Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1b. Clinical Reasoning - Critical Thinking - STD Handouts - 2304
Uploaded by
ybeca0214Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1b. Clinical Reasoning - Critical Thinking - STD Handouts - 2304
Uploaded by
ybeca0214Copyright:
Available Formats
Bachelor of Nursing with Honours in General Health Care Programme
Bachelor of Nursing with Honours in Mental Health Care Programme
NURS N412F & NURS N414F Integrated Nursing
Learning Outcomes
Upon completion of the class, students should be able to:
✔ Differentiate thinking and critical thinking
✔ Appreciate the concept of critical thinking
✔ Describe the factors that affect critical thinking
✔ Describe the habits that can promote critical thinking
✔ Appreciate the concept of clinical reasoning
✔ Discuss the importance of clinical reasoning and critical thinking in the nursing
context
Pre-class activity:
⬧ Think about what you would do when a student says that old lady keeps on saying she is in
SOB?
1 NURS N412F & N414F_Clinical Reasoning & Critical Thinking_2304
Critical Thinking
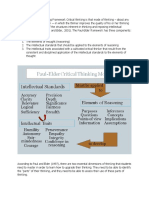
What is Critical Thinking?
It means not accepting information at face value without carefully evaluating it.
In critical thinking…. “Critical” can be replaced by _________________.
Definition of Critical Thinking
⬧ No one single definition because it is a complex process and it will change according to
the context and circumstances being discussed.
⬧ It is operationally defined as the utilization of scientific facts, principles, and laws to
identify, relate, understand, explain, predict, influence, and control nursing phenomena.
(Johnson & Webber, 2015)
Thinking vs. Critical thinking
⬧ Thinking: Merely mental activity, it can be “Mindless” like day dreaming/ reflexes.
⬧ Critical Thinking: controlled and purposeful, use well-reasoned strategies.
What “Critical Thinking” is NOT?
⬧ It is NOT simple being negative or full of criticism.
⬧ It is NOT arguing for the sake of arguing.
⬧ It is NOT accepting information at face value without carefully evaluating it.
When one thinks “critically”, he examines assumptions, evaluates evidence, uncovers
underlying values and reasons before drawing conclusion and making decision.
2 NURS N412F & N414F_Clinical Reasoning & Critical Thinking_2304
Critical thinking Non-critical thinking
Organized and explained well by using Disorganized and vague
words, examples, pictures or graphics
Criticism for the sake of improvement, Criticism for the sake of attacking without
new ideas, and doing things I the best being able to suggest new and constructive
interest of the key players involved ideas or alternatives; critical for the sake of
having it your way
Curious about intents, facts and reasons Unconcerned about motives, facts, and
behind ideas or actions reasons behind ideas or actions
Thought and knowledge-oriented Task-oriented rather than thought-oriented
Decision making based on facts, and what Decision making based on feelings/
is morally and ethically the right thing to emotion-driven
do
Communicative and collaborative with Isolated, competitive, or unable to
others when dealing with complex issues communicate with others when dealing
with complex issues.
Critical thinking in Nursing
⬧ It is used extensively in clinical reasoning
⬧ In nursing, critical thinking means using evidence-based strategies in all phases of the
nursing process
⬧ It is evident when nurses:
- Challenge assumptions
- Identify and acknowledge values and beliefs he/ she brings to the situation
- Consider the influence of context
- Generate possible explanations
⬧ It is guided by standards; driven by patient/ family & community needs; based on
principles of nursing process and scientific methods; and focus on quality and safety
Assumption
⬧ When something is taken for granted or presented as fact without supporting
evidence.
(Alfaro-LeFevre, 2020)
⬧ Need to identify assumptions, by:
- Double-check our thinking
- Apply logic
- Make judgements based on best available evidence
3 NURS N412F & N414F_Clinical Reasoning & Critical Thinking_2304
⬧ Critical thinking in nursing 🡺 Not only answering questions,
but also questioning “answers”
⬧ Rewards for critical thinking:
- Gaining confidence
- Be safe and autonomous
- Improve patient outcomes
- Enhance job satisfaction
⬧ Critical thinking is contextual & temporal
⬧ Thinking ahead:
- Anticipate what might happen
- Be proactive
- Can be difficult for novice who are lack of experience
⬧ Thinking-in-action
- It’s a rapid and dynamic reasoning
- Need to consider several things at a time
- Influenced by previous knowledge and experience
- More prone to a “knee-jerk” response and decision
⬧ Thinking back (Reflecting)
- Analyzing decision to look for flaws
- Gain more understanding and make corrections
- A reflective thinking
⬧ Critical thinking Indicators
- Observable behaviors that indicates critical thinking
- Behaviors include: (How many do you have?)
Reflective & self-corrective ___ Flexible, change as needed ___
Self-aware ___ Genuine/ authentic ___
Effective communicator ___ Careful & prudent ___
Curious and inquisitive ___ Open & fair-minded ___
Alert to context ___ Sensitive to diversity ___
Analytical & insightful ___ Creative ___
Logical & intuitive ___ Realistic and practical ___
Proactive & courageous ___ Honest and upright ___
Responsible ___ Patient and persistent ___
Confident and resilient ___
** There is no perfect critical thinker. Critical thinking ability depends on circumstances,
confidence level and previous experience.
“Pattern over time” is more important!!
4 NURS N412F & N414F_Clinical Reasoning & Critical Thinking_2304
Strategies to become a critical thinker
⬧ Gain insight and self-awareness; know your personality, learning styles and
thinking habits
⬧ Building trusting relationship with open communication and code of conduct
⬧ Committed to developing knowledge, attitudes, and skills
⬧ Use evidence-based reference
⬧ Reflect on reasoning process and ask for feedbacks
Factors affecting Critical Thinking Ability
A Personal factors
⬧ Health & Happiness
o One has to be healthy and happy to think critically
⬧ Mindfulness and work-life balance
o Pay attention to own feelings and learn how to take care of oneself
⬧ Fair-mindedness and moral development
o Aware of own values and have a good sense of right and wrong
⬧ Age and maturity
o Moral development comes with maturity (most of the time)
⬧ Personal dislikes, prejudices and biases
o Overcome prejudices and biases in order to think more objectively
and logically
⬧ Self-confidence
o Over-confident vs under-confident
⬧ Past experience
o Bad vs good experience can be enhancing or hindering factor
⬧ Knowledge of problem-solving, decision-making, the nursing process, and the
scientific method
o Familiarity with the process enhances critical thinking
⬧ Early evaluation and reflection
o Make it a habit to evaluate, so as to make correction timely
⬧ Effective writing skills
o Help to apply CT in an organized approach
⬧ Effective reading and learning skills
o Help using resources effectively
5 NURS N412F & N414F_Clinical Reasoning & Critical Thinking_2304
B Situational factors
⬧ Awareness of risks
o “think before you act”
⬧ Knowledge of related factors
o Awareness of the related factors that can help with solving the
problem
⬧ Awareness of resources
o Awareness to know where to get help
⬧ Positive reinforcement
o For confidence building
⬧ Negative “talks”
o These can impede thinking
⬧ Evaluative (judgmental) style
o Always think someone is judging you
⬧ Presence of motivating factors
o Rewarding outcome
⬧ Time limitations
o Can be enhancing or impeding
⬧ Distraction and interruptions
o Cause one to sway from focus
Habits that promote Critical Thinking & be an effective person
1 Be proactive
⬧ Be a responsible person and take initiative. Choose own actions, attitude and
moods
⬧ Do not blame others for wrong actions
⬧ Always do the right thing, without being asked, and even when no one is
looking
2 Begin with the End in mind
⬧ Plan ahead and set goals
⬧ Be an important part of the group, and contribute to common mission and
vision
3 Put first things first
⬧ Spend time on things that are most important
⬧ Set priority, make schedule, and follow the plan
6 NURS N412F & N414F_Clinical Reasoning & Critical Thinking_2304
⬧ Disciplined and organized
4 Think Win-Win
⬧ Balance courage for getting what one wants with considerations for what
others want
⬧ Look for alternatives when conflicts arise
5 Seek first to understand, then to be understood
⬧ Listen before talk
⬧ Listen to others’ ideas and feelings
⬧ See things from others’ viewpoint
6 Synergize
⬧ Value others’ strength and learn from them
⬧ Work well in groups because teaming with others can create better solutions
than working alone
⬧ Be humble
7 Sharpen the saw
⬧ Take care of self
⬧ Spend time with family and friends
Other strategies that promote critical thinking
⬧ Apply knowledge: compare and contrast
⬧ Communication: always ask “why”; replace “I don’t know” with “I need to
find out”
⬧ Use maps, diagrams, decision trees…etc to organize information
Clinical Reasoning
• It is a complex process that use
– cognition,
– meta-cognition, and
– discipline-specific knowledge
• To gather and analyze patient information,
• To evaluate its significance, and
• To weigh alternative actions
• It is used to identify and diagnose actual and potential patient problems; to make clinical
decisions for problem resolution so as to achieve positive patient outcomes.
(Simmons, 2010)
7 NURS N412F & N414F_Clinical Reasoning & Critical Thinking_2304
⬧ Clinical reasoning is important because it allows nurses to make timely and effective
patient-centered decisions
⬧ Fundamental difference between a novice and an expert
⬧ Having mere good knowledge and skills is not equal to having good clinical reasoning
skills
Clinical reasoning vs. Critical thinking
⬧ Clinical reasoning: a thinking process to direct a person to take “wise” action or
to take the best judged action in a specific context
⬧ Critical thinking: the rational examination of ideas, inferences, assumptions,
principlism, arguments, conclusions, issues, statements, beliefs and actions.
Terms
⬧ In literature, clinical reasoning, clinical judgment, problem solving, decision making, and
critical thinking are often used interchangeably.
⬧ It guides nurses in assessing, assimilating, retrieving, and/ or discarding components of
information that affect patient care.
Clinical judgment: outcome of clinical reasoning
⬧ An interpretation/ conclusion on the patient’s concerns or health problems
⬧ It is the decision:
- To/ not to take action
- To use/ modify standard approach
- To improvise new approach as deemed appropriate by the patient’s
response
8 NURS N412F & N414F_Clinical Reasoning & Critical Thinking_2304
Clinical Reasoning in Nursing
⬧ A process, which include:
- Collect cues
- Process the information
- Analysis the data
- Come to an understanding of a patient problem or situation
- Plan and implement interventions
- Evaluate outcomes
- Reflect on and learn from the process
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation
4 steps in Clinical Reasoning Process
8 steps in Clinical Reasoning Process
9 NURS N412F & N414F_Clinical Reasoning & Critical Thinking_2304
Clinical Reasoning Cycle
Reflection
Reflection-in-action: ability to interpret the patient’s response to an intervention
Reflection-on-action: subsequent thinking about the situation and what he/ she has
learned from it
Clinical Reasoning skills
1 Clustering related cues
⬧ Allows you to see patterns and relationship among data
2 Checking accuracy and reliability
⬧ Review both subjective and objective data
⬧ To avoid making assumptions
3 Distinguish normal from abnormal
⬧ Apply knowledge
4 Distinguish relevant from irrelevant
⬧ Focus on pertinent facts
5 Assessing systematically & comprehensively
⬧ Avoid making mistakes due to incomplete information
6 Identify patterns
⬧ Identify gaps in data collection
7 Identify missing information
⬧ To fill the gaps
10 NURS N412F & N414F_Clinical Reasoning & Critical Thinking_2304
8 Diagnosing actual & potential health problems
⬧ Identify risk factors
9 Setting priority
10 Determine patient-centered and individualized interventions
⬧ With SMART criteria
11 Identify assumptions
12 Making inferences
Inference: forming opinions and judgments that follow logically, based on patient’s sign
and symptoms
⬧ Avoid jumping to conclusion too quickly
⬧ Think of alternative conclusions
⬧ Use statements “ I suspect this…….”
Goals of Nursing
⬧ The most important starting point in becoming a nurse
– What do we, nurses, aim to do?
• Prevent illness
• Promote, maintain and restore health
• Maximize sense of well-being, independence & functional ability
• Provide cost-effective and efficient care
• Continually work to improve patient outcomes
11 NURS N412F & N414F_Clinical Reasoning & Critical Thinking_2304
Reference List
Alfaro-LeFevre, R. (2014). Applying nursing process. The foundation for clinical reasoning. (8th
ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Alfaro-LeFevre, R. (2020). Critical thinking, clinical reasoning and clinical judgment. A practical
approach. (7th ed.). Elsevier Saunders.
Forsgren, S.; Christensen, T. & Hedemalm, A. (2014). Evaluation of the case method in nursing
education. Nurse Education in Practice, 14, pp. 164 – 169.
Johnson, B.M. & Webber, P.B. (2015). An introduction to theory and reasoning in nursing. (4th
ed.). Wolters Kluwer.
Kassirer, J., Wong, J. & Kopelman, R. (2010). Learning clinical reasoning. (2nd ed.). Lippincott
Williams & Wilkins.
Koharchik, L., Caputi, L., Robb, M. & Culleiton, A.L. (2015). Fostering clinical reasoning in nursing
students. AJN, January, 115 (1), p.58 – 61.
LeMone, P., Burke, K.M., Bauldoff, G., & Gubrud, P. (2015). Medical-Surgical Nursing. Clinical
reasoning in patient care. (6th ed.). Pearson.
Marwat, M.F. (2013). Nursing Process. Patel Institute of nursing & allied health sciences.
Downloaded from http://www.slideshare.net/farooqmarwat/nursing-process-26614365
Simmon, B. (2010). Clinical reasoning: concept analysis. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 66(5), pp.
1151 – 158.
12 NURS N412F & N414F_Clinical Reasoning & Critical Thinking_2304
You might also like
- Critical Thinking Secrets: Discover the Practical Fundamental Skills and Tools That are Essential to Improve Your Critical Thinking, Problem Solving and Decision Making SkillsFrom EverandCritical Thinking Secrets: Discover the Practical Fundamental Skills and Tools That are Essential to Improve Your Critical Thinking, Problem Solving and Decision Making SkillsNo ratings yet
- Business LogicDocument34 pagesBusiness LogicJotaro KujoNo ratings yet
- How to Think Critically: Question, Analyze, Reflect, Debate.From EverandHow to Think Critically: Question, Analyze, Reflect, Debate.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- 10 Nursing As A Science Critical ThinkingDocument39 pages10 Nursing As A Science Critical ThinkingArissa Jamelia Lofranco AldeanoNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking in Nursing: Presented By-Ms. Neha Barari Assistant Professor SNSRDocument23 pagesCritical Thinking in Nursing: Presented By-Ms. Neha Barari Assistant Professor SNSRSamjhana NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Rise, Reframe, Reflect: A Guide to Cultivating Powerful Thinking HabitsFrom EverandRise, Reframe, Reflect: A Guide to Cultivating Powerful Thinking HabitsNo ratings yet
- BERFIKIRKRITISdlm KepDocument32 pagesBERFIKIRKRITISdlm KepJaramen_PurbaNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Critical Thinking: Week 13Document28 pagesThe Nature of Critical Thinking: Week 13AC NaurgenNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking and MeDocument20 pagesCritical Thinking and MeNahidSultana100% (2)
- Critical Thinking: Mrs. Esther VilasiniDocument15 pagesCritical Thinking: Mrs. Esther VilasiniAnn Merlin JobinNo ratings yet
- Nursing 1050 Exam ReviewDocument41 pagesNursing 1050 Exam Reviewkittycat16No ratings yet
- Promoting and Assessing Critical Thinking - EditedDocument24 pagesPromoting and Assessing Critical Thinking - EditedPao ParelNo ratings yet
- BS 309 Module 1 ThinkingDocument22 pagesBS 309 Module 1 ThinkingSrijan Pramanik100% (2)
- Critical Thinking: Critical Thinking... The Awakening of The Intellect To The Study of ItselfDocument11 pagesCritical Thinking: Critical Thinking... The Awakening of The Intellect To The Study of ItselfLeonard Ruiz100% (1)
- CTRWDocument28 pagesCTRWMark CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument5 pagesCritical ThinkingEugelyn BondocNo ratings yet
- Jepretan Layar 2021-09-29 Pada 06.50.31Document34 pagesJepretan Layar 2021-09-29 Pada 06.50.31Amma Nurpa IndahNo ratings yet
- Critical and Creative ThinkingDocument12 pagesCritical and Creative Thinkingnavina yogeshNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking YT Insta Medico SlidesDocument27 pagesCritical Thinking YT Insta Medico Slideshammadali123hprNo ratings yet
- English 4 TerjemahanDocument7 pagesEnglish 4 TerjemahanSandra DewiNo ratings yet
- CRTW FinalsDocument12 pagesCRTW FinalsMarianne GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument8 pagesCritical Thinkingupma sharma100% (1)
- Critical ThinkingDocument42 pagesCritical ThinkingRa DiantNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking in NursingDocument37 pagesCritical Thinking in NursingAmmar Zaki NabilaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Profession Practice ContinuationDocument25 pagesLecture 3 Profession Practice Continuationfaith kinyaNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Word - Foundation5Document73 pagesCritical Thinking Word - Foundation5Saraswati Learning Center SLCNo ratings yet
- CRWT111 FinalDocument7 pagesCRWT111 FinalReyna Lea MandaweNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document24 pagesUnit 3Dr. Shweta KumariNo ratings yet
- Week 13 - The Nature of Critical ThinkingDocument5 pagesWeek 13 - The Nature of Critical ThinkingIRENE GARDONNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking SkillsDocument35 pagesCritical Thinking SkillsROSAMMA JOSEPH100% (1)
- Explain Why Critical Thinking Is Primarily About How You Think and Not Necessarily What You ThinkDocument5 pagesExplain Why Critical Thinking Is Primarily About How You Think and Not Necessarily What You ThinkMyraNo ratings yet
- Berfikir Kritis Dalam Praktek Keperawatan: by Tri PrabowoDocument32 pagesBerfikir Kritis Dalam Praktek Keperawatan: by Tri PrabowoZhiroro Peace D'TrampNo ratings yet
- Richard Paul and Linda Elder'sDocument3 pagesRichard Paul and Linda Elder'sDave FortuNo ratings yet
- FundaaaDocument13 pagesFundaaaLorna Mae MontanezNo ratings yet
- Crtical Doc FinDocument22 pagesCrtical Doc FinLennön ShönıwaNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument27 pagesCritical ThinkinggpsdurraniNo ratings yet
- Managing Yourself For StudyDocument31 pagesManaging Yourself For StudyEmellda MANo ratings yet
- How To Improve Critical ThinkingDocument3 pagesHow To Improve Critical ThinkingAISA BANSILNo ratings yet
- 5 Important Critical Thinking Skills To Master For StudentsDocument81 pages5 Important Critical Thinking Skills To Master For Students117. godlief erwin semuel migeNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument3 pagesCritical ThinkingMarjorie BenesistoNo ratings yet
- CT Pillar PDFDocument36 pagesCT Pillar PDFluisgoncaloNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking in Nursing ProcessDocument66 pagesCritical Thinking in Nursing Processgoodpromise.medicalNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument13 pagesCritical ThinkingRuqiyya Qayyum100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Nursing MidtermDocument110 pagesFundamentals of Nursing MidtermJane Heart AguilonNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Nursing ManagementDocument15 pagesCritical Thinking Nursing ManagementJosephine George JojoNo ratings yet
- Funda Lec MidtermsDocument13 pagesFunda Lec MidtermsCharisse CaydanNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument23 pagesDecision MakingCamelia zahrahNo ratings yet
- Portfilio Brayden Wirzba Ed4391Document16 pagesPortfilio Brayden Wirzba Ed4391api-308587685No ratings yet
- Understadning Critical Thinking CourseDocument31 pagesUnderstadning Critical Thinking CourseLuận DominicNo ratings yet
- Day 1 - Critical Thinking For IADocument30 pagesDay 1 - Critical Thinking For IArisafNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument5 pagesCritical ThinkingSummer Rogers100% (2)
- Critical ThinkingDocument4 pagesCritical ThinkingMaeleen Carmona SalardaNo ratings yet
- Life Skill EducationDocument10 pagesLife Skill EducationchonhaobamNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking in Nursing EducationDocument5 pagesCritical Thinking in Nursing EducationLorelie Asis100% (1)
- BATCH-2020-2025 Course - Ba LLB Subject-Philosophy: 2Nd SemesterDocument9 pagesBATCH-2020-2025 Course - Ba LLB Subject-Philosophy: 2Nd SemesterBhuvneshwari RathoreNo ratings yet
- Understanding Why Creative and Critical Thinking Skills Are ImportantDocument10 pagesUnderstanding Why Creative and Critical Thinking Skills Are ImportantGlen Carlo B. RellosoNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking and Political InquiryDocument26 pagesCritical Thinking and Political InquiryBuhari AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- CCT-Module Chapter-12 AngadananDocument62 pagesCCT-Module Chapter-12 AngadananRizette PaloganNo ratings yet
- 1the Power of Critical ThinkingDocument10 pages1the Power of Critical ThinkingMuneebNo ratings yet
- Cap 5 - StressDocument6 pagesCap 5 - StressJu OliverNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing The Success of An Organizational Change PDFDocument19 pagesFactors Influencing The Success of An Organizational Change PDFArun Ragavendar A 19MBA0039No ratings yet
- War PhotographerDocument15 pagesWar PhotographerMenon HariNo ratings yet
- Eq MocDocument17 pagesEq MocSylu SreeNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 3 - Q2 - W4Document6 pagesDLL - English 3 - Q2 - W4Jane Bunuan SaludaresNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet Increase Attraction With StyleDocument4 pagesCheat Sheet Increase Attraction With StyleCyros Rexes MaduraNo ratings yet
- 5 AnsDocument3 pages5 AnsANIRBAN PALNo ratings yet
- Psych AssignmentDocument2 pagesPsych AssignmentPatricia Xandra AurelioNo ratings yet
- FINAL ASSIGNMENT RnWdocxDocument1 pageFINAL ASSIGNMENT RnWdocxKezia Bannerara LalloNo ratings yet
- Tawek Johari Window PPT MokodDocument4 pagesTawek Johari Window PPT Mokodnikos kasiktsisNo ratings yet
- Heidegger Work of ArtDocument30 pagesHeidegger Work of ArtMichael SmithNo ratings yet
- Long Term ABA Is AbusiveDocument9 pagesLong Term ABA Is AbusiveLorena MatosNo ratings yet
- Law of Attraction - The Secret Power of The Universe (Using Your Subconscious Mind, Visualization & Meditation For Manifesting Happiness, Love, Money & Success) Inspirational Self Help Book PDFDocument89 pagesLaw of Attraction - The Secret Power of The Universe (Using Your Subconscious Mind, Visualization & Meditation For Manifesting Happiness, Love, Money & Success) Inspirational Self Help Book PDFprinceNo ratings yet
- What We Know of OdDocument5 pagesWhat We Know of OdSharath P VNo ratings yet
- 21 Lesson For 21st CenturyDocument16 pages21 Lesson For 21st CenturySamia GhafoorNo ratings yet
- Present Simple vs. Present ContinuousDocument6 pagesPresent Simple vs. Present ContinuousArchitectNo ratings yet
- Habit Will DefinedDocument5 pagesHabit Will Definedapi-550517388No ratings yet
- The Tell Tale HeartDocument1 pageThe Tell Tale HeartI'm SmilenNo ratings yet
- The Enneagram Personality Test TruityDocument1 pageThe Enneagram Personality Test Truitythehumblepotato17.4No ratings yet
- Module 4 WorksheetDocument4 pagesModule 4 WorksheetDAVE ANDREW AMOSCONo ratings yet
- Mricchakatikam Study Material 2Document9 pagesMricchakatikam Study Material 2royarko857No ratings yet
- Essay On Politicization of CultureDocument2 pagesEssay On Politicization of CultureMarkey DaquilaneaNo ratings yet
- Overcoming The Habit of Negative Self Talk PickUpLimesDocument3 pagesOvercoming The Habit of Negative Self Talk PickUpLimesSofia SiagaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior Syllabus: Independence - Freedom - HappinessDocument10 pagesConsumer Behavior Syllabus: Independence - Freedom - HappinessBăng TâmNo ratings yet
- Presentation Group 4Document14 pagesPresentation Group 4Ronit Nadar100% (1)
- Karyn McQueen Victim Impact StatementDocument13 pagesKaryn McQueen Victim Impact StatementCourtney TeagueNo ratings yet
- Power Point Presentation On Mhca 2017Document54 pagesPower Point Presentation On Mhca 2017Sampriti Roy100% (1)
- Learning Modules: Lourdes CollegeDocument13 pagesLearning Modules: Lourdes CollegeSangcad M AmboloNo ratings yet
- How To Build A Personal Brand Strategy and Communication PlanDocument5 pagesHow To Build A Personal Brand Strategy and Communication PlancccqNo ratings yet
- Too Many BananasDocument3 pagesToo Many Bananasapi-486851273No ratings yet
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (80)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- How to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingFrom EverandHow to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingNo ratings yet
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassFrom EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (26)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- An Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyFrom EverandAn Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- Self-Care for Autistic People: 100+ Ways to Recharge, De-Stress, and Unmask!From EverandSelf-Care for Autistic People: 100+ Ways to Recharge, De-Stress, and Unmask!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- Summary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)