Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Labor and Delivery
Uploaded by
HazelGrace0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesLabor and Delivery
Uploaded by
HazelGraceCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Maternal 1 Side-notes: Labor and Delivery ⁃ bloody discharge
⁃ Operculum/ mucus plug expelled
Labor ⁃ Blood with mucus
⁃ mature fetus to cope with
extrauterine life Rupture of Membranes (ROM)
⁃ Sudden gush or scanty show
Progesterone Withdrawal ⁃ Seeping clear fluid
⁃ Prostaglandins = muscle stretching ⁃ Early rupture = shortens labor and
⁃ Oxytocin = cervical pressure fetus to fit into pelvis
⁃ Oxytocin + prostaglandin = uterine
contraction Risk ROM:
⁃ Placental age = contraction ⁃ intrauterine infection
⁃ Fetal cortisol = prostaglandin ⁃ Umbilical cord prolapse (cut-off O2)
formation
⁃ Fetal membrane = prostaglandin = Induced Labor
contraction ⁃ labor NOT spontaneous within 24hrs
after rupture of membranes
Signs of Labor
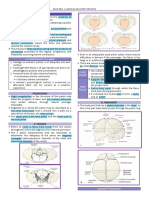
1. Preliminary Signs Components of Labor (5P’s)
Lightening (Descent) 1. Passage (Pelvis)
⁃ change abdominal contour ⁃ pelvis size and contour
⁃ Relief diaphragmatic pressure and ⁃ Route of fetus
SOB ⁃ 2 measurements: diagonal
⁃ “Lightens woman’s load” conjugate and transverse diameter
Increase Level Activity Diagonal Conjugate (INLET)
⁃ increase epinephrine (prepares body ⁃ anteroposterior diameter inlet
for labor) ⁃ Narrowest diameter inlet
Slight loss of weight Transverse Diameter (OUTLET)
⁃ Progesterone drops= body fluid ⁃ pelvic outlet
excreted ⁃ Narrowest diameter outlet
⁃ Urine= loss 1-3 pounds
2. Passenger (Fetus)
Braxston Hicks Contraction ⁃ size, position, presentation
⁃ strong contraction ⁃ Head= widest diameter
Ripening of Cervix Head
⁃ “butter soft” ⁃ difficult to pass pelvic ring
⁃ Goodell sign ⁃ Passing rate depends structure and
alignment
2. True Labor Signs
⁃ uterine and cervical changes Molding
⁃ change shape fetal skull
Uterine Contraction ⁃ Due to force of contraction
⁃ surest sign ⁃ Vertex against NOT dilated cervix
⁃ Productive, involuntary and without
warning Engagement
⁃ Increase intensity ⁃ presenting part into pelvis
⁃ Breathing exercise (discomfort) ⁃ Level of ISCHIAL SPINES (pelvis
midpoint)
Show (Bloody Show)
Fetal Attitude 2. Moderate Flexion
⁃ Degree of flexion ⁃ Alert/ Military Position
⁃ Relationship of fetal parts with each ⁃ Chin NOT touching chest
other
3. Partial Extension
Descent ⁃ Poor flexion
⁃ widest part passed pelvic inlet/ outlet ⁃ BROW presents into birth canal
Fetal Lie Descent
⁃ Fetal and maternal spine alignment ⁃ widest part into pelvic ring
⁃ Relationship long of axis of fetus to
long axis of mother 1. Biparietal Diameter
⁃ cephalic presentation
Fetal Presentation
⁃ body parts to be born 1st 2. Intertrochanteric Diameter
⁃ Determined by fetal lie and fetal ⁃ Breech presentation
attitude
Fetal Lie
Fetal Position ⁃ Alignment of long axis of mother and
⁃ Relationship presenting part to baby
quadrant of pelvis
Long axis- cephalocaudal
3. Powers of Labor (Uterine Factor)
⁃ Labor position Fetal Station
⁃ Force by fundus of uterus 1. 0 station
⁃ Uterine contraction ⁃ presenting part at level of ischial
spine
4. Psyche (Psychological Outlook) ⁃ ENGAGEMENT
⁃ Psychological state or feeling
⁃ Apprehension or fright 2. - 1 to - 4 station
⁃ Above spine (NOT ENGAGED)
5. Placental Factor
⁃ site and timing of separation 3. + 1 to + 4 station
⁃ Below spine
