Professional Documents
Culture Documents
014 - CAT-6060-AC - 60Hz - E-Drive - CAMP + SIL + BCS4 - Legend of H-Schematic - No New Available
Uploaded by
Miguel Angel RodriguezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
014 - CAT-6060-AC - 60Hz - E-Drive - CAMP + SIL + BCS4 - Legend of H-Schematic - No New Available
Uploaded by
Miguel Angel RodriguezCopyright:
Available Formats
8.
3 DESCRIPTION OF THE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM - FS
8.3 Description of the hydraulic system
8.3.1 Technical data
The technical data of the hydraulic system are listed in chapter 2 ‘Technical Data’.
8.3.2 Circuit diagram
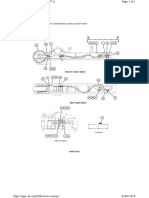
Components of the hydraulic circuit diagram RH 340 electric drive (FS) / 6060 AC FS
The position nos. refer to circuit diagram No. 3 719 200 (00)
Position Quantity Designation Location
1 1 Electric motor Engine module
2 1 Pump gearbox Engine module
3 4 Main pump A7V - SL - 1000 Pump gearbox
4 3 Swing pump A4VG 250 Pump gearbox
5 ----
6 Servo Pump (double pump) Pump gearbox
7–9 ----
10 4 Cooling pump KP 5 - 300/250 Pump gearbox
11 - 18 ----
19 Central greasing system Superstructure
20 – 22 ----
23 1 Proportional valve Engine module
24 ----
25 1 Proportional valve plate Operator modul
26 2 Solenoid valve bank Operator modul
27 ----
28 1 Distributor block Engine module
29 1 Distributor block (main pumps) Engine module
30 4 Pressure relief valve Engine module
31 ----
32 4 High pressure filter Engine module
33 ----
34 3 Filter Engine module
35 1 Emergency lowering valve Operator modul
36 1 Filter Operator modul
37 3 Check valve Operator modul
38 4 Diaphragm accumulator Engine module
3721440en - (00) - 11.09 Page 8.3 - 1
8.3 DESCRIPTION OF THE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM - FS
Position Quantity Designation Location
39 1 Check valve Engine module
40 ----
41 1 Pressure relief valve Engine module
42 1 Pressure relief valve Engine module
43 1 Check valve Engine module
44 ----
45 2 Proportional pressure reducing valve (Thermostat) Engine module
46 – 59 ----
60 1 Hydraulic oil tank Superstructure
61 2 Gate valve Hydraulic oil tank
62 2 Return oil filters Hydraulic oil tank
63 6 Bypass valve Hydraulic oil tank
64 4 Tank line pressurizing valve Hydraulic oil tank
65-74 ----
75 1 Gearbox oil cooler Engine modul
76 1 Thermostat valve Engine modul
77 1 Filter Oil cooler module
78 1 Distributor Oil cooler module
79 ----
80 2 Hydraulic Oil cooler Oil cooler module
81 4 Fan motor Oil cooler module
82 - 83 ----
84 4 Fan Oil cooler module
85 2 Distributor plate (oil cooling) Oil cooler module
86-88 ----
89 4 Pressure relief valve Oil cooler module
90 1 Travel block Superstructure
91 1 Rotor Superstructure
92 1 Travel valve block RH Rotor
93 1 Travel valve block LH Rotor
94 ----
95 1 Travel retarder valve RH Travel block
96 1 Travel retarder valve LH Travel block
97 4 Anti – cavitation valve Travel block
98 - 99 ----
100 4 Swing gearbox Superstructure
Page 8.3 - 2 3721440en - (00) - 11.09
8.3 DESCRIPTION OF THE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM - FS
Position Quantity Designation Location
101 ----
102 4 Swing motor Swing gearbox
103 - 104 ----
105 1 Pressure regulating valve (swing balance valve) Engine module
106 1 Flushing valve (swing) Engine module
107 ----
108 ----
109 1 Pressure relief valve (swing) Engine module
110 2 Safety solenoid valve (swing) Engine module
111 - 119 ----
120 2 Travel gearbox Undercarriage
121 4 Travel motor Travel gearbox
122 - 124 ----
125 1 Secondary relief valve block Undercarriage
126 4 Pressure relief valve in pos. 125
127 - 129 ----
130 2 Track tensioning cylinder Undercarriage
131 2 Diaphragm accumulator Undercarriage
132 ----
133 1 Track tensioning block Undercarriage
134 2 Track tensioning relief valve Undercarriage
135 - 144 ----
145 1 Cylinder (service lift) Superstructure
146 1 Valve Superstructure
147 1 Check valve Superstructure
148 - 149 ----
150 1 Cylinder (ladder) Superstructure
151 1 Control valve Superstructure
152 1 Bladder accumulator Superstructure
153 - 160 ----
161 2 4-spool control valve Boom
162 - 163 ----
164 4 Float valve Boom
165 - 166 ----
167 2 Check valve Superstructure
168 - 181 ----
3721440en - (00) - 11.09 Page 8.3 - 3
8.3 DESCRIPTION OF THE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM - FS
Position Quantity Designation Location
182 2 Boom cylinder Boom
183 2 Arm cylinder Boom
184 2 Crowd cylinder Boom
185 ----
186 2 Clamshell cylinder Backwall
187 1 Distributor Backwall
188 ----
189 2 Block Attachment
Page 8.3 - 4 3721440en - (00) - 11.09
8.3 DESCRIPTION OF THE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM - FS
8.3.3 Components of the hydraulic Swing pump Pos. 4
system
The 4 swing pumps to move the superstructure are
Attention variable - displacement axial - piston swashplate
pumps. They are especially suited for operation in
The following item numbers refer to hydraulic closed circuits. The pump flow is infinitely variable
circuit diagram Part-No. and increases from „0“ to „max“ while the pump
rotary group is being tilted out. If the swashplate is
3 719 200 (00) de-stroked through the „zero“ position, the direc-
tion of the oil flow is altered smoothly.
