Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7 Reciprocating Compressor
Uploaded by
vaibhav kuchekarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7 Reciprocating Compressor
Uploaded by
vaibhav kuchekarCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluid and Turbo Machinery Laboratory.
S. Y. Mechanical Engineering.
Experiment No:
Reciprocating Compressor
Roll No:
Date of Conducted :
Date of Submitted :
Signature of Invigilator :
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar.
Fluid and Turbo Machinery Laboratory.
S. Y. Mechanical Engineering.
Reciprocating Compressor
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar.
Fluid and Turbo Machinery Laboratory.
S. Y. Mechanical Engineering.
EXPERIMENT NO: -
TITLE: - Trial on reciprocating air compressor
AIM: - To study & conduct trial on reciprocating air compressor
OBJECTIVES: - 1. To find out volumetric & isothermal efficiency of reciprocating air
compressor.
2. Plot graph of: - a) Volumetric Efficiency V/S Delivery pressure.
b) Isothermal efficiency V/S Delivery pressure.
THEORY:-
Air compressor is a machine to compress air to raise its temp. The compressor sucks air
from atmosphere, and compress it & then delivers a same under high pressure storage vessel.
The compressed air is used many applications such as for operating pneumatic drills
,riveters, wood drill, paint sparing in starting of supercharging jet engines& air motors etc. A
large nu. Of compressor are used in chemical industries like fertilization parts, refrigeration
industry work on compressor only.
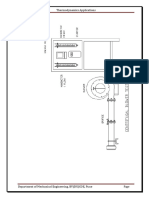
Two stage compressor consist of two cylinder ,piston, inlet & outlet valves is as shown
in fig .during the downward motion of piston ( inlet & outlet valves) pressure inside the
cylinder falls below the atmospheric pressure & inlet valve get opened due to pressure
difference ,The air is taken cylinder until the piston riches bottom dead centre .as the piston
stars the moving upwards, the inlet valve get closed& pressure inside cylinder is connected to
high pressure cylinder .At the end of delivery stroke small air at high pressure is left in cylinder
below atom. Pressure& cycle is repeated from low press. Cylinder where again with same
procedure pressure get developed then finally it is discharged to receive tank of compressed air.
TEST RIG: -
Air compressor, air box, with orifice manometer with wattmeter.
AIR COMPRESSOR SPECIFICATION: -
Model: ELGI TC 200
Reciprocating two types
Air cooled with intercooling
Free air delivered = 1531 rpm
Working pressure = 12 kgf /cm2
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar.
Fluid and Turbo Machinery Laboratory.
S. Y. Mechanical Engineering.
AIR COMPRESSOR SPECIFICATION:-
Manufacturer: ELGI Equipment’s limited. Coimbatore
Model type: - TC -200
Tank capacity: - 0.160 m3
Delivery pressure:-12 kg/cm2
Compressor inlet: - 1.5 kW
Capacity: 8.2 m3/hr.
Comp.sr. no. 1843
Tested pressure: 19 kg/cm2
PROCEDURE:-
1. Record the atmospheric temp. first
2. Start the comp.
3. Check for delivery pressure reading .It should read zero. otherwise open the pressure
relief valve
4. Closed pressure relief valve if required
5. When delivery pressure gauge shown 1 kg/cm2, note down manometer reading,
wattmeter reading.
6. When delivery press. Shown 2 kg/cm2 repeat the above reading up to 5 kg/cm2
7. Stop the compressor
8. Release air from storage tank to atmosphere. Close pressure relief valve.
OBSERVATIONS:-
1. Low pressure cylinder diameter D = 0.07 m
2. High pressure cylinder diameter D =0.05 m
3. Diameter of compressor pulley Dc = 0.3 m
4. Dia. Of motor pulley Dm = 0.125 m
5. Dia. Of orifice (d) = 0.01 m
6. Coefficient of discharge (Cd) = 0.65
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar.
