Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Choice of The Test To Do
Uploaded by
Amelie HeckmannOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Choice of The Test To Do
Uploaded by
Amelie HeckmannCopyright:
Available Formats
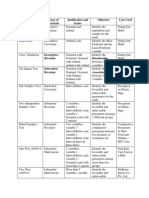
Statistical test-finder for biologists
Are there significant differences between the means or
Is there a relationship between two (or more) variables? Are there significant differences between the observed and
medians of measurements made on objects from two or
What is the mathematical relationship describing the expected numbers of objects or events classified into two or
more samples, or a single sample and a theoretical or
dependence of one variable on the other? more categories?
expected value?
Difference between a sample Difference between Difference between Strength of relationship, Strength of relationship, not
and a single value two samples more than two assuming one variable assuming one variable
samples dependent on the other dependent on the other
Paired samples
Unpaired samples
(linked in space Interval or ratio data,
Ordinal data or or time) linear relationship
not normally between X and Y,
Ratio or distributed variance of Y similar for Interval or ratio data, Ordinal data or
interval data, Ratio or increasing X values, normally distributed, one or more
Ratio or interval
normally Ordinal data or interval data, Ordinal data or residuals normal linear relationship variables non-
data, differences
distributed not normally normally not normally between X and Y normal
between pairs
normal distributed distributed distributed distributed
Regression (multiple
regression if more Rank
1-sample Wilcoxon Paired- Wilcoxon 2-sample Mann-Whitney than one ‘predictor’ Correlation correlation
t-test (signed-rank) test sample t-test (signed-rank) test t-test U test variable) (Pearson’s) (Spearman’s)
One set of treatments (different levels of one Two different types of treatment
factor or single levels of different factors) with two or more levels.
Objects or events Objects or events
Ratio or interval data,
classified into two or more classified into
Ordinal data or don’t residuals normally
Ratio or interval categories (e.g. sex) and categories by more
meet assumptions distributed, equal
data, residuals compared with predicted than one variable (e.g.
(residuals not normal, variances
normally distributed, proportions sex, eye colour)
variances equal unequal variances)
Two-way ANOVA
Chi-squared Chi-squared
One-way ANOVA Kruskal-Wallis test ANOVA significant and need to identify goodness of fit contingency table
differences between treatments
ANOVA significant and need to identify
differences between treatments
Interaction significant Interaction not significant
Multiple
comparison Tukey test of Tukey test of
test (Tukey) all means significant
treatments
You might also like
- Decision Chart PDFDocument2 pagesDecision Chart PDFSarkis Der VartanianNo ratings yet
- Which Statistical Tests To UseDocument2 pagesWhich Statistical Tests To Useian1231No ratings yet
- A Guide To Writing Thesis and Dissertation 1Document72 pagesA Guide To Writing Thesis and Dissertation 1louella repolloNo ratings yet
- 7d-Word SheetDocument6 pages7d-Word SheetKwan Ye LinNo ratings yet
- Michael Akritas - Probability Statistics With R For Engineers and Scientists (2015, Pearson)Document512 pagesMichael Akritas - Probability Statistics With R For Engineers and Scientists (2015, Pearson)JUAN JOSE ARIZA VELASCONo ratings yet
- Discrete Choice Models 2Document19 pagesDiscrete Choice Models 2Pebri HerryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10-Inference About Means and Proportions With Two PopulationsDocument69 pagesChapter 10-Inference About Means and Proportions With Two PopulationsyayayaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics: Table of ContentsDocument54 pagesAdvanced Statistics: Table of ContentsMARINANo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability - q4 - Mod4 - Identifying Parameter To Be Tested Given A Real Life-Problem - V2 PDFDocument25 pagesStatistics and Probability - q4 - Mod4 - Identifying Parameter To Be Tested Given A Real Life-Problem - V2 PDFMoreal QazNo ratings yet