Fetal Attitude
⁃ degree of flexion 4. + 3 to + 4 station
⁃ Perineum level
1. Good attitude ⁃ CROWNING
⁃ Complete flexion
⁃ Spinal bowed forward Types Fetal Presentation
⁃ Chin touches sternum ⁃ Body part 1st contact with cervix
⁃ Arms folded on chest ⁃ Fetal Attitude + Fetal Lie
⁃ Thighs towards abdomen
⁃ Calves onto posterior aspect of 1. Cephalic Presentation
thighs ⁃ frequent type
⁃ Head 1st to be born
Normal Fetal Position ⁃ 4 Types: vertex, brow, face, mentum
⁃ Smallest anteroposterior diameter
skull to pelvis 2. Breech Presentation
⁃ Whole body = OVOID SHAPE ⁃ Buttocks or feet
⁃ occupies smallest space as possible ⁃ Presenting part influence labor
difficulty
⁃ 3 Types: comple, frank, footing ⁃ effacement and dilatation
Good attitude Effacement
⁃ Knees against abdomen ⁃ shortening and thinning of cervical
canal
Poor attitude ⁃ Canal 1-2cm long
⁃ knees extended ⁃ Disappears virtually
3. Shoulder Presentation Dilatation
⁃ Acromion process ⁃ Enlargement or widening of cervical
⁃ Iliac crest, hand or elbow canal
⁃ Fully: 10cm
Fetal Position
⁃ Relationship presenting part to 511 Rule of Labor
quadrant of pelvis 5 - 5mins apart
1. Right Anterior 1 - 1min last
2. Left Anterior 1 - 1 pattern lasted 1 hour
3. Right Posterior
4. Left Posterior False Contraction VS True Contraction:
1. FALSE
Mechanism of Labor (Cardinal Movement) ⁃ Remain irregular
⁃ Keeps smallest diameter of head ⁃ 1st abdomen
always presenting to smallest diameter of pelvis ⁃ confined abdomen and groin
1. Descent ⁃ Disappear with ambulation/ sleep
2. Flexion ⁃ NO increase: duration, frequency,
3. Internal Rotation intensity
4. Extension ⁃ NO CERVICAL DILATATION
5. External Rotation
6. Expulsion 2. TRUE
⁃ Regularly and predictable
Powers of Labor ⁃ 1st lower back
⁃ Force fundus of uterus ⁃ Sweep around abdomen
⁃ Continuous
Primary Power or Force ⁃ INCREASE: duration, frequency,
⁃ after full dilatation intensity
⁃ Abdominal muscles ⁃ (+) CERVICAL DILATATION
⁃ DONT BEAR DOWN WITH
ABDOMINAL MUSCLES UNTIL FULL DILATION Types of Pelvis
OF CERVIX (impedes primary force and damages 1. Gynecoid
both fetus and cervix) ⁃ Female Pelvis
⁃ Favorable vaginal birth
1. Uterine Contraction
⁃ Effective: rhythm, lengthening and 2. Android
intensity ⁃ Male Pelvis
⁃ 3 Phases: increment, acme, ⁃ Funnel shaped
decrement ⁃ Caesarean Section NEEDED
Increment- intensity increases 3. Anthropoid
Acme- strongest contraction (PEAK) ⁃ long, narrow and oval shaped
Decrement- intensity decreases ⁃ Possible vaginal birth BUT high risk
2. Cervical Changes 4. Platypelloid
⁃ Wide and flat pelvis ⁃ from beginning of one contraction to
⁃ Caesarean Section NEEDED beginning of next contraction
Fetal Variables (affects LABOR) 2. Duration
1. Fetal Size ⁃ From beginning of one contraction to
2. Fetal Lie end of same contraction
⁃ Longitudinal, transverse, oblique
3. Fetal Presentation Note:
⁃ Vertex (head) ⁃ labor progresses relaxation intervals
⁃ Breech shortens (from 10mins to 2-3mins)
⁃ Shoulder ⁃ Duration (from 20-30sec to 60-
⁃ Compound (vertex and hand) 90sec)
⁃ Funic (umbilical cord)
4. Fetal Attitude Leopold’s Maneuver
5. Fetal Station 1. 1st Maneuver- presentation/lie
6. Number of Fetuses 2. 2nd Maneuver- back/ FHR
7. Fetal Anomalies 3. 3rd Maneuver- engagement
⁃ hydrocephalus 4. 4th Maneuver- attitude
⁃ Sacrococcygeal teratoma (tumor
coccyx) Psychological Task Pregnancy
1. 1st Trimester
Structure Fetal Skull ⁃ ambivalence/ confusion
Cranium 2. 2nd Trimester
⁃ uppermost ⁃ Acceptance
⁃ 8 bones ⁃ Day dreaming/ role playing
3. 3rd Trimester
1. Frontal (1x) ⁃ Nest building activities
2. Parietal (2x) ⁃ Parenthood
3. Occipital (1x)
4. Sphenoid (1x) Positive Signs Pregnancy
5. Ethmoid (1x) 1. Fetal Outline
6. Temporal (2x) 2. Fetal Movement
Total: 8 BONES 3. FHR audible
3 Types Breech Presentation Estriol
1. Frank Breech ⁃ to evaluate neural tube defects and
⁃ hip joints flexed structural abnormalities
⁃ Knee joints extended
OB Scoring
2. Complete Breech 1. Term- 37 weeks
⁃ hip and knee flexed 2. Pre-Term- 20 to 36 weeks
3. Abortion- less than 20 weeks
3. Incomplete Breech 4. Living- currently living
Footling 5. Multiple- Twins
⁃ hip and knee extended
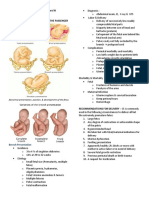
Stages of Labor
Kneeling 1. 1st stage (DILATATION)
⁃ hip extended ⁃ cervical dilatation
⁃ Knee flexed
Latent (preparatory phase)
Uterine Contraction ⁃ 0-3 cm
1. Frequency ⁃ Rapid dilatation
⁃ Mild and short contraction 3. 3rd stage (PLACENTA)
⁃ Cervical effacement ⁃ Baby to Placenta
⁃ Early analgesia= prolongs labor ⁃ Placental expulsion
⁃ Still ambulates ⁃ Brandt-Andrew Maneuver
⁃ Cephalopelvic disproportion = (suprapubic pressure and cord traction)
Caesarean section ⁃ Complete cotyledons
⁃ Excitement and still communicates ⁃ Oxytocin/ methergine after placental
expulsion
Active (difficult phase) ⁃ Uterus shape: DISCOID to OVOID
⁃ 4-6 cm ⁃ Perineum laceration
⁃ More Rapid dilatation (maximum ⁃ 2 Phase: Separation and Expulsion
slope)
⁃ Contraction q 3-5mins Placental Separation
⁃ Bloody show and ROM ⁃ Folding and separation
⁃ Irritable but still comprehend ⁃ Active bleeding helps detachment
⁃ Encourage to remain active in labor ⁃ Bleeding: 300-500mL
by assuming comfortable position
⁃ Acceleration: 4-5cm Signs Placental Delivery:
⁃ lengthening of cord
Transition ⁃ Sudden gush of blood
⁃ peak of contraction q 2-3mins ⁃ Calkins sign: change shape of
⁃ 8-10 cm uterus (from discoid to ovoid)
⁃ Loss of control (URGE TO PUSH) ⁃ Firm contraction of uterus
⁃ Bearing down techniques ⁃ Placenta at vaginal openning
⁃ Full dilatation and complete
effacement Umbrella Separation
⁃ Intense discomfort (N&V) ⁃ begins at CENTER
⁃ Peak: slight slowing rate of dilatation ⁃ Fetal surface evident
(DECELERATION)
⁃ Deceleration: 9cm reached Edges Separation
⁃ Slides uterine surface
2. 2nd stage (BABY) ⁃ Maternal surface evident
⁃ 10cm to Baby
⁃ Uncomplicated: 1hr Schultze Presentation
⁃ N and V momentarily ⁃ shiny and glistening
⁃ Neck vessels distended ⁃ Shiny fetal membrane surface
⁃ Contraction: crescendo to
decrescendo pattern Duncan Presentation
⁃ (+) Feces ⁃ Raw, red and irregular
⁃ Anus everted ⁃ (+) Ridges/ cotyledons
⁃ Perineal bulging ⁃ DIRTY PRESENTATION
⁃ Pushes abdominal muscle ⁃ Irregular maternal surface
⁃ Legs simultaneously lithotomy
position Placental Expulsion
⁃ CROWNING ⁃ Natural bearing down or CREDE’S
⁃ Modified Ritgen’s Maneuver (to MANEUVER
deliver head, prevents damage to anal sphincter,
prevents episiotomy) Crede’s Maneuver
⁃ Gentle pressure contracted uterine
Oxytocin- After birth of BABY ⁃ NEVER in NON-CONTRACTED due
Methergine- After PLACENTA EXPULSION to hemorrhage and eversion
⁃ Pressure over bladder (similar with
emptying bladder or voiding of urine)
4. 4th stage (RECOVERY)
⁃ 1st 4hrs after placental expulsion
⁃ “Bonding Time”
⁃ Recovery
You might also like
- Hernia, (Different Types) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHernia, (Different Types) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Preparing for a Gentle Birth: The Pelvis in PregnancyFrom EverandPreparing for a Gentle Birth: The Pelvis in PregnancyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Normal Labor: Obstetrics and GynecologyDocument3 pagesNormal Labor: Obstetrics and GynecologyLuis PadillaNo ratings yet
- False ContractionsDocument2 pagesFalse ContractionsMaria Donabella OngueNo ratings yet
- Labor Part 1Document7 pagesLabor Part 1RANDY ERNEST GESTOSANINo ratings yet
- Intra ReviewerDocument11 pagesIntra ReviewertephNo ratings yet
- Maternal Factors: o o o oDocument11 pagesMaternal Factors: o o o oAmadea WPNo ratings yet
- Normal Labor and DeliveryDocument29 pagesNormal Labor and DeliveryManish ShahNo ratings yet
- 1 Unit 31 Intro and Components-of-Labor - 231115 - 191959Document150 pages1 Unit 31 Intro and Components-of-Labor - 231115 - 191959Mariah Angela PonceNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1Document100 pagesNCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1marilexdomagsangNo ratings yet
- Postpartum CareDocument4 pagesPostpartum CareHazelGraceNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum: Theories of Labors OnsetDocument6 pagesIntrapartum: Theories of Labors OnsetRAYNELAH ANN NONANNo ratings yet
- INTRAPARTUMDocument174 pagesINTRAPARTUMRUSTOM JAKENo ratings yet
- Handout # 10Document22 pagesHandout # 10Ram August100% (1)
- 1.1.unit 3.care of A Woman During Intrapartum PeriodDocument188 pages1.1.unit 3.care of A Woman During Intrapartum PeriodBabyjane BalagonNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Notes On Handling and Assisting CareDocument7 pages6.1 Notes On Handling and Assisting CarePasay Trisha Faye Y.No ratings yet
- Intrapartum Complications: Kristen AzusanoDocument3 pagesIntrapartum Complications: Kristen AzusanokirbsNo ratings yet
- Malposition & Malpresentation: Ahmad MakhloufDocument72 pagesMalposition & Malpresentation: Ahmad Makhloufjssamc prasootitantraNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor 2: Let's StartDocument15 pagesStages of Labor 2: Let's StartJoe VillaroyaNo ratings yet
- BreechDocument7 pagesBreechTanya Alyssa Untalan AquinoNo ratings yet
- Ncma 217 LectureDocument8 pagesNcma 217 Lectureanjie kamidNo ratings yet
- OB Chap 22 - Normal LaborDocument4 pagesOB Chap 22 - Normal LaborChino Paolo SamsonNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of LabourDocument33 pagesMechanism of LabourNatalie AlcântaraNo ratings yet
- Labor and DeliveryDocument4 pagesLabor and DeliveryJinky Teneza100% (1)
- Semis - MCN RLEDocument12 pagesSemis - MCN RLEKorean GirlNo ratings yet
- Intra ReviewerDocument11 pagesIntra ReviewerDIAZ, GIANNA D.No ratings yet
- Ncma217 Week 7Document5 pagesNcma217 Week 7Polly ArcheronNo ratings yet
- Problems With The PassagewayDocument2 pagesProblems With The PassagewayPrilay Pring AlcopraNo ratings yet
- Intra ReviewerDocument10 pagesIntra ReviewerL Rean Carmelle MAGALLONESNo ratings yet
- Intra ReviewerDocument12 pagesIntra Reviewerjl frusaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Malpresentations: Abundo, Esther Ellise Espinol, Hazel AnnDocument21 pagesFetal Malpresentations: Abundo, Esther Ellise Espinol, Hazel AnnEsther Ellise Abundo100% (1)
- Signs of LaborDocument5 pagesSigns of LaborweleyNo ratings yet
- What Is LaborDocument8 pagesWhat Is LaborEdsylaine BumatayNo ratings yet
- Four Phases of Parturition: Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Phase 4Document2 pagesFour Phases of Parturition: Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Phase 4Elizer Mario Pre Raboy100% (1)
- The Nursing Role in LaborDocument56 pagesThe Nursing Role in LaborQuolette ConstanteNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery NotesDocument4 pagesLabor and Delivery NotesJomarNo ratings yet
- CN DystociaDocument7 pagesCN DystociaAlbert Francis BialaNo ratings yet
- 1.8 NCM 109 Lec 8Document2 pages1.8 NCM 109 Lec 8Kristine BacaniNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor & Delivery and Danger Signs of Labor: Week 11 ReportersDocument30 pagesStages of Labor & Delivery and Danger Signs of Labor: Week 11 ReportersMushy_ayaNo ratings yet
- Normal Labor and DeliveryDocument10 pagesNormal Labor and Deliverymendato marcabanNo ratings yet
- Theories of Labor OnsetDocument7 pagesTheories of Labor OnsetBogaloid100% (6)
- NCM 107maternal FinalsDocument84 pagesNCM 107maternal FinalsFranz goNo ratings yet
- (Maternal) FINALSDocument86 pages(Maternal) FINALSRM DemetilloNo ratings yet
- IntrapartumDocument16 pagesIntrapartumBrigitte CovarrubiasNo ratings yet
- MCN Lect Module 2.5 Complications of Labor and Birth 4Document6 pagesMCN Lect Module 2.5 Complications of Labor and Birth 4AmethystNo ratings yet
- n3633 MM Module 1 Unit 1Document71 pagesn3633 MM Module 1 Unit 1jonscastro450No ratings yet
- OB Dystocia Part II and IIIDocument6 pagesOB Dystocia Part II and IIICyner CruzNo ratings yet
- Labor and DeliveryDocument8 pagesLabor and DeliveryRara SorayaNo ratings yet
- MCN MidtermsDocument39 pagesMCN MidtermsJinnijinniNo ratings yet
- Day 7-9-Ncm-107-IntrapartalDocument96 pagesDay 7-9-Ncm-107-IntrapartalMaureen CuartoNo ratings yet
- Hands Out 3 LaborDocument29 pagesHands Out 3 LaborErin SaavedraNo ratings yet
- #6 - NCM 109 - TransesDocument13 pages#6 - NCM 109 - TransesJaimie BanaagNo ratings yet
- COMPONENTS OF LABOR - 5PsDocument5 pagesCOMPONENTS OF LABOR - 5PslumpiaNo ratings yet
- 3 Handling and Assiting Deliveries TransesDocument7 pages3 Handling and Assiting Deliveries TransesKeana DacayanaNo ratings yet
- MCN Lab FinalsDocument29 pagesMCN Lab FinalsTrisha100% (1)
- OB Exam 2 ObjectivesDocument42 pagesOB Exam 2 ObjectivesInsatiable CleeNo ratings yet
- Breechpresentation Copy 141124075623 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument38 pagesBreechpresentation Copy 141124075623 Conversion Gate02 PDFKathirNo ratings yet
- 5.0 Physical ExaminationDocument7 pages5.0 Physical ExaminationJennifer Pisco LiracNo ratings yet
- A Premature NewbornDocument17 pagesA Premature NewbornMegatFitriAzizNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Care of The Mother During The Intrapartal PeriodDocument14 pagesModule 3 - Care of The Mother During The Intrapartal PeriodKatie HolmesNo ratings yet
- Renal FailureDocument5 pagesRenal FailureHazelGraceNo ratings yet
- Developmental Milestones 1Document2 pagesDevelopmental Milestones 1HazelGraceNo ratings yet
- Developmental Milestones 2Document3 pagesDevelopmental Milestones 2HazelGraceNo ratings yet
- Mother and Neonatal ChangesDocument2 pagesMother and Neonatal ChangesHazelGraceNo ratings yet
- Fetal DevelopmentDocument5 pagesFetal DevelopmentHazelGraceNo ratings yet
- Postpartum CareDocument4 pagesPostpartum CareHazelGraceNo ratings yet