Fluid and Turbo Machinery Laboratory.
S. Y. Mechanical Engineering.
7. Motor efficiency = 90 %
8. Belt Efficiency = 80%
9. Motor speed (Nm) 1400rpm
a) No. of phases =3
b) Power = 1.5 kw
c) Multiplying factor of wattmeter=2 per phase * 3 phases = 6
10. Absolute pressure = 1 *105 N/m2
11. Room Temperature =
12. Stroke length = 85 mm 0.085 m
OBSERVATION TABLE:-
Wattmeter
Sr.no. Delivery pressure (P2)Kg/cm2 Manometer Reading in CM reading
(Watt)
Gauge Absolute X1 X2 X=
press.(Kg/cm2) press.(Kg/cm2) |x1-x2|
1
CALCULATION: -
Volumetric Efficiency = Actual volume / Theoretical volume
Vact. = Cd* a* √ (2*g* hair)
A= area of orifice, Diameter of orifice = 10mm
Theoretical Volume := Vth = 3.14 *D2*L*Nc
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar.
Fluid and Turbo Machinery Laboratory.
S. Y. Mechanical Engineering.
Nc =Speed of compressor = (Dm* Nm)/Dc
Nc = 0.125*1400/0.3 = 9.72 rps
Vth = 3.14 * (0.07)2*0.085*9.722
Vth = m3/sec
Isothermal Efficiency = Isothermal power/ Actual power *100
Isothermal power = P1 (abs) * Vth* Log e (p2 (abs)/p1 (abs) = watt.
Actual power = Wattmeter reading * Multiplying factor* motor efficiency* Belt
efficiency
RESULT TABLE:-
Absolute Actual Theoretical Actual
Volumetric Isothermal Isothermal
Sr.no. press. volume Volume power
2 3 3 efficiency power (W) Efficiency
Kg/cm M M (W)
1
CONCLUSION:-
1. From above result we plot graph of volumetric efficiency v/s delivery pressure & it is
concluded that volumetric efficiency of reciprocating compressor is changing as delivery
pressure increases. This is due to manual error
2. Also from graph of isothermal efficiency v/s delivery pressure, it is observed that as
absolute delivery pressure increases isothermal efficiency goes on increasing in nonlinear
Manner.
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar.
You might also like
- 4 Centrifugal PumpDocument9 pages4 Centrifugal Pumpvaibhav kuchekarNo ratings yet
- Lab Web Notes Two Stage CompressorDocument4 pagesLab Web Notes Two Stage CompressorKarthic EaswarNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lab - NGS (1) (2) - YathinDocument48 pagesHeat Transfer Lab - NGS (1) (2) - Yathinswaroopdash.201me256No ratings yet
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsFrom EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Exp No 07. Reciprocating CompressorDocument6 pagesExp No 07. Reciprocating CompressorShashwat JainNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering I MECH A 2Document3 pagesThermal Engineering I MECH A 2dinesh23cbeNo ratings yet
- Heat Engine Lab ManualDocument47 pagesHeat Engine Lab ManualAurangzaib ArshadNo ratings yet
- Lab Web Notes Two Stage CompressorDocument4 pagesLab Web Notes Two Stage CompressorAmit Singh DehuryNo ratings yet
- PERFORMANCE TEST ON CompressorsDocument5 pagesPERFORMANCE TEST ON CompressorsNavneet KumarNo ratings yet
- MORSE TEST ON 4 Cylinders Petrol EngineDocument22 pagesMORSE TEST ON 4 Cylinders Petrol EngineNavneet KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermal Lab123Document5 pagesThermal Lab123Navneet KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Performance Testing FDocument16 pagesLecture Performance Testing FVARUN VARMA JAGANATHNo ratings yet
- UtilityDocument8 pagesUtilityAmit JainNo ratings yet
- Air Comperssor Test Rig ReciprocatingDocument4 pagesAir Comperssor Test Rig ReciprocatingShashank pNo ratings yet
- Lab Rep 2Document22 pagesLab Rep 2HaveOfControlNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Test Rig Foot Mounted MotorDocument5 pagesAir Compressor Test Rig Foot Mounted MotorTinku SharmaNo ratings yet
- PressorsDocument8 pagesPressorsManoj MisraNo ratings yet
- Performance Test On Two-Stage Reciprocating Air CompressorDocument6 pagesPerformance Test On Two-Stage Reciprocating Air CompressorAji V s100% (2)
- Air Compressor Performance TestDocument7 pagesAir Compressor Performance TestRajneeshKrNo ratings yet
- Performance at Constant SpeedDocument6 pagesPerformance at Constant Speedpurnachand raNo ratings yet
- VCR EngineDocument6 pagesVCR EngineAbNo ratings yet
- 6 Centrifugal BlowerDocument7 pages6 Centrifugal BlowerdhundterahoNo ratings yet
- ICE Lab ManualDocument68 pagesICE Lab ManualAkhilNagNo ratings yet
- Exp-5 Heat Balance Sheet PDFDocument5 pagesExp-5 Heat Balance Sheet PDFNarender NarruNo ratings yet
- Exp-5 Heat Balance SheetDocument5 pagesExp-5 Heat Balance SheetRabeek RajaNo ratings yet
- 2-S Petrol EngineDocument5 pages2-S Petrol EngineAbNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Measurements Lab ManualDocument26 pagesMechanical Measurements Lab ManualseminarprojectNo ratings yet
- Ce 2258 Hydraulic Engineering Laboratory ManualDocument44 pagesCe 2258 Hydraulic Engineering Laboratory Manualjanalalli67% (3)
- Heat Transfer Lab - 1Document31 pagesHeat Transfer Lab - 1Nikhil JayanthNo ratings yet
- Assignment 04Document16 pagesAssignment 04Pritam SahNo ratings yet
- 1a. Ganga EngineDocument10 pages1a. Ganga EngineShreyas JusticeNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Axial Flow Turbine With Computer SoftwareDocument8 pagesDesign and Analysis of Axial Flow Turbine With Computer SoftwareAlekhya TNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Axial Flow Turbine With Computer SoftwareDocument8 pagesDesign and Analysis of Axial Flow Turbine With Computer SoftwareMusab muaz sarıNo ratings yet
- Performance Test On A Multi-Cylinder Diesel Engine Fitted With Forced Draught Jet Compressor SuperchargerDocument14 pagesPerformance Test On A Multi-Cylinder Diesel Engine Fitted With Forced Draught Jet Compressor Superchargersridhar_pecNo ratings yet
- 14 - Final Exam (Only Questions)Document3 pages14 - Final Exam (Only Questions)حسن محمود حسن محمد 3760No ratings yet
- Constant Speed Characteristics of Pelton TurbineDocument5 pagesConstant Speed Characteristics of Pelton TurbineanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- C.O.P Derivation and Thermodynamic Calculation of Ammonia-Water Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System-2Document8 pagesC.O.P Derivation and Thermodynamic Calculation of Ammonia-Water Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System-2ErGiteshAroraNo ratings yet
- R2017 - ME8493 - Thermal Engineering - IDocument3 pagesR2017 - ME8493 - Thermal Engineering - IP.N. MohankumarNo ratings yet
- Manual - Reciprocating PumpDocument5 pagesManual - Reciprocating PumpcodersriramNo ratings yet
- Elias Dreik A1811286 - MECH324 Simulator ProjectDocument14 pagesElias Dreik A1811286 - MECH324 Simulator Projectelia.laeilaNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass TransferDocument28 pagesHeat and Mass TransfersureshkumarNo ratings yet
- CPD Assognment CH-19048Document9 pagesCPD Assognment CH-19048Mehreen NaveedNo ratings yet
- Machine Test ReportDocument10 pagesMachine Test ReportJaenudin AbdulahNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 - 110006 - Elements of Mechenical EngineeringDocument6 pagesAssignment2 - 110006 - Elements of Mechenical EngineeringSaniya Jumani0% (1)
- r05312105 Aerospace Propulsion IDocument8 pagesr05312105 Aerospace Propulsion ISrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Trial On Reciprocating CompressorDocument3 pagesTrial On Reciprocating CompressorHardik S. Borse100% (1)
- Centrifugal Pump Test Rig (With A.C Motor, 3 Speed With Step Cone Pulley)Document9 pagesCentrifugal Pump Test Rig (With A.C Motor, 3 Speed With Step Cone Pulley)Sandeep SainiNo ratings yet
- 13 - Machinery Service System - Starting Air System-1Document13 pages13 - Machinery Service System - Starting Air System-1Denis Irwin MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Test On Reciprocating Air CompressorDocument5 pagesTest On Reciprocating Air CompressorSuresh ChinnasamyNo ratings yet
- Study, Fabrication and Testing of Helical Blades (FYP) Final Year Presentation (Latest)Document40 pagesStudy, Fabrication and Testing of Helical Blades (FYP) Final Year Presentation (Latest)Hassan ArshadNo ratings yet
- Ramjet EngineDocument9 pagesRamjet EngineRajath ShettyNo ratings yet
- ME 430 Project 2Document16 pagesME 430 Project 2Izzy MirandillaNo ratings yet
- 2 Stage Air Compressor 2h PDocument9 pages2 Stage Air Compressor 2h PNilesh Vijay SabnisNo ratings yet
- Direct - Indirect - Regenerative Method of TestingDocument29 pagesDirect - Indirect - Regenerative Method of TestingASHIM KUMAR SAHUNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab ManualDocument37 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab ManualMohith MarripatiNo ratings yet
- 7 National Certification Examination FOR Energy Auditors - Nov., 2008Document8 pages7 National Certification Examination FOR Energy Auditors - Nov., 2008venkatraman1985No ratings yet
- Exp 2 Performance Parameter of Diesel EngineDocument7 pagesExp 2 Performance Parameter of Diesel EngineShashwat JainNo ratings yet
- Blood RelationDocument30 pagesBlood Relationvaibhav kuchekarNo ratings yet
- PeltonDocument14 pagesPeltonvaibhav kuchekarNo ratings yet
- Rit Ty Scholastic Aptitude Ut-Ii SyllabusDocument1 pageRit Ty Scholastic Aptitude Ut-Ii Syllabusvaibhav kuchekarNo ratings yet
- Series CompletionDocument10 pagesSeries Completionvaibhav kuchekarNo ratings yet
- Ty Mech (A) QBDocument36 pagesTy Mech (A) QBvaibhav kuchekarNo ratings yet
- Ty Mech (A) QBDocument36 pagesTy Mech (A) QBvaibhav kuchekarNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan CRS (J08E-VT) New - 500 (REDESIGN)Document30 pagesPengenalan CRS (J08E-VT) New - 500 (REDESIGN)jabrik bobelNo ratings yet
- Nomor Spare Part Opel BlazerDocument8 pagesNomor Spare Part Opel BlazerkulanavhieaNo ratings yet
- 202-24P EngDocument328 pages202-24P EngtehFattManNo ratings yet
- Waukesha Engine Bulletin 1079 20m 12 01Document18 pagesWaukesha Engine Bulletin 1079 20m 12 01Gustav MolMedNo ratings yet
