Professional Documents
Culture Documents
N3 Engineering Science February 2022 Memorandum
Uploaded by
Nkazimulo MbonaniCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
N3 Engineering Science February 2022 Memorandum
Uploaded by
Nkazimulo MbonaniCopyright:
Available Formats
MARKING GUIDELINE
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE
ENGINEERING SCINCE N3
3 February 2022
This marking guideline consists of 6 pages.
Copyright reserved Please turn over
QUESTION 1
1.1 D (1)
1.2 C (2)
1.3 A (1)
1.4 A (2)
1.5 C (2)
1.6 B (1)
1.7 C (2)
1.8 A (3)
1.9 A (2)
[16]
QUESTION 2
2.1 Force multiplied by the perpendicular distance from the turning point to the line
of action of the force. (1)
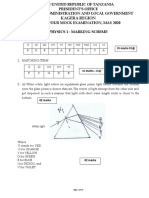
2.2 2.2.1 40 N 10 N 30 N
5 N/m
2m 5m 1m 2m
A B C D E
(1 mark for position of the correct positions of the supports)
(½ mark for correct position of distributed load)
(1 ½ mark for correct concentrated loads) (3)
2.2.2 Taking moments about B
∑CM =∑ACM
40x2 + Cx5 + 10x1 =25x2,5 + 5x5.5 + 10x6 + 10x7 + 30x8
C = 74N
Taking moments about C
∑CM =∑ACM
40x7 + 25x2.5 + 10x6 = 5xB +10X1 + 5x0.5 + 2x10 + 30x3
B = 56N (4)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
2.2.3
55 N√ 50 N√
6 N√ 30 N√
40 N√
0N
-19 N√
-40 N√ -50 N√
(4)
[12]
QUESTION 3
3.1.1 ∑Vc = 25 +20sin45º + 80sin30º -15sin60º√
= +66,152kN (North)
∑Hc = -20cos45º + 80cos30º + 15cos60º√
= +62,64kN (East) (4)
3.1.2 R 2 = 66,1522 + 62,642 α = tan-1(66,152/62,64)
R = 91,076kN = 46,560 = E46,56N (4)
3.1.3 Therefore the Equilibrant = W46,56S (1)
3.2 Sin 45 = 15 /AB Tan45 = 15/ BC
BC=15kN tie
AB = 15 /sin45
=21,213kN strut (6)
[15]
Copyright reserved Please turn over
QUESTION 4
4.1 Causes objects moving across one another to wear away
Causes irritating noise in some cases
Causes fluids to move with difficulty through pipes
Cause objects like scissors to get blunt
Friction causes heat which causes car tyres to slip
(Any 3 × 1) (3)
4.2 4.2.1 Fc = Wcos200
= 100 × 9,8cos20
= 920,899N
4.2.2 Fs = Wsin200
= 100x9,8xsin200
= 335,18N
4.2.3 Fµ = N x µ
= 920,899 x 0,36
= 331,524N
4.2.4 Fup = Fµ + Fs
= 331,524 +335,18
= 666,704N
(4 × 2) (8)
[11]
QUESTION 5
5.1 5.1.1 Mass of oil = 2.1 × 0.85
= 1.785 kg
Qoil = m × c ×(T2- T1)
= 1.785 × 2000 × (135 - 32)
= 367.710kJ (4)
5.1.2 Qfuel = Qoil /ɳ
= (367.710/0.45)
= 817.133kJ (2)
5.1.3 E = hv × m
hv = 817.13 /5
=163.426kJ/kg (2)
5.1.4 P = Qfuel/t
= 817.13 /(30 × 60)
= 0.452 kW (2)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
5.2 5.2.1 hf = 1042 kJ/kg × 5 kg = 5210 kJ (1)
5.2.2 hg = 2802 kJ/kg × 5 kg = 14010 kJ (1)
5.2.3 hfg =1760 kJ/kg × 5 kg = 8800 kJ (1)
5.2.4 hwet = (hf + xhfg ) × 5 kg
= (1042 + 0.9 × 1760) kJ/kg × 5 kg
= 13130 kJ (2)
[15]
QUESTION 6
6.1 6.1.1 WD = P × V = ρgh × V = 1000 × 9,8 × 20 × (π × 302 × 10)/4
= 1386856077 J
= 1386.856 MJ
6.1.2 P = WD/t
= 1386856077/3600 × 3
= 128.333 kW
(2 × 2) (4)
6.2 6.2.1 F/f = D2 /d2
F = 254 × 0.42 /(0.07)2
F = 8293.878N 0R 8.294 kN
6.2.2 D 2 × h = d2 × H × n
h = (0,072 × 0,8 × 30) / 0,42
= 0,735 m
= 735 mm
6.2.3 D 2 × h = d2 × H × n
n = 0,42 × 7,5 /(0,072 × 0,8)
= 306,122
≈ 307 strokes
6.2.4 V = ((π × D2) / 4 × h)
= (π × 0.42) / 4) × 7.5
