Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Y4 KO - Living Things and Their Habitats.202733287
Uploaded by
sadviau3Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Y4 KO - Living Things and Their Habitats.202733287
Uploaded by
sadviau3Copyright:
Available Formats
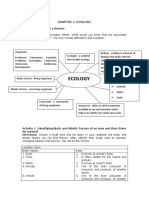
Key previous learning (see vocab for definitions) What is a classification key?
A classification key is a tool that uses yes/no questions amphibian a cold-blooded vertebrate that can live in water and on land.
herbivore/carnivore/omnivore
to group living things by different criteria.
biomes a natural area of vegetation and animals .
vertebrate/invertebrate
bird warm-blooded vertebrates with feathers, pointed beaks and wings.
mammals/birds/fish/amphibians/reptiles
carnivore an animal that eats meat.
classification key a system which divides things into groups or types.
How can living things be grouped?
All living things, which can also be called organisms, criteria a factor on which something is judged.
have to do environment all the physical surroundings on Earth including everything living and
certain non-living.
things to excretion the process of eliminating waste from the body.
stay alive.
fish cold-blooded (mainly) vertebrates that can only live in water.
these are
the life habitat the natural environment in which an animal or plant lives or grows.
processes: How can environments change? herbivore an animal that only eats plants.
Living things can be grouped according to different Habitats can change throughout the year and this can invertebrate creature that does not have a spine.
criteria—where they live, what type of organism they have an effect on the plants and animals living there.
life processes the seven processes that tell us that living things are alive.
are, what features they have. E.g., a camel can belong Humans can have positive effects on the environment,
e.g. nature reserves, but instead often damage it. mammal a warm-blooded vertebrate that breaths air and grows hair.
in a group of vertebrates, a group of animals that live
in the desert, and a group of animals with four legs. microhabitat a small part of the environment that supports a habitat.
People-made Threats to the Environment
nutrition the process of taking food into the body and absorbing nutrients.
Air-pollution from cars, e.g. carbon monoxide, and the
omnivore person or animal that eats both meat and plants.
Carl burning of fossil fuels.
Linnaeus (1707-1778) was a botanist, zoolo- organism a living thing.
Water pollution through indus-
gist and physician. He’s most famous for sim- reproduction when an animal or plant produces one or more copies of itself.
trial waste and farm fertilisers
plifying the naming system scientists use to
that can pollute rivers and reptile cold-blooded vertebrates.
describe the millions of species on Earth.
streams. respiration process of respiring; breathing ; inhaling and exhaling air.
Rachel Carson (1907-1964)
was a marine biologist. She was most famous Rubbish—Plastic and household waste ends up on the sensitivity responding to the external environment.
for her book Silent Spring (1962) which streets, in the sea or in rubbish dumps, destroying hab-
warned of the damage humans were doing to the environ- vegetation plants, trees and flowers.
itats and wildlife.
ment and led to the modern environmental movement.
vertebrate a creature which has a spine.
You might also like
- EcosystemDocument86 pagesEcosystemvishalNo ratings yet
- Life ScienceDocument16 pagesLife ScienceJNo ratings yet
- Biology VII Section 1 Lesson 1 Characterisitcs of Living ThingsDocument64 pagesBiology VII Section 1 Lesson 1 Characterisitcs of Living ThingsGideon CavidaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Section 1 Lesson 1Document44 pagesIGCSE Biology Section 1 Lesson 1Zhuko Suko AdiNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument13 pagesCharacteristics of Living ThingsZheela EsmaelNo ratings yet
- What Is The Basic Structural and Functional Unit of LifeDocument14 pagesWhat Is The Basic Structural and Functional Unit of LifeZheela EsmaelNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Biology Section 1 Lesson 1Document44 pagesiGCSE Biology Section 1 Lesson 1aastha dograNo ratings yet
- Vision of Al Nahda National School Everyone Engages, Everyone Learns, Everyone ReflectsDocument29 pagesVision of Al Nahda National School Everyone Engages, Everyone Learns, Everyone ReflectsSalma DAGAMSEHNo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper For Week 2 GEE1Document3 pagesLesson Proper For Week 2 GEE1Russel Kent PaduaNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument16 pagesEcosystemruchith bhoopalam100% (1)
- Form 2 Chapter 2 EcosystemDocument60 pagesForm 2 Chapter 2 EcosystemAmer Malek71% (14)
- Presentation On Ecology Claass 1Document51 pagesPresentation On Ecology Claass 1Soumyajit NandiNo ratings yet
- Unit I EcologyDocument58 pagesUnit I EcologyGokul SirsatNo ratings yet
- Ecology Review NotesDocument6 pagesEcology Review NotesMaKylah ClevelandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Ecology TasksDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - Ecology TasksAngelica PacquingNo ratings yet
- Science Lecture 1Document17 pagesScience Lecture 1Naila AfzalNo ratings yet
- Balance of Naturestudy GuideDocument8 pagesBalance of Naturestudy GuideedwinmasaiNo ratings yet
- LecturesDocument11 pagesLecturesMariel CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Bio1 - Unit 1 LectureDocument7 pagesBio1 - Unit 1 LectureCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Classifying Living OrganismsDocument54 pagesClassifying Living Organismstiya.bakugo.katsuki01No ratings yet
- Biodiversity: Explore the Diversity of Life on Earth with Environmental Science Activities for KidsFrom EverandBiodiversity: Explore the Diversity of Life on Earth with Environmental Science Activities for KidsNo ratings yet
- Community Ecology Community Ecology Looks at The InteractionsDocument5 pagesCommunity Ecology Community Ecology Looks at The InteractionsLeah MacalipayNo ratings yet
- B7 Ecology Glossary Combined ScienceDocument8 pagesB7 Ecology Glossary Combined ScienceoladokunrachelNo ratings yet
- EnSci Reviewer #1 - Ecosystem ReviewerDocument2 pagesEnSci Reviewer #1 - Ecosystem ReviewerJohn PaulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 ESDocument14 pagesLecture 3 ESErico TambanganNo ratings yet
- Myp3 Scavenger HuntDocument2 pagesMyp3 Scavenger Huntminajaved5No ratings yet
- Geography NotesDocument22 pagesGeography NotesSinethma KarunatilakeNo ratings yet
- 1.2 - Ecology and Ecosystem: Deciduous and Taiga (Boreal) (Links To An External Site.) Forests 3. FreshwaterDocument6 pages1.2 - Ecology and Ecosystem: Deciduous and Taiga (Boreal) (Links To An External Site.) Forests 3. FreshwatercarlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document20 pagesChapter 19Vidavathi Vidyavathi KasibhatlaNo ratings yet
- AQA Biology (Combined Science) Unit 7: Ecology Knowledge OrganiserDocument3 pagesAQA Biology (Combined Science) Unit 7: Ecology Knowledge OrganiserDan LiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 APPSC G2 S&T MainsDocument61 pagesUnit 3 APPSC G2 S&T Mainsswtsweetie88No ratings yet
- 2 Compressed Notes EcologyDocument15 pages2 Compressed Notes EcologyLIM ZHI SHUENNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document5 pagesLesson 2angelina cajuraoNo ratings yet
- Grouping Living OrganismsDocument8 pagesGrouping Living OrganismsOsmany MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Community Ecology Community Ecology Looks at The InteractionsDocument5 pagesCommunity Ecology Community Ecology Looks at The InteractionsLeah MacalipayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Interdependence Among Living Organism andDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Interdependence Among Living Organism andNantha KumaranNo ratings yet
- The Study of Life: Teacher Notes and AnswersDocument4 pagesThe Study of Life: Teacher Notes and AnswersHector AguilarNo ratings yet
- Ecology of LifeDocument10 pagesEcology of LifePaul Jeremy MendozaNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMDocument43 pagesECOSYSTEManon_40967343No ratings yet
- Ecosystem: Prepared By: Ms. Sheryl G. Docto CS BPS FacultyDocument18 pagesEcosystem: Prepared By: Ms. Sheryl G. Docto CS BPS FacultyKarren mae YgloriaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Life ScienceDocument62 pagesIntroduction To Life ScienceDannylene DindinNo ratings yet
- Living Organisms and Their SurroundingsDocument4 pagesLiving Organisms and Their SurroundingsPavani KumariNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PDFDocument45 pagesUnit 2 PDFHamid RabaniNo ratings yet
- Envi SciDocument23 pagesEnvi SciJeanelle Ledesma MarabutNo ratings yet
- Biology CSEC PrepDocument43 pagesBiology CSEC PrepMarcellus Lee100% (1)
- Ecology For Uce NewDocument4 pagesEcology For Uce NewHasifa KonsoNo ratings yet
- EcologyDocument19 pagesEcology2022303299No ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentFrances Samson GianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 EcosystemDocument60 pagesChapter 2 EcosystemJu WenNo ratings yet
- Ecology DiscussionDocument31 pagesEcology DiscussionAl Marjorie Abrasaldo TatingNo ratings yet
- Unit 4. Ecosystems 1Document11 pagesUnit 4. Ecosystems 1M.J.RNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems: Environment Studies (BITS F225) Suman KapurDocument38 pagesEcosystems: Environment Studies (BITS F225) Suman KapurShubham VarshneyNo ratings yet
- NatureDocument3 pagesNatureFea CimeniNo ratings yet
- Principles and Concept of EcosystemDocument16 pagesPrinciples and Concept of EcosystemJay Bianca Abera Alistado100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Biodiversity: Learning OutcomesDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Biodiversity: Learning OutcomesREKSHENA A/P PERKAS MoeNo ratings yet
- Term 3 - 8. EcosystemDocument22 pagesTerm 3 - 8. EcosystemcindyNo ratings yet
- LEC BiodiversityDocument2 pagesLEC BiodiversityMariz RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Science6 - q2 - CLAS6 - Interactions Among Living Things and Nonliving Things - v6 - Liezl ArosioDocument11 pagesScience6 - q2 - CLAS6 - Interactions Among Living Things and Nonliving Things - v6 - Liezl ArosioJeffrey VigonteNo ratings yet
- DPS Science Skills ProgressionDocument8 pagesDPS Science Skills Progressionsadviau3No ratings yet
- NZLPE Online Tuitions 2024Document1 pageNZLPE Online Tuitions 2024sadviau3No ratings yet
- KS1 Curriculum Guide 18 - 19Document26 pagesKS1 Curriculum Guide 18 - 19sadviau3No ratings yet
- Suggested Route Plan For 100% IPC Learning Goals Coverage - All MilepostsDocument1 pageSuggested Route Plan For 100% IPC Learning Goals Coverage - All Milepostssadviau3No ratings yet
- Y2 Time TravellersDocument2 pagesY2 Time Travellerssadviau3No ratings yet
