Professional Documents
Culture Documents
COM, Momentum & Collision
Uploaded by
Riya Shah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesCOM, Momentum & Collision
Uploaded by
Riya ShahCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
COM, Momentum and
Collision
All 2023 PYQ in CBT and PDF Format
https://t.me/vedantumath1/3944
Click on the above Link
COLLISIONS COM, Momentum
We define a collision as an isolated event in which two or more colliding
bodies exert relatively strong forces on each other for a relatively short and Collision
time.
Two key rules of the collision game are:
(i) Law of conservation of linear momentum, and CENTRE OF MASS
(ii) Law of conservation of energy.
(a) Elastic Collision: A collision in which there is absolutely no loss
of kinetic energy is called an elastic collision.
The basic characteristics of an elastic collision are:
(i) The linear momentum is conserved.
(ii) Total energy of the system is conserved.
(iii) The kinetic energy is conserved.
(iv) The forces involved during elastic collisions must be conservative
Kinematics of COM
forces.
(b) Inelastic Collision: A collision in which there occurs some loss
of kinetic energy is called an inelastic collision.
The basic characteristics of an inelastic collision are
(i) The linear momentum is conserved.
(ii) Total energy is conserved.
(iii) Kinetic energy is NOT conserved. Obviously, a part of kinetic energy
is converted into some other form of energy e.g., heat energy, sound
energy etc.
(iv) Some or all the forces involved in an inelastic collision may be
non-conservative in nature
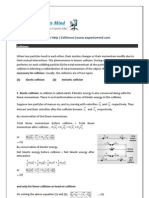
COM, Momentum Inelastic Collision in One Dimension
and Collision m1 u 1 + m 2 u 2 = m 1 v 1 + m 2
v2
Elastic Collision in One Dimension
Elastic Collision in two Dimension of Oblique Collision
0 = m1 v1 sin θ - m2 v2 sin ϕ
v2 - v 1 = u 1 - u 2
Hence, in one dimensional elastic collision
relative velocity of separation after collision is
equal to relative velocity of approach before
collision. Perfectly inelastic collision in two dimensions
m1 u1 sin θ + 0 = (m1 + m2) V sin ϕ
COM, Momentum and
Collision
All 2023 PYQ in CBT and PDF Format
https://t.me/vedantumath1/3944
Click on the above Link
You might also like
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Fundamentals of Maxwel's Kinetic Theory of a Simple Monatomic Gas: Treated as a Branch of Rational MechanicsFrom EverandFundamentals of Maxwel's Kinetic Theory of a Simple Monatomic Gas: Treated as a Branch of Rational MechanicsNo ratings yet
- COM, Momentum and Collision: All 2023 PYQ in CBT and PDF FormatDocument4 pagesCOM, Momentum and Collision: All 2023 PYQ in CBT and PDF FormatRiya ShahNo ratings yet
- Com, Momentum and CollisionDocument2 pagesCom, Momentum and Collisionaadiv2012006No ratings yet
- L MomentumDocument7 pagesL Momentumtrioasa3No ratings yet
- g484 Module 1 4 1 2 CollisionsDocument8 pagesg484 Module 1 4 1 2 Collisionsapi-236179294No ratings yet
- Com Magnetism CollisionDocument2 pagesCom Magnetism CollisionnevereverprabhasNo ratings yet
- Pages From Collossion 11Document4 pagesPages From Collossion 11Rohit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Elastic Collision Questions - Practice Questions With AnswersDocument3 pagesElastic Collision Questions - Practice Questions With AnswersAkhtar lokhandwalaNo ratings yet
- Momentum: © 2016 Pearson Education, IncDocument44 pagesMomentum: © 2016 Pearson Education, IncMaRk KenchiNo ratings yet
- Law of Conservation of MomentumDocument4 pagesLaw of Conservation of MomentumGianne Karl AlmarinesNo ratings yet
- Class22 Collisions PDFDocument3 pagesClass22 Collisions PDFprakash tyagiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Linear Momentum and CollisionsDocument18 pagesChapter 9: Linear Momentum and CollisionsSehati FisikaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 151 - Notes For Online Lecture #19: Conservation of Linear Momentum in 2-DDocument4 pagesPHYSICS 151 - Notes For Online Lecture #19: Conservation of Linear Momentum in 2-DCece SantosNo ratings yet
- Momentum LabatoryDocument0 pagesMomentum LabatoryDaniel LiuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Physics LectureDocument13 pagesChapter 2 - Physics LectureTirso FabillarNo ratings yet
