Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Titration Lab 3rd QRTR Genchem Ha Peta
Uploaded by
antonellaeve.lopez.shsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Titration Lab 3rd QRTR Genchem Ha Peta
Uploaded by
antonellaeve.lopez.shsCopyright:
Available Formats
GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 2nd Term; SY 2023-2024
UNIVERSITY OF SANTO TOMAS
Senior High School – Health Allied
2nd Term / SY 2023-2024
PeTa – 3rd Quarter
EXPERIMENT 1: TITRATION
Group Members in alphabetical order: (Surname, First Name) Section:
Group No.:
Date:
Introduction
Titration is the slow addition of one solution of a known concentration (called a titrant) to a known volume of another solution of
unknown concentration until the reaction reaches neutralization, which is often indicated by a color change. The solution called the
titrant must satisfy the necessary requirements to be a primary or secondary standard. In a broad sense, titration is a technique to
determine the concentration of an unknown solution.
Objective
This activity aims to enable the learners to:
1. Apply laboratory safety protocols and procedure.
2. Demonstrate proper titration techniques.
3. Prepare a hydrochloric acid solution and determine its exact concentration for use as standard solution in titrimetric analysis.
4. Prepare a sodium hydroxide solution and determine its exact concentration for use as standard solution in titrimetric analysis.
Materials:
Acidimetry:
1. Unknown HCl Solution
2. Anhydrous Sodium Carbonate (Primary Standard)
3. Methyl Orange Indicator
4. Distilled Water
5. Teflon Valve Burette (Red – Lined)
6. Analytical balance
7. Iron stand & Clamp
8. Butterfly clamp
Alkalimetry:
1. Unknown NaOH Solution
2. Phenolphthalein
3. Distilled Water
4. Teflon Valve Burette (Red – Lined)
5. Teflon Valve Burette (Blue– Lined)
6. Iron stand & Clamp
7. Butterfly clamp
Instructions:
Preparation of Burette for Titration
1. Wash the burette with solution of dishwashing liquid, allow the soap solution to reach up to the tip of the burette.
2. Using a beaker, rinse the burette thoroughly with tap water followed by distilled water.
3. Rinse the burette with a small amount of the standard solution. Be sure to drain the solution through the tip of the burette.
Repeat this 3rd step twice.
4. Secure the burette in the burette clamp then attach it to the iron stand.
5. Close the pinchcock of the burette and introduce the standard NaOH/HCl solution filling it up to more than the 50-mL
mark.
6. Run down the solution above a clean beaker and ensure that no air space is in the burette especially inside its tip.
7. Use the collected solution to fill the burette up to the 50-mL mark. Record the initial volume on the burette to 2 decimal
places. (Note: look for the lower meniscus).
Acidimetry (ODD GROUPS):
1. Weigh accurately 0.1 to 0.2 g of anhydrous sodium carbonate (primary standard) in a tared Erlenmeyer flask.
2. Dissolve the sodium carbonate in 80 mL of dist. H2O and shake until solution is complete
clear colorless solution.
3. Add 3 drops of methyl orange and observe the change of color to yellow.
4. Titrate with HCl to a salmon or peach color endpoint.
5. Compute for the Molarity of HCl
University of Santo Tomas, Senior High School Page 1 of 2
GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 2nd Term; SY 2023-2024
Alkalimetry (EVEN GROUPS):
1. Run down 20.0 mL of standard HCl solution (2o standard) from the Geissler Burette (red lined burette) to the Erlenmeyer
flask.
2. Add 40 mL of dist. Water.
3. Add 2 drops of phenolphthalein.
4. Titrate with NaOH solution using a Mohr burette (blue lined burette) to a light pink color endpoint.
5. Compute for the Molarity of NaOH
General Reminders:
o Document all initial and final appearances using a plain background.
o NEVER wear your laboratory gowns outside laboratory premises.
o Make sure to clean and dry all glass wares used
Data:
ENDPOINT (50 Points)
Reached the correct endpoint and equivalence point. 50 points
Overstep 20 points
Computation of Molarity (25 points each) :
PERCENTAGE ERROR (%) POINTS
0 – 25 25
26 - 50 15
51 - 75 10
76 - 100 5
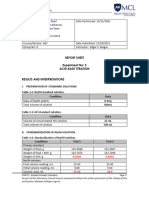
ACIDIMETRY
1st Trial 2nd Trial
Amount of Na2CO3 0.1g 0.2g
Initial Volume of HCl 0 0
Final Volume of HCl 28.4 mL 33.5mL
Molarity of HCl 6.6x10^-2 1.1x10^-1
Average Molarity 8.9x10^-2
Solution to computation/s
!"## %& '()*+,%-# .%+/-! 0",1%("23 /( 4
MHCl =
5%6-!3 %& 706 /( !8 9 .;<=
Trial 1 : MHCl = 0.06643635397
Trial 2: MHCl = -.1123090746
Molarity Average = 0.08937271427
Equation
Na2CO3 + 2HCl ---> 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
ALKALIMTERY
1st Trial 2nd Trial
Volume of HCl 20.0 mL 20.0mL
Initial Volume of NaOH 0mL 0mL
Final Volume of NaOH 27.6mL 27.3mL
Molarity of NaOH 4.8x10^-2 8.1x10^-2
Average Molarity 6.4x10^-2
Solution to computation/s
MaVa = MbVb
Trial 1: MNaOH =
Trial 2: MNaOH = 0.08058608059
Molarity Average: 0.06420608377
Equation
NaOH + HCl --> NaCl + H2O
Signature of Instructor:
University of Santo Tomas, Senior High School Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Hydrolysis of Methyl AcetateDocument6 pagesHydrolysis of Methyl AcetateZhu Chen Chuan100% (2)
- Expt 5 Analysis of Soda AshDocument8 pagesExpt 5 Analysis of Soda AshJustine Camille CastilloNo ratings yet
- Investigating The Kinetics of A Crystal Violet Reaction Prelab QuestionsDocument9 pagesInvestigating The Kinetics of A Crystal Violet Reaction Prelab QuestionsconnieNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 CHM476Document10 pagesExperiment 4 CHM476Hazwan Hamim100% (1)
- Lab Report CHM 131 Exp 3Document8 pagesLab Report CHM 131 Exp 3Wilbert WanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report PFR PDFDocument11 pagesLab Report PFR PDFMohd Saiful RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Department of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Analysis of An AntacidDocument5 pagesDepartment of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Analysis of An Antacidkat katNo ratings yet
- Chm432 Expt 4Document9 pagesChm432 Expt 4Ievana InsyirahNo ratings yet
- Chem87l Expt2 Padel PedarseDocument5 pagesChem87l Expt2 Padel Pedarsevince padelNo ratings yet
- International University-Vnu HCM City School of BiotechnologyDocument10 pagesInternational University-Vnu HCM City School of BiotechnologyĐỗ Huỳnh Lan AnhNo ratings yet
- Exp 3Document8 pagesExp 3AmirahNo ratings yet
- Determination of Volume of Base.Document9 pagesDetermination of Volume of Base.MinichNo ratings yet
- 29 Ethyl Acetate LQDocument3 pages29 Ethyl Acetate LQAlisa MinasyanNo ratings yet
- Adamson University College of EngineeringDocument14 pagesAdamson University College of EngineeringJosef RentaNo ratings yet
- CHM1207 Lab 3 2023 - DRAKES, Tameica (1042436) PDFDocument6 pagesCHM1207 Lab 3 2023 - DRAKES, Tameica (1042436) PDFNikoli MajorNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Edvair Paula Moreira Filho 000837578Document7 pagesLab Report: Edvair Paula Moreira Filho 000837578Edvair FilhoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 13: Volumetric Analysis II: Determination of Active Ingredients in Commercial Bleach and Vinegar OutcomesDocument5 pagesExperiment 13: Volumetric Analysis II: Determination of Active Ingredients in Commercial Bleach and Vinegar OutcomesSafwan m.tNo ratings yet
- Beers Law - Lab Report ExampleDocument2 pagesBeers Law - Lab Report Exampleapi-239855791No ratings yet
- Determining The Order of A Chemical Reaction LabDocument8 pagesDetermining The Order of A Chemical Reaction LabJonathan_Khan7100% (1)
- Titration Lab With Kinetics: Experiment 1 (Old)Document3 pagesTitration Lab With Kinetics: Experiment 1 (Old)api-296033722No ratings yet
- Chem Lab#11 PostlabDocument5 pagesChem Lab#11 PostlabAthia Ava Luna100% (1)
- Chm256 - Experiment 2 - Determination of Ethanoic Acid Content in VinegarDocument6 pagesChm256 - Experiment 2 - Determination of Ethanoic Acid Content in VinegarNatra AffaaninNo ratings yet
- MTT 2207 Measurement Error Analysis and Instrumentation: Chemistry Laboratory Assignment 01Document5 pagesMTT 2207 Measurement Error Analysis and Instrumentation: Chemistry Laboratory Assignment 01Indusara RamanayakaNo ratings yet
- CHM 131 Redox Lab ReportsDocument8 pagesCHM 131 Redox Lab ReportsWilbert WanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering AssignmentsDocument43 pagesChemical Engineering AssignmentsMalik DaniyalNo ratings yet
- 3022gnr Practical Material Not For Sale ......Document41 pages3022gnr Practical Material Not For Sale ......Desetty Sri LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Practical Book Analytical ChemistryDocument14 pagesPractical Book Analytical Chemistrysalman ahmedNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: Neutralization Capacity of Commercial Antacid TabletDocument6 pagesExperiment 3: Neutralization Capacity of Commercial Antacid TabletNur Aliya Ikmal Hisham100% (1)
- Titration of HCIDocument2 pagesTitration of HCIJOFFA LING JUN XIANGNo ratings yet
- Chm256 Odl Exp 1 2 3 Lab ReportDocument18 pagesChm256 Odl Exp 1 2 3 Lab Reportmaya adamNo ratings yet
- Vinegar Analysis: Experiment No. 1Document9 pagesVinegar Analysis: Experiment No. 1dumb dumbNo ratings yet
- (Analytical Chemistry) Acid - Base Titration Lab ReportDocument4 pages(Analytical Chemistry) Acid - Base Titration Lab ReportThu Hien VuNo ratings yet
- Chemy 310 Experiment 2Document5 pagesChemy 310 Experiment 2Faisal MumtazNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Chemical Reactions: Report 1Document6 pagesExperiment 1: Chemical Reactions: Report 1Thư NguyễnNo ratings yet
- LAb Report 6Document4 pagesLAb Report 6Faisal MumtazNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Titration Experiment 1Document7 pagesAcid-Base Titration Experiment 1John Evans BwireNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Dissolved Oxygen AlcantaraquijanotabaranzaDocument8 pagesExperiment 7 Dissolved Oxygen AlcantaraquijanotabaranzaISAAC ZCAR EBLACAS ASOKNo ratings yet
- Lab Report TemplateDocument6 pagesLab Report Templatemostafamahmoud9918No ratings yet
- FST556 Preparation and Standardisation of Base and Acid SolutionDocument6 pagesFST556 Preparation and Standardisation of Base and Acid SolutionNurizzatiainiNo ratings yet
- Complexometric Determination of Water Hardness Lab ReportDocument5 pagesComplexometric Determination of Water Hardness Lab ReportMichelle50% (2)
