Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RMA - Research Midterms
Uploaded by
Joji BorromeoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RMA - Research Midterms
Uploaded by
Joji BorromeoCopyright:
Available Formats
Community Resilience: The Construction of
Modular Disaster Relief Shelter in
Lower Bicutan, Taguig City
AUTHOR 1: BORROMEO, JOJI One critical aspect of disaster
MAERELTON D. preparedness is the establishment of a modular
disaster relief shelter, serving as an immediate
jmdborromeo2020@plm.edu.ph
central hub for coordinating emergency
response efforts. The shelter's construction aims to
AUTHOR 2: ROSCA, ASHLEE DANE S.
provide a safe haven for residents during
adsrosca2020@plm.edu.ph disasters, reducing human casualties, property
damage, and displacement. Additionally, the
AUTHOR 3: Ar. Antonio C. Nudas III shelter can alleviate the strain on existing
healthcare facilities by offering temporary
acnudas@plm.edu.ph
medical services to those in need, mitigating the
impact of the area's scarcity of hospitals.
Natural disasters such as floods and By employing empirical research
earthquakes, pose significant threats to the methodologies, including surveys, interviews, and
residents of Lower Bicutan, Taguig City, data analysis, this study seeks to evaluate the
Philippines. In response to these challenges, this tangible benefits of the modular disaster relief
study investigates the effectiveness of shelter in Lower Bicutan. This study will examine
constructing a modular disaster relief shelter in the feasibility and effectiveness of constructing a
Lower Bicutan, with a focus on mitigating the modular disaster relief shelter in Lower Bicutan,
impacts of floods and earthquakes and Taguig City, to enhance community resiliency
addressing the deficiency in immediate and emergency medical response.
healthcare facilities during calamities.
Keywords: Modular, Disaster relief shelter,
Lower Bicutan is characterized by its community resiliency, emergency medical
vulnerability to flooding, compounded by its response, temporary shelter
flood-susceptible open and residential areas,
and insufficient drainage systems in major road I. Introduction
networks. Additionally, the area is situated within
an active seismic zone, the West Valley Fault
Natural Disasters pose significant
System, facing a heightened risk of earthquakes.
challenges to communities worldwide, often
This combination of environmental factors
resulting in displacement, loss of lives, and
underscores the urgent need for resilient disaster
damage to infrastructure. The Philippines, a
country prone to various natural hazards such as
response measures tailored to the community's
typhoons, earthquakes, and floods, the need for
unique circumstances.
effective disaster response and recovery
ARR 150: RESEARCH METHODS IN ARCHITECTURE 1
College of Architecture and Sustainable Built Environments - PLM
COMMUNITY RESILIENCE: THE CONSTRUCTION OF MODULAR DISASTER RELIEF SHELTER TO ENHANCE
EMERGENCY RESPONSE IN LOWER BICUTAN, TAGUIG CITY
BORROMEO | ROSCA 2024
mechanisms is paramount. One critical aspect of deployment and user-friendly solutions. These
disaster preparedness is the provision of suitable include:
shelter for affected populations, particularly in
the immediate aftermath of a disaster. ● Speedy construction: Modular structures
allow for swift assembly, reducing
In addition, the provision of temporary construction timeframes compared to
sheltering stands as a fundamental aspect of traditional building methods.
disaster management protocols. In the context of ● End-user friendliness: Modular housing
the COVID-19 pandemic, there is a heightened designs prioritize user needs and
need for rapid and modular temporary sheltering comfort, offering functional and
solutions in densely populated urban areas to customizable living spaces.
enhance the capacity of hospitals for treatment ● Cost-effectiveness: The prefabricated
and care services. nature of modular construction can
result in cost savings, making it a viable
However, effective emergency option for large-scale housing projects.
management strategies for contemporary ● Versatility: Modular structures can be
societies necessitate the integration of resilience adapted to various terrain types and
principles into all stages of emergency response. environmental conditions, ensuring
suitability for diverse disaster-affected
The concept of resilience introduces a areas.
fresh perspective to disaster management ● Quality assurance: Controlled factory
practices, with recent research indicating that environments ensure consistent quality
resilience initiatives lead to notable control standards, enhancing the
enhancements in traditional safety and security durability and resilience of modular
measures during disasters. housing solutions.
The construction of a modular disaster By leveraging these characteristics,
relief shelter in Lower Bicutan, Taguig City, modular construction offers a comprehensive
presents an opportunity to enhance community and immediate approach to permanent/
resilience and emergency response in the area. temporary housing reconstruction in
disaster-stricken regions, addressing both shelter
Modular structures can provide a
needs, medical recovery, and long-term
holistic approach to permanent housing
community recovery efforts.
reconstruction in disaster-struck areas. By
evaluating the design, construction, and The study aims to assess the impact of
functionality of the modular shelter, the study modular disaster relief shelter design and
seeks to identify key features and improvements construction to Lower Bicutan, Taguig City in
that can enhance its effectiveness in providing the context of emergency disaster response and
safe and secure housing for disaster-affected community resilience. By evaluating the
populations. effectiveness of the modular shelter and its
impact on community resilience and emergency
Modular construction presents several
response, the study also seeks to expand the
inherent characteristics that facilitate rapid
application modular disaster relief shelter
ARR 150: RESEARCH METHODS IN ARCHITECTURE 2
College of Architecture and Sustainable Built Environments - PLM
COMMUNITY RESILIENCE: THE CONSTRUCTION OF MODULAR DISASTER RELIEF SHELTER TO ENHANCE
EMERGENCY RESPONSE IN LOWER BICUTAN, TAGUIG CITY
BORROMEO | ROSCA 2024
construction to temporary storage facilities, materials that were used, the layout of the shelter, and
modular homes, and emergency medical evaluating its potential impact on the community.
facilities.