- SMK Tat Beng Physics Form 4 2.4 Linear MomentumDocument41 pagesSMK Tat Beng Physics Form 4 2.4 Linear MomentumTee Ting QINo ratings yet
- Moi PDFDocument16 pagesMoi PDFHsjajNo ratings yet
- لقطة شاشة 2023-11-16 في 9.11.43 صDocument35 pagesلقطة شاشة 2023-11-16 في 9.11.43 ص5sr6xmsbsbNo ratings yet
- Physics (HRK) Chapter 10: CollisionsDocument10 pagesPhysics (HRK) Chapter 10: Collisionstariq8physicsNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument8 pagesMomentumapi-3806615No ratings yet
- Physics I Class 11: Conservative Forces, Non-Conservative Forces, and CollisionsDocument18 pagesPhysics I Class 11: Conservative Forces, Non-Conservative Forces, and Collisionsjai yadavNo ratings yet
- Physics I Class 11: Conservative Forces, Non-Conservative Forces, and CollisionsDocument18 pagesPhysics I Class 11: Conservative Forces, Non-Conservative Forces, and CollisionsAhmed FahmyNo ratings yet
- Collision PresentationDocument17 pagesCollision PresentationBokstarwel nongsiejNo ratings yet
- Metode Conjugate BeamDocument5 pagesMetode Conjugate Beamnurul saniyyahNo ratings yet
- LM & Collisions MaterialDocument27 pagesLM & Collisions MaterialNETHAKANI SUJATHA0% (1)
- PHY 1 Mod 09 Mod (Collision)Document9 pagesPHY 1 Mod 09 Mod (Collision)Shamim ImtiazNo ratings yet
- CollisionsDocument2 pagesCollisionsExpertsmindEduNo ratings yet
- Conservation of MomentumDocument19 pagesConservation of MomentumwscienceNo ratings yet
- Program of "Physics": Lecturer: Dr. DO Xuan Hoi Room A1. 503 E-MailDocument33 pagesProgram of "Physics": Lecturer: Dr. DO Xuan Hoi Room A1. 503 E-MailThu HòaNo ratings yet
- Rotational Strain in Weyl Semimetals: A Continuum Approach: PHYSICAL REVIEW B 97, 201404 (R) (2018)Document4 pagesRotational Strain in Weyl Semimetals: A Continuum Approach: PHYSICAL REVIEW B 97, 201404 (R) (2018)DanielAlejandroBonillaMorenoNo ratings yet
- Linear MomentumDocument8 pagesLinear Momentumasegamorish246No ratings yet
- Linear Momentum and CollisionsDocument22 pagesLinear Momentum and CollisionsAliyah CortezaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Momentum and CollisionsDocument59 pagesChapter 6 - Momentum and CollisionsAchiri TangeNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Collision and Centre of Mass SystemDocument23 pages3.1 Collision and Centre of Mass Systemraki tetNo ratings yet
- Mod 3Document12 pagesMod 3S M AkashNo ratings yet
- CollisionDocument34 pagesCollisionAshutoshYelgulwar100% (4)
- Class - XI - ch-6, Work Energy Power, Module 5Document14 pagesClass - XI - ch-6, Work Energy Power, Module 5Sayan MajiNo ratings yet
- Physics ConceptDocument2 pagesPhysics ConceptSyahirah RosliNo ratings yet
- NaveedGhani 2986 17586 3 Chapter06Document38 pagesNaveedGhani 2986 17586 3 Chapter06Muhammad Ahmed AsimNo ratings yet
- 2 Linear Momentum PDFDocument16 pages2 Linear Momentum PDFJacquelyn CocamasNo ratings yet
- Linear Momentum SlideDocument32 pagesLinear Momentum SlideZhi QingNo ratings yet
- Module 4-Mechanics: CollisionsDocument32 pagesModule 4-Mechanics: CollisionsHead LightNo ratings yet
- CollisionsDocument3 pagesCollisionsapi-242844746No ratings yet
- 7 (II) Circular Motion & Rotational Dynamics-TheoryDocument13 pages7 (II) Circular Motion & Rotational Dynamics-TheoryTarun RajputNo ratings yet
- Collision (Tumbukan)Document43 pagesCollision (Tumbukan)bat.laughNo ratings yet
- FAP0015 Ch07 MomentumDocument46 pagesFAP0015 Ch07 MomentumMuhammad AnwarNo ratings yet
- GR 12 Physics Collisions Lesson (Elastic and Inelastic)Document13 pagesGR 12 Physics Collisions Lesson (Elastic and Inelastic)AN - 12BM 795510 Harold M Brathwaite SSNo ratings yet
- Collisions: Mu Mu MV MVDocument15 pagesCollisions: Mu Mu MV MVReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of A System of ParticlesDocument32 pagesDynamics of A System of ParticlesIzham IsmailNo ratings yet
- EXP 6 Fundamentals of KinematicsDocument4 pagesEXP 6 Fundamentals of KinematicsRajesh KherdeNo ratings yet
- Momentum: Physicists have defined a quantity called (動量) of a moving object as..Document27 pagesMomentum: Physicists have defined a quantity called (動量) of a moving object as..eltytanNo ratings yet
