Professional Documents
Culture Documents
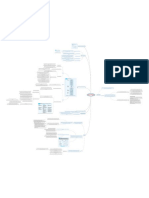
Chapter 2 - Analyzing and Recording Transactions
Uploaded by
Lê Nguyễn Anh ThưCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2 - Analyzing and Recording Transactions
Uploaded by
Lê Nguyễn Anh ThưCopyright:
Available Formats
Identify and describe transactions and events
entering the accounting system.
Source Documents
ale receipts, checks, purchase orders, bills
S
Can be in hard copy or electronic form from suppliers, payroll records, bank
statement
Identify each transaction and event from
source documents
Debit for increases; credit for decreases
Cash
Accounts Receivable
list of all ledger accounts and their
A
Note Receivable
balances at a point in time.
ist each account title and its amount in the
L Asset accounts Prepaid Accounts
trial balance
Supplies Accounts
ompute the total of debit balances and the
C
total of credit balances. Equipment Accounts
erify to total debit balances equal total
V Building Accounts
credit balances.
Trial Balance
Land
erify that the trial balance columns are
V
correctly added. Debit for decreases; credit for increases
nalyze each transaction and event using
A
erify that account balances are accurately
V the accounting equation Account Payable
entered from the ledger.
Liability accounts Note Payable
ee whether a debit or credit balance is
S
mistakenly listed in the trial balance as a Unearned Revenue Accounts
credit or debit.
Searching for Errors
Accrued Liabilities
ecompute each account balance in the
R
ledger.
Owner Capital Debit for decreases; Credit for increases
The processing transactions
erify that each journal entry is properly
V
posted.
ANALYZING AND Owner Withdrawals Debit for increases; credit for decreases
Equity accounts
erify that the original journal entry has
V RECORDING Revenue Accounts Debit for decreases; Credit for increases
equal debits and credits.
TRANSACTIONS Expense Accounts Debit for increases; credit for decreases
ecord relevant transactions and events in a
R
Date of transaction journal
nter titles of account debited and the enter
E Ledger or General ledge is used to collect
A
amounts in the Debit column on the same all accounts and their balances
line. journal is a complete record of each
A
hile companies can use various journals,
W transaction in one place. It also shows debits
list of all ledger accounts and has an
a
nter titles of accounts credited and the
E every company uses a general journal. and credits for each transaction. Recording
Chart of Accounts identification number assigned to each
enter amounts in the credit column on the transactions in a journal is called journalizing.
account.
same line.
epresents a ledger account and is used to
R
nter a brief explanation of the transaction
E show the effects of transactions.
on the line below the entry. Post journal information to ledger accounts
J ournalizing and Posting he left side of an account is called the debit
T
Identify transactions and source documents side or Dr.
transactions
T-account
nalyze transactions using the accounting
A he right side of an account is called the
T
equation. credit side, of Cr.
Record journal entry
he difference between total debits and total
T
Double-entry accounting credits for an account, including any
Post entry to ledger.
beginning balance, is the account balance.
t least two accounts are involved, with at
A
least one debit and one credit.
Double-entry system
otal amount debited must equal total
T
amount credited.
repare and analyze the trial balance and
P
financial statements.