The effectiveness of the shelter may be
A. Research Problem influenced by external factors such as the frequency
and severity of disasters, access to resources and
1. How can modular disaster relief shelters in support services, and the capacity of local authorities
Lower Bicutan, Taguig City enhance and organizations to manage and maintain the shelter.
community resilience and emergency
response to disasters? D. Assumptions and Hypothesis
2. How can modular disaster relief shelters in
The establishment of such a modular
Lower Bicutan improve the relationship path
disaster relief shelter will lead to improved
between sheltering and recovering period
emergency response coordination, medical recovery
during disasters?
efforts, and community resilience during
3. How do prefabricated modular unit
disaster-stricken times due to the prefabricated nature
structures’ building material impact the
of modular construction, cost-effectiveness, speedy
durability, deployability and versatility of
assembly, rapid deployment, versatility and
disaster relief shelters?
adaptability to different terrain types and
B. Goals and Objectives environmental conditions, ensuring suitability for
disaster-affected areas in Lower Bicutan, Taguig City
● To conduct a comprehensive assessment of
the disaster risks and vulnerabilities in E. Significance
Lower Bicutan, Taguig
The significance of assessing the
● To identify the key features and
construction of a modular disaster relief shelter in
functionalities required for a modular
Lower Bicutan, Taguig City, lies in its potential to
disaster relief shelters to effectively serve
enhance community resilience and emergency
the community’s needs
response. By evaluating the feasibility and
● To assess the potential impact of the
effectiveness of such a shelter, this can provide
modular disaster relief shelter based on the
valuable insights into improvising disaster
identified requirements and feasibility
preparedness and response mechanisms in the area.
assessment
● To conduct a review of existing literature on
The findings can inform local government
materials commonly used in disaster relief
agencies, NGOs, and other stakeholders about the
shelter construction
key features and functionalities needed for an
effective modular shelter, enabling them to make
C. Scope and Limitation
informed decisions regarding its implementation.
The scope of implementing a modular
Additionally, the study can serve as a model
disaster relief shelter in Lower Bicutan, Taguig City,
for similar initiatives in other disaster-prone areas,
includes assessing the feasibility and effectiveness of
contributing to the broader field of disaster risk
such a shelter in enhancing community resilience and
reduction and management.
emergency response.
F. Concepts and Framework
This involves identifying key features and
functionalities required for the shelter to serve the
1. Theoretical Framework
community’s needs, assessing the sustainable
ARR 150: RESEARCH METHODS IN ARCHITECTURE 3
College of Architecture and Sustainable Built Environments - PLM
COMMUNITY RESILIENCE: THE CONSTRUCTION OF MODULAR DISASTER RELIEF SHELTER TO ENHANCE
EMERGENCY RESPONSE IN LOWER BICUTAN, TAGUIG CITY
BORROMEO | ROSCA 2024
Modular Systems as Temporary Sheltering in underpinned by multifaceted reasons. Modular
Emergency Response construction affords the flexibility to fashion bespoke
buildings and spaces in a manner that is ecologically
The necessity for effective emergency sound, operationally seamless, and easily scalable.
management during hazard impacts, particularly in
densely populated urban areas, is emphasized. Design criteria of Post-disaster Temporary
Temporary sheltering emerges as a fundamental Shelters
requirement, especially given the challenges posed by
the COVID-19 pandemic.
Urgency exists in deploying fast and
modular temporary sheltering solutions to enhance
medical treatment and care services, particularly for
overwhelmed hospitals. Agile and adaptable
sheltering strategies are highlighted as essential for
meeting evolving emergency needs and ensuring
effective disaster management in urban settings
(Nekooie, 2020).
The utilization of modular structures as
temporary sheltering presents a practical and efficient
solution to address the housing needs of populations
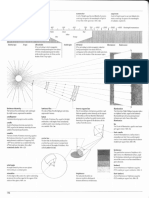
affected by emergencies or disasters. These Figure 1. A model for the design criteria development of
prefabricated structures offer several advantages in post-disaster temporary shelter
emergency response scenarios.
The theoretical framework for assessing the
They are highly adaptable to various construction of modular disaster relief shelters can be
environmental conditions and can be configured to related to the international standards and
accommodate different spatial requirements and recommendations for temporary shelters, as outlined
withstand harsh weather conditions. Additionally, the in various studies and resources. These standards
modular design allows for scalability, enabling the emphasize several key characteristics for temporary
expansion or contraction of sheltering facilities based shelters, including resistance, durability, stability,
on changing population needs. cost-effectiveness, upgradability, simplicity, ease of
transport, climatic suitability, recyclability, privacy
Modular Construction provision, and property protection (Bashawri, Garrity
& Moodley, 2014; Kim, Kim & Kim, 2021; UNHCR,
The historical connotation of modular or 2012).
prefabricated construction often evokes memories of
post-war architecture, where rapid reconstruction was The design criteria for modular disaster
imperative to restore what had been lost. However, shelters encompass various aspects, spanning
contemporary perspectives are evolving. Driven by technology, construction, materials, ecology, cost,
advancements in technology, heightened building physics, spatial organization, sociology, and
environmental consciousness, and shifting economic aesthetics.
paradigms, modular construction is transcending its In terms of technology, the selection of
historical confines to emerge as a prominent and materials and systems is crucial, focusing on
sustainable building methodology. Far from being a structural performance, ease of production, storage,
fleeting trend, its burgeoning acceptance is
ARR 150: RESEARCH METHODS IN ARCHITECTURE 4
College of Architecture and Sustainable Built Environments - PLM
COMMUNITY RESILIENCE: THE CONSTRUCTION OF MODULAR DISASTER RELIEF SHELTER TO ENHANCE
EMERGENCY RESPONSE IN LOWER BICUTAN, TAGUIG CITY
BORROMEO | ROSCA 2024
and transportation, as well as integration of service performance, moisture control, sound insulation, fire
systems. safety, and lighting, while spatial organization
Durability is paramount to withstand addresses user needs, privacy, flexibility, and
movements and ensure longevity, while accessibility for diverse demographics, including
considerations for ease of cleaning contribute to disabled and elderly users.
hygiene and maintenance.
Ecology is another key aspect, emphasizing
minimal environmental impact, sustainable
building-ground interaction, and eco-friendly
materials.
2. Conceptual Framework
Figure 2. Conceptual framework for modular disaster
relief shelters
Cost-effectiveness is essential, balancing
quality and affordability to maximize resources.
Building physics considerations ensure
indoor climatic comfort, air quality, thermal
ARR 150: RESEARCH METHODS IN ARCHITECTURE 5
College of Architecture and Sustainable Built Environments - PLM
COMMUNITY RESILIENCE: THE CONSTRUCTION OF MODULAR DISASTER RELIEF SHELTER TO ENHANCE
EMERGENCY RESPONSE IN LOWER BICUTAN, TAGUIG CITY
BORROMEO | ROSCA 2024
Figure 3. Modular disaster relief shelters and community
resilience influencing variables
efficient, flexible, and sustainable building solutions
Prefabricated Modular Unit Structures for diverse projects.
Prefabricated modular unit structures, also Community Resilience
known as PMUS, are innovative building solutions
characterized by their off-site construction and Community resilience refers to the
assembly in modular components. These units are collective ability of a community to effectively adapt,
fabricated in controlled factory settings, where they respond, and recover from adversity or challenges,
undergo stringent quality control measures before such as natural disasters, economic downturns, social
being transported to the construction site for disruptions, or health crises. It involves the
assembly. PMUS offer several advantages, including collaboration and coordination of various
accelerated construction timelines, cost-efficiency, stakeholders within a community, including
and versatility in design and application. individuals, families, businesses, community
organizations, government agencies, and
They can be customized to meet specific non-governmental organizations (NGOs).
project requirements and are suitable for various
purposes, including residential, commercial, and The concept of system resilience, as outlined
industrial applications. Additionally, PMUS are by Gopalakrishnan and Peeta (2010), is built upon
known for their sustainability benefits, as they often two main pillars: systematic impact and total
incorporate eco-friendly materials and construction recovery effort. These pillars encompass three
methods, minimizing waste and environmental capacities crucial for resilience: absorptive capacity,
impact. Overall, prefabricated modular unit structures adaptive capacity, and restorative capacity.
represent a modern approach to construction, offering
ARR 150: RESEARCH METHODS IN ARCHITECTURE 6
College of Architecture and Sustainable Built Environments - PLM
COMMUNITY RESILIENCE: THE CONSTRUCTION OF MODULAR DISASTER RELIEF SHELTER TO ENHANCE
EMERGENCY RESPONSE IN LOWER BICUTAN, TAGUIG CITY
BORROMEO | ROSCA 2024
1. Absorptive Capacity: The ability to withstand ● Environmental Impact Assessment:
shocks or stressors without significant Assessing the ecological consequences of
damage. the disaster, such as pollution, habitat
2. Adaptive Capacity: The ability to adapt and destruction, and contamination of water
respond to changing conditions or challenges. sources. It helps in mitigating
3. Restorative Capacity: The ability to recover environmental hazards and planning for
and restore functionality after disruption. ecosystem restoration.
II. Methods of Inventory ● Infrastructure Assessment: Examining
the functionality of critical infrastructure
A. Research Design such as hospitals, schools, communication
networks, and utilities (electricity, water,
The study will involve a mixed-use approach, sanitation) to identify areas needing urgent
combining various research methods to compare and attention and resources for repair.
correlate data and information in finding and
● Risk Assessment: Analyzing ongoing
identifying disaster damage assessment and impact of
risks posed by the disaster, such as the
modular disaster relief shelters on community
potential for secondary hazards (e.g.,
resilience in the people of Lower Bicutan, Taguig
landslides, aftershocks) and vulnerabilities
City.
in infrastructure or communities. This
1. Disaster Assessment assessment informs safety protocols and
disaster preparedness measures.
Disaster assessment is a qualitative and
● Socio-Economic Assessment:
quantitative comprehensive evaluation process
Understanding the socio-economic impact
conducted after a natural or man-made disaster to
of the disaster on communities, including
gauge its impact and determine the extent of damage
loss of livelihoods, disruptions to
to infrastructure, communities, and the environment.
economic activities, and strain on local
The process will involve surveys and information
resources. It helps in designing recovery
collection activities to determine the effects on
programs and allocating resources to
disaster victims, the stricken community of Lower
support affected populations.
Bicutan in general.
2. Qualitative Analysis
● Damage Assessment: This involves
surveying the affected areas to determine In assessing the effectiveness of modular
the extent of physical damage to buildings, disaster relief shelters on community resiliency in
roads, bridges, utilities, and other Lower Bicutan, Taguig City, a qualitative approach
infrastructure. It helps in prioritizing areas will be adopted, employing content analysis and
for immediate repair and restoration. interviews with community members.
● Human Impact Assessment: Evaluating
Content analysis will be utilized to
the impact of the disaster on human lives,
systematically examine various textual and visual
including injuries, fatalities, displaced
materials, including government reports, media
populations, and disruptions to livelihoods.
coverage, and community documents, to identify
This assessment guides emergency
prevalent themes, trends, and discourses related to the
medical response efforts and the provision
implementation and impact of modular shelters.
of humanitarian aid.
ARR 150: RESEARCH METHODS IN ARCHITECTURE 7
College of Architecture and Sustainable Built Environments - PLM
COMMUNITY RESILIENCE: THE CONSTRUCTION OF MODULAR DISASTER RELIEF SHELTER TO ENHANCE
EMERGENCY RESPONSE IN LOWER BICUTAN, TAGUIG CITY
BORROMEO | ROSCA 2024
Additionally, semi-structured interviews will government halls are mostly converted to evacuation
be conducted with residents, local leaders, and centers that are not equipped to cater large numbers
stakeholders to gain firsthand insights into their of victims of calamities. Modular disaster relief
perceptions, experiences, and opinions regarding the shelters have emerged as a viable solution, offering
shelters' role in enhancing community resilience. quick deployment and flexibility to meet the evolving
needs of disaster-affected communities.
