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderDocument11 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderOlivelhynn BernaldoNo ratings yet
- Bio 3 InternalsDocument16 pagesBio 3 InternalsROHAN T ANo ratings yet
- Wepik The Breath of Life Exploring The Human Respiratory System 20240307155132FjwV (1) 1Document11 pagesWepik The Breath of Life Exploring The Human Respiratory System 20240307155132FjwV (1) 1Grijesh MishraNo ratings yet
- PhysioDocument3 pagesPhysioChristian Rey AbuanNo ratings yet
- Educational ProgramsDocument28 pagesEducational ProgramsEsha KuttiNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory SystemconnievelardeNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bhs Inggris Sistem RespirasiDocument13 pagesMakalah Bhs Inggris Sistem RespirasiDewa Ayu Made FebriariNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 (Respiratory System)Document10 pagesLecture 6 (Respiratory System)Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology CopdDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology CopdAssenav MayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 RespirationDocument26 pagesChapter 1 RespirationaqilajandinNo ratings yet
- COPD May Include Diseases That Cause Airflow Obstruction (E.g., Emphysema, ChronicDocument13 pagesCOPD May Include Diseases That Cause Airflow Obstruction (E.g., Emphysema, Chronicmaxmay07No ratings yet
- Form 3 Science Chapter 1Document25 pagesForm 3 Science Chapter 1Mukilan MurugasanNo ratings yet
- Ext RespDocument17 pagesExt RespMuuubbbbbbbbNo ratings yet
- Science Senior 2Document4 pagesScience Senior 2ajichristianbaniadamNo ratings yet
- Altitude Physiology: PRESENTED BY Dick WilliamsDocument52 pagesAltitude Physiology: PRESENTED BY Dick WilliamsDeepak ArkalgudNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory SystemjoimaciascorreaNo ratings yet
- Sistem RespirasiDocument26 pagesSistem RespirasiAnnida LegiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System AssignmentDocument3 pagesRespiratory System AssignmentzainaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System AssignmentDocument3 pagesRespiratory System AssignmentzainaNo ratings yet
- 3.6 Respiratory SystemDocument11 pages3.6 Respiratory SystemJhonnyNo ratings yet
- Reflection Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesReflection Respiratory SystemAin Sufiza0% (1)
- Module 21 RAWDocument51 pagesModule 21 RAWCordelia TobinNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange NewDocument30 pagesGas Exchange Newmariaamkhaann22No ratings yet
- Respiratory-System 1Document12 pagesRespiratory-System 1xavier patacsilNo ratings yet
- SantiDocument1 pageSantiSanti TirtaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy & PhysiologyJohn Erlan LipataNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System Year 10 GZDocument6 pagesHuman Respiratory System Year 10 GZLabeenaNo ratings yet
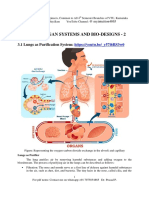
- Human Organ Systems and Bio-Designs - 2: at Myintuition4865Document8 pagesHuman Organ Systems and Bio-Designs - 2: at Myintuition48651NC21IS038 POLATHALA MOUNIKANo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentDungani AllanNo ratings yet
- Bio 3Document28 pagesBio 3AngelNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System For PowelDocument41 pagesRespiratory System For PowelNikko Bondoc ManaloNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory SystemRaluca MoldovanNo ratings yet
- Biology 3Document48 pagesBiology 3Chandana KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange in Plants and AnimalsDocument51 pagesGaseous Exchange in Plants and AnimalsJesimie OriasNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory SystemAsma AbbasNo ratings yet
- Salcedo ANPH 111 Lec Respiratory System 23Document30 pagesSalcedo ANPH 111 Lec Respiratory System 23balazoedwin16No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory SystemUzumaki Naruto (NARUTADIKS)No ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet