Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DISPENSING
Uploaded by
JENSEL CLOUIE C. REGLOSCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DISPENSING
Uploaded by
JENSEL CLOUIE C. REGLOSCopyright:
Available Formats
Dispensing
prescription analysis extemporaneous
Proper analysis and interpretation of various
prescriptions and medication orders by the Pharmacist compounding
are vital steps in dispensing.
Extemporaneous compounding is an essential role of a
√ Prescriber information and signature Pharmacist that aims to cater to the special needs of the
√ Patient information and signature patients.
√ Date prescription was written
√ Superscription
√ Inscription Categories of Compounding:
√ Subscription • Simple
√ Signa • Moderate
√ Special Instructions • Complex
Pharmacists should be keen on checking prescriptions to
avoid prescription errors. The Need for Extemporaneous Compounding:
• Erroneous Prescription • Lack of market
• Violative Prescription • Drug stability issues
• Impossible Prescription • Off label use of the drug
• Higher dose requirements
• Endogenous biologicals
Appropriate medication • Changing route for existing drug
scheduling and dosing are • Region specific requirements
essential in achieving • Rare disorders/ diseases
compliance for the • Orphan drugs
patients. • Unpreserved drugs for hyper sensitive patients
Additional dispensing
Patient compliance instructions should be
can be achieved given to the patient
through proper about storage and
dispensing techniques handling including the
by the Pharmacist. beyond-use-date, to
ensure maximum
therapeutic outcome of
the medication.
Medication Review medication assessment and
The primary goal of Medication Review is to maximize the
therapeutic outcome of the therapy and minimize therapeutic planning
adverse effects.
Medication Assessment greatly improves the patient’s
quality of health by maximizing the course of medication
Types of medication review:
therapy and minimizing medication errors.
• Prescription review
• Compliance and concordance review
• Clinical medication review Path to Patient-Centered Care Improve Outcomes
Approaches in Medication Review:
Enhance Improvement
1. Reviews that are carried out
without patient involvement Drive Accountability
2. Face-to-face review
Involve Patient and Family
Medication Review Process
Engage Staff
Identifying patients
Carrying out the review Partner with Leadership
Quality Assurance and Audit
Pharmaceutical Care Process
Medication
Reconciliation is an Complete Intervention
essential part of and Implement Follow
the Medication
Review Process Develop pharmaceutical care plan
since it ensures
quality and safe use Assess info (patient assessment)
of medicines as
patients transition Gather patient information (subjective & objective)
between the
community and Initiate relationship with the patient or caregiver
hospital.
Therapeutic planning is one of the most essential part of
medication assessment which endpoint is to cure or
prevent a disease as well as to help medical practitioners
in diagnosing a disease.
You might also like
- 1-Introduction To Clinical PharmacyDocument25 pages1-Introduction To Clinical PharmacyDr-Muhammad Junaid Hassan SharifNo ratings yet
- 5 Role of Pharmacist in PHDocument20 pages5 Role of Pharmacist in PHمحمد العمريNo ratings yet
- ACCP - Comprehensive Medication Management in Team-Based CareDocument8 pagesACCP - Comprehensive Medication Management in Team-Based CareThuane SalesNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Care Process:: Assessment - Care Plan - Follow UpDocument54 pagesPharmaceutical Care Process:: Assessment - Care Plan - Follow UpRaharjo AdityaNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy MonitoringDocument38 pagesDrug Therapy MonitoringSumanthNo ratings yet