Through these qualitative research methods,
a comprehensive understanding of the strengths, 3.1 Local Studies
challenges, and implications of modular disaster
relief shelters on the resilience of the Lower Bicutan 3.1.1 Determination of Flood-Prone Areas in
community will be achieved, informing future Taguig City
disaster response and recovery efforts.
Cañaveral, E. V., & Refrima, C. (2022, June
B. Data gathering procedures 8). Determination of Flood-Prone Areas in
Taguig, Metro Manila. Story Maps. March 31, 2024,
The procedure will focus on gathering data https://storymaps.arcgis.com/stories/6299f3d125c748
and information from previous disaster assessment 9e91c6c9a982cbf313
records of Lower Bicutan, Taguig City from local
government units that is emphasized on most recent Taguig City currently has 36 barangays
activities of flooding, earthquakes, and from the existing. And it is located in the southern section of
aftereffects of COVID 19’ pandemic. Metro Manila and southwestern shore of Laguna de
Bay which makes it susceptible to flooding.
Another method that will be utilized are surveys and According to Cabalza et al. (2017), six (6) barangays
interviews. Surveys will be administered to a and around 800 families were affected during the
representative sample of community members, to onslaught of Typhoon Maring in 2017 and the most
gather quantitative data on their perceptions, recent flooding, which rose to waist-high affecting
experiences, and satisfaction levels regarding the two barangays due to habagat only (Zurbano, 2021).
shelters' impact on resilience. Interviews with disaster Monteverde (1996) observed that the eastern part of
victims, local leaders, and residents will be conducted the city is particularly prone to flooding. Moreover,
to gain insight about disaster experiences and major road networks such as C-5,C-6, Manuel L.
recovery as well as perspectives about strengths, Quezon Ave/St, and SLEX are also at risk of
challenges, and implications of modular disaster flooding, especially from neighboring inundated
relief shelters on the resilience of the Lower Bicutan areas.
as a community.
To mitigate flood risks, Cañaveral, E. (2021)
III. Review of Related Literature recommends a combination of structural and
non-structural measures. These include urban
Disasters, whether natural or man-made, can have greening to prevent land subsidence, infrastructure
devastating effects on the community. A country that improvements to enhance drainage systems, and the
is highly susceptible to different hazards such as establishment of an early warning system to save
typhoons, earthquakes, and flooding such as the lives. Priority should be given to areas identified as
Philippines, are in need of effective disaster response highly susceptible to flooding in the hazard maps.
and preparedness. One critical aspect of disaster
preparation is the provision of suitable shelter for 3.1.2 Design of Green Emergency Housing for
affected populations, particularly for the aftermath of Calamity-Stricken Communities
a disaster. According to Balante et. al (2018),
gymnasium, courts, classrooms, and local
ARR 150: RESEARCH METHODS IN ARCHITECTURE 8
College of Architecture and Sustainable Built Environments - PLM
COMMUNITY RESILIENCE: THE CONSTRUCTION OF MODULAR DISASTER RELIEF SHELTER TO ENHANCE
EMERGENCY RESPONSE IN LOWER BICUTAN, TAGUIG CITY
BORROMEO | ROSCA 2024
Salvame, E. J., & Quebral, R. (n.d.). Design Natural disasters pose a significant threat to
of green emergency housing for calamity – stricken communities in the Philippines, often leaving
communities. IRB NET. thousands homeless and placing strain on local
https://www.irbnet.de/daten/iconda/CIB_DC26757 resources. To address this challenge, Ravina & Shih
(2020), proposed the construction of a permanent
The study focuses on the development of typhoon shelter that is both affordable and easily
transient evacuation centers in the Philippines using a enhanced. The shelter utilized Coco lumber (its main
modular design approach with recycled container structural component) which is readily available
vans. This innovative approach addresses the material in the Philippines. The design features a
country’s need to enhance its disaster preparedness, simple rectangular building form with a hip roof,
especially in the face of its susceptibility to damaging making it easy for local workers to construct. The
natural disasters. Salvame, E. (2021) proposes a shelter’s design also incorporates slanted wall design
modular design that allows for easy expansion and which enhances interior space and provides
subdivision of structures, enabling quick relocation as additional storage options. The slanted roof design
requirements change. The use of eco-friendly encourages rainwater harvesting, addressing the need
construction materials, such as recycled container for sustainable water sources for toilet and kitchen,
vans, simplifies assembly and installation process. the shelter also creates job opportunities for the local
The researchers presented two layout options: one community. Overall, the proposed shelter offers a
with container vans stacked at three-storey levels and flexible and cost effective solution to the housing
another with two container vans stacked to form a needs of disaster-affected communities.
two-storey structure. Each unit includes an average of
32 double-deck beds for the two-storey layout and 46 3.2 International Studies
double-deck beds for the three-storey layout,
complete with wall fans and CFL lamps. 3.2.1. Time-Efficient Post-Disaster Housing
Additionally, separate vans are allocated for Reconstruction with Prefabricated Modular
administration offices, wash areas, kitchen areas, and Structures
restrooms. Solar electricity is also incorporated into
the system, ensuring sustainability and efficiency. Gunawardena, T., Ngo, T., Mendis, P., Aye,
L., & Crawford, R. (2014). Time-efficient
The study suggests that introducing post-disaster housing reconstruction with
alternative shelters using used container vans is prefabricated modular structures. Open House
achievable, more economical compared to International, 39(3), 59–69.