- Overview Of Bayesian Approach To Statistical Methods: SoftwareFrom EverandOverview Of Bayesian Approach To Statistical Methods: SoftwareNo ratings yet
- PsychAssess 13 TableStatisticsDocument7 pagesPsychAssess 13 TableStatisticsMaricrise FernandezNo ratings yet
- Q2 PR2-Weeks-7-8-CONCLUSIONDocument12 pagesQ2 PR2-Weeks-7-8-CONCLUSIONmacristinaisabel.talladorNo ratings yet
- Giped OutlineDocument3 pagesGiped Outlineapi-525576012No ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics: Paper #6Document11 pagesAdvanced Statistics: Paper #6Precious NosaNo ratings yet
- 408 MidDocument7 pages408 Midshishirar.12No ratings yet
- Assumptions For Different Kinds of StatisticsDocument3 pagesAssumptions For Different Kinds of StatisticsErika ToralbaNo ratings yet
- PsychAssess 13 TableStatisticsDocument6 pagesPsychAssess 13 TableStatisticsWinona JardinelNo ratings yet
- Psychological Assessment HW #4Document8 pagesPsychological Assessment HW #4maerucelNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method in The Social SciencesDocument3 pagesScientific Method in The Social SciencesLemon LakwatseraNo ratings yet
- ResumenDocument10 pagesResumencwdfcvqfsvNo ratings yet
- PR ReviewerDocument3 pagesPR ReviewerMika VillarazaNo ratings yet
- Sigmaxl SummaryDocument24 pagesSigmaxl Summaryleonel alejandro peña ramirezNo ratings yet
- Lesson For T TestsDocument53 pagesLesson For T TestsShin GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Activity 4 - Visual Representation of Data WorksheetDocument2 pagesUnit 3 - Activity 4 - Visual Representation of Data WorksheetNidhi VyasNo ratings yet
- Statistical Test Decision TreeDocument2 pagesStatistical Test Decision TreeCelyn GaholNo ratings yet
- Statistics InfographicDocument1 pageStatistics Infographic422001262No ratings yet
- Linear RegressionDocument10 pagesLinear RegressionAlan RamirezNo ratings yet
- Principles of Correlation Analysis: Statistics For ResearchersDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Correlation Analysis: Statistics For ResearchersMKashifKhurshid100% (1)
- 9-Principles of Correlation-1 PDFDocument4 pages9-Principles of Correlation-1 PDFPrince Alexis GarciaNo ratings yet
- MKT500 - Week 11 - Winter 2023 - D2LDocument81 pagesMKT500 - Week 11 - Winter 2023 - D2Lsyrolin123No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Compare Groups)Document11 pagesChapter 4 (Compare Groups)Hend maarofNo ratings yet
- Umar Zahid 2022-MBA-628 Applied Data AnalysisDocument12 pagesUmar Zahid 2022-MBA-628 Applied Data AnalysisTECH CENTRALNo ratings yet
- Chap011 UpdatedDocument34 pagesChap011 UpdatedTiến Bùi MinhNo ratings yet
- Inferential Statistics: IdentifyDocument7 pagesInferential Statistics: Identifysean michael leomoNo ratings yet
- Immanuel T. San Diego, M.S.: Range, RDocument2 pagesImmanuel T. San Diego, M.S.: Range, RDUQUE DANA KATENo ratings yet
- Activity 3-Table Completion On Parametric Test-Hazel P. PatalotDocument2 pagesActivity 3-Table Completion On Parametric Test-Hazel P. PatalothazelppatalotNo ratings yet
- Learning Log Group 4 Student Name/NpmDocument3 pagesLearning Log Group 4 Student Name/Npmwisnu adiNo ratings yet
- Steps and Techniques For SpssDocument11 pagesSteps and Techniques For SpssShreyas BhasinNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 - Correlation CorrelationDocument6 pagesLECTURE 1 - Correlation CorrelationJANISCHAJEAN RECTONo ratings yet
- Covariance and Correlation-9Document3 pagesCovariance and Correlation-9Shobha Kumari ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Stat Sa ResearchDocument2 pagesStat Sa ResearchLhiana Mari PeñaredondoNo ratings yet