- Pelindungan Hukum Bagi Bidan Memberikan Pelayanan Obat Kepada Pasien Dalam Praktik Kebidanan Di Daerah TerpencilDocument11 pagesPelindungan Hukum Bagi Bidan Memberikan Pelayanan Obat Kepada Pasien Dalam Praktik Kebidanan Di Daerah Terpencilmariyaniyuni2No ratings yet
- Obst 5 - All Obstetrics 1 2021Document22 pagesObst 5 - All Obstetrics 1 2021Menna KamalNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 5Document8 pagesJurnal 5Aprinita S. MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Common ManagementDocument7 pagesCommon ManagementaslanNo ratings yet
- Admission FormDocument3 pagesAdmission Formdarajati septia wNo ratings yet
- Assisted Breech Delivery1Document28 pagesAssisted Breech Delivery1swatisinghnigeria100% (4)
- Complications During Labor and DeliveryDocument27 pagesComplications During Labor and DeliveryMA. JYRELL BONITONo ratings yet
- Resume Obs 21-27 Februari 21Document6 pagesResume Obs 21-27 Februari 21imamsantos1191No ratings yet
- NASKAH PUBLIKASI NurfadilahDocument10 pagesNASKAH PUBLIKASI Nurfadilahfauziah nurNo ratings yet
- DOMINGO - OB RequirmentsDocument10 pagesDOMINGO - OB RequirmentsJick Esteva de VicenteNo ratings yet
- Breeding Ornamental FishDocument29 pagesBreeding Ornamental FishJLR 2crNo ratings yet
- Journal Atonia Uteri YuyunDocument6 pagesJournal Atonia Uteri YuyunMoh RamliNo ratings yet
- Kehamilan GandaDocument18 pagesKehamilan GandaLaris Donar Marukkap SihombingNo ratings yet
- Hyperglycemia in PregnancyDocument17 pagesHyperglycemia in PregnancyIza WidzNo ratings yet
- Worksheets With AnswersDocument48 pagesWorksheets With Answersshreyas100% (1)
- Secondary Postpartum Haemorrhage (PPH) Following PartialDocument14 pagesSecondary Postpartum Haemorrhage (PPH) Following PartialparamitastellaNo ratings yet
- Roles of HormonesDocument13 pagesRoles of Hormoneshafizah_90100% (6)
- Multiple PregnancyDocument15 pagesMultiple PregnancyM.S.H TubeNo ratings yet
- Intrapartal Complications: Problems With The PowerDocument10 pagesIntrapartal Complications: Problems With The PowerkeinwayNo ratings yet
- Visting (EBR)Document3 pagesVisting (EBR)Christian HarvestNo ratings yet
- MK Fetal Lie and Presentation (OBGY)Document9 pagesMK Fetal Lie and Presentation (OBGY)Moses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Checklist - Assisting - Circulating DeliveryDocument2 pagesChecklist - Assisting - Circulating DeliveryLue Vigiem M. GuiasNo ratings yet
- Normal Labor: Rumelle B. Reyes, M.D. Department of Obstretrics and Gynecology Eastern Visayas Regional Medical CenterDocument33 pagesNormal Labor: Rumelle B. Reyes, M.D. Department of Obstretrics and Gynecology Eastern Visayas Regional Medical CenterRumelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- ID Peran Kader Kesehatan Dalam Program Perencanaan Persalinan Dan Pencegahan Kompli PDFDocument9 pagesID Peran Kader Kesehatan Dalam Program Perencanaan Persalinan Dan Pencegahan Kompli PDFSukma Nisa CaemNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Theory Module 2MDocument31 pagesNCM 109 Theory Module 2MSecreto ParabiboNo ratings yet
- Strengthening Quality Midwifery Education Part 1Document10 pagesStrengthening Quality Midwifery Education Part 1Sheilla Tania MarcelinaNo ratings yet
- Acog Vbac PDFDocument14 pagesAcog Vbac PDFFrancyn Rossi YangsonNo ratings yet
- Cesarean Section: By: Fitri RuzaniDocument18 pagesCesarean Section: By: Fitri RuzaniFitriNo ratings yet
- 2019 Midwife CVDocument2 pages2019 Midwife CVapi-455508133No ratings yet
- Labor and DeliveryDocument7 pagesLabor and Deliveryplethoraldork100% (20)