Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New Revised Abstract Citation
New Revised Abstract Citation
Uploaded by
April John ArbutanteOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
New Revised Abstract Citation
New Revised Abstract Citation
Uploaded by
April John ArbutanteCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract
Blended learning addresses educational challenges by combining face-to-face and online instruction, but
obstacles exist in implementation, including issues with students, educators, and systems. Factors like
poor time management, diverse backgrounds, and learning styles can impact participation. This study
aims to investigate the relationship between time management, socio-economic background, and
learning style in blended learning.
In this study, the respondents were students from second year, particularly the BTLED-HE program. There
were a total of 182 students officially enrolled in the BTLED-HE program. The researchers chose this
respondent because these specific respondents are the ones who are immediately impacted and
involved in the implementation of the Blended Learning. Since these respondents experienced 50% of
face-to-face classes and 50% of online class, they were chosen to participate in the study.
Purposive random sampling shall be applied. The researches employed a descriptive-correlational
research design. Instruments underwent validity and reliability tests, and expert evaluation and pilot
testing addressed any potential issues.
Findings indicate that time management had a perceived level of (m= 3.02, s- 0.60), socio-economic
background had a perceived level of (m= 2.96, s= 0.65) and learning styles had a perceived level of (m=
3.06, s= 0.61). These three factors were found to be agreeable. Therefore, this suggested that there was
a significant relationship or correlation between these factors and addressing factors such as time
management, socio-economic background, and learning styles and crucial for optimizing the
effectiveness of blended learning initiatives among second-year students in the BTLED-HE program.
To optimize blended learning for BTLED-HE students, addressing time management, finances, and
learning styles is crucial. The College of Science and Technology of Education should develop long-term
support initiatives, while continuous monitoring and collaboration between parents and educators are
essential. Future research should gather student recommendations through surveys and delve deeper
into student needs through qualitative research.
SOP citation
Ahmad, S. Batool, A., & Choudhry, A.H. (2019). Path relationship of time management and academic
achievement of students in distance learning institutions. Pakistan Journal of Distance and Online
Learning, 5(2), 191-208.
: Mehic, Adrian; Olofsson, Charlotta (2021) : Get Rich or Fail Your ExamTryin': Gender, Socioeconomic
Status and Spillover Effects of Blended Learning, WorkingPaper, No. 2021:8, Lund University, School of
Economics and Management, Department ofEconomics, Lund
Shamshuddin, N, & Kaur, J (2020). Students’ learning style and its effect on blended learning. 2020.
International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education
You might also like
- Research TitleDocument2 pagesResearch TitleDaniela LotinoNo ratings yet
- Perceptions and Factors Influencing StudDocument11 pagesPerceptions and Factors Influencing StudJaela PulmanoNo ratings yet
- Revised AbstractDocument1 pageRevised AbstractApril John ArbutanteNo ratings yet
- PR Chap 1Document19 pagesPR Chap 1ferlousheenNo ratings yet
- 10 1080@0309877X 2020 1781801 PDFDocument18 pages10 1080@0309877X 2020 1781801 PDFRatu Dintha Insyani Zukhruf Firdausi SulaksanaNo ratings yet
- Students Engagement and Academic Performance AmongDocument33 pagesStudents Engagement and Academic Performance AmongJoan CanilloNo ratings yet
- 36-Research Materials-125-1-10-20220315Document27 pages36-Research Materials-125-1-10-20220315Fearl Hazel Languido BerongesNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument11 pagesReview of Related LiteratureZaldy CruzNo ratings yet
- Script ProposalDocument5 pagesScript ProposalNeil Patrick Lajera CruzNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting in Blended Learning On The Academic Performance of Grade34 1Document28 pagesFactors Affecting in Blended Learning On The Academic Performance of Grade34 1Marchee AlolodNo ratings yet
- Adjustment To College and Academic Performance Insights From Filipino College Freshmen in An Allied Health Science CourseDocument43 pagesAdjustment To College and Academic Performance Insights From Filipino College Freshmen in An Allied Health Science CourseMalu ArchividoNo ratings yet
- RRLeyyDocument3 pagesRRLeyyRaffy Superales MarquezNo ratings yet
- Te Eurisa Research ProposalDocument57 pagesTe Eurisa Research ProposalJakz ConsNo ratings yet
- Burnt Orange 1 5 Draft.a4Document54 pagesBurnt Orange 1 5 Draft.a4Angela A. ArquezaNo ratings yet
- Articles 2019 and UpDocument5 pagesArticles 2019 and UpApple Mae Balunan AndujarNo ratings yet
- Learning Strategies, Motivation, and Online Learning Environment Among First Year College Students in A Private Higher Educational Institution: A Correlational StudyDocument7 pagesLearning Strategies, Motivation, and Online Learning Environment Among First Year College Students in A Private Higher Educational Institution: A Correlational StudyPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Final Whole Research Paper 2Document45 pagesFinal Whole Research Paper 2Ahron LapazNo ratings yet
- Final Output AcenasDocument24 pagesFinal Output AcenasacenasapriljeanNo ratings yet
- 97 386 1 PMDocument11 pages97 386 1 PMFemyte KonseptzNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between School Climate, Student EngagementDocument34 pagesThe Relationship Between School Climate, Student EngagementLuthfiana may sarahNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument17 pagesINTRODUCTIONTrixie Pablo AgustinNo ratings yet
- Ic 024Document7 pagesIc 024raphanuslactuca2024No ratings yet
- Donovan Et Al., 2023Document6 pagesDonovan Et Al., 2023Hasibul HossenNo ratings yet
- Tracer Study of Grade 12 Strand Alignment With College CourseDocument27 pagesTracer Study of Grade 12 Strand Alignment With College CourseferlousheenNo ratings yet
- Understanding How Senior High School Students Choose A College Degree PProgram A Phenomenological StudyDocument10 pagesUnderstanding How Senior High School Students Choose A College Degree PProgram A Phenomenological StudyJournal of Interdisciplinary PerspectivesNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument11 pagesChapter IIJonathan AlugNo ratings yet
- This Comprehensive Review Aims To Explore The Existing Body of Literature and Studies Related To The Coping Mechanisms Employed by Students in Response To The Return To FaceDocument11 pagesThis Comprehensive Review Aims To Explore The Existing Body of Literature and Studies Related To The Coping Mechanisms Employed by Students in Response To The Return To Facetroyguimary9No ratings yet
- Final PaperDocument21 pagesFinal PaperXimena AvilezNo ratings yet
- Face To Face and Blended Learning As Strategy in Teaching MathematicsDocument10 pagesFace To Face and Blended Learning As Strategy in Teaching MathematicsAJHSSR JournalNo ratings yet
- Cruz Research ProposalDocument21 pagesCruz Research ProposalNeil Patrick Lajera CruzNo ratings yet
- Attachment Theory and Trauma Part 3Document13 pagesAttachment Theory and Trauma Part 3CamilleNo ratings yet
- Goty 2Document9 pagesGoty 2alonsobarragan97No ratings yet
- Unleashing The Power of Blended Learning - Amplifying Academic Success-2Document5 pagesUnleashing The Power of Blended Learning - Amplifying Academic Success-2mildredbilarma1208No ratings yet
- Environmental Factors That Affect AcademDocument13 pagesEnvironmental Factors That Affect AcademAngel Mae CristobalNo ratings yet
- Leamel C. Osnan, LPTDocument6 pagesLeamel C. Osnan, LPTpontemayorrustom2No ratings yet
- Educational Interface PostprintDocument18 pagesEducational Interface PostprintLetsie SebelemetjaNo ratings yet
- Student Engagement and Student Online Learning Challenges During The PandemicDocument19 pagesStudent Engagement and Student Online Learning Challenges During The PandemicJohn Bricks NakilaNo ratings yet
- Research Final Report (Mukuta)Document18 pagesResearch Final Report (Mukuta)Nelson Kdm NellyNo ratings yet
- Balancing Work and StudyDocument26 pagesBalancing Work and StudyJohanna Grace G OcupeNo ratings yet
- Jv's Chapter 2Document6 pagesJv's Chapter 2Ronan EmpreseNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Study Habits of Senior High School StudentsDocument11 pagesFactors Affecting The Study Habits of Senior High School StudentsKhyla PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper PresentationDocument9 pagesConcept Paper PresentationJhasmia RevillezaNo ratings yet
- The Association Between Teacher Student Relationship and Academic Achievement: The Moderating Effect of Parental InvolvementDocument17 pagesThe Association Between Teacher Student Relationship and Academic Achievement: The Moderating Effect of Parental InvolvementAshu TyagiNo ratings yet
- Student Engagement and Academic Performance in Pandemicdriven Online Teaching An Exploratory and Machine Learning ApproachDocument25 pagesStudent Engagement and Academic Performance in Pandemicdriven Online Teaching An Exploratory and Machine Learning ApproachjinfantezNo ratings yet
- Good University GovernanceDocument10 pagesGood University GovernanceTin2xNo ratings yet
- PR2 Mary Anne JavierDocument21 pagesPR2 Mary Anne JavierAnna Marie Andal RanilloNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id3655154Document8 pagesSSRN Id3655154Charls Luiz S. PalermoNo ratings yet
- Three Abstracts and Its CitationsDocument3 pagesThree Abstracts and Its CitationsPia Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Related Literature - Paraphrased - Activity 2Document8 pagesRelated Literature - Paraphrased - Activity 2JULIE JOY ALDAYNo ratings yet
- Related Literature: NationalDocument7 pagesRelated Literature: Nationaljoshuachan939No ratings yet
- EJ1112855Document5 pagesEJ1112855alibabaNo ratings yet
- Ej 1112855Document5 pagesEj 1112855Kreizel FajaNo ratings yet
- Sample Quantitative StudyDocument43 pagesSample Quantitative StudyJuanito PikitNo ratings yet
- Academic PerformanceDocument6 pagesAcademic PerformanceQuame Enam KunuNo ratings yet
- Foreign Study:: During The Pandemic Period of COVID 19Document7 pagesForeign Study:: During The Pandemic Period of COVID 19Dr.Charlie I. CariñoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 RRLDocument16 pagesChapter 2 RRLMa. Cristina NolloraNo ratings yet
- Study On Academic Performance and Learning StrategDocument12 pagesStudy On Academic Performance and Learning StrategNickole Margareth Dominique ApanNo ratings yet
- Online FLLDocument2 pagesOnline FLLRuba AbuRajabNo ratings yet
- Chap 1-4 FinalDocument94 pagesChap 1-4 FinalDanjever Buen LumbreNo ratings yet
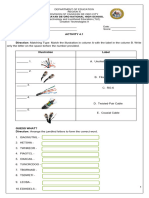
- Electronics ComponentsDocument11 pagesElectronics ComponentsApril John ArbutanteNo ratings yet
- Materials, Tools and Equipment Uses and Specifications in Electronics AssemblyDocument38 pagesMaterials, Tools and Equipment Uses and Specifications in Electronics AssemblyApril John ArbutanteNo ratings yet
- Use of Personal Protective EquipmentDocument18 pagesUse of Personal Protective EquipmentApril John ArbutanteNo ratings yet
- Mounting ComponentsDocument10 pagesMounting ComponentsApril John ArbutanteNo ratings yet
- HAZARD and Risk Assessment Mechanisms in Electronics AssemblyDocument19 pagesHAZARD and Risk Assessment Mechanisms in Electronics AssemblyApril John ArbutanteNo ratings yet
- Splicing and Jointing Electrical WiresDocument35 pagesSplicing and Jointing Electrical WiresApril John ArbutanteNo ratings yet
- Activity 4.1 CopperDocument2 pagesActivity 4.1 CopperApril John ArbutanteNo ratings yet
- Modules 1 6Document116 pagesModules 1 6April John ArbutanteNo ratings yet
- Handicrafts QuestionsDocument8 pagesHandicrafts QuestionsApril John ArbutanteNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5 Lesson2Document4 pagesMODULE 5 Lesson2April John ArbutanteNo ratings yet
- DLLL MathDocument5 pagesDLLL MathMark Cañete PunongbayanNo ratings yet
- Homework For Grown Ups Daily MailDocument7 pagesHomework For Grown Ups Daily Mailafmtcbjca100% (1)
- Hawi Vel Ila Class 4Document210 pagesHawi Vel Ila Class 4Nsso ImphalNo ratings yet
- Bels - Accomplishment ReportDocument9 pagesBels - Accomplishment ReportMaribel G. MontiarNo ratings yet
- English 4 Cause and EffectDocument20 pagesEnglish 4 Cause and EffectLeona Marie DoctorNo ratings yet
- Motion Debate FixDocument2 pagesMotion Debate FixALAN MANTEGANo ratings yet
- (03022023 0533) l3 Efaw Aed Assessment Pack 2023 FillableDocument2 pages(03022023 0533) l3 Efaw Aed Assessment Pack 2023 FillableBhargaviNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, Bhilai (C.G.) : Computer SCDocument2 pagesDelhi Public School, Bhilai (C.G.) : Computer SCPranav VermaNo ratings yet
- You Are Special - ReflectionDocument5 pagesYou Are Special - Reflectionapi-590551556No ratings yet
- 2023 24wusdtk 5thgradecalendarDocument2 pages2023 24wusdtk 5thgradecalendarapi-523268779No ratings yet
- Narrative Report Immersion NathleenDocument5 pagesNarrative Report Immersion NathleenXpertz PrintingNo ratings yet
- Performance Standard, Transfer Goal and Grasps First QuarterDocument5 pagesPerformance Standard, Transfer Goal and Grasps First QuarterRochelle ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Combined Competitive PRELIMINARY ExaminationDocument15 pagesSyllabus For Combined Competitive PRELIMINARY ExaminationRJ RanjitNo ratings yet
- Screeningforadmissionofshortlistedcandidatesat AFMCNEETUG2021Document33 pagesScreeningforadmissionofshortlistedcandidatesat AFMCNEETUG2021robert hookeNo ratings yet
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and The House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDocument3 pagesBe It Enacted by The Senate and The House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledsamNo ratings yet
- DOMAIN 3 (Diversity of Learners)Document1 pageDOMAIN 3 (Diversity of Learners)Patrick MartinezNo ratings yet
- MJ Iz MTQDocument2 pagesMJ Iz MTQMoniruzzaman MahadiNo ratings yet
- Reading A Good Digital CitizenDocument3 pagesReading A Good Digital CitizenFatima Beatriz Vasquez VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Year of Implementation Name of The Capability Enhancement SchemeDocument8 pagesYear of Implementation Name of The Capability Enhancement Schemepwnsingh07No ratings yet
- Modulo de Aprendizaje Ingles 11Document8 pagesModulo de Aprendizaje Ingles 11Avelino SandovalNo ratings yet
- SBKGDocument2 pagesSBKGRaja KumarNo ratings yet
- Donbosco Application Form 2022Document2 pagesDonbosco Application Form 2022Mike DinhoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Bi Dan PK Week 7 Dan 8Document13 pagesLesson Plan Bi Dan PK Week 7 Dan 8Sugunes SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Proposal RNDDocument50 pagesProposal RNDAdib RizalNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Unit 1: My New School Lesson 2: A Closer Look 1Document5 pagesLesson Plan: Unit 1: My New School Lesson 2: A Closer Look 1Quoc Anh PhamNo ratings yet
- Module 1 English Year 2Document15 pagesModule 1 English Year 2SANGEETHA A/P MAHDEVAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Font To Use For DissertationDocument7 pagesFont To Use For DissertationOrderAPaperBillings100% (1)
- Study Skills Middle SchoolDocument24 pagesStudy Skills Middle SchoolRiya LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Decision MakingDocument12 pagesUnit 3 - Decision MakingNicol VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report July 2022Document7 pagesAccomplishment Report July 2022Jennelyn Sulit50% (2)