- Techniques & Steps To Follow in SPSSDocument10 pagesTechniques & Steps To Follow in SPSSPragya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Techniques & Steps To Follow in SPSSDocument10 pagesTechniques & Steps To Follow in SPSSRicha ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- Lesson - 4.2 - Exploratory Data Analysis - Analyze - PhaseDocument50 pagesLesson - 4.2 - Exploratory Data Analysis - Analyze - PhaseHarika KalluriNo ratings yet
- Summar Quant Designs ChartDocument1 pageSummar Quant Designs ChartYoni MacNo ratings yet
- Pearson Correlation - SPSS Tutorials - LibGuides at Kent State UniversityDocument13 pagesPearson Correlation - SPSS Tutorials - LibGuides at Kent State Universityjohn gabrielNo ratings yet
- Lesson-2 Psych AssDocument3 pagesLesson-2 Psych Assalliahc.vergaraNo ratings yet
- What Does A Statistical Test DoDocument16 pagesWhat Does A Statistical Test DoRenato PanesNo ratings yet
- Zometric Qtools Features ListDocument1 pageZometric Qtools Features ListRakesh JangraNo ratings yet
- SPSS Procedures SummaryDocument1 pageSPSS Procedures SummaryMohnmad ZaitoonNo ratings yet
- Correlation Regression - Summary NotesDocument4 pagesCorrelation Regression - Summary NotesRockyNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research: Ninth EditionDocument44 pagesMarketing Research: Ninth EditionSara DassouliNo ratings yet
- Common Statistical Tools For AnalysisDocument9 pagesCommon Statistical Tools For AnalysisCyeonjNo ratings yet
- Choosing The Appropriate Statistic: Some Factors To ConsiderDocument15 pagesChoosing The Appropriate Statistic: Some Factors To Considerfiel borataNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 1. Introduction and FrameworkDocument22 pagesPertemuan 1. Introduction and FrameworkJONATHAN SOELISTYONo ratings yet
- Analysing Quantitative DataDocument33 pagesAnalysing Quantitative DataSumayyah ArslanNo ratings yet
- Statistical ToolsDocument3 pagesStatistical ToolsReizhelle AbisNo ratings yet
- 05 1 Correlation PDFDocument7 pages05 1 Correlation PDFKristen DiazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Probability and StatisticsDocument19 pagesChapter 4 Probability and StatisticsIsokingNo ratings yet
- Statistical TreatmentDocument7 pagesStatistical TreatmentIvy Frias JapaNo ratings yet
- Distribution Test: Nadira Wulan Ramadhini 190403093 Kelompok VII Gelombang I CDocument10 pagesDistribution Test: Nadira Wulan Ramadhini 190403093 Kelompok VII Gelombang I CDira WRNo ratings yet
- Predictive Analytics-Mid Sem Exam Question BankDocument28 pagesPredictive Analytics-Mid Sem Exam Question BankyashpatelykpNo ratings yet
- Brainsci 07 00026Document11 pagesBrainsci 07 00026somayealinaghiNo ratings yet
- Roadmap For A Statistical InvestigationDocument2 pagesRoadmap For A Statistical InvestigationAbhishekKumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Biostatistics for Geneticists and Epidemiologists: A Practical ApproachFrom EverandBasic Biostatistics for Geneticists and Epidemiologists: A Practical ApproachNo ratings yet
- Table For Spearman CorrelationDocument1 pageTable For Spearman CorrelationAmelie HeckmannNo ratings yet
- Sequencing Macrogen EZSeqDocument2 pagesSequencing Macrogen EZSeqAmelie HeckmannNo ratings yet
- Citation of The Results of Statistical TestsDocument2 pagesCitation of The Results of Statistical TestsAmelie HeckmannNo ratings yet
- HMMER User's Guide: Version 3.1b2 February 2015Document120 pagesHMMER User's Guide: Version 3.1b2 February 2015Amelie HeckmannNo ratings yet
- Zadok S 1974Document8 pagesZadok S 1974Amelie HeckmannNo ratings yet
- Explanation of The Decimal Code For The Growth Stages of Cereals, With IllustrationsDocument14 pagesExplanation of The Decimal Code For The Growth Stages of Cereals, With IllustrationsAmelie HeckmannNo ratings yet
- Review snrk1Document7 pagesReview snrk1Amelie HeckmannNo ratings yet
- Ciaran Septo EarlyDocument12 pagesCiaran Septo EarlyAmelie HeckmannNo ratings yet