- Acid Base Titration Reah Joyce CastilloDocument11 pagesAcid Base Titration Reah Joyce Castillorhyscastillo28No ratings yet
- Determining The Molar Concentration of Vinegar by TitrationDocument18 pagesDetermining The Molar Concentration of Vinegar by TitrationYasinaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document5 pagesExperiment 3miaz150150% (8)
- Decomposition of Diacetone AlcoholDocument3 pagesDecomposition of Diacetone Alcoholaryajs2017No ratings yet
- CHM131L Group-4Document8 pagesCHM131L Group-4Long ENo ratings yet
- Titration, Acetic Acid, Household Vinegar, Sodium Hydroxide (Naoh) TitrantDocument6 pagesTitration, Acetic Acid, Household Vinegar, Sodium Hydroxide (Naoh) TitrantPatrickTulayNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 Lab 2Document6 pagesChem 1 Lab 2Nguyễn Tiến NghĩaNo ratings yet
- Reaction KineticsDocument15 pagesReaction KineticsSadiaShoaibNo ratings yet
- Titration AnalysisDocument5 pagesTitration AnalysisKashish DoshiNo ratings yet
- Oxidation of Isopropanol by Chromium (Vi) ReportDocument12 pagesOxidation of Isopropanol by Chromium (Vi) ReportGideonNo ratings yet
- An Chem II Practical 1Document8 pagesAn Chem II Practical 1Nhlakanipho VilakaziNo ratings yet
- Earl's Practical Test Part 2 (Lab Report Template) - Dk014Document5 pagesEarl's Practical Test Part 2 (Lab Report Template) - Dk014MALIUS BIN SUNGGI MoeNo ratings yet
- LAb Report 7Document3 pagesLAb Report 7Faisal MumtazNo ratings yet
- Theory: Sodium Carbonate Is The Salt of A Week Acid, Carbonic Acid (HDocument4 pagesTheory: Sodium Carbonate Is The Salt of A Week Acid, Carbonic Acid (HSadia afrinNo ratings yet
- Titrimetric AnalysisDocument49 pagesTitrimetric AnalysisNjabulo PetronelNo ratings yet
- Report - Chem Lab - TemplateDocument21 pagesReport - Chem Lab - TemplateMinh TríNo ratings yet
- Heats of Reactions LABDocument17 pagesHeats of Reactions LABAudrey LacNo ratings yet
- Compound Forming Extractants, Solvating Solvents and Inert Solvents: Iupac Chemical Data SeriesFrom EverandCompound Forming Extractants, Solvating Solvents and Inert Solvents: Iupac Chemical Data SeriesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Ninth Edition Spencer L Seager Full Chapter PDF ScribdDocument67 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Ninth Edition Spencer L Seager Full Chapter PDF Scribdamanda.swarr169100% (6)
- Study Guide and Student Solutions Manual For Mcmurrys Organic Chemistry John Mcmurry Full Chapter PDF ScribdDocument67 pagesStudy Guide and Student Solutions Manual For Mcmurrys Organic Chemistry John Mcmurry Full Chapter PDF Scribdcharles.bowman556100% (5)
- Preparation of Acetanilide - Chemistry Practicals Class 12Document1 pagePreparation of Acetanilide - Chemistry Practicals Class 12tmqj5qxvykNo ratings yet
- New Document 1Document16 pagesNew Document 1juan jaraNo ratings yet
- Important Notice: Additional Combined Science 5130 GCE O Level 2007Document37 pagesImportant Notice: Additional Combined Science 5130 GCE O Level 2007rodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-7 Solution-Properties ExercisesDocument13 pagesChapter-7 Solution-Properties Exercisestran huyNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0360319920345109 MainDocument16 pages1 s2.0 S0360319920345109 MainMihirduttaNo ratings yet