You might also like
- Tray Play Ebook PDFDocument60 pagesTray Play Ebook PDFkaren megsanNo ratings yet
- Creative Writers and Daydreaming by Sigmund Freud To Print.Document7 pagesCreative Writers and Daydreaming by Sigmund Freud To Print.Robinhood Pandey82% (11)
- Audit of Cash BalancesDocument1 pageAudit of Cash BalancesThe True MuslimNo ratings yet
- Core Sector 19-20 PDW Bill Barobisa 1Document3 pagesCore Sector 19-20 PDW Bill Barobisa 1asovvokuttaNo ratings yet
- Register of Cash in Bank and Other Related Financial TransactionsDocument2 pagesRegister of Cash in Bank and Other Related Financial Transactionsjplaurel barangayNo ratings yet
- HIRA For Loading or Unloading ActivityDocument4 pagesHIRA For Loading or Unloading ActivityMD Abdullah100% (2)
- New Assignment (Journal Ledger and Trial Balance)Document6 pagesNew Assignment (Journal Ledger and Trial Balance)Zargham Durrani50% (2)
- Cash Audit ProgramDocument8 pagesCash Audit ProgramtemedebereNo ratings yet
- Debit & CreditDocument1 pageDebit & CreditMian Ahmed RazaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Cycle Far0Document8 pagesAccounting Cycle Far0NivekNo ratings yet
- Maine - Budget Planner - FRESHDocument1 pageMaine - Budget Planner - FRESHsharmaine garciaNo ratings yet
- Trading IncomeDocument15 pagesTrading IncomeJalees Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Customer Service Collections Processing WorkflowDocument1 pageCustomer Service Collections Processing WorkflowJancy KattaNo ratings yet
- Heart Attack Prevention TipsDocument1 pageHeart Attack Prevention TipsMLastTryNo ratings yet
- Understanding Your Utilities BillDocument1 pageUnderstanding Your Utilities BillresoloxicNo ratings yet
- ShieldGruppe Dashboard Model Work Task 1Document1 pageShieldGruppe Dashboard Model Work Task 1Charielle Esthelin BacuganNo ratings yet
- P&I Guidelines: West of England Practical Notes For Ships' PersonnelDocument1 pageP&I Guidelines: West of England Practical Notes For Ships' PersonnelnostremarumNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Posting Transactions: No. Account: Account NO. Post. Ref. Debit Credit BalanceDocument4 pagesModule 2: Posting Transactions: No. Account: Account NO. Post. Ref. Debit Credit BalanceRechelleRuthM.DeiparineNo ratings yet
- Vendor & Customer Setup: Login To Opsdog To Purchase The Full Workflow Template (Available in PDF, VisioDocument1 pageVendor & Customer Setup: Login To Opsdog To Purchase The Full Workflow Template (Available in PDF, VisioLIGAYA SILVESTRENo ratings yet
- Ab-H-12 - Level 3 WestDocument1 pageAb-H-12 - Level 3 Westicas2017secaNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting SummaryDocument23 pagesFinancial Accounting SummaryKapeLatte (카페라떼)No ratings yet
- Form Pendaftaran KKN TA 2021-2022 (Responses) - 2Document21 pagesForm Pendaftaran KKN TA 2021-2022 (Responses) - 2keropsesNo ratings yet
- Plant Arrangement Level + 0.00Document1 pagePlant Arrangement Level + 0.00JC DC AcostaNo ratings yet
- MPR - (SEP-23) - DNDocument2 pagesMPR - (SEP-23) - DNExecutive Engineer I.B.DivisionNo ratings yet
- 6018 p1 Akuntansi Lembar Kerja Buku BesarDocument24 pages6018 p1 Akuntansi Lembar Kerja Buku BesarHeri BaskoroNo ratings yet
- 3408E and 3412E Engines Electrical System PDFDocument2 pages3408E and 3412E Engines Electrical System PDFssinokrot100% (2)
- Belgrade SECAPDocument135 pagesBelgrade SECAPgiorgos traikosNo ratings yet
- Aarti Drugs (2021)Document337 pagesAarti Drugs (2021)insaafduggal33No ratings yet
- Piping and Instrumentation Diagram: Fixed Firewater System - Deluge Distribution Upper Deck / Main Deck System 53Document1 pagePiping and Instrumentation Diagram: Fixed Firewater System - Deluge Distribution Upper Deck / Main Deck System 53Mohd KhaidirNo ratings yet
