Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Primitive Brain (More Than 500 Million Years Ago)
Primitive Brain (More Than 500 Million Years Ago)
Uploaded by
ansofy354Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Primitive Brain (More Than 500 Million Years Ago)
Primitive Brain (More Than 500 Million Years Ago)
Uploaded by
ansofy354Copyright:
Available Formats
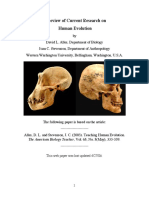
Primitive brain (more than 500 million years ago):
The first brains were simple structures consisting mainly of nerve ganglia.
These primitive brains were found in marine organisms, such as annelids (worms) and
mollusks.
Reptilian brain (approximately 300 million years ago):
With the evolution of reptiles, a larger, more complex brain known as the "reptilian brain"
developed.
This brain controls basic functions such as survival, aggression, reproduction and regulation
of the body.
Paleomammal brain (about 200 million years ago):
Early mammals developed a structure called the "paleomammal brain" or the "limbic brain."
This brain added the ability to experience emotions and care for offspring.
Neomammalian brain (about 150 million years ago):
Mammals further evolved to develop the "neomammal brain," which includes the neocortex.
The neocortex is a highly folded outer layer of the brain that is responsible for advanced
cognitive functions such as rational thinking, language, planning, and decision making.
Human brain (approximately 2 million years ago):
Human ancestors, such as Homo habilis, began to develop larger, more complex brains.
The evolution of the Homo species, including Homo erectus and Homo neanderthalensis,
continued with an increase in brain size and complexity.
Modern humans, Homo sapiens, have notoriously large brains relative to their body size and
are capable of a wide range of complex cognitive functions.
Hadic Aeon:
About 4.6 billion years ago to about 4 billion years ago.
This eon began with the formation of the Earth and was a period characterized by high
temperatures, intense volcanic activity, and the formation of early oceans.
Archaic Aeon:
Approximately 4 billion years ago to about 2.5 billion years ago.
During this time, the initial continents were formed, and it is believed that life in the form of
primitive microorganisms began to develop.
Proterozoic Eon:
About 2.5 billion years ago to about 541 million years ago.
In this eon, important changes occurred in the atmosphere and life began to diversify,
including the emergence of multicellular organisms.
Phanerozoic Eon:
It began approximately 541 million years ago and continues to the present.
It is divided into three main eras: Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic.
Paleozoic (Age of Ancient Organisms):
About 541 million years ago to about 252 million years ago.
During this era, the first vertebrates, land plants, and giant arthropods developed. The
explosion of life known as the "Cambrian Explosion" also occurred.
Mesozoic (Age of Dinosaurs):
About 252 million years ago to about 66 million years ago.
This era is famous for the domination of dinosaurs and the development of birds and
mammals.
Cenozoic (Age of Mammals):
It began about 66 million years ago and continues to the present.
During this era, mammals diversified and became the dominant form of terrestrial life.
Human evolution also occurred.
You might also like
- History of Life On Earth EvolutionDocument3 pagesHistory of Life On Earth EvolutionpatriciaNo ratings yet
- Alles Revision Conocimiento Fosil Evolucion HumanaDocument62 pagesAlles Revision Conocimiento Fosil Evolucion HumanagimenezNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Life On EarthDocument18 pagesEvolution of Life On Earthfrancisjohn echemaniNo ratings yet
- GEN-BIO-2-History of Life On EarthDocument22 pagesGEN-BIO-2-History of Life On EarthGeminiNo ratings yet
- Evolving Concept of Life MODULE 1Document15 pagesEvolving Concept of Life MODULE 1brigittediaceno09No ratings yet
- Storyofevolutionbyjakeandtoby 23 StemDocument9 pagesStoryofevolutionbyjakeandtoby 23 Stemapi-242529550No ratings yet
- Evolution of MammalsDocument27 pagesEvolution of MammalsuzumakitobiNo ratings yet
- Summary of Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind By Yuval Noah HarariFrom EverandSummary of Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind By Yuval Noah HarariRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (3)
- In the Beginning: Creation Myths Across CulturesFrom EverandIn the Beginning: Creation Myths Across CulturesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Ucsp (Lesson 1)Document28 pagesUcsp (Lesson 1)united nationNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument5 pagesGeologic Time ScaleKarylle TubbanNo ratings yet
- Sapiens: A Brief History of HumankindFrom EverandSapiens: A Brief History of HumankindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1894)
- SS2 LG 2.1 Introduction To Prehistory Students Copy 1Document6 pagesSS2 LG 2.1 Introduction To Prehistory Students Copy 1WengNo ratings yet
- The Laws of Nature and Other StoriesDocument128 pagesThe Laws of Nature and Other StoriesAila Reopta100% (1)
- Unit 1 Hunting and Gathering: StructureDocument16 pagesUnit 1 Hunting and Gathering: Structurebedanta04No ratings yet
- Sapiens – Summarized for Busy People: A Brief History of Humankind: Based on the Book by Yuval Noah HarariFrom EverandSapiens – Summarized for Busy People: A Brief History of Humankind: Based on the Book by Yuval Noah HarariNo ratings yet
- Social Science 8Document39 pagesSocial Science 8John paul siaNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time Scale NotesDocument69 pagesGeologic Time Scale NotesercilloNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Evoluton of LifeDocument8 pagesIntroduction of Evoluton of LifeRubina AmirNo ratings yet
- History of Life On EarthDocument71 pagesHistory of Life On EarthRaineir PabiranNo ratings yet
- Summarize The Three Video CulturalDocument2 pagesSummarize The Three Video CulturalChan SokhongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Part IDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Part IJessica Jimenez SaltingNo ratings yet
- PP29. Geological Time Scale and Cambrian Explosion 1Document43 pagesPP29. Geological Time Scale and Cambrian Explosion 1ntombenhleprincess01No ratings yet
- The Evolutionary History of The AnimalDocument52 pagesThe Evolutionary History of The AnimalNova Balones NaolNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Origin of BiodiversityDocument25 pagesEvolution and Origin of Biodiversitykaren milloNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument2 pagesEarth SciencegomezcrisjohnpauleNo ratings yet
- Ch-7-Study Material-2024-25Document10 pagesCh-7-Study Material-2024-25zahraababy123No ratings yet
- Homo Sapiens To Early Civilisation: History EssayDocument3 pagesHomo Sapiens To Early Civilisation: History EssayMyles BrokenSneakers OwenNo ratings yet
- History of Life On Earth - 210513 - 212301Document17 pagesHistory of Life On Earth - 210513 - 212301Christine FayeNo ratings yet
- Eons - BiologyDocument4 pagesEons - BiologyA - UNO, France Jhondale B.No ratings yet
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument51 pagesGeologic Time ScaleLance Francis DanielesNo ratings yet
- GTSDocument14 pagesGTSMariel LolincoNo ratings yet
- Homo ErectusDocument3 pagesHomo ErectuslalahahalalaNo ratings yet
- Module1evolvingconceptoflifebasedonemergingpiecesofevidence 230903093853 654b06fbDocument12 pagesModule1evolvingconceptoflifebasedonemergingpiecesofevidence 230903093853 654b06fbcharlitosolijon977No ratings yet
- Where Lived: Evolved in Africa, Now Worldwide When Lived: About 200,000 Years Ago To PresentDocument2 pagesWhere Lived: Evolved in Africa, Now Worldwide When Lived: About 200,000 Years Ago To PresentLiah RosarioNo ratings yet
- History of The EarthDocument2 pagesHistory of The EarthednakNo ratings yet
- History of Life On EarthDocument40 pagesHistory of Life On Earthgarrylosenales1977No ratings yet
- Astonishing Animals: Extraordinary Creatures and the Fantastic Worlds They InhabitFrom EverandAstonishing Animals: Extraordinary Creatures and the Fantastic Worlds They InhabitRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (25)
- From Monkey to Homo Sapiens A Journey Through the Stages that Led to HumankindFrom EverandFrom Monkey to Homo Sapiens A Journey Through the Stages that Led to HumankindRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- EvolutionDocument27 pagesEvolutionasmikisaini006No ratings yet
- Human EvolutionDocument10 pagesHuman EvolutionVenn Bacus Rabadon0% (1)
- Module1evolvingconceptoflifebasedonemergingpiecesofevidence 230903093853 654b06fbDocument13 pagesModule1evolvingconceptoflifebasedonemergingpiecesofevidence 230903093853 654b06fbKrisjelyn GumaroNo ratings yet
- History of EuropeDocument200 pagesHistory of EuropeAdedolapo AjayiNo ratings yet
- Cenozoic EraDocument3 pagesCenozoic EraTricia Marie MarcosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 History of LifeDocument15 pagesChapter 1 History of LifeJonard PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Els PPT EvidencesDocument13 pagesEls PPT EvidencesAizle Trixia AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Timeline of Life On EarthDocument4 pagesTimeline of Life On EarthReymart Imat SupleoNo ratings yet
- PunchinelloDocument1 pagePunchinelloansofy354No ratings yet
- FractionsDocument1 pageFractionsansofy354No ratings yet
- Window CleanerDocument4 pagesWindow Cleaneransofy354No ratings yet
- Documento Sin Título-8Document4 pagesDocumento Sin Título-8ansofy354No ratings yet
- Page 64Document1 pagePage 64ansofy354No ratings yet