- Integrated Therapeutics IDocument74 pagesIntegrated Therapeutics IMelekNo ratings yet
- NCM 212 - Nursing Process in PharmacologyDocument10 pagesNCM 212 - Nursing Process in PharmacologyLYRIZZA LEA BHEA DESIATANo ratings yet
- Phm423: Clinical Pharmacy Week 1: Introduction: Hadassah M. Reyes-Cendana, RPH January 2022Document36 pagesPhm423: Clinical Pharmacy Week 1: Introduction: Hadassah M. Reyes-Cendana, RPH January 2022Hadassah ReyesNo ratings yet
- 3063-20220805085327-PD Pharmacist July 2022Document7 pages3063-20220805085327-PD Pharmacist July 2022Raheel KhanNo ratings yet
- p2371 Sample Chapter 4Document22 pagesp2371 Sample Chapter 4Kayla Andrea CalibaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Skills For Pharmacists-APatient-FocusedApproach3rdeditionDocument13 pagesClinical Skills For Pharmacists-APatient-FocusedApproach3rdeditionNADYA FEBRIYANTINo ratings yet
- Pharma Nursing ApplicationDocument53 pagesPharma Nursing ApplicationRiegne Chiara Fay AcuzarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Medication Management: Key Terms & Definitions Drug MonographDocument3 pagesChapter 4: Medication Management: Key Terms & Definitions Drug MonographcoooleNo ratings yet
- Monitoring & Evaluation SlidesDocument31 pagesMonitoring & Evaluation Slidesansir ahmedNo ratings yet
- Statements Pharmaceutical CareDocument3 pagesStatements Pharmaceutical CareDiegoAndrésYiZapataNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 The Nursing Process in PharmacologyDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 6 The Nursing Process in Pharmacologyryanescueta090702No ratings yet
- 3C DTCDocument40 pages3C DTCekramNo ratings yet
- Drug Use EvaluationDocument27 pagesDrug Use Evaluationshanthi dasariNo ratings yet
- MDS3 Ch45 HospitalPharmacyMgmt Nov2011Document17 pagesMDS3 Ch45 HospitalPharmacyMgmt Nov2011Andre SamsungNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical CareDocument17 pagesPharmaceutical CareDr Aniqa SundasNo ratings yet
- Medication SafetyDocument30 pagesMedication SafetyAprilSenseng100% (1)
- MODULE 4 PharmacovigilanceDocument20 pagesMODULE 4 PharmacovigilanceJUDYANN PINEDANo ratings yet
- Review of Pharmaceutical Care Services Provided by The PharmacistsDocument3 pagesReview of Pharmaceutical Care Services Provided by The PharmacistsellianaeyNo ratings yet
- Medicine Use Evaluation: A Guide To ImplementationDocument26 pagesMedicine Use Evaluation: A Guide To ImplementationmrboredguyNo ratings yet
- Griese Mammen2018Document19 pagesGriese Mammen2018Keytiane JVNo ratings yet
- Pharma Lesson 1Document3 pagesPharma Lesson 1BabyJane GRomeroNo ratings yet
- Sample Chapter PDFDocument12 pagesSample Chapter PDFMini Bekti NingsihNo ratings yet
- 04 The Nursing ProcessDocument6 pages04 The Nursing ProcessChelzie LasernaNo ratings yet
- 1s PERSPECTIVES BSPHDocument28 pages1s PERSPECTIVES BSPHKathleenjoyce BongatoNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument2 pagesPharmacologyRia HadzimahmutovicNo ratings yet
- Communication With Other Healthcare ProfessionalsDocument16 pagesCommunication With Other Healthcare ProfessionalsSittie Fahieda Aloyodan100% (1)
- TDM Clinic Guide PDFDocument5 pagesTDM Clinic Guide PDFamalNo ratings yet
- Medication Use Evaluation CurrentDocument3 pagesMedication Use Evaluation CurrentSarahkheridNo ratings yet
- How To Improve Clinical Pharmacy Practice Using Key Performance IndicatorsDocument5 pagesHow To Improve Clinical Pharmacy Practice Using Key Performance IndicatorsTaufik Qur RaufNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - PHR514-Pharmacy Law and Regulatory AffairsDocument31 pagesWeek 7 - PHR514-Pharmacy Law and Regulatory AffairsNeymar ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Ward Round Participation & Drug Therapy MonitoringDocument20 pagesWard Round Participation & Drug Therapy MonitoringAman UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Hospital Pharmacy Practice - Prelim Notes - Hospital PharmacyDocument4 pagesHospital Pharmacy Practice - Prelim Notes - Hospital PharmacyJan Elishah Camarador AllareyNo ratings yet
- Collaborative Drug Therapy ManagementDocument10 pagesCollaborative Drug Therapy ManagementAyu Dina UnifahNo ratings yet
- Prof. Gregory PetersonDocument17 pagesProf. Gregory PetersonandrianiNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Care PlanDocument19 pagesPharmaceutical Care PlanDaenica Lorraine Abella SebastianNo ratings yet
- 4Document5 pages4Creepy PotatoesNo ratings yet
- Drug Utilization Study in The Department of Medicine at A Teaching HospitalDocument11 pagesDrug Utilization Study in The Department of Medicine at A Teaching HospitalFaizan Ali UniqueNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Care (S1-2006)Document26 pagesPharmaceutical Care (S1-2006)Devaki देवनNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 PHARMACOLOGY FOR NURGEC Medication Errors and Risk ReductionDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 7 PHARMACOLOGY FOR NURGEC Medication Errors and Risk Reductionryanescueta090702No ratings yet
- A Guide To Patient Medication Review: September 2003Document33 pagesA Guide To Patient Medication Review: September 2003Muhamad GunturNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills in Pharmacy PracticeDocument7 pagesCommunication Skills in Pharmacy PracticemasorNo ratings yet
- Dispensing 2 TerminologiesDocument12 pagesDispensing 2 TerminologiesDianie VillapaniaNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma: "Using Six Sigma To Reduce Medication Errors in A Home-Delivery Pharmacy Service Kelompok 2Document7 pagesSix Sigma: "Using Six Sigma To Reduce Medication Errors in A Home-Delivery Pharmacy Service Kelompok 2ricoferyantoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacist JDDocument5 pagesClinical Pharmacist JDSalna Susan AbrahamNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Pharmaco-EpidemiologyDocument21 pagesAn Introduction To Pharmaco-EpidemiologyMr.ShazNo ratings yet
- Personalised Medicine Sem1Document19 pagesPersonalised Medicine Sem1RAKSHA ARUNNo ratings yet
- Basic - Concepts - in - Pharmaceutical - Care CLINICAL PHARMACYDocument17 pagesBasic - Concepts - in - Pharmaceutical - Care CLINICAL PHARMACYPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Drug Monitoring in A Developing Nation: A Clinical GuideDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Drug Monitoring in A Developing Nation: A Clinical GuideAsriSupring PadangngarengNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology (Chapter 1 - Introduction)Document1 pageNursing Pharmacology (Chapter 1 - Introduction)Jemima GasconNo ratings yet
- Career OptionsDocument28 pagesCareer OptionsFaizan DonNo ratings yet
- Concept of Clinical PharmacyDocument30 pagesConcept of Clinical PharmacyKishori Kedia100% (4)
- Pharmacy Department Strategy Plan: Goals Objective IndicatorsDocument102 pagesPharmacy Department Strategy Plan: Goals Objective IndicatorsLegend WritersNo ratings yet
- Medication Use Evaluation (MUE)Document16 pagesMedication Use Evaluation (MUE)tsedaleNo ratings yet
- Biomarkers, Diagnostics and Precision Medicine in the Drug Industry: Critical Challenges, Limitations and Roadmaps for the Best PracticesFrom EverandBiomarkers, Diagnostics and Precision Medicine in the Drug Industry: Critical Challenges, Limitations and Roadmaps for the Best PracticesNo ratings yet
- Megan Firlotte 2020Document2 pagesMegan Firlotte 2020api-544351197No ratings yet