- Y4 Lets Plant ItDocument4 pagesY4 Lets Plant Itsadviau3No ratings yet
- Y6 Bake ItDocument2 pagesY6 Bake Itsadviau3No ratings yet
- Y6 Being HumanDocument2 pagesY6 Being Humansadviau3No ratings yet
- Jumbled Sentences - Test One: Rearrange The Following Words/phrases To Make A Complete and Correct SentenceDocument5 pagesJumbled Sentences - Test One: Rearrange The Following Words/phrases To Make A Complete and Correct SentenceirshadNo ratings yet
- Cap 310 Final ExamDocument7 pagesCap 310 Final Examapi-534989812No ratings yet
- Merge ProductionDocument208 pagesMerge ProductionParadise CommunicationNo ratings yet
- Đề Kiểm Tra 1 Tiết Tiếng Anh 8: NĂM 2019 - 2020 CÓ ĐÁP ÁNDocument6 pagesĐề Kiểm Tra 1 Tiết Tiếng Anh 8: NĂM 2019 - 2020 CÓ ĐÁP ÁNHà NguyễnNo ratings yet
- CHIKMAGALUR Tourist GuideDocument18 pagesCHIKMAGALUR Tourist GuideBibhas PalNo ratings yet
- Oferta Seminte AmatoriDocument5 pagesOferta Seminte Amatoriionutz_dutzaNo ratings yet
- Exhibit B2 GEN-02 Product Labeling - Edition No. 02Document3 pagesExhibit B2 GEN-02 Product Labeling - Edition No. 02Gagan Sai Reddy100% (1)
- Communication Skills Exercise 1 (Expressing Greetings & Saying Goodbye) : Choose The Best Answer To Complete Each of The Following SentencesDocument15 pagesCommunication Skills Exercise 1 (Expressing Greetings & Saying Goodbye) : Choose The Best Answer To Complete Each of The Following SentencesThanh Dang MinhNo ratings yet
- Thomson Confinement FoodDocument2 pagesThomson Confinement FoodandreeatalosNo ratings yet
- Business Plan: (School Based Assessment)Document13 pagesBusiness Plan: (School Based Assessment)IsraelNo ratings yet
- LUBCON Cutting Oils Corrugator enDocument2 pagesLUBCON Cutting Oils Corrugator enOmin PostingNo ratings yet
- HW Beg TRD Unit Test 7aDocument2 pagesHW Beg TRD Unit Test 7aFrctybzNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed-Lesson-Plan-of-Figures-of-Speech Emmilyn FloresDocument4 pagesSemi-Detailed-Lesson-Plan-of-Figures-of-Speech Emmilyn FloresEmz Bueza Flores100% (1)
- MICARYDocument12 pagesMICARYLoveth BethelNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal English Grade 8Document7 pagesLatihan Soal English Grade 8Ade NurulNo ratings yet
- Moview Review - Ratatouille (VALDEZ 12ABM)Document2 pagesMoview Review - Ratatouille (VALDEZ 12ABM)Kimberly ValdezNo ratings yet
- Collocations FoodDocument2 pagesCollocations FoodMintNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Williams Basic Nutrition and Diet Therapy 15th Edition by Nix PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Williams Basic Nutrition and Diet Therapy 15th Edition by Nix PDF Full Chaptergladdenbugler.uy6kz100% (20)
- 8 Grade GM 2Document1 page8 Grade GM 2Randy Alexander GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Burger SteakDocument14 pagesBurger SteakMaureenValdezSeguiNo ratings yet
- 1800 Calorie Diet Meal Plan For Diabetic Mellitus PatientsDocument5 pages1800 Calorie Diet Meal Plan For Diabetic Mellitus PatientsKisis HoneyNo ratings yet
- Argentine Food GlossaryDocument16 pagesArgentine Food GlossarypfreteNo ratings yet
- Fbs Basic Types of Tablewares 1Document2 pagesFbs Basic Types of Tablewares 1hunter kurosakiNo ratings yet
- Metro Cash & CarryDocument10 pagesMetro Cash & Carrysyedumar2031cuilNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document2 pagesLab 4Teresa YanNo ratings yet
- FriarDocument16 pagesFriarsamcaridoNo ratings yet
- Various Text TypesDocument14 pagesVarious Text TypesMelanie SorianoNo ratings yet
- Science MilletsDocument5 pagesScience MilletsHana Umar100% (2)
- Video - Worksheets - Unit 8 - 9Document4 pagesVideo - Worksheets - Unit 8 - 9El Jerry 7u7No ratings yet
- INDOSA Technology: The World's No. 1 in Can MachineryDocument25 pagesINDOSA Technology: The World's No. 1 in Can Machinery高金辉No ratings yet