- 1993 Yamaha XVZ13D - E - EC Parts CatalogDocument108 pages1993 Yamaha XVZ13D - E - EC Parts CatalogKevin M. CampbellNo ratings yet
- Service Manual For Briggs and Stratton 16 HP Twin Cylinder L Head EnginesDocument171 pagesService Manual For Briggs and Stratton 16 HP Twin Cylinder L Head EnginesKevins Small Engine and Tractor Service86% (83)
- 2008 Yamaha XV1900 Custom Raider SDocument10 pages2008 Yamaha XV1900 Custom Raider SIpoel StekelenburgNo ratings yet
- Qg18de WikiDocument3 pagesQg18de WikiGerald MoralesNo ratings yet
- Clark - C20 - 25 - 30 - 33 - 35LDocument374 pagesClark - C20 - 25 - 30 - 33 - 35LRoberto CarmelloNo ratings yet
- Auto GR 10 RELAB HOMEWORK ACTVITIES LEARNERSDocument68 pagesAuto GR 10 RELAB HOMEWORK ACTVITIES LEARNERSNaCo MúSįcîænNo ratings yet
- 1104A-44TG1 PerkinsDocument8 pages1104A-44TG1 PerkinsMario Eduardo Santos MartinsNo ratings yet
- 2019 Chevrolet Camaro V6-3.6L Vehicle Powertrain Management Diagrams Electrical - Interactive Color (Non OE) Engine Controls - Page 1 of 8Document5 pages2019 Chevrolet Camaro V6-3.6L Vehicle Powertrain Management Diagrams Electrical - Interactive Color (Non OE) Engine Controls - Page 1 of 8HelioEynerPrudencioCarreraNo ratings yet
- CH20S Service ManualDocument232 pagesCH20S Service ManualJennifer Surritt BissellNo ratings yet
- Nissan PF6-TB-TCDocument30 pagesNissan PF6-TB-TCready prima wijaya100% (3)
- Camshaft 1Document3 pagesCamshaft 1digyoNo ratings yet
- Motor Zongshen ZS156FMI-2ADocument191 pagesMotor Zongshen ZS156FMI-2Aserg perNo ratings yet
- WisecoDocument116 pagesWisecoAda TopanNo ratings yet
- User Manual: LM-1 RPM Converter (Aux. Input Cable #2)Document9 pagesUser Manual: LM-1 RPM Converter (Aux. Input Cable #2)Mohd Safian ZakariaNo ratings yet
- 026 StihlDocument48 pages026 StihlManuel PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Genebraldo Solved ProblemsDocument5 pagesGenebraldo Solved ProblemsDarwin Lim50% (2)
- Doosan Engine Dl06k Tier4i Operation Maintenance ManualDocument20 pagesDoosan Engine Dl06k Tier4i Operation Maintenance Manualcharlyn100% (39)
- Unit 16 Worksheet: Cooling Systems Competency Unit: AURTTC003 Diagnose and Repair Cooling SystemsDocument6 pagesUnit 16 Worksheet: Cooling Systems Competency Unit: AURTTC003 Diagnose and Repair Cooling SystemsajayNo ratings yet
- Renault K-Type EngineDocument24 pagesRenault K-Type EngineTaimoor AhmedNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics ME250: Submitted ToDocument12 pagesApplied Thermodynamics ME250: Submitted Tomad eye m00dyNo ratings yet
- Wet Stacking: Standby Power Systems Use The Diesel Engine. Diesel Is A ConvenientDocument2 pagesWet Stacking: Standby Power Systems Use The Diesel Engine. Diesel Is A ConvenientJ Alberto P ArrazateNo ratings yet
- Service - Service Manual Code 950 - 994 - 653Document30 pagesService - Service Manual Code 950 - 994 - 653Victor UribeNo ratings yet
- Bendix Air CompressorsDocument8 pagesBendix Air CompressorsPSNo ratings yet
- Marine Spec 12V2000M61 1A PDFDocument2 pagesMarine Spec 12V2000M61 1A PDFnaufragatoNo ratings yet
- Azera 2016 Engine RepairDocument186 pagesAzera 2016 Engine RepairReza Varamini0% (1)
- Group 13E Electronically Controlled Fuel SystemDocument57 pagesGroup 13E Electronically Controlled Fuel Systemandleralfonso7308No ratings yet