Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ANAPHY Final
Uploaded by
reized020 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesANAPHY Final
Uploaded by
reized02Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
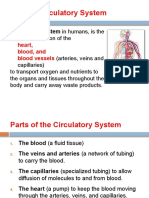
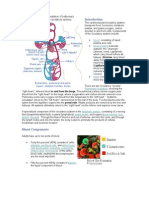
Anatomy and Physiology:
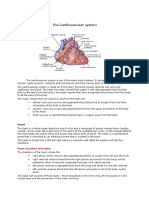
Cardiovascular System (Circulatory System)
The Circulatory system is made up of the heart and the blood vessels.
Functions of CVS:
The primary function of providing oxygen, nutrients and hormones to muscles, tissues,
and organs throughout our body.
Another duty of the circulatory system is to remove waste from cells and organs brought
to the kidneys for excretion.
These waste products include:
- CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) from respiration
- Other chemical byproducts from organs
- Wastes from things we eat and drink.
Parts of the Circulatory System
Heart – A muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body
Blood vessels – Includes, Arteries, Veins and Capillaries
- Arteries – They are the blood vessels that supply the body with oxygenated
blood with the only exception being the Pulmonary arteries from the heart which
carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs and umbilical artery which carries
deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta.
- Veins – They return oxygen-depleted blood back to the heart. They start
small (Venules) and get larger as they approach the heart. Two central veins
deliver blood to the heart.
o Superior Vena cava – carries blood from upper body (head and Arms)
to the heart.
o Inferior Vena Cava – brings blood up from the lower body (stomach,
pelvis and the legs) to the heart. Veins in the legs have valves to keep
blood from flowing backwards.
- Capillaries: These blood vessels connect very small arteries (Arterioles) and
veins (venules). Capillaries have thin walls that allow oxygen, carbon dioxide and
waste products to pass in and out of cells.
Blood – made up of solids and liquids which are Red Blood Cells, White Blood Cells,
Plasma, And Platelets.
The solid part of the blood contains RBC, WBC, and Platelets while the Liquid part is
plasma.
- Plasma – It is the liquid part of the blood made up of water, salts, and protein.
Over half of blood is plasma.
- Red Blood Cells – Deliver oxygen from your lungs to your tissues and organs.
- White Blood Cells – Fights infection and is a part of the immune system.
- Platelets – help blood to clot when you have a cut or wound.
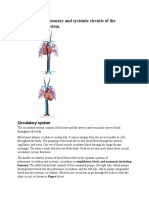
Circulatory System Circuits:
- The pulmonary circuit – This carries blood without oxygen from the heart to the
lungs and the pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood to the heart.
- The Systemic Circuit – In this circuit, blood with oxygen, nutrients and
hormones travel from the heart to the rest of the body. In the veins, the blood
picks up waste products as the body uses up the oxygen, nutrients and
hormones.
- The Coronary Circuit – Coronary refers to your heart’s arteries. This circuit
provides the heart muscles with oxygenated blood. The coronary circuit then
returns the oxygen-poor blood to the heart’s right upper chamber (atrium) to send
to the lungs for oxygen.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21775-circulatory-system
https://medlineplus.gov/blood.html
https://www.physio-pedia.com/Cardiovascular_System
You might also like
- Cardiovascular System PPT FeDocument26 pagesCardiovascular System PPT FeAngel Grace GaliasNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As ADocument6 pagesCardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As AMalaquias VallejosNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCardiovascular SystemKerwin LimNo ratings yet
- General.: Blood CirculationDocument3 pagesGeneral.: Blood CirculationJessica MichaelNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory SystemKrizza Dawn QueNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-09-01 at 5.39.08 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2022-09-01 at 5.39.08 PMTrishia EspejaNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System (Cardiovascular System) Pumps Blood From TheDocument6 pagesThe Circulatory System (Cardiovascular System) Pumps Blood From ThevanNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument19 pagesCirculatory SystemСоня КропельницкаяNo ratings yet
- BodysystemDocument1 pageBodysystemapi-320549212No ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 12 Notes (Grade 11)Document5 pagesBio Chapter 12 Notes (Grade 11)Tammy Lam100% (6)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular SystemMr. Christian ParabuacNo ratings yet
- 3.1 CirculatorySystemDocument29 pages3.1 CirculatorySystemMuhammad AsfarNo ratings yet
- What Is The Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Circulatory Systemmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCardiovascular SystemNatalie Odette Zárate BeristainNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System - PPTDocument16 pagesThe Circulatory System - PPTrenztheoapuliNo ratings yet
- Major Part of The Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesMajor Part of The Circulatory SystemBrettnia Angela AradoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument46 pagesCirculatory Systemmirasol1206100% (1)
- Blood CirculationDocument8 pagesBlood CirculationnorafidaishakNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular SystemDaniel PancuNo ratings yet
- Transports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsDocument46 pagesTransports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsElla LlamasNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesCirculatory SystemEzequiel ManluluNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument33 pagesCirculatory SystemRhynette NaridoNo ratings yet
- GIDB4288666-Circulatory System NotesDocument6 pagesGIDB4288666-Circulatory System Notessky moonNo ratings yet
- Biology-The HeartDocument7 pagesBiology-The Heart2k7wmbhxqfNo ratings yet
- Medical Science Part 2Document21 pagesMedical Science Part 2Gauge FalkNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesThe Circulatory Systemhaniyasherif40No ratings yet
- Structures of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument1 pageStructures of The Cardiovascular SystemMimi MonteNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14.1 - Cardiovascular System - Blood VesselsDocument56 pagesChapter 14.1 - Cardiovascular System - Blood VesselsMichael PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Types of Circulation of BloodDocument5 pagesTypes of Circulation of BloodZerria Ashley PatocNo ratings yet
- Types of Circulation of BloodDocument4 pagesTypes of Circulation of BloodZerria Ashley PatocNo ratings yet
- Anatomy L9 PPDocument22 pagesAnatomy L9 PPTara WifaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument12 pagesCirculatory SystemKeyur SharmaNo ratings yet
- CirculatoryDocument9 pagesCirculatoryJason Vinluan Carinan100% (1)
- Transportation NotesDocument12 pagesTransportation NotesavanishNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument71 pagesCirculatory SystemAnas Mustafa HashmiNo ratings yet
- Research Questions-: How The Blood FlowsDocument5 pagesResearch Questions-: How The Blood FlowsAasritha SenagapallyNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument9 pagesAcknowledgementJovin AshickNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportDocument39 pagesScience Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportNadzirah RedzuanNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Word OfficeDocument6 pagesCirculatory Word OfficeMaria Christina CaceresNo ratings yet
- Systemic Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesSystemic Circulatory SystemTinaRahmawatiKadabraNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument2 pagesThe Cardiovascular SystembluewindNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesCirculatory Systemkashaf bhuttaNo ratings yet
- Compare The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCompare The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits of The Cardiovascular Systememanuel coatesNo ratings yet
- Ron Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Document4 pagesRon Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Mute GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Lec-21,22,23 - Circulatory SystemDocument28 pagesLec-21,22,23 - Circulatory SystemAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- The Circulatory System 2024 1 20 22 51 0Document12 pagesThe Circulatory System 2024 1 20 22 51 0Andre GreenNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesThe Circulatory SystemJoiSatannNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument31 pagesThe Circulatory SystemAyesha DuaNo ratings yet
- CIRCULATORYDocument3 pagesCIRCULATORYSumbul ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument30 pagesCirculatory SystemIra Lavigne De VillaNo ratings yet
- Transport Systems Objective 2-1Document4 pagesTransport Systems Objective 2-1darielleollivierreNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Presented by DR Aparna Ramachandran Mds 1 Dept of Public Health DentistryDocument73 pagesCardiovascular System: Presented by DR Aparna Ramachandran Mds 1 Dept of Public Health DentistryAparna RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SysDocument10 pagesCirculatory SysnaviNo ratings yet
- CIRCULATORYDocument20 pagesCIRCULATORYDannica Trisha CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- HusnaDocument6 pagesHusnajenifferNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: Karan Arora Ix-B byDocument33 pagesThe Circulatory System: Karan Arora Ix-B bykaranarorarafaNo ratings yet
- 1 Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pages1 Cardiovascular SystemWaltz PadlanNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Diffusion WorksheetDocument7 pagesOsmosis and Diffusion WorksheetAbir Omar25% (4)
- Human ReproductionDocument14 pagesHuman ReproductionANA MARY JOY PEPENo ratings yet
- Molecules: Banana Lectin: A Brief ReviewDocument11 pagesMolecules: Banana Lectin: A Brief ReviewVincent William RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Iji2013 151028Document8 pagesIji2013 151028Kershaun MathewNo ratings yet
- Importanceof CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesImportanceof CarbohydratescraigNo ratings yet
- FAQs: Dr. Sarojini SahooDocument4 pagesFAQs: Dr. Sarojini SahooSarojini SahooNo ratings yet
- Review Questions For Online Pre Final ExamDocument5 pagesReview Questions For Online Pre Final ExamReygie MataNo ratings yet
- AQA Bioenergetics Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesAQA Bioenergetics Knowledge OrganiserDan LiNo ratings yet
- Invertebrates in Testing of Environmental Chemicals - Are They AlternativesDocument19 pagesInvertebrates in Testing of Environmental Chemicals - Are They AlternativesTiago TorresNo ratings yet
- Vernier CV Master Aug 2023Document7 pagesVernier CV Master Aug 2023api-619519250No ratings yet
- Common Medical Abbreviations For MedTech and Gen SciDocument14 pagesCommon Medical Abbreviations For MedTech and Gen SciRigel AntilegandoNo ratings yet
- TTPB7THESTORYOFAUXIN ShortDocument65 pagesTTPB7THESTORYOFAUXIN ShortDiksha GahlotNo ratings yet
- Considerations and Consequences of Allowing DNA Sequence Data As Types of Fungal TaxaDocument20 pagesConsiderations and Consequences of Allowing DNA Sequence Data As Types of Fungal TaxaDiáfana OrozcoNo ratings yet
- LC Bright BrochureDocument1 pageLC Bright Brochureapi-528907705No ratings yet
- Gen Bio PDFDocument6 pagesGen Bio PDFGwyne Shenette Karylle NoscalNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Campbell Biology in Focus 1st Edition Urry PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Campbell Biology in Focus 1st Edition Urry PDF Full Chapterirefulofterimrgb100% (13)
- Bitw ProductdirectoryDocument89 pagesBitw ProductdirectorySHIVANINo ratings yet
- Fluorimeter Application Note: A10-007A: Phosphatase Assays Using Difmup As SubstrateDocument3 pagesFluorimeter Application Note: A10-007A: Phosphatase Assays Using Difmup As SubstrateloNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: Bussines Case StudyDocument4 pagesNutrition: Bussines Case StudyAntonia Michaela IonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Organs and Their FunctionDocument61 pagesEndocrine System: Organs and Their FunctionSherifaNo ratings yet
- MergedDocument427 pagesMergedNishit kumar100% (1)
- Intro BotanyDocument192 pagesIntro BotanyMelissa100% (1)
- APEX The Organ SystemsDocument171 pagesAPEX The Organ Systemsjt100% (2)
- CellDocument5 pagesCellsumitkguptaNo ratings yet
- 06 Collection and Handling of Biopsy SpecimensDocument7 pages06 Collection and Handling of Biopsy SpecimensAudrey CobankiatNo ratings yet
- CharophyceaeDocument17 pagesCharophyceaeAisyatur RobiaNo ratings yet
- EnterobacteriaceaeDocument67 pagesEnterobacteriaceaevaidyamNo ratings yet
- DNA Profiling: DNA Profiling (Also Called DNA Fingerprinting, DNA Testing, or DNA Typing) IsDocument3 pagesDNA Profiling: DNA Profiling (Also Called DNA Fingerprinting, DNA Testing, or DNA Typing) IsShaik MoqtiyarNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Lec No 6 ChloroplastDocument18 pagesCell Biology Lec No 6 ChloroplastsaleemNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Vol 2 David E. MetzlerDocument1,040 pagesBiochemistry Vol 2 David E. Metzlerysmnsnmz100% (2)