Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rebollido Research 201 Midterms Reviewer
Uploaded by
dannytheregressor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views6 pagesOriginal Title
REBOLLIDO-RESEARCH-201-MIDTERMS-REVIEWER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views6 pagesRebollido Research 201 Midterms Reviewer
Uploaded by
dannytheregressorCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
RESEARCH 201 STEPS in Reviewing Literature
1. Finding relevant materials
LITERATURE -It is the researcher’s priority to enrich his or
-Is the process of compiling, classifying, her work by reading literatures containing
and evaluating what other researchers have important data related to the research problem
written on a certain topic. in order to fully comprehend the variables
-serves with the following purposes: being studied.
•It helps in placing the work beingreviewed in 2. Selecting credible sources
its context. -References come in different sorts and
•It describes the relationship of each work to shapes. The researcher should keep in mind
the research being undertaken. that critical evaluation of sources is crucial to
•It identifies new ways to interpret and shed the credibility of one’s research.
light on various gaps based on previous -When evaluating the credibility of sources, it is
researches. important to ask the following (Perfecto,
•It helps in solving conflicts among seemingly Paterno. & Pison, 2011.):
contradictory previous studies. ⦾ Who published it?
•It identifies the areas that are subject to a ⦾ Who wrote it?
prior study to prevent duplication of efforts. ⦾ For whom is it written?
•It points to another research undertaken. ⦾ Is the information current?
⦾ Does the author provide his or her sources?
TYPES OF READING ⦾ What type of publication is it?
• Elementary reading ⦾ How is it reviewed?
-This is the most common kind of reading. It ⦾ Is there any bias?
consist merely of the recognition of letters and 2.1 Hierarchy of sources
basic sounds and literal comprehension of -The following is the arrangement of the
sentences. different types of library sources from the least
• Systematic skimming/reading authoritative (general), down to the most
-The reader must establish a system through authoritative (specialized):
which he or she can maximize time in 1. General encyclopedia
searching for pertinent or relevant literature. 2. General Interest magazines and
• Analytical reading newspapers
-The reader asks questions to understand the 3. Specialized magazines
article such as: 4. Reference materials
⦾ What is the book or article all about? 5. Government documents
⦾ What is being said in detail and how? 6. Vertical files
⦾ What of it? 7. Theses/dissertations
The reader takes time to understand every 8. Scholarly books
detail of the piece. 9. Academic journals
• Comparative reading 3. Actual reading
-This is the highest level of reading which -After the preselection process, the researcher
requires the reader to placewhat he or she is must thoroughly critique the contents of the
currently reading in relation to other materials materials.
he or she has previously read. -Some of examples of questions to ask are as
-This type of reading helps the reader identify follows:
the similarities and differences between two or a. What variables are mentioned?
more articles in terms of their variables and b. What are the Characteristics or descriptions
propositions. of the variables?
c. What relationship exists between the -Always note that the main idea in the
variables based on the information paragraph is important to know, as supporting
given? details play a part in carefully understanding
d. How can the information provided in this the details.
material be of use to my research? > Actual reading
4. Note taking -The following are guidelines on how to
-One of the characteristics of a good annotate while and after reading (New
researcher is being systematic. The researcher Hampshire School Administrative Unit #53,
must establish a system of note-taking to save n.d.):
time and effort. He or she must take notes, While Reading:
putting only the important data in his or her a. Ask Questions
own words. b. React to what you read
c. Give an opinion
STRATEGIES in Reviewing Literature d. Locate important passages
> Previewing e. Make Connections
-It is the process of reading to get the general f. Define new words
idea of the things to look for in the text. g. Track Themes
Systematic skimming is done here.
> Highlighting After Reading:
It is done by marking the text to identify key a. Give a title to the chapters or article sections
details and to note the relationship among b. Summarize the material read
ideas. c. Respond to the reading itself
-In using highlighting symbols, one should take d. Make a prediction
note of the following:
A. The important ideas are underlined. DIFFERENT STYLES OF WRITING
B. Words, phrases, or images that need -In research writing, there are many
further analysis should be boxed. different style guides that are allowed by
C. Question marks are written beside researchers.
confusing passages, unfamiliar The three most common styles followed at
references, or words that need to be present are the following:
defined. •Modern Language Association (MLA) Style
D. Related words, ideas, or images are -The MLA style evolved from a three-page
encircled. Lines can be drawn to show style sheet created in 1931 for PMLA, the
their connection journal of the Modern Language Association of
E. Incidents that occur in sequence are America. The style further developed as the
numbered. association published a booklet about it in
F. Key portions of the text should be set 1951 and a handbook in 1977. Eventually,
off with a vertical line in the margin. MLA style became a universally accepted
G. Stars are placed beside particularly guide for writing and publishing papers on
important ideas. language, literature, liberal arts, and other
> Annotating fields of Humanities.
-This pertains to the recording of the reader’s •American Psychological Association (APA)
reaction as marginal notes Style
-It is important to distinguish essential versus -The APA developed its own uniform style of
nonessential ideas and details in the text. formatting written works. Originally, the
Details that lead to the main idea are essential, resulting style book was provided to their
while details that are not become nonessential. associates as a guide for composing scientific
publications, articles, handbooks, journals, and
the like for the organization. It was in 1929 Elements of a Theoretical Framework
when the original APA style guidelines were ●Relevant Theories
featured in a magazine write-up. The APA style These are theories that are partially or fully
is commonly used in the Social Sciences, relevant to the present study and are
Philosophy, Education, and Economics. discussed to provide a basis for the variables
Because of the practicality it brings and the being tested. The following parts should be
relatively popular usage, many institutions mentioned:
prescribe the use of APA style as the standard 1. Name/s of the author/s
for writing research papers. 2. Title/s of their theory/ies
•Chicago or Turabian Style 3. Theoretical statement or principles
-The University of Chicago Press manages the 4. Explanation of theoritcal statement
standards and rules for the Chicago Style. The 5. Relationship of the theory to the present
University of Chicago Press produced the study
original Chicago Style Manual in 1906. ●Review of Related Literature
-The Turabian Style and Chicago Style are of These are published materials (books,
the same style because they have identical but encyclopedias, published journals, newspaper,
slightly refined rules. The two styles are nearly magazines, etc) that compare the study with
similar that professors often refer to them in existing knowledge on the research topic.
combination. Turabian Style permits the use of
footnotes for citing sources, which splits it from
other styles on writing formal papers. While
Chicago Style typically less formal papers and
not designed for publication.
RESEARCH FORMAT
●Review of Related Studies
These include the theses or dissertations on
research topics carrying the same variables. In
writing a review of a related study, the
following data must be indicated:
1. The name of the author, the date, and the
setting of the study.
2. The title
3. The salient findings, which are the most
important "ingredientsh to include since the
discussion of the variables and their
relationship/s will be based on them.
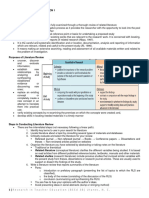
RESEARCH FRAMEWORK ●Paradigm of the sutdy
-It as a “set of ideas that provide support to It is a diagrammatic presentation of the study
something”. used to visually summarize the whole study.
-In research, it serves as the building FORMULATING THE THEORETICAL
blocks for the foundation of research. FRAMEWORK COGNITIVE BEHAVIORAL
Types of research framework: Theories:
Theoretical Framework 1. Examine your thesis title and research
-describes the theories relevant to the problem
research problem and the position the 2. Brainstorm about what is considered as the
researcher takes in the study. key variables in the research
3. Review related literature and studies ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS OF A LITERATURE
4. List the constructs and variables REVIEW
5. Review key theories - Literature Review serves as an in-depth
6. Discuss the assumptions or propositions summary of the literatures related to the study.
Conceptual Framework It does not only restate facts but rather critique
-Derived from a combination of theories or and highlight their relevance to the research.
parts of theories Several elements should be observed in
Ipo (INPUT-PROCESS-OUTPUT) Model writing this section:
✔ Overview of the subject or topic, issues or
theories to be considered
✔ Division of work such as those that support
a particular position, those against, and those
that offer other ideas
✔ Explanation of the comparison of the
gathered literature
✔ Conclusion and the best arguments
STAGES IN WRITING THE LITERATURE
REVIEW
1. Problem Formulation. The researcher must
determine the research problem before the
RELATED LITERATURE review of literature is conducted to fully
also called “Conceptual Literature” understand the variables considered in the
-Clarifies the different variables being studied. study.
-It removes vagueness surrounding the central 2. Literature Search. Any reading material that
concepts of the research. Therefore, it is very is related to the study must include a
important to identify your variables before discussion and explanation of at least one
writing your review of literature. of the variables.
-The related literature examines facts and 3. Date Evaluation. The indicators that are
principles from other resources that are related synthesized from various relevant sources
to the present study. must further build the researcher’s
-As the literature is gathered, the different confidence as the variables of his or her study
major variables, as well as the sub-variables, are made clear.
are clarified and the delimitation of the study is 4. Analysis and interpretation. Breaking the
established. entire reading article into smaller parts will help
-The indicators for each variables are identified the researcher correctly interpret the
and objectively established. information in the reviewed materials.
Types of Variables:
1. Major Variable FORMAT OF A LITERATURE REVIEW
-The central idea of the entire literature. The Introduction
2. Sub-Variables The literature review is not merely a
-Helps specify which particular aspect of the restatement of facts. Thus, the
major is being referred to. organization of thought should be duly
3. Indicators considered when writing:
-Specific information that describes the a)The general problem and variable should be
sub-variables. defined.
b)Every important data should be highlighted
to effectively discuss the problem or the
variables such as theory, methodology, to identify how a central ‘problem’ or
evidences, conclusions and even gaps. question(s) has been dealt with over a period
are pertinent and relevant. of time. Doing so will help you to present and
c)The criteria in selecting the literature should explain the need for your research at this point
be considered to assess which resources in time of the research evolution, and how it
The Body extends the studies and debates to date.
Your body should contain the following: When do you opt for a Chronological
a) Chosen approaches, conclusion of authors, structure?
specific objectives, and the • If your study provides an overview of the
link should be included. sequential development of a certain topic, or
b) Studies and Literature should be aspect of the topic at hand. This overview
summarized. In choosing the literature, allows a broader understanding of the field.
the following should be considered: Methodological
i.Credibility. This refers to the author’s -This framework focuses on how the author(s)
credentials and the empirical basis of the or the person(s) administering a study applied
article similar methods as another study. As a result,
or literature. the types of literature in a literature review
ii.Objectivity. This refers to the rationality of materials
every data or facts cited. When do you opt for a Methodological
iii.Persuasiveness. This refers to the degree of structure?
credibility of the data. •Can be helpful when evaluating the strengths
iv. Value. This refers to the degree of the and limitations of different approaches
contribution of the literature to clarify variables especially comparing methods.
The Conclusion
a) Major Contributions of the studies or articles RELATED STUDIES
should be summarized. -It serves as the basis of the analysis of results
b)Current developments and new information because it allows the researchers to compare
should be evaluated. and contrast his or her findings with those of
c)The review should be concluded by relating past studies.
the gathered data to the central -It provides an insight into the methods through
theme or problem. which the validity of the results is to be
established. It also serves as the basis of the
SAMPLE STRUCTURES IN ORGANIZING interpretation of results by allowing the
THE CONTENTS OF YOUR RRL researcher to compare and contrast the
Thematic findings of previous studies.
-involves organizing and synthesizing the -Studies are considered related to one another
existing literature based on recurring themes if they have the following similarities:
or topics rather than a chronological or • They use the same major variables,
methodological sequence. sub-variables, concepts or construct.
When do you opt for a thematic structure? • They have the same subject.
• Broad Research Questions
• Interdisciplinary Research REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
• Emerging Research Areas In writing a review of a related study, the
• Complex Issues following data must indicated:
Chronological 1.Name of the author, the date, and the
The main focus in a chronological literature setting of the study
review is to trace the development of studies, 2.The title
debates or theories in your subject area, and
3.The salient findings, which are the most
important “ingredient” to include since the
discussion of the variables and their
relationship/s will be based on them
By JC Rebollido
You might also like
- A PERFORMANCE GUIDE TO GABRIEL FAURÉ - S - em - LA CHANSON D - ÈVE - emDocument136 pagesA PERFORMANCE GUIDE TO GABRIEL FAURÉ - S - em - LA CHANSON D - ÈVE - emEunice ngNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Academic TextsDocument41 pagesThe Structure of Academic TextsJosh Bhon56% (9)
- (Language Policy 11) Robert Kirkpatrick (Eds.) - English Language Education Policy in Asia-Springer International Publishing (2016) - 1 PDFDocument388 pages(Language Policy 11) Robert Kirkpatrick (Eds.) - English Language Education Policy in Asia-Springer International Publishing (2016) - 1 PDFSalsabila Kaamalia100% (2)
- In The Great GatsbyDocument8 pagesIn The Great GatsbyEthanNo ratings yet
- Moss - Plato's Epistemology. Being and SeemingDocument266 pagesMoss - Plato's Epistemology. Being and SeemingJosue GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Chapter IiDocument68 pagesChapter IiCristine Joy PublicoNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument26 pagesRRLElaine Loreen Villanueva50% (2)
- How To Do A Literature ReviewDocument20 pagesHow To Do A Literature ReviewMuhammad Akbar HariyonoNo ratings yet
- Eapp Lesson1 Fundamentals of ReadingDocument5 pagesEapp Lesson1 Fundamentals of Readingcroixeu (. . .)No ratings yet
- Practical Research Chapter 2Document15 pagesPractical Research Chapter 2Dexter RimorinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Exploring RRLDocument56 pagesLesson 2 Exploring RRLJose Gabriel Odrigo100% (1)
- Learning Activity Sheet: Chapter 3 Review of Related LiteratureDocument4 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: Chapter 3 Review of Related LiteratureLorianne ArcuenoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 DELTA One To OneDocument16 pagesModule 3 DELTA One To OnePhairouse Abdul Salam100% (3)
- The Review ProcessDocument19 pagesThe Review ProcessMaria ArleneNo ratings yet
- CE5412 - Literature Review - Part 2 - CompressedDocument25 pagesCE5412 - Literature Review - Part 2 - CompressedthamiradNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Learning From Others and Reviewing The LiteratureDocument31 pagesUnit 4: Learning From Others and Reviewing The Literaturegmpimentel2221lagNo ratings yet
- Learning From Others and Reviewing The LiteratureDocument14 pagesLearning From Others and Reviewing The LiteraturemariacieloNo ratings yet
- Research Lecture 5Document31 pagesResearch Lecture 5Shosha BangtanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 ResearchersDocument3 pagesChapter-2 ResearchersMercado, AltheaNo ratings yet
- Research Method The View of Literature An OverviewDocument7 pagesResearch Method The View of Literature An OverviewQamar AhmedNo ratings yet
- The Review ProcessDocument28 pagesThe Review ProcessGian Nikolai MeniaNo ratings yet
- Las 6 Prac Research 1Document4 pagesLas 6 Prac Research 1Ben A MalanyaonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER TWO - Lecture 6 &7Document43 pagesCHAPTER TWO - Lecture 6 &7Evans DrumkNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Locating and Reviewing Literature-BMSDocument40 pagesLecture 2 - Locating and Reviewing Literature-BMSconnaissance.amyNo ratings yet
- Research IiDocument10 pagesResearch IiGennrick PajaronNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7.review LiteratureDocument14 pagesLesson 7.review LiteratureAngelo OlavareNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Practical ResearchDocument5 pagesWeek 5 Practical ResearchG-32 Porcelo, Ayeshanie Emanuele I.No ratings yet
- Structure and Parts of An Article: August 2019Document8 pagesStructure and Parts of An Article: August 2019Alexandra AramayoNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing Skills: Quarter 2 - Week 2 Module 9 & 10Document15 pagesReading and Writing Skills: Quarter 2 - Week 2 Module 9 & 10Ray DomagasNo ratings yet
- MODULE 8 The Review of Litersature Overview, Essentials, and StructureDocument7 pagesMODULE 8 The Review of Litersature Overview, Essentials, and StructureXander CabalquintoNo ratings yet
- LITERATUREDocument23 pagesLITERATUREGcs GomezNo ratings yet
- Lit ReviewDocument22 pagesLit ReviewCindy Lou LawasNo ratings yet
- CHP 04Document17 pagesCHP 04Mahnoor TahirNo ratings yet
- PR1 11 Q1 Week 7-8Document4 pagesPR1 11 Q1 Week 7-8Lex Aine June D. TaborNo ratings yet
- Structureand Partsofan Article Word DocDocument8 pagesStructureand Partsofan Article Word DocAGUIA 63No ratings yet
- Structureand Partsofan Article Word DocDocument8 pagesStructureand Partsofan Article Word DocLaw DexunNo ratings yet
- For Distribution Sample Session GuideDocument14 pagesFor Distribution Sample Session GuideMark Bryan CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter9 Methods of Research ModuleDocument8 pagesChapter9 Methods of Research ModuleSteffany RoqueNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument171 pagesCombinepdfjonas ventolinaNo ratings yet
- Learning From Others and Reviewing The Literature: Practical Research 1 Quarter 3 - Week 5Document4 pagesLearning From Others and Reviewing The Literature: Practical Research 1 Quarter 3 - Week 5Jhude JosephNo ratings yet
- Research LP3Document15 pagesResearch LP3Hero BuckyNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument16 pagesLiterature ReviewIswariya KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Rev. of LitDocument108 pagesRev. of LitAngelica Marie MacaslingNo ratings yet
- Raguindin, Lansang Literature PowerpointDocument23 pagesRaguindin, Lansang Literature Powerpointsoleilramirez217No ratings yet
- RRL and HoDocument27 pagesRRL and HoAshley GarciaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 5: Review of Related Literature and APA CitationDocument21 pagesLESSON 5: Review of Related Literature and APA CitationAdrian CamasosaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 5: Review of Related Literature and APA CitationDocument21 pagesLESSON 5: Review of Related Literature and APA CitationAdrian CamasosaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review CimDocument38 pagesLiterature Review CimOmosa Elijah MochamaNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument15 pagesReview of Related LiteratureTobiichi OrigamiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document2 pagesLecture 4guillenkeithhyacinthNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Reading On Related StudiesDocument5 pagesLesson 3 - Reading On Related StudiesJeiel Collamar GozeNo ratings yet
- Literature Survey: 1) Definition of Literature and Literature Survey Definition of LiteratureDocument9 pagesLiterature Survey: 1) Definition of Literature and Literature Survey Definition of LiteratureEm JayNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing 1Document24 pagesAcademic Writing 1HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Learning From Others and Reviewing The Literature Lesson 1: Selecting Relevant LiteratureDocument8 pagesLearning From Others and Reviewing The Literature Lesson 1: Selecting Relevant LiteratureLINDSAY PALAGANASNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Lecture 7-8 - Literature ReviewDocument37 pagesUnit 1 - Lecture 7-8 - Literature ReviewPradip Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Reviewing The LiteratureDocument20 pagesReviewing The Literaturea bcNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Ihlp-Las - Practical Research 1Document4 pagesWeek 5 - Ihlp-Las - Practical Research 1Tristan Genesis AmistadNo ratings yet
- RRL PR1Document50 pagesRRL PR1Mark Froilan NamiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Selection of TopicDocument27 pagesUnit 1. Selection of Topicrajatsharma.sdsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Literature ReviewDocument16 pagesLecture 4 Literature ReviewABDULSWAMADU KARIMUNo ratings yet
- The Review of Related Literature and Studies: Week 7Document16 pagesThe Review of Related Literature and Studies: Week 7Clarisse LucenaNo ratings yet
- Format For A Literature ReviewDocument2 pagesFormat For A Literature ReviewshishankisNo ratings yet
- Rev. of LitDocument108 pagesRev. of LitAngelica Marie MacaslingNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document24 pagesWeek 5Sedie PrempsNo ratings yet
- Module 5-Review of LitDocument22 pagesModule 5-Review of LitKrizza BathanNo ratings yet
- Pr1 Factors Influencing The Tardiness of Students in Saint Joseph High School of Talakag IncDocument27 pagesPr1 Factors Influencing The Tardiness of Students in Saint Joseph High School of Talakag IncdannytheregressorNo ratings yet
- BalayDocument2 pagesBalaydannytheregressorNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 3 Group 3Document16 pagesCHAPTER 1 3 Group 3dannytheregressorNo ratings yet
- PR 1 RRL 1Document1 pagePR 1 RRL 1dannytheregressorNo ratings yet
- (C) Ives Eugenia - IGeneration. The Social Cognittive Efectes of Digital Technology On TeenagersDocument107 pages(C) Ives Eugenia - IGeneration. The Social Cognittive Efectes of Digital Technology On TeenagersGerson Godoy RiquelmeNo ratings yet
- Black and White Modern Professional Business Proposal PresentationDocument39 pagesBlack and White Modern Professional Business Proposal PresentationdannytheregressorNo ratings yet
- RRL 6 EchavezDocument2 pagesRRL 6 EchavezdannytheregressorNo ratings yet
- 1649Document336 pages1649tariq khanNo ratings yet
- Pe Lesson Plan 2 16 17Document7 pagesPe Lesson Plan 2 16 17api-350775200No ratings yet
- Percentage Sheet - 04Document2 pagesPercentage Sheet - 04mukeshk4841258No ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument5 pagesArgumentative Essayraynold raphaelNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics 2004 November Paper 1Document8 pagesAdditional Mathematics 2004 November Paper 1lornarifaNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1 5Document81 pagesChapters 1 5ogost emsNo ratings yet
- HR Interview QuestionsDocument22 pagesHR Interview QuestionsShamshu ShaikNo ratings yet
- Tribute To An Academic IconDocument7 pagesTribute To An Academic IconDr. Umaru Ahmadu100% (1)
- 10 Tools To Make A Bootable USB From An ISO FileDocument10 pages10 Tools To Make A Bootable USB From An ISO Filedds70No ratings yet
- The Art of Peace: The Value of Culture in Post-Conflict RecoveryDocument20 pagesThe Art of Peace: The Value of Culture in Post-Conflict RecoveryLi AriasNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Communication in The Multicultural World: Central Luzon State UniversityDocument11 pagesModule 3: Communication in The Multicultural World: Central Luzon State UniversityJam CamaligNo ratings yet
- Qlik Nprinting Training Brochure Qlik Nprinting Training BrochureDocument2 pagesQlik Nprinting Training Brochure Qlik Nprinting Training BrochureCarlo RossiNo ratings yet
- Voices Intermediate U01-05 Mid Course Speaking TestDocument3 pagesVoices Intermediate U01-05 Mid Course Speaking TestDouglas EkonNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 Theoratical Framework and HypothesisDocument18 pagesChapter-5 Theoratical Framework and Hypothesiszia uddin khattakNo ratings yet
- Quantitative ResearchDocument10 pagesQuantitative ResearchAixa Dee MadialisNo ratings yet
- Investing in The 21 Century Skilled Filipino WorkforceDocument72 pagesInvesting in The 21 Century Skilled Filipino WorkforceRhemz Guino-oNo ratings yet
- CTU Public Administration Thoughts and InstitutionDocument3 pagesCTU Public Administration Thoughts and InstitutionCatherine Adlawan-SanchezNo ratings yet
- Salisu Bala Curriculum Vites: Flat 23 New Ecobank Road, Kaura Namoda Metropolis, Kaura Namoda Local Govt Zamfara StateDocument5 pagesSalisu Bala Curriculum Vites: Flat 23 New Ecobank Road, Kaura Namoda Metropolis, Kaura Namoda Local Govt Zamfara StateAaron YakubuNo ratings yet
- Rouse On The Typological MethodDocument4 pagesRouse On The Typological MethodLuciusQuietusNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Arts 8 I. Objectives: at The End of The Lesson The Students Are Expected ToDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Arts 8 I. Objectives: at The End of The Lesson The Students Are Expected ToBeaMaeAntoniNo ratings yet
- Carl Jung's and Isabel Briggs Myers'Document5 pagesCarl Jung's and Isabel Briggs Myers'Venkat VaranasiNo ratings yet
- Digital Booklet - X (Deluxe Version) - UnlockedDocument10 pagesDigital Booklet - X (Deluxe Version) - UnlockedНики ДимитровNo ratings yet
- Epic Fails in Global Branding: Intercultural CommunicationDocument9 pagesEpic Fails in Global Branding: Intercultural Communicationrose ynqueNo ratings yet
- Rubank Intermediate Method - Clarinet - Skornicka, J. E. (Joseph Edward) Miller, Robert Miller, Robert - 1938 - Chicago - Rubank - Anna's ArchiveDocument60 pagesRubank Intermediate Method - Clarinet - Skornicka, J. E. (Joseph Edward) Miller, Robert Miller, Robert - 1938 - Chicago - Rubank - Anna's Archivedesire.schoemanNo ratings yet
- Importance of Education A Persuasive EssayDocument2 pagesImportance of Education A Persuasive EssayHisagi ShuheiNo ratings yet