Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics 2 Exp. 04 Even 2324
Uploaded by
RidwanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics 2 Exp. 04 Even 2324
Uploaded by
RidwanCopyright:
Available Formats
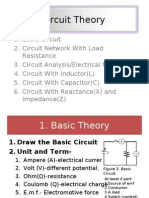
Experiment 4
Kirchhoff Voltage-Current Law and Potentiometer
I. Objectives
✓ To proof the Kirchhoff Voltage Law
✓ To proof the Kirchhoff Current Law
✓ To apply potentiometer in a circuit
II. Scope
A. Theory
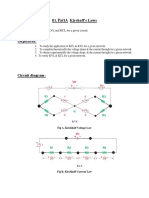
1. Kirchhoff Current Law
Kirchoff Current Law expresses that the amount of current which get in to a
node is the same as the amount of current which get out from that node.
The relation of two or more components will result in branches (nodes) with the
direct graph drawn in the following figure:
I1 + I3 = I2 + I4 + I5 (eq.4.1)
I1 I3
I4
I2 I5
Figure 4.1
2. Kirchhoff Voltage Law
Kirchoff Voltage Law expresses the total of voltage in a close loop is zero. So
the voltage from the power supply will divided to each components propotional
to the component resistance to the total resistance of the circuit.
R1 R2 R3
+ V1 - + V2 - + V3 -
+
Vs1
-
Figure 4.2
-VS1 + V1 + V2 + V3 = 0 (eq.4.2)
To analyze the circuit, the polarity should be noticed.
Physics 2 Computer Engineering Laboratory
Experiment 4 Page 1 of 7
3. Potentiometer
Potentiometer is a component which is functionately like a variable resistor that
resist current by its adjustable resistance. Potentiometer is the same as 2
resistors which are series connected and the resistive value of the potentiometer
can be adjusted. The resistive value of a resistor is on its body. Potentiometer
can be adjusted to change the resistive ratio of the two resistors. There are 2
kinds of potentiometer, logaritmic potentiometer and linier potentiometer. On
logaritmic potentiometer, the resistive change logaritmicly as it is turned per
degree. Whereas, on linier potentiometer, the resitive change constantly as it is
turned per degree. In this experiment, we will use the logaritmic one.
Figure 4.3 Typical of Potentiometer
USA and Japan Europe
Figure 4.4 Typical symbol of Potentiometer
Figure 4.5
Physics 2 Computer Engineering Laboratory
Experiment 4 Page 2 of 7
B. Reference(s)
• Meade, 2003. “Foundations Of Electronics 4”. Thomson. US.
• Floyd, 2007. “Electric Circuit Fundamental 7”. Prentice Hall. US
• Floyd, 1999.” Principle of Electrical Circuit 5”. Prentice Hall. US
• Tony R Kuphaldt. 2006. “Lessons in Electric Circuit. Vol I. DC”. Design Science
License. US
• Tony R Kuphaldt. 2007. “Lessons in Electric Circuit. Vol II. AC”. Design Science
License. US
• http://www.allaboutcircuits.com/vol_6/chpt_3/6.html
III. Devices
• Digital Multimeter
• Variable Power Supply
• Potentiometer
• Breadboard
• Components: R = 120, 150,180,220,470, 1K, 2K, 4K7
LED, Potentiometer
Physics 2 Computer Engineering Laboratory
Experiment 4 Page 3 of 7
IV. Instruction of Laboratory
A. Procedure
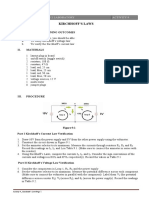
a. Kirchhoff Current Law
R1
+ _ 100
A
A B R4 E
+ 300 F
+ V PS C R3
R2
V
_ 5V D 1K 220
_ R5
220 G
X Y H
Figure 4.6
1. Design the circuit in Figure 4.4 into a breadboard.
2. Connect the power supply to the circuit.
3. Adjust the power supply to 5V.
4. Measure the current in the circuit according to table 4.1
Table 4.1
VPS (V) IAB ICD IEF IGH IXY
5V
10 V
Physics 2 Computer Engineering Laboratory
Experiment 4 Page 4 of 7
b. Kirchhoff Voltage Law
R1 R2 R3
+ -
A
470 1K 2K
I
+ +
4K7 R4
V -
Figure 4.7
1. Design the circuit in Figure 4.5 into a breadboard.
2. Connect the power supply to the circuit.
3. Adjust the power supply to 10V.
4. Measure the current and voltage in the circuit according to table 4.2.
Table 4.2
VPS I VR1 VR2 VR3 VR4
5V
10 V
Physics 2 Computer Engineering Laboratory
Experiment 4 Page 5 of 7
c. Voltage Divider Using Potentiometer
+
VAB
+ A -
+
VPS=10V VAC
-
-
B +
C VBC
-
1K
A
Figure 4.8
1. Design the components in Figure 4.6 into a breadboard.
2. Turn on the power supply and adjust the voltage to 10V (after the probe
connected to the circuit).
3. Turn the potentiometer CCW (Counter Clock Wise)
4. Write down the current and voltage according to table 4.3.
5. Look at the intensity of the LED.
6. Repeat the measurement by turning the potentiometer approximately in
the middle of the potentiometer and CW (Clock Wise).
Table 4.3
Potentiometer I VAB VBC VAC
CCW
Middle
CW
Physics 2 Computer Engineering Laboratory
Experiment 4 Page 6 of 7
B. Final Reports requirement for minimum grade
Analyze each experiment that you have done. In the analysis, give the explanation
about:
1. Kirchoff Voltage Law and Kirchoff Current Law
2. The difference between potentiometer and resistor
3. Potentiometer and how it works
4. Proof of Kirchoff Voltage Law on Potentiometer, the equivalent equation.
Explain how potentiometer can functionate as DC voltage divider[6]
5. Analyze every circuit
6. Make the calculation of each experiment
7. Compare the result that you get from the practicum with the simulation and
the theory
Make the theory and your experiment data as the reference in making
analysis and give the conclusion (5) about the experiment.
Physics 2 Computer Engineering Laboratory
Experiment 4 Page 7 of 7
You might also like
- Physics Percobaan 4 BOLDocument6 pagesPhysics Percobaan 4 BOLShafira PuspaningrumNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Kirchoff Voltage-Current Law and Potentiometer: I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesExperiment 7 Kirchoff Voltage-Current Law and Potentiometer: I. ObjectivesTasy WijayaNo ratings yet
- C&S 2 - Series Circuits, Parallel Circuits and Series-Parallel Circuits Ganjil 1920Document5 pagesC&S 2 - Series Circuits, Parallel Circuits and Series-Parallel Circuits Ganjil 1920Ambleh AmblehNo ratings yet
- Islamic University of Technology (Iut) : Course: Name of The ExperimentDocument2 pagesIslamic University of Technology (Iut) : Course: Name of The ExperimentshiamNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Kirchhoff's Laws: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesExperiment 5 Kirchhoff's Laws: ObjectiveLaxman TanwarNo ratings yet
- KirchoffDocument4 pagesKirchoffDavies SegeraNo ratings yet
- Eee111 Experiment 4Document6 pagesEee111 Experiment 4Amirul 0205No ratings yet
- Experiment#2 ENEE2103 Circuit Laws and Theorems: A. KVL, KCLDocument3 pagesExperiment#2 ENEE2103 Circuit Laws and Theorems: A. KVL, KCLhiba ibrahemNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff Laws and Network TheoremDocument12 pagesKirchhoff Laws and Network TheoremDeepak KumbharNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument43 pagesLab Manualrakesh143kasseNo ratings yet
- Analogue Electronics Iv - Practical UpdatedDocument8 pagesAnalogue Electronics Iv - Practical UpdatedAbba AbubakarNo ratings yet
- EE221 Lab Experiment #4: Inverting Amplifier Investigation: Fall 2014Document5 pagesEE221 Lab Experiment #4: Inverting Amplifier Investigation: Fall 2014MalikAlrahabiNo ratings yet
- Bee Manual PDFDocument32 pagesBee Manual PDFKishan VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Exp02v H1Document6 pagesExp02v H1jaswinder singhNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 LCA 15032022 085801amDocument3 pagesLab 4 LCA 15032022 085801amTayyab RizwanNo ratings yet
- Activity 5Document9 pagesActivity 5Fatima BaylasNo ratings yet
- EEE 234 - Electronics II LabDocument40 pagesEEE 234 - Electronics II Labjery tomNo ratings yet
- Activity 4: Mesh Analysis, Nodal Analysis and Superposition TheoremDocument23 pagesActivity 4: Mesh Analysis, Nodal Analysis and Superposition Theoremjian cool dudeNo ratings yet
- 112 SyllabusDocument10 pages112 Syllabusluoaier1016No ratings yet
- A9 Kirchhoff's Laws 2-1Document3 pagesA9 Kirchhoff's Laws 2-1Lance CadiangNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology 08082016Document46 pagesElectrical Technology 08082016AkNo ratings yet
- BEEI Lab Manual CompressedDocument85 pagesBEEI Lab Manual CompressedkavithaNo ratings yet
- Eee141 Lab ManualDocument29 pagesEee141 Lab ManualSakib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document5 pagesLab 6svijiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology Lab: Dronacharya College of Engineering Khentawas, Gurgaon - 123506Document46 pagesElectrical Technology Lab: Dronacharya College of Engineering Khentawas, Gurgaon - 123506Shreyansh RajNo ratings yet
- PUT Experiment EditedDocument9 pagesPUT Experiment EditedReineirDuranNo ratings yet
- Circuit TheoryDocument18 pagesCircuit Theorygokulphd100% (1)
- Physics Experiment 8 About ElectronicDocument9 pagesPhysics Experiment 8 About ElectronicFelixNo ratings yet
- Basic Analog For Digital Designers: What Is This Application Note Trying To Accomplish?Document6 pagesBasic Analog For Digital Designers: What Is This Application Note Trying To Accomplish?KidalaNo ratings yet
- Masuma Mam Lab 4 & 5Document8 pagesMasuma Mam Lab 4 & 5Md. HarunNo ratings yet
- Star DeltaDocument7 pagesStar DeltagopikrishnaraoNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: Table 1: Measured ValuesDocument7 pagesObjectives:: Table 1: Measured ValuesGian Jelo SalleNo ratings yet
- Ac Circuit Analysis by CorcoranDocument609 pagesAc Circuit Analysis by CorcoranPantho BaruaNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 6 Date Performed: - Rating: - Date Submitted: - Parallel RC - RL CircuitDocument3 pagesActivity No. 6 Date Performed: - Rating: - Date Submitted: - Parallel RC - RL CircuitSherwin PagpaguitanNo ratings yet
- Circuits and Electronic Laboratory: Purpose of ExperimentDocument5 pagesCircuits and Electronic Laboratory: Purpose of ExperimentFurkan YıldızNo ratings yet
- CAPE U2 LAB#2 Azariah BarrettDocument6 pagesCAPE U2 LAB#2 Azariah BarrettazaribarrNo ratings yet
- Practicle 1 KVL & KCLDocument5 pagesPracticle 1 KVL & KCLPritesh PandyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity - Presentation2Document25 pagesBasic Electricity - Presentation2andrew smithNo ratings yet
- Expt No 1 & 2 PDFDocument7 pagesExpt No 1 & 2 PDFd5vated5endNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Exp. 05 Even 2324Document11 pagesPhysics 2 Exp. 05 Even 2324ValerianNo ratings yet
- EEL 7300 - Chapter IV - Comparators 2022-2 - VisualsDocument26 pagesEEL 7300 - Chapter IV - Comparators 2022-2 - VisualsVanderson Xavier vandilolNo ratings yet
- Pw3 - Ac RL Parallel Circuit - v1Document6 pagesPw3 - Ac RL Parallel Circuit - v1Hairul Anuar Masrol100% (1)
- KVL and KCL Lab Report Number 06 Kirchofs Law To Verify Ohm LawDocument6 pagesKVL and KCL Lab Report Number 06 Kirchofs Law To Verify Ohm LawMuhAmmad AqiB ShAykh0% (1)
- ElectricalEngineerigLabManual IIECE PDFDocument75 pagesElectricalEngineerigLabManual IIECE PDFUpender Rao SunkishalaNo ratings yet
- Labreport TwoDocument11 pagesLabreport TwoTeshome GirmaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis LabDocument34 pagesCircuit Analysis LabveeraNo ratings yet
- Lab 04 - KVL, KCL, Nodal AnalysisDocument9 pagesLab 04 - KVL, KCL, Nodal Analysismatteo rossiNo ratings yet
- Prac1 For Egb120Document10 pagesPrac1 For Egb120Tam NguyenNo ratings yet
- Week1 NotesDocument53 pagesWeek1 NoteskkkprotNo ratings yet
- EEE 111 Lab Manual 4Document6 pagesEEE 111 Lab Manual 4SHADOW manNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Thevenin StevensDocument7 pagesLab 4 Thevenin StevenskarthikhrajvNo ratings yet
- Potentiometers and The Wheatstone BridgeDocument5 pagesPotentiometers and The Wheatstone Bridgekumarkushagra7777No ratings yet
- Intermediate Lab PHYS 3140 CircuitsDocument36 pagesIntermediate Lab PHYS 3140 CircuitsHighway RiderNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual I Sem Basic ElectricalDocument48 pagesLab Manual I Sem Basic ElectricalGoutami T SunthankarNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Electric Circuit Analysis I CPE121Document8 pagesLab Manual: Electric Circuit Analysis I CPE121earn moneyNo ratings yet
- A9 Kirchhoffs LawsDocument3 pagesA9 Kirchhoffs LawsjakeNo ratings yet
- EgfuiefeufhedfDocument44 pagesEgfuiefeufhedfDimple EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- Lab 11 - RC and RL FiltersDocument8 pagesLab 11 - RC and RL FiltersTanzim ElahiNo ratings yet
