Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Slowing of population growth
Uploaded by
MADAYAG, RUTH L.Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Slowing of population growth
Uploaded by
MADAYAG, RUTH L.Copyright:
Available Formats
Slowing of population growth- Today, global fertility rates are declining.
In the 1960s, the average
world fertility rate was nearly five children per woman; in 2019, the rate was 2.4 children per woman.
This is largely a result of increased access to contraception and abortion, allowing people greater control
over the number of children they have.
Slowing of population growth- is the declining rate of population, where in the fertility rate decreases that
affects the growth of population. In the 1960s, the average world fertility rate was nearly five children per
woman; in 2019, the rate was 2.4 children per woman.
Factors that contribute to slowing of population growth:
1. Aging-
2. What causes population growth and decline?
3. Three factors influence population: births, deaths, and migration. Of
course, giving birth, dying, or moving to another country are deeply
personal and life-changing moments for individuals and their families.
Although totaling up such events into a handful of statistics seems
impersonal, policymakers have to do just that, because those statistics
can have profound effects on a country as a whole.
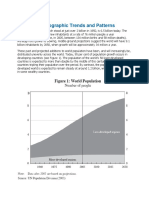
4. For much of human history, population sizes were relatively stable
because deaths were so frequent that people could barely have children
fast enough to sustain growth. But the mortality rates, or the proportion
of people who die in a year, in many countries began to decline during
the Industrial Revolution due to advances in hygiene, infrastructure,
and vaccinations. Major developments in health care starting in the
twentieth century also resulted in longer and healthier lives. Those gains
set off a period of exponential global population growth, with global life
expectancy skyrocketing from just thirty-two years in 1900 to over
seventy today.
You might also like
- Mortality DeclineDocument13 pagesMortality DeclineKathrina GabrielNo ratings yet
- GLOBAL PERSPECTIVES Final RevisionDocument25 pagesGLOBAL PERSPECTIVES Final RevisionApparatus BoxNo ratings yet
- China's One-Child Policy Success Slowing Population GrowthDocument42 pagesChina's One-Child Policy Success Slowing Population Growthreem aldanafNo ratings yet
- Population Growth and Economic Development:: Causes, Consequences and ControversiesDocument14 pagesPopulation Growth and Economic Development:: Causes, Consequences and Controversiesjainaastha111No ratings yet
- Development Economics Chapter 2Document1 pageDevelopment Economics Chapter 2ZohaibNo ratings yet
- 4 PopulationDocument39 pages4 PopulationJoseph MusosoNo ratings yet
- Demography (Supplemental Lecture)Document3 pagesDemography (Supplemental Lecture)Roldan MapeNo ratings yet
- Global Demography ReportDocument19 pagesGlobal Demography ReportSamantha Isabel Villaruel ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Biology Project Class 12Document14 pagesBiology Project Class 12bhaveshtupe06No ratings yet
- A Pivotal Moment: Population, Justice, and the Environmental ChallengeFrom EverandA Pivotal Moment: Population, Justice, and the Environmental ChallengeNo ratings yet
- Understanding Global Population TrendsDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Global Population TrendsArvie TVNo ratings yet
- Human PopulationDocument7 pagesHuman PopulationCHARLESTON DONALDNo ratings yet
- ENGLISHDocument15 pagesENGLISHElen. UnusyanNo ratings yet
- Tafelberg Short: The Politics of Pregnancy: From 'population control' to women in controlFrom EverandTafelberg Short: The Politics of Pregnancy: From 'population control' to women in controlNo ratings yet
- Demographic Transition PowerPointDocument63 pagesDemographic Transition PowerPointTechnoShindoNo ratings yet
- Population ExplosionDocument3 pagesPopulation ExplosionAnonymous 5CZJEbGvNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 Pandemic and Global DemographyDocument3 pagesCovid-19 Pandemic and Global DemographyGil TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Human Impact On The EnvironmentDocument32 pagesHuman Impact On The EnvironmentHiếu VũNo ratings yet
- The Population Explosion: Causes and Consequences of Rapid GrowthDocument11 pagesThe Population Explosion: Causes and Consequences of Rapid GrowthShashi CampherNo ratings yet
- How Does Population Change?Document2 pagesHow Does Population Change?Pramodini De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Global Demographic TrendsDocument6 pagesGlobal Demographic TrendsRoyce Bog-aconNo ratings yet
- 10global Demography (58 69)Document12 pages10global Demography (58 69)Tam Gerald CalzadoNo ratings yet
- Demograpy and developmentDocument12 pagesDemograpy and developmentAditya GogoiNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper On Population AgingDocument7 pagesConcept Paper On Population AgingCamila Jayz VillarNo ratings yet
- Demographic transition theory explainedDocument11 pagesDemographic transition theory explainedMorya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- IB Revision The Core Topic 1 - Populations in TransitionDocument10 pagesIB Revision The Core Topic 1 - Populations in TransitiontomNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 Pandemic Impact on Demographic TransitionDocument3 pagesCovid-19 Pandemic Impact on Demographic TransitionAnnie JoeNo ratings yet
- WINTER SEMESTER 2021-22 ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES DIGITAL ASSIGNMENT FIVEDocument10 pagesWINTER SEMESTER 2021-22 ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES DIGITAL ASSIGNMENT FIVEDevarakonda SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Reproduction in Human Part 2Document10 pagesChapter 2-Reproduction in Human Part 2HealNo ratings yet
