Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Interview Questions Segregated
Uploaded by
nhempire1717Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Interview Questions Segregated
Uploaded by
nhempire1717Copyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Interview Questions
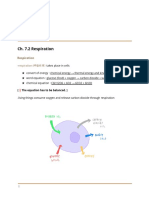
1. What is responsible for ozone layer depletion?
Answer - 1- Ozone layer is a region of earth’s stratosphere that absorbs most of the sun’s ultraviolet radiation.
2- The ozone layer is mainly found in the lower portion of the stratosphere.
3 -Absorbs 97-99% of sun’s UV rays.
4 -Ozone layer is also called ozonosphere
5 -Ozone layer acts as a filter for harmful UV rays from sun.
Depletion of Ozone layer causes skin cancer.
Depletion of Ozone layer is caused by use of (CFC’s)
CFC means Chlorofluoro carbons
CFCs are formed in aerosol spray case and refrigerants.
From 2020, ships will be using HFC’s (Hydro fluoro carbons)
Tip: A very common question, read thoroughly about it and don’t confuse with Global warming.
2. Explain Charles’s Law ,Boyle’s Law , Avogadro’s Law, Ideal Gas law , Pascal’s law and their applications ?
Answer –
Boyle’s Law- At constant Temperature, pressure is inversely proportional to volume. Example using a
syringe, sucking out blood from our veins.
Charles’s law – At constant Pressure , Volume is directly proportional to Temperature . Example boiling of
water in an open container.
Pascal’s law – In a confined space filled with incompressible fluid, when pressure is transmitted through the
fluid, then the same pressure acts everywhere. Example Hydraulic lifts or Hydraulic jacks for lifting a car or a
truck.
Gay Lussac’s law – At constant Volume, Pressure is directly proportional to temperature. Example boiling of
water in pressure cooker, where volume is constant so with increase in pressure inside the pressure cooker the
boiling point of water increases.
Ideal Gas Law – An ideal gas is defined as one in which all the collisions between atoms or molecules are
perfectly elastic and in which there are no intermolecular forces. PV =n RT
3. What is isomerism?
Answer - Isomerism is the existence of molecules that have the same numbers of the same kinds of atoms and
hence same formula but differ in chemical and physical properties.
Tip: Know some examples of Isomerism as well.
4. What is evaporation, boiling, sublimation, condensation and distillation?
Answer –
(1) Evaporation-Process in which liquid converts into vapour state.
(2) Boiling – Process in which liquid converts into vapour state when heated to a certain temperature called
Boiling point.
Difference between Evaporation and Boiling?
Evaporation is a slow process where as Boiling is a fast process. Evaporation takes place only at the surface
where as Boiling takes place throughout the volume of liquid. Evaporation takes place at all temperatures
where as Boiling takes place only at Boiling point.
(3) Condensation – Process in which vapours changes into liquid state. The gas has to be cooled, like if you
cool steam, it converts back into water,
Dew point – The temperature at which water vapour present in air starts getting condensed.
(4) Distillation – Method of purification or separation of impurity from a liquid.
Distillation is a process of Evaporation followed by Condensation. A process to make drinking water by sea
Water.
Fractional Distillation: Separating a mixture of liquids with separate boiling points. This is how we get
Aviation oil, diesel oil, petrol etc from crude oil extracted from Earth.
5) Sublimation – Transition from solid state to gaseous state (no involvement of liquid state)
Ex- Naphthalene balls, camphor balls
5. What is endothermic and exothermic reaction?
Answer –
Exothermic Endothermic
1- An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction An endothermic process is any process which
that releases energy through light or heat. requires or absorb energy from its surrounding.
2- It can be for physical OR chemical change.
- Ex Chemical change It can be for physical OR chemical changes.
Reactant gives Product + Energy - EX Chemical changes
Eg Acid + Alkali form Reactant + Energy gives product
Water + Salt Eg Electrolysis
Respiration Photosynthesis
Physical changes Physical changes
Water – ice – gas gas – ice – water
Energy release absorb Energy
(-
6. What are isotopes?
Answer - Elements with same atomic no. but different mass number.
Mass no = no of Protons + no of neutrons
Example 1 C- 12, C-13, C- 14
Example 2 U– 234, U- 235, U – 238
7. How do you make a saturated and a super saturated solution?
Answer –
A saturated solution is one containing as much solute as possible without forming a precipitate
There are 3 ways to make saturated solution
1- Add solute to a liquid until no more will dissolve
2- We can also make a saturated solution by evaporation of the solvent from an unsaturated solution.
ii) An unsaturated solution is a chemical solution in which the solute concentration is lower than its
equilibrium stability that means more solute can be added without forming precipitate.
For example:
Take a glass of water and add sugar to it, here sugar is solute and water is solvent.
Initially it is an unsaturated solution because we can easily add sugar to it in fully dissolved condition. Now
one stage comes that no more sugar can be easily dissolved. This condition is called saturated solution. Now if
you increase the temperature of water, you can easily add more sugar to it – this is called super saturated
solution.
Example of super saturated solution – Gulab jamun syrup.
8. Why evaporation gives cooling effect?
Answer - Evaporation causes cooling because the process requires heat energy. The energy is taken away by
the molecules when they convert from liquid into gas, thus breaking the liquid bonds and causes cooling.
9. What are isomers?
Answer - Isomers are the chemical compounds that have chemical formula but different chemical structure
resulting in different chemical properties.
Tip: Know a few examples.
10. What are alkanes, alkenes and alkynes?
Answer - They are simple hydrocarbon compounds with no functional group.
Alkane: Carbon-Carbon single bond.
Alkene: Carbon-Carbon double bond.
Alkene: Carbon-Carbon triple bond.
Tip: A few examples are always good to know by name like methane, ethane etc.
11. What will you prefer, to pour acid into water or water into acid?
Answer - I will prefer to pour acid into water instead of water into acid because if water is poured into acid its
a massive exothermic reaction that may splash acid out of container, therefore always add acid into water
slowly and steadily to cover up the heat produced in the process.
12. How can we produce or liberate Hydrogen gas?
Answer - We can liberate hydrogen gas by reacting an acid with an active metal, for example reaction of
hydrochloric acid with zinc produces zinc chloride and hydrogen gas. Hydrogen gas can be detected by
burning splint test.
13. How will you recognize H2S gas?
Answer - Hydrogen sulphide has a characteristic foul odour of rotten eggs.
14. Chemical used for Artificial Rain?
Answer - The most common chemicals used for cloud seeding i.e. making artificial rain include silver iodide,
potassium iodide and dry ice (solid carbon dioxide).
15. Bone contains what elements?
Answer - Major elements in bone are Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium and Sulphur and trace elements are
Iron, Zinc, Manganese and Cadmium.
16. Cigarette lighter contain which gas?
Answer - Cigarette lighter contain flammable gas such as propane or butane.
17. What causes Acid Rain?
Answer - Acid rain results when Sulphur dioxide and Nitrogen dioxide are emitted into atmosphere which
then react with water, oxygen and other chemicals to form sulphuric and nitric acids.
18. Which is most malleable metal?
Answer - Gold is the most malleable of all metals.
19. Difference between Electrovalent Bond and Covalent Bond?
Answer - In Electrovalent bond there is complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another atom.
Electrovalent compounds are more soluble in polar solvents like water.
In Covalent bond there is mutual sharing of electrons between the atoms. Covalent compounds are more
Soluble in non-polar solvents like benzene.
20. Difference between atom & molecule?
Answer - Atoms are single neutral particles. Molecules are neutral particles made of two or more atoms
bonded together.
21. Which gas is soluble in water at room temperature? NH4, Cl, O2, CO2
Answer - Carbon dioxide is readily soluble in water at room temperature. Co2 is soluble because water
molecules are attracted to Co2 because of its polar nature. Carbonated drinks are one such example.
22. Which has highest density? Water, C6H6, CCl4
Answer - CCl4(1.5g/ml) has highest density then H20(1.0g/ml) and least dense is C6H6(0.874g/ml).
23. Maximum percentage of which gas is present in air? N2, O2, CO2
Answer - The air in Earth's atmosphere is made up of approximately 78 percent Nitrogen,21 percent Oxygen
and 0.04 percent Carbon dioxide.
24. Lemon contains which acid?
Answer - Lemon contains citic acid.
25. Why do aromatic compounds give sooty flame?
Answer - Aromatic compound burn with sooty flame because they have ring structure of carbon atom. This
causes incomplete combustion of the carbon chain. Thus they give sooty flame.
26. CNG LPG
27. Oxidation
28. What is metallurgy
29. What is ore of iron & aluminium
30. Ideal Gas equation
You might also like
- Surface ChemistryDocument17 pagesSurface ChemistryFourte GuNo ratings yet
- 电化学专业英语Document115 pages电化学专业英语Bruce LiNo ratings yet
- All About Exothermic ReactionDocument11 pagesAll About Exothermic ReactionAkshay IndoraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 - Reactivity Topic: Lesson 1 Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument19 pagesChemistry 2 - Reactivity Topic: Lesson 1 Physical and Chemical ChangesAmr ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument10 pagesChemistry NotesRaya DhanushNo ratings yet
- 8.1 & 8.2 - Notes - 14022023 - 120722Document3 pages8.1 & 8.2 - Notes - 14022023 - 120722Prince DanielNo ratings yet
- Final Research (Hady)Document6 pagesFinal Research (Hady)Hady SalehNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Chemistry Important Solved Short Notes For Exam 2013Document34 pages9th Class Chemistry Important Solved Short Notes For Exam 2013HAFIAZ MUHAMMAD IMTIAZ100% (4)
- Unit - 5 Surface ChemistryDocument14 pagesUnit - 5 Surface ChemistryLatha RajuNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry DefinitionsDocument5 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Definitionsjenifer100% (1)
- Chapter 9Document6 pagesChapter 9rickyNo ratings yet
- Unit One 2 Language of Chemistry First ClassDocument18 pagesUnit One 2 Language of Chemistry First ClassLoveless BhartalNo ratings yet
- Chem RxnsDocument7 pagesChem Rxnsanoj kumarNo ratings yet
- X Ch.1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Key ConsentsDocument13 pagesX Ch.1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Key ConsentsheroNo ratings yet
- Chemical Changes WorkbookDocument11 pagesChemical Changes WorkbookKaitlyn DuarteNo ratings yet
- Questions - Answers Bank Class - Xii Subject - Chemistry UNIT-5 (Surface Chemistry)Document6 pagesQuestions - Answers Bank Class - Xii Subject - Chemistry UNIT-5 (Surface Chemistry)Abhay BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Complete NotesDocument13 pagesChemistry Complete NotesMuazamAliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 To 4 IcDocument66 pagesLesson 1 To 4 IcscientistgenerosoNo ratings yet
- Gix - Question BankDocument8 pagesGix - Question BankDeva GuruNo ratings yet
- Sci. 411 Chemical Reactions Edleen AquinoDocument26 pagesSci. 411 Chemical Reactions Edleen Aquinojoebane capapas jr.No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2Document2 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2jcjimz259No ratings yet
- UTS EnglishDocument10 pagesUTS EnglishNindys AprilliaNo ratings yet
- Class: IX Topic: Matter in Our Surrounding Subject: Chemistry Date - 28/04/2021Document3 pagesClass: IX Topic: Matter in Our Surrounding Subject: Chemistry Date - 28/04/2021SD art collectionNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reactions - NotesDocument6 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions - NotesYOGESHNo ratings yet
- Chem. - F8term 2 Chem 2019Document40 pagesChem. - F8term 2 Chem 2019Lobna ShabanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module For Remidial ClassDocument52 pagesChemistry Module For Remidial ClassMuktaar HassenNo ratings yet
- C 5 - Notes - Surface ChemistryDocument14 pagesC 5 - Notes - Surface ChemistryAtharva BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument7 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Question Answer Chapter 1 Class 9thDocument10 pagesQuestion Answer Chapter 1 Class 9thSania TyagiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry The Study of MatterDocument25 pagesChemistry The Study of MatterAnand Philip PrasadNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument30 pagesChemical ReactionsAdeeba FatimaNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument6 pagesScience NotesKhushal BachwaniNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Book 2015Document188 pagesYear 10 Book 2015api-317749980No ratings yet
- REVISION FINAL - MATTER IN OUR SURROUNDINGS - DoneDocument14 pagesREVISION FINAL - MATTER IN OUR SURROUNDINGS - DoneRaghvendra ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction 4fb79727Document47 pagesChemical Reaction 4fb79727Tabish RahimNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations2Document28 pagesChemical Equations2Saleem BashaNo ratings yet
- "Chemical Reactions": Chemistry Experiment ReportDocument26 pages"Chemical Reactions": Chemistry Experiment ReportLivia AsriNo ratings yet
- Ma. Eloisa R. Jurilla: Humss X1 - ADocument44 pagesMa. Eloisa R. Jurilla: Humss X1 - AcatrinaNo ratings yet
- C9e Answers Active Reading 03Document6 pagesC9e Answers Active Reading 03Jaden Ventura0% (1)
- Class10 Science Notes Chapter1 PDFDocument6 pagesClass10 Science Notes Chapter1 PDFdineshhissarNo ratings yet
- ST - Xaviers Cathedral School, Amravati: ROLL No - 32 Subject-Science Topic - Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument16 pagesST - Xaviers Cathedral School, Amravati: ROLL No - 32 Subject-Science Topic - Matter in Our SurroundingsParth SonkhaskarNo ratings yet
- What Is ChemistryDocument10 pagesWhat Is ChemistryAjitabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 - Chapters (1,2,3,4)Document10 pagesUnit-4 - Chapters (1,2,3,4)Farah AounNo ratings yet
- English 2Document49 pagesEnglish 2mujieNo ratings yet
- Abhishek GuptaDocument5 pagesAbhishek GuptaAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemical Reactions NotesDocument12 pagesClass 10 Chemical Reactions NotesShreyash VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ImpDocument11 pagesChemistry ImpSadhana PradhanNo ratings yet
- Group InvestigationDocument4 pagesGroup InvestigationNohelia GradizNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions BookletDocument21 pagesChemical Reactions BookletSu AlghNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry: Physical Adsorption Chemical AdsorptionDocument6 pagesSurface Chemistry: Physical Adsorption Chemical Adsorptioniipud072.giridhar.k MESKKPUCNo ratings yet
- Sciene - Chemistry Ans 10.: Tyndall EffectDocument8 pagesSciene - Chemistry Ans 10.: Tyndall EffectSmriti AnguranaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 Matter and Its ClassificationDocument9 pagesLESSON 1 Matter and Its ClassificationscientistgenerosoNo ratings yet
- Speed, Distance, TimeDocument3 pagesSpeed, Distance, Timesheela baralNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 (Eng. Vers.)Document11 pagesExperiment 5 (Eng. Vers.)Akwila Eka MelianiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations - Docx NotesDocument9 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations - Docx NotesRodel AzaresNo ratings yet
- Cy1104 - Engineering Chemistry Unit - 2 Surface Chemistry and Catalysis Lecture PlanDocument28 pagesCy1104 - Engineering Chemistry Unit - 2 Surface Chemistry and Catalysis Lecture PlanBeuna.No ratings yet
- Biology Ch. 7Document9 pagesBiology Ch. 7sumsumNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheet Answers - Yr10 The Chemical WorldDocument8 pagesSummary Sheet Answers - Yr10 The Chemical WorldStudy RecoilzNo ratings yet
- Combining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandCombining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Reactions : 6th Grade Chemistry Book | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandPhysical and Chemical Reactions : 6th Grade Chemistry Book | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- November 2007 Paper 4 Mark SchemeDocument9 pagesNovember 2007 Paper 4 Mark SchemenehemiahedwardsNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument33 pagesAir PollutionKapil BudasanaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Copy of Topic 3.1 Chemistry of The AtmosphereDocument70 pages2nd Copy of Topic 3.1 Chemistry of The AtmosphereEvan John MontejoNo ratings yet
- Carbon Black User's GuideDocument36 pagesCarbon Black User's Guidealexusmatrix100% (1)
- Threats and Human Impact On The Marine EnvironmentDocument46 pagesThreats and Human Impact On The Marine EnvironmentGizelRiveraSantiagoNo ratings yet
- Msds Dietilamina PDFDocument6 pagesMsds Dietilamina PDFabi9f100% (1)
- Analysis of Carbon Sequestration by Dominant TreesDocument11 pagesAnalysis of Carbon Sequestration by Dominant TreesFarjad KhanNo ratings yet
- 2016 O Level Biology Specimen Paper 3Document12 pages2016 O Level Biology Specimen Paper 3Lola BeeNo ratings yet
- EO User GuidanceDocument96 pagesEO User GuidancesurawutwijarnNo ratings yet
- Catalytic: Cracking Acetic Acid To AceticDocument6 pagesCatalytic: Cracking Acetic Acid To AceticPawan NagarNo ratings yet
- Thermochemical Ethanol Via Direct Gasification and Mixed Alcohol Synthesis of Lignocellulosic BiomassDocument144 pagesThermochemical Ethanol Via Direct Gasification and Mixed Alcohol Synthesis of Lignocellulosic BiomassCristina Garcia RamosNo ratings yet
- Singa Gas Development Project: 4 of 12 Process Loadsheet For Flare Package (42-KZZ-791)Document9 pagesSinga Gas Development Project: 4 of 12 Process Loadsheet For Flare Package (42-KZZ-791)false mailNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration in YeastDocument11 pagesCellular Respiration in YeastxshelyNo ratings yet
- John A. - Factors Influencing Rate of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesJohn A. - Factors Influencing Rate of PhotosynthesisjuanNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Cause and Effect Worksheet Templates Layouts - 120120Document2 pagesClimate Change Cause and Effect Worksheet Templates Layouts - 120120Omayra MontealegreNo ratings yet
- Chem ch23Document9 pagesChem ch23ChandlerNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Introduction To Water and Water PollutionDocument19 pagesUNIT 1 Introduction To Water and Water PollutionRG SegaranNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide Capture Handbook 2015Document116 pagesCarbon Dioxide Capture Handbook 2015Florencia Capurro100% (2)
- Photosynthesis Lab Gizmo™, You Can Monitor The Rate of Photosynthesis by Measuring OxygenDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis Lab Gizmo™, You Can Monitor The Rate of Photosynthesis by Measuring OxygenSabrinaNo ratings yet
- Endogenetic and Exogenetic ForcesDocument40 pagesEndogenetic and Exogenetic ForcesKhushiNo ratings yet
- ProposalDocument19 pagesProposalJustel Paul MiadoNo ratings yet
- Walker Energy Plants and ManDocument274 pagesWalker Energy Plants and ManCristhian100% (2)
- Unicool R-404A: Catalogue Number: 905623 Version No: 4.4Document14 pagesUnicool R-404A: Catalogue Number: 905623 Version No: 4.4asdfasdfNo ratings yet
- 6.25 Transient Analysis Start Up (Pipeline) PDFDocument71 pages6.25 Transient Analysis Start Up (Pipeline) PDFMuhammad Ibad AlamNo ratings yet
- Vidya StoichiometryDocument34 pagesVidya StoichiometryNarendraNo ratings yet
- Material Balance 1725 MTPDDocument11 pagesMaterial Balance 1725 MTPDসাইদুর রহমানNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal - Australian National University FRT FellowshipDocument2 pagesResearch Proposal - Australian National University FRT FellowshipLokesh SangabattulaNo ratings yet
- Battery Management System (BMS) Simulation Environment For Electric VehiclesDocument6 pagesBattery Management System (BMS) Simulation Environment For Electric VehiclesNavanath MahadikNo ratings yet
- Animals and Climate ChangeDocument5 pagesAnimals and Climate ChangeAyesha IshaqNo ratings yet
- MSENSE® DGA 9 Technical Data 03 2021 enDocument4 pagesMSENSE® DGA 9 Technical Data 03 2021 enTa Huy CuongNo ratings yet