Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Statistics Infographic
Uploaded by
422001262Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Statistics Infographic
Uploaded by
422001262Copyright:
Available Formats
Kimberlie Joy S.
Zabala
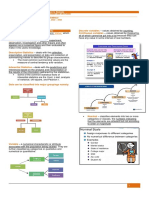
Statistics
The primary objective of the mathematical discipline known as
statistics is the study of collecting, organizing, analyzing,
interpreting, and presenting data.
BRANCHES OF STATISTICS
Descriptive Statistics Inferential Statistics
It involves methods of organizing, It involves making inferences or predictions
summarizing, and presenting data in an about a population based on a sample of data.
informative way. It helps to describe and It uses the information gathered from a
understand the features of a specific data sample to make generalizations or predictions
set. about a larger group.
Kinds of Data
Quantitative data is numerical data
Qualitative data is descriptive data that is
that can be measured and counted. It
categorical in nature. It describes qualities
represents quantities and can be used
or characteristics and cannot be measured
to perform mathematical calculations.
in numerical terms. (Colors, Emotions,
(Heights, Weights, Ages, Test scores,
Names, Shapes, Textures)
Number of items
Variables
Variables are characteristics or
properties that can take on different
values.
Qualitative vs Quantitative Levels of
Measurement
Qualitative variables represent characteristics.
Nominal Interval
Quantitative variables represent numerical
values. Ordinal Ratio
Descriptive Descriptive statistics are used to
Statistics
describe the basic features of the data.
Frequency Percentage Cross Grouped and
Distribution Distribution Tabulations Ungrouped
Data
shows the number shows the used to show the Data can be
of occurrences of percentage of relationship presented in
each value. occurrences of between two grouped or
each value variables. ungrouped form.
Measures of Central Tendency
RANGE MEAN MEDIAN MODE
The Range is the In mathematics and The median is the The mode is the value that
difference between the statistics, the mean refers middle value in a set of appears most frequently in
lowest and highest values. to the average of a set of data. a data set.
values.
used to make inferences or predictions about
Inferential Statistics
a population based on a sample of data.
PEARSON'S HYPOTHESIS
T-TEST
CORRELATION TESTING
Independent Pearson's correlation Hypothesis testing
Paired coefficient measures involves making
the strength and inferences about a
direction of the population based
relationship between on a sample.
two variables.
You might also like
- Statistics: Population and Sample Parameter and StatisticsDocument5 pagesStatistics: Population and Sample Parameter and StatisticsShanna Basallo AlentonNo ratings yet
- Lesson-6 - Data AnalysisDocument24 pagesLesson-6 - Data AnalysisLloyd PawaonNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Data Analysis GuideDocument3 pagesStatistics and Data Analysis GuideMika VillarazaNo ratings yet
- Intro To StatisticsDocument11 pagesIntro To StatisticsYan DuyoNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument27 pagesStatisticspsychic_jason0071319100% (1)
- Practical Research Wk. 5Document5 pagesPractical Research Wk. 5Jamelle AbitNo ratings yet
- Psych Assessment Chap 2Document4 pagesPsych Assessment Chap 2Elijah DiazNo ratings yet
- CLEOFAS MidtermResearch2Document11 pagesCLEOFAS MidtermResearch2keithNo ratings yet
- Distribution Test: Nadira Wulan Ramadhini 190403093 Kelompok VII Gelombang I CDocument10 pagesDistribution Test: Nadira Wulan Ramadhini 190403093 Kelompok VII Gelombang I CDira WRNo ratings yet
- Data Management: Bryan S. AmbreDocument104 pagesData Management: Bryan S. AmbreAlexander SiccuanNo ratings yet
- Regression Analysis and Statistical Learning in Social Science ResearchDocument59 pagesRegression Analysis and Statistical Learning in Social Science ResearchA Y I E SNo ratings yet
- PSYCH 2104 Stats OverviewDocument21 pagesPSYCH 2104 Stats Overviewzy- SBGNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 1. Introduction and FrameworkDocument22 pagesPertemuan 1. Introduction and FrameworkJONATHAN SOELISTYONo ratings yet
- Stats Crib Sheet ExamDocument2 pagesStats Crib Sheet ExamthandiNo ratings yet