- Eepc28 Jun 2019Document2 pagesEepc28 Jun 2019AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Antioxidant Enzyme Activity During Germination of Alfalfa Under Salt and Drought StressesDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Antioxidant Enzyme Activity During Germination of Alfalfa Under Salt and Drought StressesJimenoNo ratings yet
- RCC BoxDocument85 pagesRCC Boxabhijeet sahuNo ratings yet
- DR Tian Sing NG, BOSFA Fibres For Crack Control PDFDocument68 pagesDR Tian Sing NG, BOSFA Fibres For Crack Control PDFsaiNo ratings yet
- Msds NitobenzeneDocument5 pagesMsds NitobenzeneAnngie Nove SimbolonNo ratings yet
- OLIVE VIEW HOSPITAL-San Fernando Earthquake 1971 PDFDocument5 pagesOLIVE VIEW HOSPITAL-San Fernando Earthquake 1971 PDFZakir UllahNo ratings yet
- Principle of Virtual Work and Its ApplicationDocument7 pagesPrinciple of Virtual Work and Its Applicationprem adhikari100% (1)
- Fluidization - Expansion Equations For Fluidized Solid Liquid Systems (Akgiray and Soyer, 2006)Document10 pagesFluidization - Expansion Equations For Fluidized Solid Liquid Systems (Akgiray and Soyer, 2006)Moisés MachadoNo ratings yet
- BOSCH FLEXIDOME Multi 7000 - DatasheetDocument8 pagesBOSCH FLEXIDOME Multi 7000 - DatasheetMarlon Cruz CruzNo ratings yet
- P.B.B.SC Nsg. Syllabus Original PDFDocument57 pagesP.B.B.SC Nsg. Syllabus Original PDFRajalakshmi SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- An Open Letter To Annie Besant PDFDocument2 pagesAn Open Letter To Annie Besant PDFdeniseNo ratings yet
- Solving Poisson's Equation Using The FFTDocument9 pagesSolving Poisson's Equation Using The FFTJhon CerónNo ratings yet
- Mic Fright and Camera PanicDocument5 pagesMic Fright and Camera PanicNica Arizapa100% (1)
- Tugas Basing MandaDocument5 pagesTugas Basing MandaSalman AlfariziNo ratings yet
- 10th PET POW EM 2023 24Document6 pages10th PET POW EM 2023 24rpradeepa160No ratings yet
- GG IFA CPCC FV V5 2 enDocument151 pagesGG IFA CPCC FV V5 2 enNys Del Tropico SaNo ratings yet
- Forklift Bucket 1400B - ManualDocument4 pagesForklift Bucket 1400B - ManualVie LiesnaNo ratings yet
- Australian Mathematics Competition 2017 - SeniorDocument7 pagesAustralian Mathematics Competition 2017 - SeniorLaksanara KittichaturongNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument110 pagesPDFBikash NayakNo ratings yet
- RELI 280 NotesDocument7 pagesRELI 280 NotesFaith KentNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Developing and Evaluating Utility Substation Cyber Security - Schneider ElectricDocument10 pagesA Framework For Developing and Evaluating Utility Substation Cyber Security - Schneider ElectricHugh cabNo ratings yet
- AC Centrifugal Fan: D4E225-CC01-02Document5 pagesAC Centrifugal Fan: D4E225-CC01-02Santosh KumarNo ratings yet
- (Ethics) AttitudeDocument46 pages(Ethics) AttitudeAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- 2004 Timbre To DissonanceDocument4 pages2004 Timbre To DissonancetgraubaenaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Studies GR 11 Revision Term 1 2023 FinalDocument20 pagesConsumer Studies GR 11 Revision Term 1 2023 FinalCerboh MazibukoNo ratings yet
- Engrave-O-Matic Custom Laser Engraving CatalogDocument32 pagesEngrave-O-Matic Custom Laser Engraving Catalogds8669No ratings yet
- PHontDawg Vol.2 2007Document8 pagesPHontDawg Vol.2 2007Tanczos AndrasNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Chapter-1Document61 pagesComputer Graphics Chapter-1abdi geremewNo ratings yet
- 04 Dispersion MeasuresDocument17 pages04 Dispersion MeasuresMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Analisis Sensori Produk Stik Sukun (Artocarpus Altilis) Dengan Perlakuan Pendahuluan Blanching Dan Perendaman Dalam Larutan Kalsium KloridaDocument6 pagesAnalisis Sensori Produk Stik Sukun (Artocarpus Altilis) Dengan Perlakuan Pendahuluan Blanching Dan Perendaman Dalam Larutan Kalsium KloridaTommy ChandraNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutics Exam 3 - This SemesterDocument6 pagesPharmaceutics Exam 3 - This Semesterapi-3723612100% (1)