conventional concrete structures, and easier to install https://doi.org/10.1108/ohi-03-2014-b0007
and dismantle. Establishing these transient evacuation
centers would enhance the country’s ability to A study conducted in the University of
provide immediate and acceptable evacuation shelters Melbourne, Australia discussed how prefabricated
for displaced citizens during calamities. modular structures can provide a more time-efficient
solution by analyzing several present-day examples
3.1.3 Ocho Balay: Design of a permanent taken from published post disaster housing
typhoon shelter for the rural areas in the reconstruction processes that have been carried out in
Philippines different parts of the world. It also evaluated how
other features of modular construction, such as ease
Shih, R. R., & Ravina, D. (2020). Ocho of decommissioning and reusability, can add value to
Balay: Design of a permanent Typhoon shelter for the post disaster reconstruction processes and
rural areas in the Philippines. Pollack Periodica, organizations that contribute to the planning, design,
15(2), 221–232. and construction stages of the reconstruction process.
https://doi.org/10.1556/606.2020.15.2.20 The study also delved into the suitability of modular
ARR 150: RESEARCH METHODS IN ARCHITECTURE 9
College of Architecture and Sustainable Built Environments - PLM
COMMUNITY RESILIENCE: THE CONSTRUCTION OF MODULAR DISASTER RELIEF SHELTER TO ENHANCE
EMERGENCY RESPONSE IN LOWER BICUTAN, TAGUIG CITY
BORROMEO | ROSCA 2024
construction along with context of guidelines and REFERENCES:
best practice guides for post-disaster housing
reconstruction published by international Cañaveral, E. V., & Refrima, C. (2022, June
organizations. 8). Determination of Flood-Prone Areas in
Taguig, Metro Manila. Story Maps. March 31,
Modules can be pre-engineered to perform 2024,
at various climatic conditions in order to provide a https://storymaps.arcgis.com/stories/6299f3d1
better indoor climate to the dwellers. Better 25c7489e91c6c9a982cbf313
preparedness and having a set of modules that were
prototyped previously with well-established Gunawardena, T., Ngo, T., Mendis, P., Aye, L.,
production logistics, can result in even faster delivery & Crawford, R. (2014). Time-efficient
of final products. Techniques such as BIM can be post-disaster housing reconstruction with
used to efficiently gather and channel all such design prefabricated modular structures. Open House
requirements from a disaster-stricken community to International, 39(3), 59–69.
the designers, and modular construction will be https://doi.org/10.1108/ohi-03-2014-b0007
highly compatible to associate such requirements to
produce custom-designed houses in a much faster Mottaki, Z., Hosseini Sabzevari, S. A., &
time frame. This is a great way to ensure that the Aslani, F. (2023). Designing post-earthquake
livelihoods of the affected communities are restored temporary shelter in hot and arid climate
to their satisfaction, and to ensure that their basic (Case study: Isfahan city, Iran). Architectural
human rights on permanent housing are provided as Engineering and Design Management, 1–18.
early as possible. Through this analysis and https://doi.org/10.1080/17452007.2023.22705
discussion, it is concluded that prefabricated modular 49
structures are a highly desirable time-efficient
solution to post-disaster housing reconstruction. Quaglia, C. P., Dascanio, A. J., & Thrall, A. P.
(2014). Bascule shelters: A novel erection
3.2.2. Resilient and Sustainable Modular System strategy for origami-inspired deployable
for Temporary Sheltering in Emergency structures. Engineering Structures, 75,
Condition 276–287.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2014.06.00
This study proposes that effective 3
emergency management in contemporary societies
can be attained through the integration of a Salvame, E. J., & Quebral, R. (n.d.). Design of
resilience-based approach into all emergency green emergency housing for calamity –
procedures. The concept of resilience offers a fresh stricken communities. IRB NET.
perspective on disaster management, as recent studies https://www.irbnet.de/daten/iconda/CIB_DC2
demonstrate its substantial enhancement of traditional 6757.pdf
safety and security methods during crises. In line
with this, Temporary shelters serve a critical function Shih, R. R., & Ravina, D. (2020). Ocho Balay:
in providing temporary accommodation and Design of a permanent Typhoon shelter for the
managing emergency situations throughout disaster rural areas in the Philippines. Pollack
periods. Accordingly, what determines the critical Periodica, 15(2), 221–232.
success factors for resiliency and sustainability of a https://doi.org/10.1556/606.2020.15.2.20
modular temporary shelter are the reduction of mortar
usage, using industrialized building system and
interconnected structure.