- Nursing research data analysisDocument3 pagesNursing research data analysisRomeo RiveraNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statisitics Sir EricDocument46 pagesDescriptive Statisitics Sir Ericwendydeveyra7No ratings yet
- MathDocument13 pagesMathmmeiylia6No ratings yet
- Bahan - Matrikulasi Statistik-Bag 1Document68 pagesBahan - Matrikulasi Statistik-Bag 1Arisa MayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To StatisticsDocument3 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To StatisticsRae WorksNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3-Data-ManagementDocument21 pagesChapter-3-Data-ManagementroivincentblasNo ratings yet
- MMW Notes IiDocument14 pagesMMW Notes IiMervis EncelanNo ratings yet
- RapportDocument11 pagesRapportAMINA BEN TAHARNo ratings yet
- Statistics: Defining Data, Variables, Levels of MeasurementDocument1 pageStatistics: Defining Data, Variables, Levels of MeasurementRiyan HidayatNo ratings yet
- Week 5A - Statistics HandoutDocument9 pagesWeek 5A - Statistics HandoutPeter John TevesNo ratings yet
- mmw-reviewer-data-managementDocument17 pagesmmw-reviewer-data-managementgwenayatsNo ratings yet
- Basics of statistics for postgraduatesDocument5 pagesBasics of statistics for postgraduatesWahid QureshiNo ratings yet
- Notes 3i'sDocument14 pagesNotes 3i'sdevy mar topiaNo ratings yet
- 408 midDocument7 pages408 midshishirar.12No ratings yet
- Distribution Test: Nadira Wulan Ramadhini 190403093 Kelompok VII/I CDocument5 pagesDistribution Test: Nadira Wulan Ramadhini 190403093 Kelompok VII/I CDira WRNo ratings yet
- StatisticDocument13 pagesStatisticnandaaungwdnNo ratings yet
- Psychological Assessment (Midterms)Document20 pagesPsychological Assessment (Midterms)ale.cristianNo ratings yet
- Bioe211 Week 1-NB - DPDocument3 pagesBioe211 Week 1-NB - DPFormosa G.No ratings yet
- MATM: Introduction to StatisticsDocument2 pagesMATM: Introduction to StatisticsANGEL ESTRADANo ratings yet
- Thesis Statistical TreatmentDocument8 pagesThesis Statistical TreatmentCarlville Jae EdañoNo ratings yet
- Group Research Introduction To StatisticsDocument5 pagesGroup Research Introduction To StatisticsJustine Leigh Garcia FloresNo ratings yet
- A Date With Data - Introduction To DataDocument30 pagesA Date With Data - Introduction To DataDarryl Mark LapuzNo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics Day 1Document61 pagesAdvanced Statistics Day 1촏교새벼No ratings yet
- Nature of StatisticsDocument5 pagesNature of StatisticsShenne Ann MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research: Ninth EditionDocument44 pagesMarketing Research: Ninth EditionSara DassouliNo ratings yet
- Scale of MeasurementDocument10 pagesScale of MeasurementOloyede TosinNo ratings yet
- Psychological Assessment HW #3Document7 pagesPsychological Assessment HW #3maerucelNo ratings yet
- Basic Terms and Concept of Statistics: Here Starts The Lesson!Document8 pagesBasic Terms and Concept of Statistics: Here Starts The Lesson!Joan Shin MaghanoyNo ratings yet
- Statistics AND Probabilit YDocument8 pagesStatistics AND Probabilit YDenise Jane DesoyNo ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis and InterpretationDocument4 pagesStatistical Analysis and InterpretationgailNo ratings yet
- 3 Matm111Document3 pages3 Matm111wooziwaegNo ratings yet
- Stats 201 Midterm SheetDocument2 pagesStats 201 Midterm SheetLisbon AndersonNo ratings yet
- The Data Analyst's Guide To Data Types, Distributions, and Statistical TestsDocument38 pagesThe Data Analyst's Guide To Data Types, Distributions, and Statistical TestsMiltonNo ratings yet
- Finals Research LecDocument4 pagesFinals Research LecKylle AlimosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 2Document4 pagesChapter 1 2Julius BoitizonNo ratings yet
- STATISTICAL TOOLS NEEDED IN ANALYZING TEST RESULTSDocument110 pagesSTATISTICAL TOOLS NEEDED IN ANALYZING TEST RESULTSJo MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Quiz ReviewerDocument10 pagesQuiz ReviewerVince Luigi ZepedaNo ratings yet
- Week 01, PT 1Document16 pagesWeek 01, PT 1Jane DoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Data AnalysisDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Data AnalysisGahnzelle Eidref FerreriaNo ratings yet
- Summary Topic Coverage For Prelim Grading PeriodDocument20 pagesSummary Topic Coverage For Prelim Grading PeriodfabyunaaaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledLwmdasja DhshdsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1:: Basic Terminologies in StatisticsDocument3 pagesLesson 1:: Basic Terminologies in StatisticsDmzjmb SaadNo ratings yet
- Q2 PR2-Weeks-7-8-CONCLUSIONDocument12 pagesQ2 PR2-Weeks-7-8-CONCLUSIONmacristinaisabel.talladorNo ratings yet
- Overview Of Bayesian Approach To Statistical Methods: SoftwareFrom EverandOverview Of Bayesian Approach To Statistical Methods: SoftwareNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics Explored Through R Software: An OverviewFrom EverandBiostatistics Explored Through R Software: An OverviewRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- CCNA 200 125 171q by PenPineappleApplePen Protected 1 PDFDocument66 pagesCCNA 200 125 171q by PenPineappleApplePen Protected 1 PDFmsansari1984No ratings yet
- Excel INDIRECT Function TutorialDocument14 pagesExcel INDIRECT Function TutorialLITTLE HEARTS JOHNNo ratings yet
- RSS4BHARAT: Debunking Myths Around RSS VisionDocument13 pagesRSS4BHARAT: Debunking Myths Around RSS VisionLekshminarayanan SNo ratings yet
- SQL Interview Questions 2021Document18 pagesSQL Interview Questions 2021K RUKESHNo ratings yet
- C2 - Enriched Viewing Comprehension - Ritu BhasinDocument2 pagesC2 - Enriched Viewing Comprehension - Ritu Bhasin4103511No ratings yet
- Files PDFDocument76 pagesFiles PDFArun prakashNo ratings yet
- Smirnov - A Course of Higher Mathematics - Vol 3-2 - Complex Variables Special FunctionsDocument713 pagesSmirnov - A Course of Higher Mathematics - Vol 3-2 - Complex Variables Special FunctionsDungNo ratings yet
- Religion and SpiritualityDocument1 pageReligion and SpiritualityJuris Kim A. ParingNo ratings yet
- RTP MIL LAS Q3 Wk4 MELC4Document6 pagesRTP MIL LAS Q3 Wk4 MELC4Mikhaila FernandezNo ratings yet
- March 23, Unit 8B: U N A M F D C I I VI English at HomeDocument3 pagesMarch 23, Unit 8B: U N A M F D C I I VI English at HomeLuis CastelanNo ratings yet
- Create AD Domain Users and Groups On The AD Domain ControllerDocument19 pagesCreate AD Domain Users and Groups On The AD Domain ControllerAlfred SalazarNo ratings yet
- Rotten Beef and Stinking FishDocument11 pagesRotten Beef and Stinking FishLyn Gajete100% (1)
- Direct Instruction: Present, Apply, Review (PAR) : Presenter: Regie A. RamisoDocument20 pagesDirect Instruction: Present, Apply, Review (PAR) : Presenter: Regie A. RamisoRegie RamisoNo ratings yet
- College Nursing Research Framework VariablesDocument6 pagesCollege Nursing Research Framework VariablesJoshua MendozaNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Grammatical Forms Are Built by Means of The Morphemic Composition of TheDocument3 pagesSynthetic Grammatical Forms Are Built by Means of The Morphemic Composition of TheСергей АлександровNo ratings yet
- Getting Into A Relationship _ PDF _ LoveDocument1 pageGetting Into A Relationship _ PDF _ Lovemanfamily305No ratings yet
- Kinds of SentencesDocument11 pagesKinds of SentencesLorena ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Order ManagementDocument53 pagesOrder ManagementJamme CeraNo ratings yet
- The Manobo Tasaday: Real People, Real FilipinoDocument1 pageThe Manobo Tasaday: Real People, Real FilipinoBea RosalesNo ratings yet
- Barbie CommercialsDocument4 pagesBarbie Commercialsapi-569001207No ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Computer Hardware - INPUTDocument11 pagesChapter 2. Computer Hardware - INPUTMomina B KhanNo ratings yet
- CSC 3216 COMPILER DESIGN Course Outline Spring-21-22Document14 pagesCSC 3216 COMPILER DESIGN Course Outline Spring-21-22MD RIYADH SHEIKHNo ratings yet
- 02 OnScreen 2 Unit 2Document12 pages02 OnScreen 2 Unit 2Kami MagNo ratings yet
- P1Document44 pagesP1Miquel Pelegrí QuevedoNo ratings yet
- Letter H PronunciationDocument4 pagesLetter H PronunciationAntonioNo ratings yet
- Written Test 12º Language MattersDocument3 pagesWritten Test 12º Language MattersclarasoaresNo ratings yet
- P810 For Windows - Manual PDFDocument133 pagesP810 For Windows - Manual PDFSiding BarroNo ratings yet
- Max Flow AlgorithmDocument6 pagesMax Flow Algorithmjbanik85No ratings yet
- 7.7 Making ComparisonsDocument32 pages7.7 Making ComparisonsYuenYing TseNo ratings yet
- Web Technologies Lab ManualDocument107 pagesWeb Technologies Lab ManualEdward Williams100% (1)