- Early Stage Recovery of Lithium From Tailored Thermal Conditioned Black Mass Part I (Schwich Et Al 2021)Document30 pagesEarly Stage Recovery of Lithium From Tailored Thermal Conditioned Black Mass Part I (Schwich Et Al 2021)irdantoNo ratings yet
- Zintek® 300 HP + Techseal® Glossy Black SLDocument9 pagesZintek® 300 HP + Techseal® Glossy Black SLSyedMazharAliShahNo ratings yet
- S4 Biology Practical CBC by Smutes With GuideDocument7 pagesS4 Biology Practical CBC by Smutes With GuideUV Vïpêr UnïcôrnNo ratings yet
- Modern Chemistry Chapter 9 Homework 9-1Document4 pagesModern Chemistry Chapter 9 Homework 9-1g3zrema0100% (1)
- TG No. 5 Bleaching and Finishing of RattanDocument12 pagesTG No. 5 Bleaching and Finishing of RattanAdolf NainggolanNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde, Ketone & Carboxylic Acid CHEMHACKDocument12 pagesAldehyde, Ketone & Carboxylic Acid CHEMHACKplightpixelNo ratings yet
- Use of Industrial Scale Chromatography in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing.Document26 pagesUse of Industrial Scale Chromatography in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing.Dolores Anahí LópezNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument131 pagesHydrocarbonsyeet LmaoNo ratings yet
- Y12 January Revision QuestionsDocument36 pagesY12 January Revision Questionsyathinp822No ratings yet
- Ujian PRA US 1 Kelas 9 Dengan Kunci JawabanDocument7 pagesUjian PRA US 1 Kelas 9 Dengan Kunci JawabanSinta NovaliaNo ratings yet
- wch14 01 Que 20231021Document36 pageswch14 01 Que 20231021ibrkhan2005zNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Activation of Graphite Electrode For Nitrate ReductionDocument9 pagesElectrochemical Activation of Graphite Electrode For Nitrate Reductionwonkyoung789No ratings yet
- SCH3U - Unit 1 Test 2022 - PracticeDocument7 pagesSCH3U - Unit 1 Test 2022 - PracticealexrennieloveNo ratings yet
- 2024超威MSDS (6-DZF-12) (2024-03-21 04 - 35 - 14)Document4 pages2024超威MSDS (6-DZF-12) (2024-03-21 04 - 35 - 14)Dieudonne CoulibalyNo ratings yet
- Green Synthesis of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles ThesisDocument7 pagesGreen Synthesis of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Thesisbk156rhq100% (2)
- Metal and Acid Fizz HomeworkDocument7 pagesMetal and Acid Fizz Homeworkafeugwedg100% (1)
- Ebook Pericyclic Reactions A Mechanistic and Problem Solving Approach PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Pericyclic Reactions A Mechanistic and Problem Solving Approach PDF Full Chapter PDFjeffery.killay269100% (24)
- EXP CHEM F5 - ACT 1d - Displacement of HalogenDocument3 pagesEXP CHEM F5 - ACT 1d - Displacement of HalogenRoszamzuliani SharipuddinNo ratings yet
- Understanding Advanced Chemistry Through Problem Solving The Learners Approach (Volume 1) - Revised Edition (Kim Seng Chan, Jeanne Tan) (Z-Library)Document339 pagesUnderstanding Advanced Chemistry Through Problem Solving The Learners Approach (Volume 1) - Revised Edition (Kim Seng Chan, Jeanne Tan) (Z-Library)loxadegoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Assertion-ReasonDocument267 pagesChemistry - Assertion-ReasonDont KnowNo ratings yet
- 2.8.5.c WorksheetDocument2 pages2.8.5.c WorksheetAftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Liang Et Al 2024 Dynamic Defects Boost in Situ H2o2 Piezocatalysis For Water CleanupDocument11 pagesLiang Et Al 2024 Dynamic Defects Boost in Situ H2o2 Piezocatalysis For Water CleanupToàn HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument14 pagesIsomerismAruna SriNo ratings yet