= 0.943 m3
= 943 litres
(4 × 2) (8)
[12]
QUESTION 7
7.1 7.1.1 Rp = r1 × r2 /{r1 + r2)
= 6 × 12 /(18)
= 4 Ω
Rt = 4 + 2 +1.6
= 7.6 Ω (3)
Copyright reserved Please turn over
7.1.2 It = V / R
= 24/7,6
= 3.158 A (2)
7.2 7.2.1 P = WD/t
750 = WD/(5 × 60)
WD = 225 kJ (2)
7.2.2 Q = m × c × (t2-t1)
= 5 × 4187 × (98 – 20)
= 1632.930kJ
P = W/t
1632,930 /750 = t
t = 2177.24 s = 36mins 18s (4)
7.2.3 P = VI
I = 750 /220
I = 3.409A (2)
[13]
QUESTION 8
8.1 Metals Non-metals
Found on the far left of the periodic Found on the Right side√
table√
Give up free electrons√ Take up free electrons√
Good conductors of electricity Poor conductors of electricity
(Any TWO)
(2)
8.2 Painting the metal
Applying oil and grease
Electroplating
Galvanising
Tinning (Any 4 × 1) (4)
[6]
TOTAL: 100
Copyright reserved
You might also like
- N3 Engineering Science August 2018 MemorandumDocument7 pagesN3 Engineering Science August 2018 MemorandumNkazimulo MbonaniNo ratings yet
- Lakshya JEE (2024)Document10 pagesLakshya JEE (2024)sunilbadgoti488No ratings yet
- N3 Engineering Science August 2019 MemorandumDocument7 pagesN3 Engineering Science August 2019 MemorandumNkazimulo MbonaniNo ratings yet
- Topic Test Memo (Electrodynamics 2023) - 1Document5 pagesTopic Test Memo (Electrodynamics 2023) - 1hlsetlalentoasecNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2023 - 24th JAN - Evening Shift - Solutions PDFDocument18 pagesJEE Main 2023 - 24th JAN - Evening Shift - Solutions PDFHarshilNo ratings yet
- MS Set 08Document10 pagesMS Set 08MUHAMMAD MOMINNo ratings yet
- AIS VTUPulse - Com ModDocument10 pagesAIS VTUPulse - Com Modnaga rajNo ratings yet
- (Main) : Computer Based Test (CBT)Document8 pages(Main) : Computer Based Test (CBT)Resonance EduventuresNo ratings yet
- N4 Electrotechnics April 2020 MemorandumDocument8 pagesN4 Electrotechnics April 2020 MemorandumPetro Susan BarnardNo ratings yet
- N3 Engineering Science August 2021 MemorandumDocument8 pagesN3 Engineering Science August 2021 MemorandumNkazimulo MbonaniNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2019 Paper Answer Physics 09-01-2019 1stDocument7 pagesJEE Main 2019 Paper Answer Physics 09-01-2019 1stDeepak SainiNo ratings yet
- 2022 JEE Main 18 SolutionsDocument20 pages2022 JEE Main 18 SolutionsHimanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Physics v2 1213 Ms FinalDocument10 pagesPhysics v2 1213 Ms Finalfarid oluwasegun SHITTUNo ratings yet
- Module-4: Flexibility Matrix MethodDocument10 pagesModule-4: Flexibility Matrix MethodCE 11 Aryan VyasNo ratings yet
- T760 - INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS N2 MEMO APR 2021 Signed OffDocument8 pagesT760 - INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS N2 MEMO APR 2021 Signed Off2pietersmit1997No ratings yet
- Trans ANL 6Document8 pagesTrans ANL 6Natchuta LailangNo ratings yet
- Chem Practice Paper 2 MsDocument8 pagesChem Practice Paper 2 MsSANAJ BSNo ratings yet
- Memo Phy SC Provp1 Grade 11 June 2016Document8 pagesMemo Phy SC Provp1 Grade 11 June 2016Michael EbenezerNo ratings yet
- 5 1 1answerkeyDocument20 pages5 1 1answerkeysuvaan.g13No ratings yet
- N3 Engineering Science April 2021 MemorandumDocument9 pagesN3 Engineering Science April 2021 MemorandumNkazimulo MbonaniNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 2020 P2 MemoDocument11 pagesMathematics 2020 P2 Memolindort00No ratings yet
- Engineering Science N4 Exam Paper 2 Memo 2018Document15 pagesEngineering Science N4 Exam Paper 2 Memo 2018Bradley Da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Physics SyllabusDocument8 pagesPhysics Syllabussinghayush.cktNo ratings yet
- Dielectric ConstantDocument4 pagesDielectric Constantupadhye21No ratings yet
- CST 01 QPDocument18 pagesCST 01 QPmidhatsyedpukhtaNo ratings yet
- Microelectronic Circuit Design Third Edition - Part I Solutions To ExercisesDocument20 pagesMicroelectronic Circuit Design Third Edition - Part I Solutions To ExercisesvoonmingchooNo ratings yet
- C Q V Q CV Q 6× 2.1× 10 × 10 Q 1.26 × 10 F: 1. (A) (I) Define The Term Capacitance'. (1 Mark)Document24 pagesC Q V Q CV Q 6× 2.1× 10 × 10 Q 1.26 × 10 F: 1. (A) (I) Define The Term Capacitance'. (1 Mark)Adam mahabirNo ratings yet
- Jee-2024 Part Test-02 SolutionsDocument13 pagesJee-2024 Part Test-02 Solutionsarmaankaushik310No ratings yet
- PHYSICS 1 Marking SchemeDocument10 pagesPHYSICS 1 Marking SchemeEddie Michael RwegasiraNo ratings yet
- Ix Ro Kolkata 2022-2023Document15 pagesIx Ro Kolkata 2022-2023Ritam AichNo ratings yet
- D0679MA2 Ans 1Document10 pagesD0679MA2 Ans 1AnantNo ratings yet
- g10 PSC p1 Jun 2019 and MemoDocument17 pagesg10 PSC p1 Jun 2019 and MemoSamkele SibiyaNo ratings yet
- 2211 Enthusiast NSEP-04 Answerkey & SolutionDocument11 pages2211 Enthusiast NSEP-04 Answerkey & SolutionGeeta Kirit MithiyaNo ratings yet
- Ma2-048 MS PDFDocument10 pagesMa2-048 MS PDFMonginis - Bharati VidyapeethNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: (Jee Advance) Paper-2Document14 pagesAnswer Key: (Jee Advance) Paper-2DrManoj Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electrotechnics N4 August 2022 Memorandum PDFDocument8 pagesElectrotechnics N4 August 2022 Memorandum PDFPetro Susan BarnardNo ratings yet
- MathsBasic MSDocument13 pagesMathsBasic MSHans rajNo ratings yet
- MathsBasic MSDocument13 pagesMathsBasic MSHarish Jayaraj JANo ratings yet
- N4 Electrotechnics August 2021 MemorandumDocument8 pagesN4 Electrotechnics August 2021 MemorandumPetro Susan BarnardNo ratings yet
- Xii PB Physics MS - 231207 - 172617Document10 pagesXii PB Physics MS - 231207 - 172617Hitesh PerniNo ratings yet
- Answers & Solutions: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2019 (Online) Phase-2Document22 pagesAnswers & Solutions: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2019 (Online) Phase-2Gagan GoyalNo ratings yet
- T Cot An Cosec Cos + - (3) : 15 11 (A) (I) Show ThatDocument15 pagesT Cot An Cosec Cos + - (3) : 15 11 (A) (I) Show ThatRichard FernandezNo ratings yet
- EjerciciosResueltos Mathematics For Nurses Chapter2Document9 pagesEjerciciosResueltos Mathematics For Nurses Chapter2Andrew EstupiñanNo ratings yet
- Topic Test Memo g12 (Electric Circuits 2023) - 1Document5 pagesTopic Test Memo g12 (Electric Circuits 2023) - 1hlsetlalentoasecNo ratings yet
- t530 - Electrotechnics n4 MG April 2021Document9 pagest530 - Electrotechnics n4 MG April 2021Logan JesseNo ratings yet
- Soalan Ramalan Fizik SPM2020 (Skema Jawapan)Document8 pagesSoalan Ramalan Fizik SPM2020 (Skema Jawapan)Aunee AfifahNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class IX Mathematics Paper 3 - Solution: SECTION - A (40 Marks) Q. 1Document16 pagesICSE Board Class IX Mathematics Paper 3 - Solution: SECTION - A (40 Marks) Q. 1Niloy SahaNo ratings yet
- Bacsafra StrucDocument9 pagesBacsafra StrucjohnnycollideNo ratings yet
- Class XII Physics DPP Set (22) - Prev Chaps + EMFDocument20 pagesClass XII Physics DPP Set (22) - Prev Chaps + EMFVarun PatilNo ratings yet
- H2 MYE Revision Package Vectors SolutionsDocument11 pagesH2 MYE Revision Package Vectors SolutionsTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 09B CF+OYM (P1) 2024 SolDocument8 pagesPractice Test 09B CF+OYM (P1) 2024 SolDeenatrushna SahooNo ratings yet
- BrushUp 21404 21Document47 pagesBrushUp 21404 21nantichaNo ratings yet
- CE Test 10 Obj Solution PDFDocument9 pagesCE Test 10 Obj Solution PDFRAHUL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan Matematik Percubaan PMR 2010 (Perlis)Document7 pagesSkema Jawapan Matematik Percubaan PMR 2010 (Perlis)Farah Shafiqah AmiruddinNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-03-03 - (12th & 13th) Paper 1.pdf SOLUTIONDocument8 pagesPHYSICS-03-03 - (12th & 13th) Paper 1.pdf SOLUTIONRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 2022 Mock JEE Main-4 - SolutionsDocument18 pages2022 Mock JEE Main-4 - SolutionsAshish GuleriaNo ratings yet
- T630 - Engineering Science N2 APRIL 21 MG Sign OffDocument6 pagesT630 - Engineering Science N2 APRIL 21 MG Sign Offseete.sybilNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- N3 Engineering Science August 2022 Question PaperDocument11 pagesN3 Engineering Science August 2022 Question PaperNkazimulo MbonaniNo ratings yet
- N3 Engineering Science April 2021 MemorandumDocument9 pagesN3 Engineering Science April 2021 MemorandumNkazimulo MbonaniNo ratings yet
- N3 Engineering Science April 2023 Question PaperDocument10 pagesN3 Engineering Science April 2023 Question PaperNkazimulo MbonaniNo ratings yet
- European Journal 2002Document15 pagesEuropean Journal 2002Nkazimulo MbonaniNo ratings yet
- n3 Physics Revision Notes - Waves and Radiation Farr HsDocument10 pagesn3 Physics Revision Notes - Waves and Radiation Farr HsNkazimulo MbonaniNo ratings yet
- n3 Physics Revision Notes - Electricity and Energy Farr HsDocument6 pagesn3 Physics Revision Notes - Electricity and Energy Farr HsNkazimulo MbonaniNo ratings yet
- Foreign Aid, Institutions, and Governance inDocument32 pagesForeign Aid, Institutions, and Governance inNkazimulo MbonaniNo ratings yet
- Physics 430: Lecture 17 Examples of Lagrange's Equations: Dale E. GaryDocument10 pagesPhysics 430: Lecture 17 Examples of Lagrange's Equations: Dale E. GaryGary Gelmer Luque LuqueNo ratings yet
- DH-HAC-HDW1400EMP-A - Datasheet - 20200420 Rlos OlivosDocument3 pagesDH-HAC-HDW1400EMP-A - Datasheet - 20200420 Rlos OlivosHugo Americo Condori BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Course OutlineDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics Course Outlinemeku44No ratings yet