- Piping and Instrumentation Diagram: Fixed Firewater System - Deluge Distribution Upper Deck / Main Deck System 53Document1 pagePiping and Instrumentation Diagram: Fixed Firewater System - Deluge Distribution Upper Deck / Main Deck System 53Mohd KhaidirNo ratings yet
- Outcome 10 Quarterly Reporting July Sept 2012 0Document19 pagesOutcome 10 Quarterly Reporting July Sept 2012 0sandraNo ratings yet
- University Business Expense Reimbursement FormDocument1 pageUniversity Business Expense Reimbursement FormRohit NayyarNo ratings yet
- Application For Admission To The General Provident Fund GP FundDocument1 pageApplication For Admission To The General Provident Fund GP FundAbbas KhanNo ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument1 pageSodapdfCollins EmynekNo ratings yet
- Week 9-GSLC-BB55Document1 pageWeek 9-GSLC-BB55ANGELYCA LAURANo ratings yet
- Senr1026-03 Pub SchematicsDocument2 pagesSenr1026-03 Pub Schematicsjf3337006No ratings yet
- Mammoth Cave MapDocument1 pageMammoth Cave MapLaura SpearsNo ratings yet
- The Books OF AccountingDocument37 pagesThe Books OF AccountingediwowNo ratings yet
- RCF Art705as-Input BoardDocument1 pageRCF Art705as-Input BoardHaroldo CosmeNo ratings yet
- SampleDocument1 pageSampleNeeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lembar Kerja Mengelola Buku Besar Lembar Kerja Mengelola Buku BesarDocument21 pagesLembar Kerja Mengelola Buku Besar Lembar Kerja Mengelola Buku Besarprihatini kurniasihNo ratings yet
- P&ID DRAWING 1 New (Pepsi-Chiller System)Document1 pageP&ID DRAWING 1 New (Pepsi-Chiller System)Hồng Quang LêNo ratings yet
- 26 August 2021Document2 pages26 August 2021NidaulKhoirNo ratings yet
- Cat Dcs Sis ControllerDocument2 pagesCat Dcs Sis ControllerLuis ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- 2023-02-14 MAR-065 Concrete Deisgn Mix Using Type 1 For Water Retaining Structures - EXAN Rev. B RRAADocument1 page2023-02-14 MAR-065 Concrete Deisgn Mix Using Type 1 For Water Retaining Structures - EXAN Rev. B RRAAjaymarNo ratings yet
- Weekly Progress Report From 21-Oct-2023 To 26-Oct-2023 XDocument70 pagesWeekly Progress Report From 21-Oct-2023 To 26-Oct-2023 XErickson MalicsiNo ratings yet
- Ab-H-16 - Level 4 WestDocument1 pageAb-H-16 - Level 4 Westicas2017secaNo ratings yet
- Ab-H-08 - Level 2 WestDocument1 pageAb-H-08 - Level 2 Westicas2017secaNo ratings yet
- 1.procedure For Marketing-Ms - mkt.p.01Document3 pages1.procedure For Marketing-Ms - mkt.p.01Mojis V HNo ratings yet
- Special JournalsDocument2 pagesSpecial JournalsabsidycoNo ratings yet
- XXXX - PTC-XXXX - E - 0 Oct 2Document49 pagesXXXX - PTC-XXXX - E - 0 Oct 2pjosesmNo ratings yet
- Church Renovation CDsDocument4 pagesChurch Renovation CDsrobert ortizNo ratings yet
- Risk Assesment For Shifting of MEP Services and Re-Installations 26-03-2022Document5 pagesRisk Assesment For Shifting of MEP Services and Re-Installations 26-03-2022Zameer Basha Navzath AliNo ratings yet
- RCF Art705as-Preamp BoardDocument3 pagesRCF Art705as-Preamp BoardHaroldo CosmeNo ratings yet
- This Original Drawing Created For "Din" (German) Standard Steels and Redlined For "Is" (Indian) Equivalent SteelDocument2 pagesThis Original Drawing Created For "Din" (German) Standard Steels and Redlined For "Is" (Indian) Equivalent SteelsbjamdadeNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need To Memorise - Part 3, Statistics PDFDocument1 pageEverything You Need To Memorise - Part 3, Statistics PDFTripleFireWingsNo ratings yet
- Utility Bill Template 01Document2 pagesUtility Bill Template 01Ooo SssNo ratings yet
- Mammoth Cave NPDocument1 pageMammoth Cave NPapi-19487128No ratings yet
- Diag, Schem Pp-Fire Protection 121T1290Document3 pagesDiag, Schem Pp-Fire Protection 121T1290Bounezra OussamaNo ratings yet
- Examining Regulatory Frameworks For Digital Currencies and BlockchainDocument15 pagesExamining Regulatory Frameworks For Digital Currencies and BlockchainAnonymous 8RR1A8ClpNo ratings yet
- Stone Chrusher - Functional Schematic Block AGEV1Document5 pagesStone Chrusher - Functional Schematic Block AGEV1Ahmed SalamaNo ratings yet
- Manual Murray OkDocument52 pagesManual Murray OkGIOVANNINo ratings yet
- Steve Allen - The Public HatingDocument8 pagesSteve Allen - The Public HatingDavid SalvatierraNo ratings yet
- Test 5 - C Reading SectionDocument13 pagesTest 5 - C Reading SectionFaby SanchezNo ratings yet
- 2 CSS Word FileDocument12 pages2 CSS Word Fileronak waghelaNo ratings yet
- GE1451 NotesDocument18 pagesGE1451 NotessathishNo ratings yet
- Rules & Regulations BDC NTUDocument5 pagesRules & Regulations BDC NTUMohammad YasinNo ratings yet
- Ismu in EnglishDocument2 pagesIsmu in EnglishIsmilaYulianaNo ratings yet
- Shahid Change ManagementDocument1 pageShahid Change Managementtanveer azamNo ratings yet
- Ultimate India Bucket ListDocument5 pagesUltimate India Bucket Listgacawe6143No ratings yet
- Safeguarding Humanitarian Spce Chellenges UNHCRDocument367 pagesSafeguarding Humanitarian Spce Chellenges UNHCRalvaromelladoNo ratings yet
- Willis, D. - Visualizing Political StruggleDocument11 pagesWillis, D. - Visualizing Political StruggleAndreea Mitreanu100% (3)
- The Achaeans (Also Called The "Argives" or "Danaans")Document3 pagesThe Achaeans (Also Called The "Argives" or "Danaans")Gian Paul JavierNo ratings yet
- Barnum Distributors Wants A Projection of Cash Receipts and CashDocument1 pageBarnum Distributors Wants A Projection of Cash Receipts and CashAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Empson Peacock AngelDocument274 pagesEmpson Peacock AngelV.F.No ratings yet
- Medical Professionalism Across Cultures: A Challenge For Medicine and Medical EducationDocument7 pagesMedical Professionalism Across Cultures: A Challenge For Medicine and Medical EducationYoNo ratings yet
- PAL v. CIR (GR 198759)Document2 pagesPAL v. CIR (GR 198759)Erica Gana100% (1)
- Mision de Amistad Correspondence, 1986-1988Document9 pagesMision de Amistad Correspondence, 1986-1988david_phsNo ratings yet
- Analisa Getaran BerlebihDocument5 pagesAnalisa Getaran BerlebihMatsaid ReksonoNo ratings yet
- The Global Workforce Crisis BCG PDFDocument28 pagesThe Global Workforce Crisis BCG PDFdakintaurNo ratings yet
- Acordes para GuitarraDocument12 pagesAcordes para GuitarraLucas Sebastian MuñozNo ratings yet
- Social Class 10 2019Document14 pagesSocial Class 10 2019krishnareddy_chintalaNo ratings yet
- Sample Activity ReportDocument2 pagesSample Activity ReportKatrina CalacatNo ratings yet
- Summary Prof EdDocument19 pagesSummary Prof EdFloravie Onate100% (2)
- Can Amitriptyline Makes You Feel More Awake Instead of DrowsyDocument3 pagesCan Amitriptyline Makes You Feel More Awake Instead of Drowsyteddypol100% (1)
- The Double Conjunctions Worksheet (Both ... And, Neither ... Nor, Either ... Or)Document2 pagesThe Double Conjunctions Worksheet (Both ... And, Neither ... Nor, Either ... Or)Ibrahim BenamiraNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Contracts in Context From Transaction To Litigation Aspen Casebook PDFDocument40 pagesEbook PDF Contracts in Context From Transaction To Litigation Aspen Casebook PDFflorence.padilla424100% (35)
- Proposal For Pitch An IdeaDocument2 pagesProposal For Pitch An Ideaaaron mathewsNo ratings yet
- Assessment Items: Fifth Grade Tri 2a - Ava Farley: A Good Reason To Look Up Do What You LoveDocument7 pagesAssessment Items: Fifth Grade Tri 2a - Ava Farley: A Good Reason To Look Up Do What You Loveapi-348637033No ratings yet