ARR 150: RESEARCH METHODS IN ARCHITECTURE 10
College of Architecture and Sustainable Built Environments - PLM
You might also like
- Climate change response actions the adverse effects of Climate change on the Widikum community in CameroonFrom EverandClimate change response actions the adverse effects of Climate change on the Widikum community in CameroonNo ratings yet
- Borromeo Rosca RmaDocument7 pagesBorromeo Rosca RmaJoji BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Askar 2019 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 225 012032Document9 pagesAskar 2019 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 225 012032austinwhite347No ratings yet
- Disaster Management MidtermDocument9 pagesDisaster Management MidtermSheryl Anne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Hazards and Disasters ManagementDocument33 pagesHazards and Disasters ManagementumairbinsaadNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature: Bareng, King Philmill S. Student Res-MethDocument5 pagesReview of Related Literature: Bareng, King Philmill S. Student Res-MethGroup4RamosNo ratings yet
- Role of Structural Engineers in Face of Natural DisastersDocument4 pagesRole of Structural Engineers in Face of Natural DisastersIsuru Udayanga NanayakkaraNo ratings yet
- Conceptualizando y Midiendo La ResilenciaDocument5 pagesConceptualizando y Midiendo La ResilenciamarcoaerazoNo ratings yet
- Researh Paper - Anubhuti SinghalDocument5 pagesResearh Paper - Anubhuti SinghalAnubhuti SinghalNo ratings yet
- Fostering A Culture of Disaster Preparedness With Alternative Temporary SheltersDocument10 pagesFostering A Culture of Disaster Preparedness With Alternative Temporary SheltersarchstephsngNo ratings yet
- Review Paper of PratikDocument3 pagesReview Paper of PratikMahesh ghorpadeNo ratings yet
- Designing For Disaster Resilience-ThesisDocument10 pagesDesigning For Disaster Resilience-ThesisMark MallariNo ratings yet
- DRRM Orientation 1Document58 pagesDRRM Orientation 1jcgabb0521No ratings yet
- Flood Hazard Mitigation Plan Goals and ObjectivesDocument2 pagesFlood Hazard Mitigation Plan Goals and ObjectivesAbigail CaloniaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Planning Emergency PlanDocument2 pagesEmergency Planning Emergency PlanChristine Ann JuguanNo ratings yet
- Shelter Design and Disaster Education Final 4.30.19Document14 pagesShelter Design and Disaster Education Final 4.30.19zebaNo ratings yet
- AmphiDocument10 pagesAmphiaff DNo ratings yet
- Week 14 17 Crim 6 Unit Viii and XiDocument33 pagesWeek 14 17 Crim 6 Unit Viii and XiLouella Kaye C. LopezNo ratings yet
- Northern Manhattan Climate Action PlanDocument1 pageNorthern Manhattan Climate Action PlanAurash KhawarzadNo ratings yet
- RR324 Mid ReviewerDocument14 pagesRR324 Mid ReviewerJun VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- NCDMM The Role of Civil Engineering in Disaster Response and RecoveryDocument3 pagesNCDMM The Role of Civil Engineering in Disaster Response and RecoverydrbhumikaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts and Terminologies in Disaster Management: Eld in Feb Adopted From 8 Evrccourse 2009 in BangkokDocument51 pagesBasic Concepts and Terminologies in Disaster Management: Eld in Feb Adopted From 8 Evrccourse 2009 in BangkokJomar Llarenas ZosaNo ratings yet
- Ainuddin (2012) Communityresilienceframeworkforanearthquake Prone Area in BaluchistanDocument12 pagesAinuddin (2012) Communityresilienceframeworkforanearthquake Prone Area in Baluchistanmichael17ph2003No ratings yet
- Prioritization Strategies To Reduce The Seismic Risk of The Public and Strategic BuildingsDocument16 pagesPrioritization Strategies To Reduce The Seismic Risk of The Public and Strategic BuildingsMoriom MuktaNo ratings yet
- Dinil PushpalalDocument8 pagesDinil PushpalalnusangsaraNo ratings yet
- Envisci Revised FloodingDocument5 pagesEnvisci Revised Floodingrjosephine529No ratings yet
- Chapter2 TerminologyDocument64 pagesChapter2 TerminologyIshwor PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Sustainability 13 12389Document23 pagesSustainability 13 12389Jane EdullantesNo ratings yet
- 4.chapter 1Document10 pages4.chapter 1Jenidal B. Mana-ayNo ratings yet
- Barangay Disaster ManualDocument19 pagesBarangay Disaster ManualLeah MoyaoNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Disaster Resilient HousingDocument6 pagesLiterature Review Disaster Resilient HousingkarunaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts and Terminologies in Disaster Management: Adopted From 8 EVRC Course Held in Feb 2009 in BangkokDocument46 pagesBasic Concepts and Terminologies in Disaster Management: Adopted From 8 EVRC Course Held in Feb 2009 in BangkokAngel Jimmyly EstanillaNo ratings yet
- Vulnerability Atlas of India PDFDocument8 pagesVulnerability Atlas of India PDFiamshakeyNo ratings yet
- DRRRDocument10 pagesDRRRpmasamiana.tshsNo ratings yet
- Disaster Mitigation: Initial Response: Review ArticleDocument4 pagesDisaster Mitigation: Initial Response: Review ArticleWawan JokoNo ratings yet
- Terms and Concepts On Disaster Risk ReductionDocument34 pagesTerms and Concepts On Disaster Risk ReductionKINGA TANDIN SHERPANo ratings yet
- NSTP1 MODULE 3 Disaster Awareness Preparedness and ManagementDocument16 pagesNSTP1 MODULE 3 Disaster Awareness Preparedness and Managementrenz dave100% (2)
- Project 8Document7 pagesProject 8Anselm IbehNo ratings yet
- Disaster Management in Public HealthDocument23 pagesDisaster Management in Public Healthtuba sarfrazNo ratings yet
- DRRMC 10121 Report AsgDocument9 pagesDRRMC 10121 Report AsgChrisNo ratings yet
- Rma Manuscript Totoo NaDocument5 pagesRma Manuscript Totoo NaJessa Mae S. SilvelaNo ratings yet
- 2 Disaster RiskDocument3 pages2 Disaster RiskapaszaldyNo ratings yet
- 2014 Anh Climate Resilient HousingDocument12 pages2014 Anh Climate Resilient HousingALINANo ratings yet
- Natasha - Kapai - MT20UPL022 - Assignment 1 - UDRRDocument9 pagesNatasha - Kapai - MT20UPL022 - Assignment 1 - UDRRNatasha KapaiNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 - Lesson 4 Earth and ScienceDocument8 pagesBio 1 - Lesson 4 Earth and SciencePaul Omar PastranoNo ratings yet
- Editorial: Why Is Community Action Needed For Disaster Risk Reduction and Climate Change Adaptation?Document11 pagesEditorial: Why Is Community Action Needed For Disaster Risk Reduction and Climate Change Adaptation?diana patricia carvajal riveraNo ratings yet
- How and When An Event Becomes A Disaster?Document32 pagesHow and When An Event Becomes A Disaster?boyoy burnokNo ratings yet
- Role of Civil Enginers in Distaster MitigationDocument10 pagesRole of Civil Enginers in Distaster MitigationMIGUEL ANGELNo ratings yet
- Disaster Planning and PreparednessDocument19 pagesDisaster Planning and PreparednessMaria Pilar ParreñasNo ratings yet
- The - Importance - of - Architecture - Education - For - Disaster MitigationDocument13 pagesThe - Importance - of - Architecture - Education - For - Disaster MitigationMar Kenneth Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Disaster PreparednessDocument3 pagesDisaster PreparednessLandice Myoui0% (1)
- Department of Civil Engineering: Mirpur University of Science and Technology (Must), MirpurDocument31 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering: Mirpur University of Science and Technology (Must), MirpurKhalil SheikhNo ratings yet
- Sns College of Engineering: An Autonomous InstitutionDocument3 pagesSns College of Engineering: An Autonomous InstitutionMohammed Mian ANo ratings yet
- Structural N Non-Structural MitigatinoDocument6 pagesStructural N Non-Structural MitigatinoBiplab PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Community Based Disaster Preparedness-Peripheral LevelDocument50 pagesCommunity Based Disaster Preparedness-Peripheral Levelsmodi_92No ratings yet
- Disaster Management and ReliefDocument5 pagesDisaster Management and ReliefIsmaeel mohamed odigeediNo ratings yet
- How Communities and States Deal With Emergencies and DisastersDocument22 pagesHow Communities and States Deal With Emergencies and DisastersNicole FrancisNo ratings yet
- Planning For Post-Disaster Recovery Briefing PapersDocument8 pagesPlanning For Post-Disaster Recovery Briefing Papersjohn emerson YabutNo ratings yet
- Emergency Architecture: Tutor: Tilo Amhoff Third Year Dissertation Architectural Humanities III by Laura GomesDocument56 pagesEmergency Architecture: Tutor: Tilo Amhoff Third Year Dissertation Architectural Humanities III by Laura Gomesliaa46162No ratings yet
- Colorful Scrapbook Nostalgia Class Syllabus Blank Education PresentationDocument8 pagesColorful Scrapbook Nostalgia Class Syllabus Blank Education PresentationmillardfroggyNo ratings yet
- SpecificationsDocument2 pagesSpecificationsJoji BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Ancient Civilizations and Their DiscoveriesDocument2 pagesAncient Civilizations and Their DiscoveriesJoji BorromeoNo ratings yet
- The Image of The City. ARD ACT01.Document5 pagesThe Image of The City. ARD ACT01.Joji BorromeoNo ratings yet
- BORROMEO - EFFICIENCY Robotics 3 - Assignment 2Document2 pagesBORROMEO - EFFICIENCY Robotics 3 - Assignment 2Joji BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Architectural Drawing SamplesDocument6 pagesArchitectural Drawing SamplesJoji BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Riverine Community A Landscape Development Approach To Enhance The Ecological and Economic Growth of Navotas Waterways Through Sustainable TourismDocument12 pagesRiverine Community A Landscape Development Approach To Enhance The Ecological and Economic Growth of Navotas Waterways Through Sustainable TourismJoji BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Luminaire and LightingDocument61 pagesLuminaire and LightingJoji BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities 3Document11 pagesBuilding Utilities 3Joji BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Pasig River Esplanade ResearchDocument4 pagesPasig River Esplanade ResearchJoji BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Reading Activity-FloodsDocument6 pagesReading Activity-FloodsRenee LeNo ratings yet
- Research Report Hakdog 1Document4 pagesResearch Report Hakdog 1Xyza LeeNo ratings yet
- AnhnguLea-E8-Ôn tập GK2Document27 pagesAnhnguLea-E8-Ôn tập GK2Đình KIên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Ocha DPDHL Report On Public Private PartnershipsDocument151 pagesOcha DPDHL Report On Public Private PartnershipsChitra Carre CCSLNo ratings yet
- nstp101 Lo5Document16 pagesnstp101 Lo5Elena MoralesNo ratings yet
- 3 Basic Concept of HazardDocument43 pages3 Basic Concept of HazardJezrael SaetNo ratings yet
- PNP Adoption Re PNP Disaster ManualDocument2 pagesPNP Adoption Re PNP Disaster ManualErwin V. OrdanNo ratings yet
- MDRRMP 2023-2025Document116 pagesMDRRMP 2023-2025Josephine Templa-JamolodNo ratings yet
- English 1 - Meeting 7 - Structure PrepositionDocument12 pagesEnglish 1 - Meeting 7 - Structure Prepositionm irfan jalilNo ratings yet
- Chuyên đề Word Form: Exercise 1. Give the correct forms of the words in brackets to complete the sentencesDocument4 pagesChuyên đề Word Form: Exercise 1. Give the correct forms of the words in brackets to complete the sentencesVan TranNo ratings yet
- How Was The Distribution of Clothes and Medicines That Poured in For The Tsunami Victims Handled? (4marks)Document12 pagesHow Was The Distribution of Clothes and Medicines That Poured in For The Tsunami Victims Handled? (4marks)Kota VinayNo ratings yet
- Why Are Some Countries More Developed Than Others? What Can Be Done To Reduce The Development GapDocument6 pagesWhy Are Some Countries More Developed Than Others? What Can Be Done To Reduce The Development GapAttiya73% (11)
- Hellen NyakundiDocument146 pagesHellen NyakundiGerome Kevin ArgaoNo ratings yet
- PagesfromResilience OrientedUrbanPlanning 2 - 2 PDFDocument14 pagesPagesfromResilience OrientedUrbanPlanning 2 - 2 PDFHasanain KarbolNo ratings yet
- 20 RRLSDocument14 pages20 RRLSNathalie Jazzi LomahanNo ratings yet
- 2nd Unit DPPMDocument25 pages2nd Unit DPPMJyothi GNo ratings yet
- TEM 9 Lerbinger 2012 The Crisis Manager Chapter 1Document22 pagesTEM 9 Lerbinger 2012 The Crisis Manager Chapter 1valeskaNo ratings yet
- Lets Talk About Natural Disasters Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form - 2600Document1 pageLets Talk About Natural Disasters Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form - 2600Asz MalinaNo ratings yet
- eSRC TemplateDocument81 pageseSRC Templatejc jones corpuzNo ratings yet
- DRRR ST3Document2 pagesDRRR ST3Alvin GultiaNo ratings yet
- Tape Scripts Bai Nghe Tieng Anh 8 Thi DiemDocument24 pagesTape Scripts Bai Nghe Tieng Anh 8 Thi Diembảo trân lê100% (1)
- Đề Tuyển Sinh Lớp 10 Môn Tiếng Anh: Chuyên Đề Đọc Hiểu Đoạn VănDocument17 pagesĐề Tuyển Sinh Lớp 10 Môn Tiếng Anh: Chuyên Đề Đọc Hiểu Đoạn VănJenny ĐoànNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DisastersDocument52 pagesIntroduction To DisastersNmn FaltuNo ratings yet
- DRRR22 Q1 W2Document10 pagesDRRR22 Q1 W2LIZA MAE JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- DRRR Final Exam 2020Document3 pagesDRRR Final Exam 2020Argie Joy Marie AmpolNo ratings yet
- Action PlanDocument47 pagesAction PlanKristel Banag Acordon LptNo ratings yet
- DISASTER READINESS and RISK REDUCTION LESSON 1Document17 pagesDISASTER READINESS and RISK REDUCTION LESSON 1Cher Z 2No ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument1 pageDisaster Managementritika malikNo ratings yet
- Green Productivity PDFDocument341 pagesGreen Productivity PDFSiddharth PalNo ratings yet
- Mental HealthDocument146 pagesMental HealthAnggraeni Beti Dwi LestariNo ratings yet
- The E-Myth Chief Financial Officer: Why Most Small Businesses Run Out of Money and What to Do About ItFrom EverandThe E-Myth Chief Financial Officer: Why Most Small Businesses Run Out of Money and What to Do About ItRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (13)
- Working Backwards: Insights, Stories, and Secrets from Inside AmazonFrom EverandWorking Backwards: Insights, Stories, and Secrets from Inside AmazonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- PMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamFrom EverandPMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisFrom EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- The Goal: A Process of Ongoing Improvement - 30th Aniversary EditionFrom EverandThe Goal: A Process of Ongoing Improvement - 30th Aniversary EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (685)
- Working Backwards: Insights, Stories, and Secrets from Inside AmazonFrom EverandWorking Backwards: Insights, Stories, and Secrets from Inside AmazonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- The Age of Agile: How Smart Companies Are Transforming the Way Work Gets DoneFrom EverandThe Age of Agile: How Smart Companies Are Transforming the Way Work Gets DoneRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Project Planning and SchedulingFrom EverandProject Planning and SchedulingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Revolutionizing Business Operations: How to Build Dynamic Processes for Enduring Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandRevolutionizing Business Operations: How to Build Dynamic Processes for Enduring Competitive AdvantageNo ratings yet
- Design Thinking for Beginners: Innovation as a Factor for Entrepreneurial SuccessFrom EverandDesign Thinking for Beginners: Innovation as a Factor for Entrepreneurial SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness Simplified: Analyzing OEE to find the Improvement OpportunitiesFrom EverandOverall Equipment Effectiveness Simplified: Analyzing OEE to find the Improvement OpportunitiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Influential Product Manager: How to Lead and Launch Successful Technology ProductsFrom EverandThe Influential Product Manager: How to Lead and Launch Successful Technology ProductsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Process!: How Discipline and Consistency Will Set You and Your Business FreeFrom EverandProcess!: How Discipline and Consistency Will Set You and Your Business FreeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- The Supply Chain Revolution: Innovative Sourcing and Logistics for a Fiercely Competitive WorldFrom EverandThe Supply Chain Revolution: Innovative Sourcing and Logistics for a Fiercely Competitive WorldNo ratings yet
- The Influential Product Manager: How to Lead and Launch Successful Technology ProductsFrom EverandThe Influential Product Manager: How to Lead and Launch Successful Technology ProductsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- Strategic KAIZEN™: Using Flow, Synchronization, and Leveling [FSL™] Assessment to Measure and Strengthen Operational PerformanceFrom EverandStrategic KAIZEN™: Using Flow, Synchronization, and Leveling [FSL™] Assessment to Measure and Strengthen Operational PerformanceRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- The Lean Product Playbook (Review and Analysis of Olsen's Book)From EverandThe Lean Product Playbook (Review and Analysis of Olsen's Book)No ratings yet
- Kaizen: The Step-by-Step Guide to Success. Adopt a Winning Mindset and Learn Effective Strategies to Productivity Improvement.From EverandKaizen: The Step-by-Step Guide to Success. Adopt a Winning Mindset and Learn Effective Strategies to Productivity Improvement.No ratings yet
- The Toyota Way, Second Edition: 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerFrom EverandThe Toyota Way, Second Edition: 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (103)
- Toyota Supply Chain Management: A Strategic Approach to the Principles of Toyota's Renowned SystemFrom EverandToyota Supply Chain Management: A Strategic Approach to the Principles of Toyota's Renowned SystemNo ratings yet























































































































![Strategic KAIZEN™: Using Flow, Synchronization, and Leveling [FSL™] Assessment to Measure and Strengthen Operational Performance](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/508787682/149x198/fca988adb2/1714101324?v=1)