- Acute MedicineDocument5 pagesAcute MedicinesuggaplumNo ratings yet
- Morning Report Obs FebrisDocument10 pagesMorning Report Obs FebrisJessicaNo ratings yet
- Demodex Infestation Requires Immediate, Aggressive Treatment by Doctor, Patient - Primary Care Optometry NewsDocument5 pagesDemodex Infestation Requires Immediate, Aggressive Treatment by Doctor, Patient - Primary Care Optometry NewsΔιονύσης ΦιοραβάντεςNo ratings yet
- Glossary and Acronyms of FreedivingDocument2 pagesGlossary and Acronyms of FreedivingIvo XNo ratings yet
- Dexmedetomidine - Drug Information - UpToDateDocument21 pagesDexmedetomidine - Drug Information - UpToDateRicardo Ortiz NovilloNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The Philippinesmazie lopezNo ratings yet
- Bianca Gildersleeve Resume 1Document3 pagesBianca Gildersleeve Resume 1api-486984312No ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases PDFDocument31 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases PDFMedicoz HeroNo ratings yet
- TESTDocument22 pagesTESTjuniati samparaNo ratings yet
- Impaction Case-history-NAGARAJ TANNERUDocument8 pagesImpaction Case-history-NAGARAJ TANNERUmedicmayaNo ratings yet
- Guideline of Urolithiasis PDFDocument34 pagesGuideline of Urolithiasis PDFMelia IndasariNo ratings yet
- Reading Synthesis # 2: San Roque Extension, Roxas City, Capiz, Philippines 5800Document10 pagesReading Synthesis # 2: San Roque Extension, Roxas City, Capiz, Philippines 5800Jay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Waste Management Colour Coding For BeginnersDocument3 pagesBiomedical Waste Management Colour Coding For BeginnersMotherterrasa VocationalNo ratings yet
- Hospice Care sc2Document5 pagesHospice Care sc2Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Haematology Physical ExaminationDocument8 pagesHaematology Physical Examinationrodahlyu100% (1)
- UGH Syndrome After Lens Implantation PDFDocument2 pagesUGH Syndrome After Lens Implantation PDFkameliasitorusNo ratings yet
- Newcastle Disease The Vaccines & Vaccination: by Haas Md. Yatim D.V.M (UPM)Document36 pagesNewcastle Disease The Vaccines & Vaccination: by Haas Md. Yatim D.V.M (UPM)zainodin adhomNo ratings yet
- Herpesviruses, Poxviruses & Human Papilloma Virus: Fort SalvadorDocument33 pagesHerpesviruses, Poxviruses & Human Papilloma Virus: Fort SalvadorFort SalvadorNo ratings yet
- 356 Mastering Psychiatry Textbook PDFDocument356 pages356 Mastering Psychiatry Textbook PDFdragutinpetricNo ratings yet
- SteatorrheaDocument43 pagesSteatorrheaJohnRobynDiezNo ratings yet
- Most Common Chronic Pain ConditionsDocument7 pagesMost Common Chronic Pain ConditionsNicolas RitoNo ratings yet
- Juni Save Root Pulp J LSTR LDocument6 pagesJuni Save Root Pulp J LSTR LAntony SebastianNo ratings yet
- Bipolar 1 Disorder NCPDocument3 pagesBipolar 1 Disorder NCPJoy-Rena Sabinay OchondraNo ratings yet
- Psychoneuroimmunology Anu Final 1 1Document30 pagesPsychoneuroimmunology Anu Final 1 1Haris AhmedNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology Chapter 3Document5 pagesMedical Terminology Chapter 3Gregg ProducerNo ratings yet
- KDIGO 2023 Lupus Nephritis Guideline - Public Review - 9 Mar 2023 PDFDocument102 pagesKDIGO 2023 Lupus Nephritis Guideline - Public Review - 9 Mar 2023 PDFlucasnatalia21bNo ratings yet
- The Role of Systemic Treatments For Skin Lightening: Margit L. W. Juhasz MD MDDocument14 pagesThe Role of Systemic Treatments For Skin Lightening: Margit L. W. Juhasz MD MDDr. Bhawna GuptaNo ratings yet
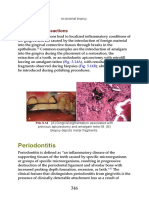
- Periodontitis: Foreign-Body ReactionsDocument25 pagesPeriodontitis: Foreign-Body ReactionsAisyah Arina NurhafizahNo ratings yet
- Physician CertificationDocument1 pagePhysician CertificationcwadotorgNo ratings yet