Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Act 2.1
Uploaded by
Paola AguileraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Act 2.1
Uploaded by
Paola AguileraCopyright:
Available Formats
IIM144: Heat Transfer
Unit II: Steady State Conduction
Assignment 2.1: Exercises for Steady State Conduction
Instructions: Solve the following exercises critically and analytically.
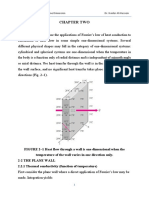
1. A technique for measuring convection heat transfer coefficients involves bonding one surface of a thin metallic
foil to an insulating material and exposing the other surface to the fluid flow conditions of interest.
Figure 2.1.1. Schematics for exercise 1.
By passing an electric current through the foil, heat is dissipated uniformly within the foil and the corresponding
flux, P′′elec, may be inferred from related voltage and current measurements. If the insulation thickness L and
thermal conductivity k are known and the fluid, foil, and insulation temperatures (T∞, Ts, Tb) are measured, the
convection coefficient may be determined.
′′
Consider conditions for which 𝑇∞ = 𝑇𝑏 = 25°C, 𝑃𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑐 = 2000 W/𝑚2 , L = 10 mm, and k = 0.040 W/m ⋅ K.
(a) With water flow over the surface, the foil temperature measurement yields Ts = 27°C. Determine the
convection coefficient. What error would be incurred by assuming all the dissipated power to be transferred to
the water by convection?
(b) If, instead, air flows over the surface and the temperature measurement yields Ts = 125°C, what is the
convection coefficient? The foil has an emissivity of 0.15 and is exposed to large surroundings at 25°C. What
error would be incurred by assuming all the dissipated power to be transferred to the air by convection?
(c) Typically, heat flux gages are operated at a fixed temperature (Ts), in which case the power dissipation provides
a direct measure of the convection coefficient. For Ts = 27°C, plot P′′elec as a function of ho for 10 ≤ ho ≤ 1000
W/m2 ⋅ K. What effect does ho have on the error associated with neglecting conduction through the insulation?
Dr. Alan Gabriel Ayala Bautista
alan.ayala@cetys.mx
IIM144: Heat Transfer
Unit II: Steady State Conduction
Assignment 2.1: Exercises for Steady State Conduction
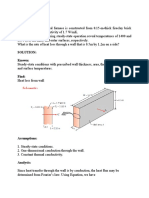
2. A house has a composite wall of wood, fiberglass insulation, and plaster board, as indicated in the sketch. On a
cold winter day, the convection heat transfer coefficients are ho = 60 W/𝑚2 ⋅K and ℎ𝑖 = 30 W/𝑚2 ⋅K. The total wall
surface area is 350 𝑚2 .
Figure 2.1.2. Schematics for exercise 1.
a) Determine a symbolic expression for the total thermal resistance of the wall, including inside and outside
convection effects for the prescribed conditions.
b) Determine the total rate of heat loss through the wall.
c) If the wind were blowing violently, raising ho to 300 W/m2 ⋅ K, determine the percentage increase in the rate of
heat loss.
d) What is the controlling resistance that determines the amount of heat flow through the wall?
Dr. Alan Gabriel Ayala Bautista
alan.ayala@cetys.mx
You might also like
- Tutorial Sheet 3Document10 pagesTutorial Sheet 3kushalNo ratings yet
- Physical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsFrom EverandPhysical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsA. H. BeckNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document7 pagesAssignment 1AdarshpatankarNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document10 pagesSheet 1محمود بسيوني نصارNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lectures Chemical Engineering Department University of Technology, IraqDocument1 pageHeat Transfer Lectures Chemical Engineering Department University of Technology, IraqChemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- ME 346 (S3) Tutorial 1 - SolutionsDocument18 pagesME 346 (S3) Tutorial 1 - SolutionsdivyanshuNo ratings yet
- L5 ConductionDocument44 pagesL5 ConductionRonel Mendoza100% (1)
- Tutorial 1-13 PDFDocument27 pagesTutorial 1-13 PDFPavanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2-1Document4 pagesTutorial 2-1chandan rajNo ratings yet
- B.TECH-2020-21 Assignment 1 Heat and Mass Transfer EME 303 Q-1Document1 pageB.TECH-2020-21 Assignment 1 Heat and Mass Transfer EME 303 Q-1HimanshuNo ratings yet
- 1 - Mechanisms - ExercisesDocument2 pages1 - Mechanisms - ExercisesIñigoAlberdiNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer WorksheetDocument5 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer WorksheetBISRAT YIHUNNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet 1 2022Document6 pagesWork Sheet 1 2022Fikadu GonfaNo ratings yet
- Updated ProblemsDocument3 pagesUpdated Problemsmahmoud koriemNo ratings yet
- CHG 2314 Heat Transfer Operations Winter 2012: Assignment 3Document3 pagesCHG 2314 Heat Transfer Operations Winter 2012: Assignment 3Clinton OkereNo ratings yet
- Conduction Tutorial Sheet 2Document3 pagesConduction Tutorial Sheet 2Charlotte BNo ratings yet
- Conduction Tutorial Sheet 2Document3 pagesConduction Tutorial Sheet 2Charlotte BNo ratings yet
- Northern Border University College of Engineering 1403-342 Heat TransferDocument2 pagesNorthern Border University College of Engineering 1403-342 Heat TransferAj ZNo ratings yet
- Md. Alamgir Hossain: Lecturer (ME) Department of Textile Engineering Green University of Bangladesh (GUB)Document14 pagesMd. Alamgir Hossain: Lecturer (ME) Department of Textile Engineering Green University of Bangladesh (GUB)saimunNo ratings yet
- Critical Thickness PDFDocument6 pagesCritical Thickness PDFSurya KiranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Thermal Conductivity and The Mechanism of Heat TransportDocument33 pagesChapter 8: Thermal Conductivity and The Mechanism of Heat TransportConrad MonterolaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 HMTDocument5 pagesWorksheet 1 HMTmubarekjemal3279No ratings yet
- P.E.S. College of Engineering, Mandya - 571 401Document4 pagesP.E.S. College of Engineering, Mandya - 571 401KN GowdaNo ratings yet
- Assignment QB 2015Document3 pagesAssignment QB 2015RutvikLathiaNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument37 pagesHeat Transferjason1989No ratings yet
- Exercise ProblemsDocument11 pagesExercise ProblemsVijaykumar NagathanNo ratings yet
- ENG-S17-S18 - Heat Transfer Problems (Modes, Plane Wall, Thermal Resistances)Document4 pagesENG-S17-S18 - Heat Transfer Problems (Modes, Plane Wall, Thermal Resistances)fNo ratings yet
- General Heat Conduction For Rectangle, CylindersDocument18 pagesGeneral Heat Conduction For Rectangle, CylindersTamoor TariqNo ratings yet
- Anna University Heat Transfer Question BankDocument12 pagesAnna University Heat Transfer Question BankGoutham R80% (5)
- Che 131 Ps-Heat1Document1 pageChe 131 Ps-Heat1Jelor GallegoNo ratings yet
- Programa de Ingeniería Mecánica Universidad de Pamplona: 1 Examen de Termofluidos IIDocument1 pagePrograma de Ingeniería Mecánica Universidad de Pamplona: 1 Examen de Termofluidos IIReinaldo DiazNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer AssignmentDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer AssignmentrajNo ratings yet
- 4 ProblemsDocument23 pages4 ProblemsKenneth JameroNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document6 pagesAssignment 1Menna TantawiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document11 pagesLecture 2ahmed el-sayedNo ratings yet
- Question PaperDocument7 pagesQuestion PaperRitikNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument18 pagesChapter TwoGauraviNo ratings yet
- CH 2-2Document203 pagesCH 2-2Aishahed mohamedNo ratings yet
- Chn-201 Tutorial 2 - Autumn 16-17-1Document2 pagesChn-201 Tutorial 2 - Autumn 16-17-1Prashant RajNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology RoorkeeDocument2 pagesDepartment of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Roorkeepushkal0% (2)
- Chapter 3 - Examples and Exercises (Part I) NewDocument7 pagesChapter 3 - Examples and Exercises (Part I) NewtemesgenNo ratings yet
- HT AssignmDocument9 pagesHT AssignmSai Chand Arkham KingNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 1 eDocument3 pagesTutorial Chapter 1 eRotten AppleNo ratings yet
- HMT - TS 1Document2 pagesHMT - TS 1sanket PatelNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityPARMAR MAHENDRANo ratings yet
- Week 3 Lecture 2 HTDocument6 pagesWeek 3 Lecture 2 HTdanial kashifNo ratings yet
- Farooque PDFDocument17 pagesFarooque PDFMandip KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document4 pagesTutorial 1Unta Di PadAng PaSirNo ratings yet
- Cadabadi - T1 - Taller ConduccionDocument5 pagesCadabadi - T1 - Taller ConduccionAndres FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document0 pagesTutorial 2xhotdogzxNo ratings yet
- HW #1 SolutionsDocument10 pagesHW #1 SolutionsDEEPSNo ratings yet
- (Sem. Iv) Theory Examination 2013-14: PAPER ID: 151406Document2 pages(Sem. Iv) Theory Examination 2013-14: PAPER ID: 151406Sarvesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Solved ProblemsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - Solved ProblemsHashem MansiNo ratings yet
- EGF4053 Chapter 2Document35 pagesEGF4053 Chapter 2hanis izzatiNo ratings yet
- MEEG 306 Tutorial Revised May 2019Document30 pagesMEEG 306 Tutorial Revised May 2019sagar100% (1)
- Introduction PDFDocument156 pagesIntroduction PDFIsyana MelzNo ratings yet
- ConductionDocument4 pagesConductionjaibalayyaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of OpenFOAM For CFD of Turbulent Flow in Water TurbinesDocument15 pagesEvaluation of OpenFOAM For CFD of Turbulent Flow in Water TurbinesAghajaniNo ratings yet
- MP4004 Advanced Manufacturing and Nanotechnology: ContentDocument26 pagesMP4004 Advanced Manufacturing and Nanotechnology: ContentVincent KohNo ratings yet
- ASTM D4329 Standard Practice For Fluorescent UV Exposure of PlasticsDocument6 pagesASTM D4329 Standard Practice For Fluorescent UV Exposure of PlasticsDavid VegaNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic HacksawDocument6 pagesPneumatic HacksawAvinash Lad100% (1)
- Electronic Distance Measurement (EDM)Document29 pagesElectronic Distance Measurement (EDM)Kavi MaranNo ratings yet
- Physics Details SolutionDocument15 pagesPhysics Details SolutionkolodoloNo ratings yet
- #Derivation of Mechanical Properties For SandDocument8 pages#Derivation of Mechanical Properties For SandkingmajorNo ratings yet
- Rockets Away: Quadratics and Newton's Third Law of Motion: BackgroundDocument7 pagesRockets Away: Quadratics and Newton's Third Law of Motion: BackgroundPatrick WoessnerNo ratings yet
- Journal of Luminescence: Monika Mall, Lokendra KumarDocument6 pagesJournal of Luminescence: Monika Mall, Lokendra KumarAzie AzuraNo ratings yet
- NEESE-Defense Base Isolation Tests Performance of Triple-Pendulum BearingsDocument10 pagesNEESE-Defense Base Isolation Tests Performance of Triple-Pendulum BearingsciscoNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document6 pagesLab 4dragon_287No ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument50 pagesThermal Power PlantQasim KhalidNo ratings yet
- App110 20210510Document7 pagesApp110 20210510Luen HopNo ratings yet
- Flowmeter Model MP KytolaDocument2 pagesFlowmeter Model MP KytolaJimmy MirandaNo ratings yet
- Cryogenic Air Separation, Histroy and Technological ProcessDocument20 pagesCryogenic Air Separation, Histroy and Technological ProcessJason Thomas100% (2)