- Structure, Heterologous Expression, and Properties of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Family 19 ChitinasesDocument8 pagesStructure, Heterologous Expression, and Properties of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Family 19 ChitinasesAmelie HeckmannNo ratings yet
- Structure Heterologous Expression and Properties of Rice Oryza Sativa L Family 19 ChitinasesDocument9 pagesStructure Heterologous Expression and Properties of Rice Oryza Sativa L Family 19 ChitinasesAmelie HeckmannNo ratings yet
- Don State of Art Zhang2020Document9 pagesDon State of Art Zhang2020Amelie HeckmannNo ratings yet
- A7 Cruz ManalastasDocument4 pagesA7 Cruz ManalastasPatricia CruzNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum StatDas2020 - Siti Rubi'Ah (G1B019069) FISIKA ADocument59 pagesLaporan Praktikum StatDas2020 - Siti Rubi'Ah (G1B019069) FISIKA ASiti Rubi'ahNo ratings yet
- 新增 Microsoft Word DocumentDocument10 pages新增 Microsoft Word DocumentAlex MacNo ratings yet
- Properties and Implementation of Jeffreys's Prior in Binomial Regression ModelsDocument13 pagesProperties and Implementation of Jeffreys's Prior in Binomial Regression ModelssssNo ratings yet
- Forecasting Using EviewsDocument4 pagesForecasting Using EviewsLucia SpineiNo ratings yet
- Tidyverse: Core Packages in TidyverseDocument8 pagesTidyverse: Core Packages in TidyverseAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Northern - Southeast Case StudyDocument8 pagesNorthern - Southeast Case StudyYogeshLuhar100% (3)
- Chapter 6: How To Do Forecasting by Regression AnalysisDocument7 pagesChapter 6: How To Do Forecasting by Regression AnalysisSarah Sally SarahNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis - Testing General MathDocument20 pagesHypothesis - Testing General MathHa KDOGNo ratings yet
- Effectech - Calibration GasesDocument36 pagesEffectech - Calibration GasesThomas FinnsNo ratings yet
- De La Salle University - Dasmariñas: Mathematics and Statistics DepartmentDocument3 pagesDe La Salle University - Dasmariñas: Mathematics and Statistics DepartmentAxl Arboleda ValiolaNo ratings yet
- Aditya Amalda Putra Dan Shandy Marsono (2020)Document11 pagesAditya Amalda Putra Dan Shandy Marsono (2020)Jesslyn VaniaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence MCQDocument5 pagesArtificial Intelligence MCQSidraMalik100% (2)
- FINAL EXAM 2020 - INDU 6310 - Concordia UniversityDocument11 pagesFINAL EXAM 2020 - INDU 6310 - Concordia UniversityRapheal AdamNo ratings yet
- VAR Models With Exogenous VariablesDocument6 pagesVAR Models With Exogenous VariablesAbhishek PuriNo ratings yet
- S Doc1Document7 pagesS Doc1ejoneel100% (1)
- Statistics For The Non Statistician (Greenhalgh 1997)Document7 pagesStatistics For The Non Statistician (Greenhalgh 1997)Bextiyar BayramlıNo ratings yet
- PSMatchingDocument55 pagesPSMatchingJuan ToapantaNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument2 pagesStatisticsmarkNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Meco6315.501.07s Taught by John Wiorkowski (Wiorkow)Document4 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Meco6315.501.07s Taught by John Wiorkowski (Wiorkow)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Forecasting Market Share Using Predicted Values of Competitive BehaviorDocument23 pagesForecasting Market Share Using Predicted Values of Competitive BehaviormaleticjNo ratings yet
- Cohen's Conventions For Small, Medium, and Large Effects: Difference Between Two MeansDocument2 pagesCohen's Conventions For Small, Medium, and Large Effects: Difference Between Two MeansJonathan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- T Stat Vs F StatDocument2 pagesT Stat Vs F StatayyazmNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Data Pre-Processing and VisualizationDocument11 pagesCourse Title: Data Pre-Processing and VisualizationIntekhab Aslam100% (2)
- Case Processing SummaryDocument6 pagesCase Processing Summaryal ghaisaniNo ratings yet