Some items are numbered in the diagram but The pumps are fitted with a torque control that is
not mentioned here since they have less sig- controlled by the pressure regulating valve (105).
nificance for the hydraulic functioning se- Depending upon the pre - selected control pres-
quence. sure, the valve allows infinite governing of
- operating pressure and
- torque magnitude and direction
Drive unit Pos. 1
on the swing motors (102).
One Electric motor (squirrel cage type). Each swing pump has two pressure relief/anti -
cavitation valves.
The functions of these valves are:
Pump gearbox Pos. 2
1) To protect the swing circuit from overpressure
(max. 400 bar)
The pump transfer gearbox is driven via an elastic
coupling by the electric motor and distributes the
2) To ensure that the closed loop of oil in the
motor's output to the relevant hydraulic pumps.
swing circuit remains full.
A gear - type pump is also mounted on each swing
pump, and serves as a charge pump for the closed
Main pump Pos. 3 circuit. The charge pressure of the pumps is limited
by pressure relief valves integrated into the pumps.
The pump batteries each comprises a variable -
displacement pump, a 2-stage pressure sequence The pumps also have chip/contamination and tem-
valve and a shut-off valve. perature switches which send warning signals to
The 4 main pumps for attachment and travel are the BCS system if metal chips or excessive oil
axial-piston variable displacement pumps in bent- temperatures are detected.
axis design with slipper bearing.
The shut-off valves can be used to switch off the
pressure cut - off function for the main pumps.
free Pos. 5
Each pump has its own pressure - dependent reg-
ulator with a regulating range between 7,5 and
42,5 bar. At 42,5 bar, the pump`s rotary group is at Servo pump Pos. 6
its maximum and therefore at maximum flow. At
7,5 bar, the rotary group is at „zero“ oil flow. The The servo pump is a tandem gear pump which is
regulators are actuated by the proportional valve mounted to one of the swing pumps (4) and sup-
(23) via the electronic load - limit governor in the plies the whole servo circuit with oil.
PMS system.
free Pos. 7 – 9
3721440en - (00) - 11.09 Page 8.3 - 5
8.3 DESCRIPTION OF THE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM - FS
Oil cooling pump Pos. 10 Travel parking brakes
Pressure boost for travel
Four gear pumps constantly draw oil from the tank
and pump it to the fan motors and the oil coolers. Track motor adjustment ( 2 speed travel)
Two pumps are mounted directly on the gearbox,
the other two pumps are mounted onto the swing
Pressure boost for clam cylinder (P 1)
pumps (4).
Superstructure parking brakes
free Pos. 11 – 18
free Pos. 27
Greasing system Pos. 19
Distributor block Pos. 28
Hydraulic oil of the pilot pressure system is used to
operate the grease pump and the control valve of
The distributor block is supplying the connected
the central greasing system.
components with 50 bar pilot pressure.
free Pos. 20 – 22
Distributor block (main pumps) Pos. 29
Proportional valve Pos. 23 An assembly group comprising
These valve controls the main pumps (3). They are 4 primary pressure relief valves (30)
controlled by the microprocessor in the PMS sys- 4 high - pressure filters (39)
tem and govern the flows from the main pumps 1 Housing
depending upon the actual pressure. The valve is
actuated by an adjustable, oil - immersed DC sole-
noid and transforms electrical current proportional- Pressure relief valve Pos. 30
ly into hydraulic pressure.
A solenoid current of 830 mA corresponds to a
pressure of 42 bar in the pump governors. A cur- The relief valves are used as primary pressure
rent of 230 mA corresponds to 10 bar. relief valves for the main pumps. They limit the
maximum pressure that can be reached by the
pumps (3) and therefore protect the system
against overload.
free Pos. 24
The valves are pilot controlled and have variable
Servo control block Pos. 25 settings.