- Materials Science (M.SC.) - Effective 01 April 2016Document2 pagesMaterials Science (M.SC.) - Effective 01 April 2016AtharvNo ratings yet
- Me8391 Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageMe8391 Engineering ThermodynamicsAiam PandianNo ratings yet
- Handout 1 - Elements and Types of MapsDocument3 pagesHandout 1 - Elements and Types of MapsqwdqwNo ratings yet
- 222 E05Document32 pages222 E05utsmanheruNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Moisture Removal Techniques For Mineral-Based Insulation OilDocument6 pagesComparative Study of Moisture Removal Techniques For Mineral-Based Insulation OilDante FilhoNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy: S.S. Chandel, M. Nagaraju Naik, Vikrant Sharma, Rahul ChandelDocument10 pagesRenewable Energy: S.S. Chandel, M. Nagaraju Naik, Vikrant Sharma, Rahul ChandelCleiber NichidaNo ratings yet
- T78u PDFDocument1 pageT78u PDFRenny DevassyNo ratings yet
- Basic ThermoDocument22 pagesBasic ThermoRoselyn BoNo ratings yet
- Steam Stop ValveDocument15 pagesSteam Stop Valveankur raiNo ratings yet
- Buffer Index and Buffer Capacity For A Simple Buffer SolutionDocument3 pagesBuffer Index and Buffer Capacity For A Simple Buffer SolutionEduardo CastroNo ratings yet
- Footing Design CalculationsDocument5 pagesFooting Design CalculationsArnold VercelesNo ratings yet
- Momentum ProblemsDocument3 pagesMomentum ProblemsBeverly Carballo - Moguel100% (2)
- Gromacs Manual 4.5Document370 pagesGromacs Manual 4.5tumm1982No ratings yet
- Polarography: Pharmaceutical Chemistry IIIB 516-T Course Incharge: Dr. Somia GulDocument17 pagesPolarography: Pharmaceutical Chemistry IIIB 516-T Course Incharge: Dr. Somia GulTayyab Siddiqui100% (1)
- Machines and Mechanisms - 2022Document164 pagesMachines and Mechanisms - 2022Ha LinhNo ratings yet
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersFrom EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesFrom EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemFrom EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNo ratings yet
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Handbook of Fire and Explosion Protection Engineering Principles: for Oil, Gas, Chemical and Related FacilitiesFrom EverandHandbook of Fire and Explosion Protection Engineering Principles: for Oil, Gas, Chemical and Related FacilitiesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesFrom EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsFrom EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyFrom EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Nutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeFrom EverandNutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsFrom EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeFrom EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Redefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesFrom EverandRedefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesNo ratings yet
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesFrom EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementNo ratings yet
- Environmental and Health and Safety Management: A Guide to ComplianceFrom EverandEnvironmental and Health and Safety Management: A Guide to ComplianceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Plutopia: Nuclear Families, Atomic Cities, and the Great Soviet and American Plutonium DisastersFrom EverandPlutopia: Nuclear Families, Atomic Cities, and the Great Soviet and American Plutonium DisastersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (32)
- Tensor Technology Guide: Tensor Ring Benefits and UsesFrom EverandTensor Technology Guide: Tensor Ring Benefits and UsesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- General Orders for Security Personnel: A Guide to Maintaining Discipline and ProfessionalismFrom EverandGeneral Orders for Security Personnel: A Guide to Maintaining Discipline and ProfessionalismNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Demography in Public HealthFrom EverandEpidemiology and Demography in Public HealthJaphet KillewoRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)