- Sec. 2.4 Coulomb-Damped Free Vibration: (T) From Eq. (2.2.4) and Its Derivative U (T) Into Eq. (2.3.2)Document1 pageSec. 2.4 Coulomb-Damped Free Vibration: (T) From Eq. (2.2.4) and Its Derivative U (T) Into Eq. (2.3.2)Muhammad Junaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Questions On MomentumDocument12 pagesPaper 1 Questions On MomentumAhmed DataNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Crash Study Using Virtual SimulationDocument75 pagesVehicle Crash Study Using Virtual SimulationPrabhu MuniyandiNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument15 pagesPhysics ProjectNishant AgrawalNo ratings yet
- MCE 233 Mechanics of Machines III Part 1Document42 pagesMCE 233 Mechanics of Machines III Part 1Emmanuel KutaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document42 pagesChapter 15Thinesh Rau KrishnamurtyNo ratings yet
- Control Chapter 2 8EDocument25 pagesControl Chapter 2 8EE24089046林雯琪No ratings yet
- Phys111 Lecture08Document54 pagesPhys111 Lecture08Joel BulawanNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Quarter 1 - Module 8Document35 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Quarter 1 - Module 8Sarahmae MeñozaNo ratings yet
- Impulse and Momentum: Physics For Engineers - Module 8Document5 pagesImpulse and Momentum: Physics For Engineers - Module 8Camille SergioNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6: Coefficient of Restitution: Nicole Irvin H. Balbastro, Phy10L/BC2Document4 pagesExperiment 6: Coefficient of Restitution: Nicole Irvin H. Balbastro, Phy10L/BC2GedNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Melc 9Document9 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Melc 9Kyro KlinxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 MomentumDocument6 pagesChapter 6 MomentumAbdulaziz AlMuallimNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 9 AnswersDocument40 pagesPhysics Chapter 9 AnswersAbovethesystem94% (17)
- Chapter 8-Phy220Document42 pagesChapter 8-Phy220Jordan TuckerNo ratings yet
- 4th-Qrtr-dll Gr.-9Document29 pages4th-Qrtr-dll Gr.-9harold carbonelNo ratings yet
- IZhO 2023 PhysTheory 2023Document20 pagesIZhO 2023 PhysTheory 2023Radho LikaldyNo ratings yet
- Xtra C3Document2 pagesXtra C3hanimNo ratings yet
- Forces, Newton's Laws & Momentum: NameDocument47 pagesForces, Newton's Laws & Momentum: Nameapi-254547723No ratings yet
- Term Project - Pinball MachineDocument22 pagesTerm Project - Pinball Machineapi-311898795No ratings yet
- Work, Energy, and PowerDocument41 pagesWork, Energy, and PowerDebayanbasu.juNo ratings yet
- IB Physics Topic 2-4 Paper 1 ProblemsDocument20 pagesIB Physics Topic 2-4 Paper 1 Problemswonjunlim0819No ratings yet
- ProblemSet3 SolutionsDocument8 pagesProblemSet3 SolutionsnormanNo ratings yet
- Transient Recovery VoltageDocument46 pagesTransient Recovery VoltagecamNo ratings yet
- Lab Report PhyI-04 - Collisions - Ajay RamsaranDocument9 pagesLab Report PhyI-04 - Collisions - Ajay RamsaranajayramsaranNo ratings yet
- 1 Worksheet: Intermediate LevelDocument2 pages1 Worksheet: Intermediate LevelWawan RuswandiNo ratings yet
- Linear Momentum and CollisionsDocument7 pagesLinear Momentum and CollisionsFaris AlasmariNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument32 pagesPhysical ScienceAisheti Imasu Reb YaguNo ratings yet
- 9702 May June 2011 All Question Papers1Document268 pages9702 May June 2011 All Question Papers1Bilal Ahsan SalamNo ratings yet
- Centre of MassDocument32 pagesCentre of MassR.Yashwanth Raj XBNo ratings yet
- Pre-UPS1 SP015 (Copy) : Please Answer All Questions in 30 MinutesDocument11 pagesPre-UPS1 SP015 (Copy) : Please Answer All Questions in 30 MinutesWAN NUR ALEEYA TASNIM BINTI WAN MOHAMED HAZMAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Aptitude PDFDocument10 pagesAptitude PDFRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Physics Cbcs Draft SyllabusDocument106 pagesPhysics Cbcs Draft SyllabusSayantan DeyNo ratings yet
- Pendulum AnimationDocument4 pagesPendulum AnimationFeynmanFanNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases - PhysicsDocument17 pagesKinetic Molecular Theory of Gases - PhysicssrdjanNo ratings yet
- Elastic and Inelastic CollisionsDocument2 pagesElastic and Inelastic CollisionsRaymond ChanNo ratings yet
- Set3 PDFDocument36 pagesSet3 PDFvishwas100% (1)
- Momentum Problem Set PDFDocument3 pagesMomentum Problem Set PDFNirmaan ShankerNo ratings yet