The servo control block contains the pressure re- free Pos. 31
lief valves for the servo- and auxiliary circuits and
the proportional valves to control the servo valves
of the control blocks. High - pressure filter Pos. 31
The high - pressure filters in the high - pressure
Solenoid valve bank Pos. 26
lines from the main pumps protect the downline
units (e. g. control blocks and cylinders) against
2 assembly groups are comprisiesng four solenoid metal chips and particles from the pumps (3). Oth-
valves and a housing each. er than in the return flow filters (62), the oil flows
through the HP filters from outside to in.
The 4/2 - way valves control the functions:
Page 8.3 - 6 3721440en - (00) - 11.09
8.3 DESCRIPTION OF THE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM - FS
free Pos. 33 pumps (6) and therefore protect the system
against overload.
Check (Non-return) valve Pos. 43
Filter Pos. 34
The 3 filters are filtering the oil from the 3 swing
circuit charge pumps. free Pos. 44
Proportional solenoid valve Pos. 45
Emergency lowering valve Pos. 35
The proportional valves (thermostats) are regulat-
The valve block consists of a solenoid valve, a ing the control spools in the distributor plate (85)
non-return valve and an accumulator. depending on the hydraulic oil temperature.
Lowering of the attachment is possible with the
drive unit at a standstill, when operating the joy-
stick while the solenoid valve is activated. free Pos. 46 – 59
The solenoid valve will be activated by using a
press-button switch located in the control column
in the driver’s cab. Hydraulic oil tank Pos. 60
The tank stores all of the oil for the system and
contains two return flow filters (62), six by - pass
Filter (Servo control block) Pos. 36 valves (63), four tank line pressurizing valves (64),
2 shut-off gate valves (Pos. 61) and 2 tank breath-
Through this filter the servo control block (25) will er filters .
be supplied with servo oil.
Gate valve in intake line Pos. 61
Check (Non-return) valve Pos. 37 The shut - off cocks can be used to isolate the
hydraulic pumps from the oil tank. This makes it
possible to remove pumps without having to drain
all of the oil from the tank.
Diaphragm accumulator Pos. 38
Return flow filter Pos. 62
Check (Non-return) valve Pos. 39 Each return flow filter contains 7 filter elements to
clean the oil returning from inside to out. Any metal
chips are trapped by the magnetic rods installed
above the filters.
free Pos. 40
By - pass valve Pos. 63
Pressure relief valve Pos. 41 + 42
The six by - pass valves open at a pressure of 1.5
bar and prevent the return flow filters (62) bursting,
The relief valves are used as primary pressure e. g. due to clogging. Oil then flows unfiltered back
relief valves for the servo pumps. They limit the into the tank.
maximum pressure that can be reached by the
3721440en - (00) - 11.09 Page 8.3 - 7
8.3 DESCRIPTION OF THE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM - FS
Tank line pressurizing valve Pos. 64 Fan motor Pos. 81
These four valves have fixed settings of approx. 10 The fixed-displacement geared motors are driven
bar. They are arranged in the return lines and keep by the oil cooling pump (10) and drive the fan
a constant level of pressure in the hydraulic sys- wheel of the hydraulic oil cooler.
tem.
free Pos. 65 - 74
free Pos. 82 - 83
Fan Pos. 84
Gear box oil cooler Pos. 75
The fan produces the air flow to cool down the
A gear pump is pumping the gear oil through filter hydraulic oil.
(77) and via thermostat valve (76) to the gear oil
cooler (75) and back into the pump gearbox (2).
Distributor plate for oil cooling Pos. 85
Thermostat valve Pos. 76
Each of the two plates contains two pressure relief
The thermostat-valve (76) with an opening tem- valves (89) and two check valves. The check
perature of 55° C protects the oil cooler (75) valves function as anti - cavitation valves while the
against pressure peaks especially when the elec- drive units are being shut down.
tric motor is started under cold weather conditions.
free Pos. 86 - 88
Filter (Gear oil cooling) Pos. 77
Through this filter the gear oil cooling system will
be supplied with gear oil. Pressure relief valve Pos. 89
Distributor Pos. 78 Each fan motor (81) is protected by a pressure
relief valve with a setting of 65 bar.
This distributor contains the temperature sensor of
the gear oil cooling system.
Travel block Pos. 90
free Pos. 79
A complete group comprising rotor (91), the „Trav-
el“ spools (92 & 93), the travel retarder valves (95
& 96) and anti - cavitation valves (97).
Hydraulic oil cooler Pos. 80
Rotor Pos. 91
The hydraulic oil coolers transferring the heat,
generated in the hydraulic system, from the hy- The rotor is the hydraulic connection between su-
draulic oil to the atmosphere. perstructure and undercarriage. The rotor has 7
Cooling is achieved through the air stream pro- channels for the following functions:
duced by the fan wheel.
4 x travelling (4 channels)
1 x travel motor control
Page 8.3 - 8 3721440en - (00) - 11.09
8.3 DESCRIPTION OF THE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM - FS
1 x hydraulic track tensioning The spring applied multi disc brakes on the swing
gearboxes serve to hold the superstructure sta-
1 x leakage-oil return
tionary (parking brakes). They are actuated by a
toggle switch in the cab.
The brake must only be actuated when the super-
Travel valve block RH Pos. 92 structure has stopped swinging.
A servo - controlled single - spool block that actu-
ates the right - hand track. free Pos. 101
Travel valve block LH Pos. 93
Swing motor Pos. 102
A servo - controlled single - spool block that actu-
ates the left - hand track. The swing motors are 40°, fixed - displacement
axial piston pumps whose output speed is propor-
tional to the flow of oil. The output torque increases
free Pos. 94 with the pressure drop over the motor.
free Pos. 103 – 104
Travel retarder valve RH Pos. 95
Prevents the excavator from „running away“ down-
hill and keeps the track motors full of oil (to avoid Pressure regulating valve Pos. 105
cavitation). The speed of the track motors is then
always determined by the working pressure of the The valve governs the torque in the closed-loop
pumps (3). swing circuit depending on the selected control
pressure. A pressure relief valve (109) is limiting
the servo pressure to 31 bar. The ratio between
Travel retarder valve LH Pos. 96 control pressure and working pressure is 1 : 12
and with a max. servo pressure of 31 bar the max.
working pressure on swinging resp. counter-
See travel retarder valve (95).
swinging is approx. 370 bar.
Anti - cavitation valve Pos. 97
Flushing valve Pos. 106
The four valves mounted on the „Travel“ spools
The flushing valve serves the oil flow in the closed
(92 & 93) keep a constant column of oil in the track
swing circuit. During each swing operation the
motors. They open at very low pressure so that oil
valve flushes out a small oil volume from the low-
can be drawn in from the tank line.
pressure side of the swing circuit. The charge
pump replaces this oil volume by cooled oil from
the hydraulic tank.
free Pos. 98 – 99
free Pos. 107 – 108
Swing gearbox Pos. 100
The gearboxes are 2 - stage planetary reducers.
3721440en - (00) - 11.09 Page 8.3 - 9
8.3 DESCRIPTION OF THE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM - FS
Pressure relief valve Pos. 109 Pressure relief valve Pos. 126
The pressure relief valve limits the control pressure Secondary pressure relief valves for the four track
to 31 bar to be used for the pressure regulating motors that protect the motors against external
valve (105). The valve is direct acting and has a forces. Excess oil is cracked off into the relevant
variable setting. low pressure side of the motors.
Solenoid valve Pos. 110 free Pos. 127 – 129
The 3/2-solenoid valves serve the servo circuit
‘swinging’ with oil pressure.
Track tensioning cylinder Pos. 130
free Pos. 111 – 119 Single - acting (plunger) cylinders that keep the
crawler tracks tensioned.
Diaphragm accumulator Pos. 131
Travel gearbox Pos. 120
The nitrogen accumulators act as shock absorbers
3 - stage planetary reducer with integrated parking to dampen external forces acting on the crawler
brake. tracks.
The four track parking brakes are wet, multi - disk
brakes that are engaged under spring force and
released by hydraulic pressure (18 - 20 bar). free Pos. 132
Travel motor Pos. 121
Track tensioning block Pos. 133
The four track motors are variable - displacement,
bent - axis motors with tandem bearing arrange-
ments. Servo pressure at port (X) sets the motors The block contains the valves for the automatic
to either of two mechanically limited tilt angles. The track tensioning system.
maximum tilt angle is selected when servo pres-
sure is „O“ . The minimum tilt angle is reached
when servo pressure rises above 40 - 45 bar. Pressure relief valve Pos. 134
The track-tensioning assembly comprises 2 pres-
free Pos. 122 – 124 sure-relief valves with hand wheel and 2 test
points.
The hand wheels can be used to relieve the hy-
draulic track tension independently for each track.
Secondary relief block Pos. 125
free Pos. 135 – 144
Assembly group comprising four pressure relief
valves (126), four test points and a housing.
Page 8.3 - 10 3721440en - (00) - 11.09
8.3 DESCRIPTION OF THE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM - FS
Hydraulic cylinder Pos. 145 The valve blocks are servo-controlled.
For each function a secondary pressure-relief- and
anti-cavitation valve is installed.
The double-acting hydraulic cylinder is installed on The pilot-controlled pressure-relief valves protect
the superstructure and moves the service station the hydraulic cylinders of the working equipment
up and down. on the secondary side against too high pressures
which may be produced by external forces acting
on the working equipment.
Hydraulic valve Pos. 146 The integrated suction valves protect the hydraulic
cylinders against cavitation.
The 3/2 way valve has the function to activate the
cylinder for the service station.
free Pos. 162 – 163
Check (non-return) valve Pos. 147
The non-return valves are installed to avoid pres- Float valve Pos. 164
sure loss in the service system.
Save time and energy when lowering the boom
and the stick. The valves connect the piston and
free Pos. 148 - 149 rod sides of the cylinders so that the piston rods
retract only as a result of the Attachment`s own
dead weight. Only the excess oil (piston - side
Hydraulic cylinder Pos. 150 chamber has a greater volume than the rod - side)
is allowed to escape to the tank. The main pumps
The double-acting hydraulic cylinder is installed on (3) are not activated. If it is required to lower the
the superstructure and moves the access ladder boom or the stick with pressure, the „float“ valves
up and down. can be switched off using solenoid valves, activat-
ed by pressing buttons in the hand-levers.
Control valve Pos. 151
free Pos. 165 – 166
With the control valve the cylinder for the access
ladder is operated. The integrated pressure relief
valve protects the hydraulic cylinder against over-
load. Check (non-return) valve Pos. 167
Accumulator Pos. 152
free Pos. 168 – 181
The oil in the accumulator allows the lowering of
the access ladder when the drive unit is shut down.
Boom cylinder Pos. 182
free Pos. 153 – 160
The two double-acting hydraulic cylinders are in-
stalled between superstructure and boom. They
are lifting or lowering the boom and thus the com-
4-spool valve block Pos. 161 plete working equipment.
The two 4-spool valve blocks control the working
cylinders for boom, arm, bucket crowd and clam.
3721440en - (00) - 11.09 Page 8.3 - 11
8.3 DESCRIPTION OF THE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM - FS
Stick cylinder Pos. 183
The two double-acting hydraulic cylinders are in-
stalled between boom and stick and serve to ex-
tend and retract the stick.
Bucket cylinder Pos. 184
The two double-acting hydraulic cylinders are
mounted between boom and bucket and move the
bucket inwards and outwards.
free Pos. 185
Clamshell cylinder Pos. 186
The two double-acting hydraulic cylinders are
mounted on the back wall and open and close the
front lip.
Distributor block Pos. 187
The block is installed in the backwall and contains
a pressure relief valve.
The pressure relief valve secures the clamshell-
cylinder rod-side against pressure peaks.
free Pos. 188
Distributor block Pos. 189
The distributor block is mounted on the boom and
distributes the various oils flows from the control
blocks to the bucket cylinders.
Page 8.3 - 12 3721440en - (00) - 11.09
8.3 DESCRIPTION OF THE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM - FS
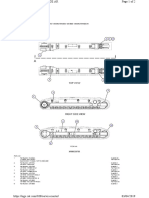
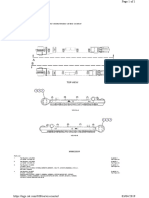
8.3.4 Hydraulic circuit diagram
The position nos. in the circuit diagram
Part-No. 3 719 200 (00)
are referred to chapter 8.3.2.
3721440en - (00) - 11.09 Page 8.3 - 13
8.3 DESCRIPTION OF THE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM - FS
Page 8.3 - 14 3721440en - (00) - 11.09
You might also like
- 014 CAT-6060 AC 60Hz E-Drive CAMP + SIL + BCS4 FS Legend H-Schematic Canada No New AvailableDocument13 pages014 CAT-6060 AC 60Hz E-Drive CAMP + SIL + BCS4 FS Legend H-Schematic Canada No New AvailableMiguel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Description of The Hydraulic System: 8.3.1 Technical DataDocument14 pages8.3 Description of The Hydraulic System: 8.3.1 Technical DatahectorNo ratings yet
- 015 RH200 FS Legend H-Schematic 08 03-3668664enDocument14 pages015 RH200 FS Legend H-Schematic 08 03-3668664enMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 015 RH200 BH Legend H-Schematic 08 03-3668665enDocument14 pages015 RH200 BH Legend H-Schematic 08 03-3668665enMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Description of The Hydraulic System (Face Shovel) : 8.3.1 Technical DataDocument15 pages8.3 Description of The Hydraulic System (Face Shovel) : 8.3.1 Technical DatahectorNo ratings yet
- 015 - Legend For 3748761 - #170112 - 08 - 03-3746450enDocument15 pages015 - Legend For 3748761 - #170112 - 08 - 03-3746450enhectorNo ratings yet