- Where World Population Has GrownDocument13 pagesWhere World Population Has GrownSyasya ZdsNo ratings yet
- Expose Croissance DemographiqueDocument4 pagesExpose Croissance Demographiquevalerielascar85No ratings yet
- Population growthDocument6 pagesPopulation growthcryptow361No ratings yet
- Population Growth and Economic DevelopmentDocument57 pagesPopulation Growth and Economic DevelopmentTasnim Hosna100% (1)
- Population growth rates and the demographic transitionDocument2 pagesPopulation growth rates and the demographic transitionDéboraFernandesNo ratings yet
- CH 9 OutlineDocument5 pagesCH 9 Outlinedklein172No ratings yet
- The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2020From EverandThe Sustainable Development Goals Report 2020No ratings yet
- What Is OverpopulationDocument19 pagesWhat Is OverpopulationChantal Yvette FregillanaNo ratings yet
- Demography Final Handout CorrectedDocument20 pagesDemography Final Handout Correctedmadanlal sainiNo ratings yet
- Population Dynamics & Processes: Birth, or Fertility, RatesDocument9 pagesPopulation Dynamics & Processes: Birth, or Fertility, RatesSamantha Ann T. TirthdasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document2 pagesChapter 6Zhane CruzNo ratings yet
- Community Health-1Document52 pagesCommunity Health-1MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Poplation ExplosionDocument19 pagesPoplation ExplosionNilanjan Gupta Biswas100% (1)
- The Demographic Transition ModelDocument19 pagesThe Demographic Transition ModelIsha BalangueNo ratings yet
- Butuan Doctors’ College Population Increases Living in the IT EraDocument10 pagesButuan Doctors’ College Population Increases Living in the IT EraJana JaboniteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - The Human Population and Its Impact To The EnvironmentDocument59 pagesChapter 6 - The Human Population and Its Impact To The Environmentgwapak83No ratings yet
- Assignment On Demography....Document4 pagesAssignment On Demography....biswasjoyNo ratings yet
- Population DynamicsDocument9 pagesPopulation DynamicsMaria Abegail Tinasas RiveroNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Ecology 7th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesEssentials of Ecology 7th Edition Miller Solutions Manualrachelhalecwqxjebfny100% (25)
- Essentials of Ecology 7th Edition Miller Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesEssentials of Ecology 7th Edition Miller Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFischiummargrave80ep100% (11)
- Global Demographic Trends and PatternsDocument5 pagesGlobal Demographic Trends and PatternsValerieAnnVilleroAlvarezValienteNo ratings yet
- 2013 - UCL - Lancet - Popn D'ment Climate Change and HealthDocument9 pages2013 - UCL - Lancet - Popn D'ment Climate Change and HealthgrowlfunNo ratings yet
- Week 8 TERMS IN DEMOGRAPHYDocument3 pagesWeek 8 TERMS IN DEMOGRAPHYJayson ReyNo ratings yet
- Living in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesLiving in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions Manual 1elizabethvasquezcmpyrnxgjb100% (26)
- Living in The Environment 18Th Edition Miller Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesLiving in The Environment 18Th Edition Miller Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFlarry.goodsell452100% (11)
- Causes of Rapid Population Growth in the PhilippinesDocument3 pagesCauses of Rapid Population Growth in the PhilippinesJulius Gabriel CallejoNo ratings yet
- What Factors Drive Population Growth RatesDocument4 pagesWhat Factors Drive Population Growth RatesJM CamalonNo ratings yet
- What Is Global Health and Why Is It ImportantDocument7 pagesWhat Is Global Health and Why Is It ImportantSanty ManuelNo ratings yet
- Review of Literature (My Part)Document1 pageReview of Literature (My Part)MADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet
- A NSWERDocument2 pagesA NSWERMADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet
- CPAR Activity LogDocument1 pageCPAR Activity LogMADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet
- CASAGRA BSN1-A GROUP 2 End-Term ReportDocument19 pagesCASAGRA BSN1-A GROUP 2 End-Term ReportMADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet
- BLOOM'S Taxonomy 2nd semester lectureDocument8 pagesBLOOM'S Taxonomy 2nd semester lectureMADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet
- TFN ReviewerDocument2 pagesTFN ReviewerMADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet
- Group 4, TFN FINALSDocument21 pagesGroup 4, TFN FINALSMADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet
- Imogene KingDocument2 pagesImogene KingMADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet
- Holy Rosary PrayersDocument9 pagesHoly Rosary PrayersMADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet
- TFN ReviewerDocument2 pagesTFN ReviewerMADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet
- Florence Nightingale Precise BiographyDocument15 pagesFlorence Nightingale Precise BiographyMADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet
- Biography and Career of DR Patricia Benner and Sister Callista RoyDocument25 pagesBiography and Career of DR Patricia Benner and Sister Callista RoyMADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet
- Inside Out - MILDocument1 pageInside Out - MILMADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet
- Biography and Career of DR Patricia Benner and Sister Callista RoyDocument25 pagesBiography and Career of DR Patricia Benner and Sister Callista RoyMADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet