Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Networks I
Computer Networks I
Uploaded by
Monika S0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views74 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views74 pagesComputer Networks I
Computer Networks I
Uploaded by
Monika SCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 74
NETWORKS
1. A network is a set of devices (often referred to as nodes)
2. connected by communication links.
3. A node can be a computer, printer, or any other device
capable of sending and/or receiving data generated by
other nodes on the network.
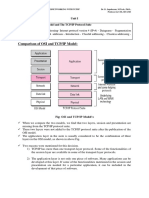
TCP/IP MODEL
4
1
The Application Layer,
The TCP/IP model was Transport Layer,
developed prior to the Network Layer,
OSI model. Data Link Layer And
Physical Layer.
2 5
The TCP/IP model is not Main work of TCP/IP is to
exactly similar to the OSI transfer the data of a computer
model. from one device to another
3 6
The TCP/IP model To make data reliable and
consists of five layers accurate
7 How Does the TCP/IP Model Work?
TCP/IP model divides
its data into packets
Whenever we want to send
something over the internet
8
using the TCP/IP Model, the
And combines them at the other TCP/IP Model divides the
end, which helps in maintaining the
accuracy of the data while
data into packets at the
transferring from one end to sender’s end and the same
another end.
packets have to be
recombined at the receiver’s
end to form the same data,
and this thing happens to
maintain the accuracy of the
data.
9
TCP/IP model divides the
data into a 4-layer
procedure,
9
Layers of TCP/IP Model
1. Application Layer
2. Transport Layer(TCP/UDP)
3. Network/Internet Layer(IP)
4. Data Link Layer (MAC)
5. Physical Layer
You might also like
- User Acceptance Test - Plant Maintenance: ScenarioDocument7 pagesUser Acceptance Test - Plant Maintenance: ScenarioBagaz KarmawanNo ratings yet
- IPv4 Subnetting for Beginners: Your Complete Guide to Master IP Subnetting in 4 Simple Steps: Computer Networking, #1From EverandIPv4 Subnetting for Beginners: Your Complete Guide to Master IP Subnetting in 4 Simple Steps: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Nissan Lanner Case study-WITNESSDocument3 pagesNissan Lanner Case study-WITNESSasrikalyanNo ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument6 pagesTCP Ipkannanperu123No ratings yet
- Presented By-: Aditi RathoreDocument7 pagesPresented By-: Aditi RathoreAditi RathoreNo ratings yet
- TCP IP Explained 17.01.2024Document5 pagesTCP IP Explained 17.01.2024aloishp36No ratings yet
- TCP - IP Model - GeeksforGeeksDocument12 pagesTCP - IP Model - GeeksforGeeksFousiya FousiNo ratings yet
- What Is TCP (03.01.2024)Document4 pagesWhat Is TCP (03.01.2024)aloishp36No ratings yet
- Quiz No 01Document5 pagesQuiz No 01Muhammad AhadNo ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument11 pagesTCP IptherealmukanyaNo ratings yet
- TCP IPModelDocument23 pagesTCP IPModelMukeshNo ratings yet
- Overview of TCP/IP Reference ModelDocument4 pagesOverview of TCP/IP Reference ModelPRODIP DEBNo ratings yet
- Naing - Min - Khant - E6I1201 - Data - Com Task-2Document5 pagesNaing - Min - Khant - E6I1201 - Data - Com Task-2Sniper- KNo ratings yet
- Data Communication & NetworksDocument8 pagesData Communication & Networksrukhsar siddiqueNo ratings yet
- Mastering The OSI & TCP - IPDocument4 pagesMastering The OSI & TCP - IPMridul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Tcp/Ip: Protocol, TCP/IP Is A Set of Rules (Protocols) Governing Communications Among All Computers On TheDocument5 pagesTcp/Ip: Protocol, TCP/IP Is A Set of Rules (Protocols) Governing Communications Among All Computers On TheAmardeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Osimodel 170406162300 PDFDocument42 pagesOsimodel 170406162300 PDFPvkkiy EceNo ratings yet
- BCA TDC III TCP-IP Reference Model 2 by Dr. Rakesh RanjanDocument5 pagesBCA TDC III TCP-IP Reference Model 2 by Dr. Rakesh RanjanSandeep DeyNo ratings yet
- TCP - IP Model - Intro NotesDocument3 pagesTCP - IP Model - Intro NotesAnonymous OsssbjNo ratings yet
- Networking Models FinalDocument36 pagesNetworking Models FinalSolan Solomon BerkessaNo ratings yet
- The Reference Model Part 2Document6 pagesThe Reference Model Part 2roysayanccp05No ratings yet
- Differences Between OSI and TCDocument2 pagesDifferences Between OSI and TCNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.assignment On 15 Well-Known Protocols, Their Port Number and FunctionsDocument6 pages1.assignment On 15 Well-Known Protocols, Their Port Number and FunctionsLimitless StatusNo ratings yet
- TCP Ip ModelDocument22 pagesTCP Ip ModelrankomanNo ratings yet
- 6-OSI Model-10-01-2022 (10-Jan-2022) Material - I - 10-01-2022 - OSI - TCP-IP - ModelDocument39 pages6-OSI Model-10-01-2022 (10-Jan-2022) Material - I - 10-01-2022 - OSI - TCP-IP - ModelPrerna SinghNo ratings yet
- The OSI and TCPDocument8 pagesThe OSI and TCPSreejith VaneryNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Osi Vs Tcp/Ip Model: Submitted To: Mr. Jobin T. JDocument16 pagesAssignment 1 Osi Vs Tcp/Ip Model: Submitted To: Mr. Jobin T. JMedia MaticNo ratings yet
- Acn May 2018Document45 pagesAcn May 2018shraddha_mundadadaNo ratings yet
- Ice L1Document14 pagesIce L1Prof. MOHAMMED JUNED SHAUKAT ALINo ratings yet
- Difference Between OSI Layer & TCP - IP LayerDocument4 pagesDifference Between OSI Layer & TCP - IP LayerEincop Netwax LabNo ratings yet
- DCN TCP AssignmentDocument11 pagesDCN TCP Assignmenttalwandi bhindranNo ratings yet
- D. The Tcp/Ip Reference Model: ProtocolDocument7 pagesD. The Tcp/Ip Reference Model: ProtocolEcho greenNo ratings yet
- What Is The TCP/IP Model? TCP/IP Model Helps You To Determine How A Specific Computer Should BeDocument18 pagesWhat Is The TCP/IP Model? TCP/IP Model Helps You To Determine How A Specific Computer Should BePhilip EdebuNo ratings yet
- TCP Ip ModelDocument5 pagesTCP Ip ModelJJ JainNo ratings yet
- Protocol, Is A Four-Layer Representation of The Network (Shown in Figure 6.1) ThatDocument2 pagesProtocol, Is A Four-Layer Representation of The Network (Shown in Figure 6.1) ThatPeilunNo ratings yet
- TCPIP - Unit IDocument35 pagesTCPIP - Unit IAnilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 PDFDocument26 pagesChapter 14 PDFLuigi AngelilNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of OSI and TCP/IP Models in Network Communication.Document7 pagesComparative Analysis of OSI and TCP/IP Models in Network Communication.Kelvin NnamaniNo ratings yet
- Ccna Day 3Document44 pagesCcna Day 3XX YYNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks TCP IpDocument15 pagesComputer Networks TCP IpSudarshan KrishnaNo ratings yet
- OSI Layer ModelDocument22 pagesOSI Layer ModelshaikNo ratings yet
- 3.9 Draw TCP IP Reference Model and State The Functions of Each LayerDocument3 pages3.9 Draw TCP IP Reference Model and State The Functions of Each Layernarendra kumar bNo ratings yet
- Assignment On NetworksDocument7 pagesAssignment On NetworksLimitless StatusNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 05 / Lecture - 03 / Osi - Tcp/IpDocument10 pagesChapter - 05 / Lecture - 03 / Osi - Tcp/IpNagaraj VaratharajNo ratings yet
- MODULE 9 - TCP/IP Protocol Suite and IP AddressingDocument7 pagesMODULE 9 - TCP/IP Protocol Suite and IP AddressingGrecu GianiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 & 6Document39 pagesLecture 5 & 6Entertainment WorldNo ratings yet
- Network LayerDocument6 pagesNetwork LayerCaleb Jedel OlivoNo ratings yet
- ProtocolDocument39 pagesProtocolمحمد ياسر محي الدينNo ratings yet
- Network Layer StackDocument13 pagesNetwork Layer Stackleslie010No ratings yet
- OSI Reference Model Cheat SheetDocument13 pagesOSI Reference Model Cheat Sheetbivixag351No ratings yet
- 2.7 Osi and TCP ModelDocument13 pages2.7 Osi and TCP ModelM M Naib KhanNo ratings yet
- OSI Model CheatSheetDocument13 pagesOSI Model CheatSheetMuslem MuslemNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document14 pagesLecture 2clely fernandesNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument7 pagesOSI ModeleugeniapalaciosdatoNo ratings yet
- Overview of TCP/IP Reference ModelDocument3 pagesOverview of TCP/IP Reference ModelReign Earl B. Gup-ayNo ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument1 pageTCP Ipgohola9880No ratings yet
- Computer Network Report - CA2 - Tirtharaj Pati - 14201619089 PDFDocument4 pagesComputer Network Report - CA2 - Tirtharaj Pati - 14201619089 PDFTirtharaj PatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2:reference Model: Layer 7 - ApplicationDocument13 pagesChapter 2:reference Model: Layer 7 - ApplicationWatiri SteveNo ratings yet
- Assignment-II: Gagandeep KaurDocument12 pagesAssignment-II: Gagandeep KaurYolomanNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP: Network+ Protocols And Campus LAN Switching FundamentalsFrom EverandTCP/IP: Network+ Protocols And Campus LAN Switching FundamentalsNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyFrom EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNo ratings yet
- research methodologyDocument8 pagesresearch methodologyMonika SNo ratings yet
- DeadLock in Operating SystemDocument15 pagesDeadLock in Operating SystemMonika SNo ratings yet
- Wa0054.Document1 pageWa0054.Monika SNo ratings yet
- Wa0055.Document1 pageWa0055.Monika SNo ratings yet
- Wa0053.Document1 pageWa0053.Monika SNo ratings yet
- ACE Scanner - 2024 - 03 - 23Document1 pageACE Scanner - 2024 - 03 - 23Monika SNo ratings yet
- Wa0002.Document17 pagesWa0002.Monika SNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Module 3.Document18 pagesComputer Network Module 3.Monika SNo ratings yet
- Tugas DMD GROUP 01Document8 pagesTugas DMD GROUP 01ulviqhj354No ratings yet
- 5.3.3.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Layer 3 Switches InstructionsDocument2 pages5.3.3.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Layer 3 Switches InstructionsAhmadHijazi50% (2)
- Battery-Powered, Handheld Potentiostat and GalvanostatDocument3 pagesBattery-Powered, Handheld Potentiostat and GalvanostatguiburNo ratings yet
- Multi-Function Wire Tracker User ManualDocument15 pagesMulti-Function Wire Tracker User ManualcharlesNo ratings yet
- Stage Lighting & Sound History of Lighting & Sound RecordingDocument55 pagesStage Lighting & Sound History of Lighting & Sound RecordingDavid SeldesNo ratings yet
- CLL261-Introduction To Process Control: Hariprasad Kodamana Iit DelhiDocument19 pagesCLL261-Introduction To Process Control: Hariprasad Kodamana Iit DelhiGARGI SHARMANo ratings yet
- Learning-From-Disagreement A Model Comparison andDocument16 pagesLearning-From-Disagreement A Model Comparison andDanish VasdevNo ratings yet
- KFC - KFX 210 - Control - System PDFDocument17 pagesKFC - KFX 210 - Control - System PDFDragomir HoffmannNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Science and Machine LearningDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Data Science and Machine LearningCHETAN V CHAUDHARINo ratings yet
- SQL For Data Science Project Week 4Document25 pagesSQL For Data Science Project Week 4Joseph Alexander ReyesNo ratings yet
- Manual Tankradar Rex Commissioning Manual Rosemount en 80812Document36 pagesManual Tankradar Rex Commissioning Manual Rosemount en 80812A-selam IbraNo ratings yet
- CV SANDEEP DUBEY Civil Engineer.Document4 pagesCV SANDEEP DUBEY Civil Engineer.Sandeep dubeyNo ratings yet
- Bash CheatsheetDocument1 pageBash CheatsheetjeffNo ratings yet
- BRM ProposalDocument6 pagesBRM ProposalSajid ZamanNo ratings yet
- Module - 2: Governance and Management of Enterprise Information Technology, Risk Management, Compliance & BCM SectionDocument114 pagesModule - 2: Governance and Management of Enterprise Information Technology, Risk Management, Compliance & BCM SectionRaghu VamsiNo ratings yet
- Mahindra Medicals and ElectronicsDocument2 pagesMahindra Medicals and ElectronicsAmandeepNo ratings yet
- Diagrams Used in SrsDocument2 pagesDiagrams Used in SrsBuggineni Vamsi Ram100% (1)
- Microsoft (MSFT) : Company DescriptionDocument2 pagesMicrosoft (MSFT) : Company DescriptionHernan DiazNo ratings yet
- Q.1 (A) Give Full Form of Following AcronymDocument16 pagesQ.1 (A) Give Full Form of Following AcronymsvNo ratings yet
- Transmission and Distribution DesignDocument79 pagesTransmission and Distribution DesignBishnuBahadur ThapaNo ratings yet
- Construction Technology Training Institute Islamabad (Ctti)Document3 pagesConstruction Technology Training Institute Islamabad (Ctti)Tariq QaisraniNo ratings yet
- EC305 Microprocessor & MicrocontrollerDocument2 pagesEC305 Microprocessor & MicrocontrollerplbonifusNo ratings yet
- Exam Az 900 Microsoft Azure Fundamentals Skills MeasuredDocument4 pagesExam Az 900 Microsoft Azure Fundamentals Skills Measuredrahulkn2009100% (1)
- Creating A SOA Composite Application With Oracle JDeveloper 12cDocument13 pagesCreating A SOA Composite Application With Oracle JDeveloper 12cheyrinNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Office 2016 VL ProPlus September 2017 - KuyhAaDocument15 pagesMicrosoft Office 2016 VL ProPlus September 2017 - KuyhAaSuratman Blanck MandhoNo ratings yet
- 0 Introduction To Electrical System Design (Lab)Document10 pages0 Introduction To Electrical System Design (Lab)EdryanPoNo ratings yet
- Samsung dvd-sh873 874 875 876 877Document130 pagesSamsung dvd-sh873 874 875 876 877Chema Don GarNo ratings yet
- Excelandia User Guide V2Document27 pagesExcelandia User Guide V2Karla Panganiban TanNo ratings yet