- RH-170 FS Legend H-Schematic 3668520Document15 pagesRH-170 FS Legend H-Schematic 3668520KJDNKJZEFNo ratings yet
- Plano Hidraulico RH-90Document15 pagesPlano Hidraulico RH-90Eduardo ZamoraNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Description of The Hydraulic System: 8.3.1 Technical DataDocument12 pages8.3 Description of The Hydraulic System: 8.3.1 Technical DataFuad JahićNo ratings yet
- 14 RH90C BH Legend H-Schematic 08 03-3720173enDocument15 pages14 RH90C BH Legend H-Schematic 08 03-3720173enMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Description of The Hydraulic System: 8.3.1 Technical DataDocument15 pages8.3 Description of The Hydraulic System: 8.3.1 Technical DataOsvaldo UrbanoNo ratings yet
- MB Actros and Arocs Heavy-Duty TruckDocument103 pagesMB Actros and Arocs Heavy-Duty Truckacademy.michael.jensenNo ratings yet
- Mercruiser Diesel 4.2L CMD QSD 270 300 350Document129 pagesMercruiser Diesel 4.2L CMD QSD 270 300 350Joswyn LopesNo ratings yet
- 3508b ManualDocument744 pages3508b ManualЕвгений Белоусов100% (1)
- Section E Section E: HydraulicsDocument109 pagesSection E Section E: HydraulicsАлександр НовиковNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument109 pages1 PDFАлександр НовиковNo ratings yet
- Case 580CK Model B Service ManualDocument631 pagesCase 580CK Model B Service Manualsamuel benavides0% (2)
- CAT 3512 Service Manual 66Z SENR2382Document465 pagesCAT 3512 Service Manual 66Z SENR2382Roman GanzhaNo ratings yet
- DATA - Mercruiser 3Document12 pagesDATA - Mercruiser 3Bakri danoNo ratings yet
- Dash 8 Classic 71-80 Power Plant June 2015 BW LogoDocument126 pagesDash 8 Classic 71-80 Power Plant June 2015 BW Logomilliewangui157No ratings yet
- TP 7052Document284 pagesTP 7052Nelson MartinezNo ratings yet
- Ciruitos de Boom, Stick y Bucket - TextoDocument46 pagesCiruitos de Boom, Stick y Bucket - Textolalo11715100% (1)
- SKF Lubricating Oil SystemDocument104 pagesSKF Lubricating Oil Systemthreek0123No ratings yet
- Atlas Copco CC125Document162 pagesAtlas Copco CC125JayapalNo ratings yet
- Rodillo 120 DynapacDocument252 pagesRodillo 120 DynapacMarcelo Gustavo Fuentes ValdiviaNo ratings yet
- SABCube SpareParts 2010-12Document90 pagesSABCube SpareParts 2010-12Mário OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Manual de Partes Troyan 2500-TB074Document330 pagesManual de Partes Troyan 2500-TB074Kl CpNo ratings yet
- Service and Parts Manual: Series 14 Hydraulic BackhoesDocument89 pagesService and Parts Manual: Series 14 Hydraulic BackhoesJoe ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Vàlvulas de Control y Retorno - TextoDocument29 pagesVàlvulas de Control y Retorno - Textolalo11715100% (4)
- Catalago de Peças Mini Rolo D.oneDocument218 pagesCatalago de Peças Mini Rolo D.oneEudes BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Nuevo Aceite - EN - TCM - 12-457868Document108 pagesNuevo Aceite - EN - TCM - 12-457868jesus ZamarripaNo ratings yet
- CA1300 Yanmar (Stage V) - Spare Parts CatalogueDocument287 pagesCA1300 Yanmar (Stage V) - Spare Parts Cataloguerlkalencar1No ratings yet
- Cat D8H Tractor 36a5328 and Up Parts PDFDocument226 pagesCat D8H Tractor 36a5328 and Up Parts PDFDaniel Silva100% (2)
- New Generation N62 Engine: Course Contents/Background MaterialDocument145 pagesNew Generation N62 Engine: Course Contents/Background Materialabdull rehmanNo ratings yet
- MF3366Document448 pagesMF3366carlos.paranhosNo ratings yet
- CC1200C VI: Vibratory RollerDocument270 pagesCC1200C VI: Vibratory RollerRonald VelascoNo ratings yet
- FuelDocument8 pagesFuelيوسف وليد عبد الرحيمNo ratings yet
- SMT Crane Maintenance ManualDocument84 pagesSMT Crane Maintenance ManualArun Tiwari100% (1)
- Fuel 2Document8 pagesFuel 2يوسف وليد عبد الرحيمNo ratings yet
- 2000-TB104 Trojan PDFDocument231 pages2000-TB104 Trojan PDFubaldo caraballoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Diagram, With Option Components: Service InformationDocument2 pagesHydraulic Diagram, With Option Components: Service InformationSONNo ratings yet
- 0293 594 0 Sys Hy en 144Document100 pages0293 594 0 Sys Hy en 144api-19483250100% (1)
- Hein Warner Series 14 SPM 9308131 Parts BookDocument8 pagesHein Warner Series 14 SPM 9308131 Parts Bookmichele100% (51)
- C5000SL инструкция по ремонту-01Document33 pagesC5000SL инструкция по ремонту-01Евгений ГубаревNo ratings yet
- Uenr6313uenr6313 01 ScoopDocument1 pageUenr6313uenr6313 01 ScoopEnzo Miguel Sarabia MontesNo ratings yet
- Shop Manual M300-III PDFDocument277 pagesShop Manual M300-III PDFBer Honza100% (5)
- Instruction ManualDocument51 pagesInstruction ManualivanivanovvNo ratings yet
- Serv1852 TXT6Document38 pagesServ1852 TXT6Noel Olvera100% (1)
- Section 2 EngineDocument5 pagesSection 2 EngineJuan Felipe Garza GNo ratings yet
- 2-1. EngineDocument14 pages2-1. EngineSumitomo ExcavatorNo ratings yet
- Steering GearDocument55 pagesSteering GearDanijel LadasicNo ratings yet
- Manuel de Réparation 5-10 TonnesDocument142 pagesManuel de Réparation 5-10 TonnesFaouzi Zorgati100% (2)
- FTX128L Manual de Partes PDFDocument256 pagesFTX128L Manual de Partes PDFDavy GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Safety Critical Parts List: MaintenanceDocument73 pagesSafety Critical Parts List: MaintenanceFelipe BecerraNo ratings yet
- 5-1 Steering SystemDocument7 pages5-1 Steering SystemSumitomo Laos Sumitomo LaosNo ratings yet
- Group 12 LubricationDocument32 pagesGroup 12 LubricationLuisTocoraNo ratings yet
- WM Porsche 928 Factory Manual - Vol 1aDocument307 pagesWM Porsche 928 Factory Manual - Vol 1a9TECHNIKNo ratings yet
- Mercruiser 4.5L Alpha BravoDocument102 pagesMercruiser 4.5L Alpha BravoLucas Oliveira100% (1)
- Instruction Manual FOR Frydenbö Steering GearDocument53 pagesInstruction Manual FOR Frydenbö Steering Gearionut100% (1)
- 14 - Auxiliary Controller - Operation Manual - CATDocument20 pages14 - Auxiliary Controller - Operation Manual - CATMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 09.2 PLC - Description Diesel RH90-340Document6 pages09.2 PLC - Description Diesel RH90-340Miguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- DimensioDocument1 pageDimensioMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Fowa - Fuel - 50305Document20 pagesMaintenance Fowa - Fuel - 50305darwin100% (1)
- 000 Cat-6060 ContentsDocument2 pages000 Cat-6060 ContentsMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 011 - CAT-6018 - Pressure Checking - FS - 08 - 06-3720177enDocument22 pages011 - CAT-6018 - Pressure Checking - FS - 08 - 06-3720177enMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 447-2262 - Track GPDocument1 page447-2262 - Track GPMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- See Latest Version of Service Advisory Sa08-007 For Assembly Instructions, Setting End Float and Spring Installation. Detail ADocument1 pageSee Latest Version of Service Advisory Sa08-007 For Assembly Instructions, Setting End Float and Spring Installation. Detail AMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 459-6712 - Cover GPDocument1 page459-6712 - Cover GPMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 447-2261 - Track GPDocument1 page447-2261 - Track GPMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Shovel Specifi Cations: Dimensions and Working RangesDocument2 pagesShovel Specifi Cations: Dimensions and Working RangesMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- BodystruDocument4 pagesBodystruMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- CruisDocument1 pageCruisMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 437-5754 - Track GPDocument1 page437-5754 - Track GPMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Illustrations: Expanded Mining Products ROTARY DRILL MD6640-DR6 UNDERCARRIAGE 437-5805 - GUARD GP-TRK GDEDocument2 pagesIllustrations: Expanded Mining Products ROTARY DRILL MD6640-DR6 UNDERCARRIAGE 437-5805 - GUARD GP-TRK GDEMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 437-5799 - Drive Gp-Final-ADocument1 page437-5799 - Drive Gp-Final-AMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 437-5810 - Idler Gp-Front-ADocument1 page437-5810 - Idler Gp-Front-AMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 394-5665 - Undercarriage ArDocument2 pages394-5665 - Undercarriage ArMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 437-5816 - Cover GPDocument1 page437-5816 - Cover GPMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 41 2osopDocument6 pages41 2osopMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 437-5809 - Idler Gp-Front-ADocument1 page437-5809 - Idler Gp-Front-AMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 41 2os01Document8 pages41 2os01Miguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- By: Beto Santillán: Date: June 23 2010Document6 pagesBy: Beto Santillán: Date: June 23 2010Miguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 41 2os04Document18 pages41 2os04Miguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 41 2os02Document12 pages41 2os02Miguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 366-3380 - Roller Gp-Single FlangeDocument1 page366-3380 - Roller Gp-Single FlangeMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Rotary Blasthole Drill UndercarrigaeDocument41 pagesRotary Blasthole Drill UndercarrigaeMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 41 2os03Document8 pages41 2os03Miguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 15.0 - CAT-6040 - E-Drive - Pulse Width Modulation CMS-PMSDocument4 pages15.0 - CAT-6040 - E-Drive - Pulse Width Modulation CMS-PMSMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Feb 07Document120 pagesFeb 07Miguel CallataNo ratings yet
- V 300 - Series - DSR - TK52344 5.2 E 18 PM - 02 11Document105 pagesV 300 - Series - DSR - TK52344 5.2 E 18 PM - 02 11Arturo Michel Moreno Jimenez100% (3)
- Fluid Machinery Problem SetDocument4 pagesFluid Machinery Problem SetJohn Vincent EslaoNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Hydraulics - RT90 PowershiftDocument5 pagesAuxiliary Hydraulics - RT90 PowershiftIonut MiroslavNo ratings yet
- Schaum - S Outline - Fluid Mechanics and HydraulicsDocument388 pagesSchaum - S Outline - Fluid Mechanics and HydraulicsJoanna Marie SantosNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic NoiseDocument4 pagesHydraulic NoiseShyam KumarNo ratings yet
- Rekapitulasi Rincian Anggaran Biaya: NO Uraian Pekerjaan Jumlah Harga (RP)Document4 pagesRekapitulasi Rincian Anggaran Biaya: NO Uraian Pekerjaan Jumlah Harga (RP)Slamet SuntoroNo ratings yet
- Hydro TestDocument2 pagesHydro TestMuhammad AbbasNo ratings yet
- MucidycDocument3 pagesMucidycamarNo ratings yet
- The Gas LawsDocument40 pagesThe Gas LawsLailanie PinedaNo ratings yet
- FanTraining ManualDocument36 pagesFanTraining ManualAnonymous P3U7dcya5vNo ratings yet
- Catalogo de Pecas GeolineDocument456 pagesCatalogo de Pecas GeolineMZ Assistência TécnicaNo ratings yet
- PFC PDFDocument3 pagesPFC PDFkwagga125No ratings yet
- Sullair VARIABLE SPEED - 1800-2200-1800V-1809V-2200V-25-30HPDocument70 pagesSullair VARIABLE SPEED - 1800-2200-1800V-1809V-2200V-25-30HPJose MontielNo ratings yet
- Train-1 Process Flow DiagramDocument1 pageTrain-1 Process Flow DiagramHtoo Htoo KyawNo ratings yet
- Ebara GS Ibb April 2022 - 220404 - 200628Document4 pagesEbara GS Ibb April 2022 - 220404 - 200628chandra atmaNo ratings yet
- 40-2-04 Rev K GBX Lubricant RecommendationsDocument2 pages40-2-04 Rev K GBX Lubricant Recommendationsjamil ahmedNo ratings yet
- Curso Cat 950-962G Steering Syst STMGDocument24 pagesCurso Cat 950-962G Steering Syst STMGSilas F Pimenta100% (18)
- Capsu Logo Word Docs 1Document4 pagesCapsu Logo Word Docs 1Ashley ZuniegaNo ratings yet
- Consist of 87 Regulations and 6 SchedulesDocument6 pagesConsist of 87 Regulations and 6 Schedulesroslanali@tnbNo ratings yet
- Bul HY14 M1 Commercial VLV SealKits 07-01-21Document20 pagesBul HY14 M1 Commercial VLV SealKits 07-01-21job saputraNo ratings yet
- Parts List Manual: I A C TS20C/V200TSDocument108 pagesParts List Manual: I A C TS20C/V200TSMarcos CabreraNo ratings yet
- High Pressure Knock Out Drum (ALF)Document12 pagesHigh Pressure Knock Out Drum (ALF)Eng AlfNo ratings yet
- WC Types With DrawingDocument1 pageWC Types With DrawingMercy CatubigNo ratings yet
- D77002 en PDFDocument36 pagesD77002 en PDFY.EbadiNo ratings yet
- D12 EngineDocument57 pagesD12 Enginesergio100% (6)
- 04-Experiment# 4 - Bernoulli's Theorem Demontration (19-24)Document6 pages04-Experiment# 4 - Bernoulli's Theorem Demontration (19-24)Fatimah Rahima JingonaNo ratings yet
- IBR Valve ScheduleDocument12 pagesIBR Valve ScheduleManikandan elumalaiNo ratings yet
- Fa' (ZL ( - 1/3) :, L/iu1llDocument3 pagesFa' (ZL ( - 1/3) :, L/iu1llcraponzelNo ratings yet
- HG VolvoProductListing WebDocument4 pagesHG VolvoProductListing Webpiyush sharmaNo ratings yet