- Syllabus For All YearsDocument29 pagesSyllabus For All YearsAshik AloyNo ratings yet
- Shop Drawing List For Anonas Station - 20230830 (For Update Floor Sleeve and Opening)Document8 pagesShop Drawing List For Anonas Station - 20230830 (For Update Floor Sleeve and Opening)Kevin John PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Breakdown Price: JasaDocument2 pagesBreakdown Price: JasaWahyu AdjiNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.1 - MotionDocument88 pagesTopic 2.1 - MotionAnton MetsgerNo ratings yet
- Signature RedactedDocument165 pagesSignature RedactedCristhianNo ratings yet
- DS Servo Motor ACM604V60-01-2500 enDocument3 pagesDS Servo Motor ACM604V60-01-2500 enRafael Morais MachadoNo ratings yet
- T Proc Notices Notices 045 K Notice Doc 41060 991081109Document7 pagesT Proc Notices Notices 045 K Notice Doc 41060 991081109YusdianNo ratings yet
- LIGHTDocument51 pagesLIGHTMaryam ShahidNo ratings yet
- Cp16 Road Crossing AnalysisDocument3 pagesCp16 Road Crossing Analysisboonico Nicco0% (1)
- Property SheetDocument6 pagesProperty SheetsivaNo ratings yet
- SCH 201 - Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesSCH 201 - Chemical Thermodynamicsjipson olooNo ratings yet
- Mecanica de Materiales Cap 8Document15 pagesMecanica de Materiales Cap 8Kevin ChicaNo ratings yet
- PS-1212 Technical SpecificationsDocument2 pagesPS-1212 Technical SpecificationsthatatkdferreiraNo ratings yet
- Pyramid Ias Academy: KaraikudiDocument12 pagesPyramid Ias Academy: KaraikudiArrow BuildersNo ratings yet
- Bamboo - Reinforced - Masonry - Shear Walls For Low Cost Housing (MSC Thesis)Document201 pagesBamboo - Reinforced - Masonry - Shear Walls For Low Cost Housing (MSC Thesis)Inzimam Ul haqNo ratings yet
- (Radition Poisoning) PPTDocument16 pages(Radition Poisoning) PPTDivithNo ratings yet
- Iso 4719 2012Document9 pagesIso 4719 2012Mohammed ShamilNo ratings yet
- Chlorella Repeated Batch Growth Algaemist Panel PBR Day-Night Cycle - 1 - MinDocument110 pagesChlorella Repeated Batch Growth Algaemist Panel PBR Day-Night Cycle - 1 - MinAntonio MoncayoNo ratings yet
- Uneb Chemistry Paper 1 2019Document12 pagesUneb Chemistry Paper 1 2019Boniface RachkaraNo ratings yet
- Dusan Ilic T: SciencedirectDocument13 pagesDusan Ilic T: SciencedirectWalter Ronaldo Cachi DelgadoNo ratings yet
- PEB2063 - Production Engineering IDocument39 pagesPEB2063 - Production Engineering IadlinaNo ratings yet
- ReportnDocument4 pagesReportnGavin MuganiNo ratings yet
- Pullout Strength Models For FRP AnchorsDocument9 pagesPullout Strength Models For FRP AnchorsJULIO VAZQUEZNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document100 pagesModule 1Reyven Recon100% (1)
- Lab 5 PDFDocument6 pagesLab 5 PDFSharifuddin RumanNo ratings yet
- Temperature Sensor With Process Connection: L Probe Length Corresponds To Installation Length ELDocument2 pagesTemperature Sensor With Process Connection: L Probe Length Corresponds To Installation Length ELImad YahyaNo ratings yet
- 2019 May ME210-H - Ktu QbankDocument2 pages2019 May ME210-H - Ktu QbankkannanNo ratings yet