- SkeletonDocument2 pagesSkeletonansofy354No ratings yet
- Equivalent Ratios (W2)Document2 pagesEquivalent Ratios (W2)ansofy354No ratings yet
- 7° Review ActivityDocument6 pages7° Review Activityansofy354No ratings yet
- Position PaperDocument4 pagesPosition Paperansofy354No ratings yet
- The Past ChirismasDocument1 pageThe Past Chirismasansofy354No ratings yet
- Sustainable Development - Water Day Tour WorkshopDocument2 pagesSustainable Development - Water Day Tour Workshopansofy354No ratings yet
- International Olympic Committee - Emun XiDocument11 pagesInternational Olympic Committee - Emun Xiansofy354No ratings yet
- Class ActivityDocument2 pagesClass Activityansofy354No ratings yet
- PDF 20230616 073104 0000Document2 pagesPDF 20230616 073104 0000ansofy354No ratings yet
- Sillitoe 2003 Iron Oxide Copper Gold Deposits An Andean ViewDocument50 pagesSillitoe 2003 Iron Oxide Copper Gold Deposits An Andean ViewRival MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Jurassic Park IV - Screenplay (JP4)Document110 pagesJurassic Park IV - Screenplay (JP4)Arjan Bos100% (1)
- Prova 9 Ano InglesDocument6 pagesProva 9 Ano InglesLeonardo Martins de SousaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Esl Topics Quiz Bugs InsectsDocument2 pages4.1 Esl Topics Quiz Bugs InsectsSiddhartha Shankar NayakNo ratings yet
- Application of Textural Quartz VeinsDocument11 pagesApplication of Textural Quartz VeinsNovia FlorensiaNo ratings yet
- Amitava Chatterjee - History - UGC-NET - SET - JRF (Paper II and III) - Pearson India (2016)Document577 pagesAmitava Chatterjee - History - UGC-NET - SET - JRF (Paper II and III) - Pearson India (2016)Gulrez M100% (1)
- Movie Script About The Paleozoic EraDocument2 pagesMovie Script About The Paleozoic Erachristine anne degorio50% (4)
- 7-Hist of EvolutionDocument23 pages7-Hist of EvolutionMarifeNo ratings yet
- Pairault - Etal - 2003 Seram Trough - MPG PDFDocument21 pagesPairault - Etal - 2003 Seram Trough - MPG PDFMuh Andika Pratama WarisNo ratings yet
- Identification of Shrimp and PrawnsDocument50 pagesIdentification of Shrimp and PrawnsRajan KumarNo ratings yet
- Evolution Quiz1Document2 pagesEvolution Quiz1api-236443418No ratings yet
- Geological Maps 1: Horizontal and Inclined StrataDocument14 pagesGeological Maps 1: Horizontal and Inclined StrataSyahir IshakNo ratings yet
- The Fossil Record: Getting StartedDocument8 pagesThe Fossil Record: Getting StartednidhiNo ratings yet
- Geology of The Etoqui ZN Au Skarn DistrictDocument29 pagesGeology of The Etoqui ZN Au Skarn DistrictHéctor SuazoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To CladisticsDocument6 pagesAn Introduction To CladisticsYosueNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument3 pagesSample QuestionshNo ratings yet
- Exams Sedimentaryi PDFDocument4 pagesExams Sedimentaryi PDFEmilia Pop100% (1)
- A New Titanosaur (Dinosauria, Sauropoda) From The Upper Cretaceous of Lo Hueco (Cuenca, Spain)Document46 pagesA New Titanosaur (Dinosauria, Sauropoda) From The Upper Cretaceous of Lo Hueco (Cuenca, Spain)noaraptorNo ratings yet
- Gr3 Dino News PR NF ReadworksDocument4 pagesGr3 Dino News PR NF ReadworksJac LedonioNo ratings yet
- Super Minds 6 Workbook 101Document1 pageSuper Minds 6 Workbook 101Dard TongNo ratings yet
- Pangaea Lab Activity 2016 PDFDocument8 pagesPangaea Lab Activity 2016 PDFJeniffer De Guzman GadiomaNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric LifeDocument378 pagesEncyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric LifeJ Alberto Lucas79% (14)
- An Introduction To Tectonophysics, Theoritical Aspects of Structural Geology - Yamaji PDFDocument383 pagesAn Introduction To Tectonophysics, Theoritical Aspects of Structural Geology - Yamaji PDFRolando WalleNo ratings yet
- PDF Sangiran Man Culture and Environment in Pleistocene Times Proceedings of The International Colloquium On Sangiran Solo Indonesia 21 24 September 1998 Review - CompressDocument4 pagesPDF Sangiran Man Culture and Environment in Pleistocene Times Proceedings of The International Colloquium On Sangiran Solo Indonesia 21 24 September 1998 Review - CompresskilatxpNo ratings yet
- January NewsletterDocument25 pagesJanuary Newsletterapi-274597520No ratings yet
- Geology: Merit Badge WorkbookDocument6 pagesGeology: Merit Badge WorkbookRazzzzzakNo ratings yet
- DK, Hazel Richardson - Dinosaurs and Other Prehistoric Life (DK Handbooks) (2021, DK) - Libgen - LiDocument224 pagesDK, Hazel Richardson - Dinosaurs and Other Prehistoric Life (DK Handbooks) (2021, DK) - Libgen - LiVictor Polecas Ayala100% (3)
- RW Van Bemmelen Geology of Indonesia Vol-IB PortfolioDocument61 pagesRW Van Bemmelen Geology of Indonesia Vol-IB PortfolioDesyAAlvrida100% (1)
- Coal & Peat of BangladeshDocument52 pagesCoal & Peat of BangladeshNoor HasanNo ratings yet
- North Sea AtlasDocument483 pagesNorth Sea Atlasjacek_sawicz100% (2)