Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Burns II - Major Burns Patho, Signs & Treatments
Burns II - Major Burns Patho, Signs & Treatments
Uploaded by
Paula BissetteOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Burns II - Major Burns Patho, Signs & Treatments
Burns II - Major Burns Patho, Signs & Treatments
Uploaded by
Paula BissetteCopyright:
Available Formats
Burns II - Major Burns
Pathophysiology Course
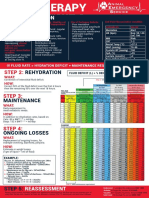
Pathophysiology
Low fluid volume
Massive tissue damage & cellular destruction leads to
widespread systemic inflammation that increases vascular
!
permeability (leaky blood vessels that fill up the body like a !
water balloon). This results in low fluid volume within the
blood vessels leading to Hypovolemic Shock & then death! !
Signs & Symptoms
First 24-hours Over 5.0
K
High Potassium (Hyperkalemia)
Over 5.0
� Potassium Priority Pumps heart
� HIGH Potassium = HIGH Pumps
� Tall, Peaked T Waves on ECG
NCLEX TIP
Fluids FLOW - electrolytes GO!!!
HEMOGLOBIN HEMATOCRIT
Low Sodium (hyponatremia) 12-18 normal 36-54% normal
Below 135 NCLEX TIP
!
Elevated H/H
� Hemoglobin: 12 - 18 normal
! Na
� Hematocrit: 36 - 54% normal !
Treatments
PRIORITY
IV Lactated Ringer’s IV Normal Saline
KEY Term (LR) solution (0.9% sodium Chloride)
LACTATED RINGER’S
#1 Intervention first 24-hours
LACTATED RINGER’S 0.9%
Sodium Chloride
250 mL
NaCl 0.9%
IV Lactated Ringer’s (LR) solution
IV Normal Saline
Assessment of Administer enteral feedings
Fluid Resuscitation ≥ 90 Systolic
Once bowel sounds return
≥ 30 mL/hr
90
1. Urine output
30 mL/hr or MORE NCLEX TIP
#1
2. Blood pressure
≥ 30 mL/hr
(90/systolic Or MORE)
< 120/min
3. Heart rate less than 120/min.
Notes
You might also like
- AES - FluidChart 2020Document1 pageAES - FluidChart 2020Christian De Leon100% (1)
- Urology MCQs For Posgraduate ExamDocument62 pagesUrology MCQs For Posgraduate ExamGhulam Ghous95% (60)
- Disorders of SodiumDocument38 pagesDisorders of SodiumMuhammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 03 - Special Clinical SituationsDocument32 pages03 - Special Clinical SituationsClaudia KosztelnikNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Sodium: Presenter: DR Bharath Kumar P Moderator: DR Ramesh K NDocument41 pagesDisorders of Sodium: Presenter: DR Bharath Kumar P Moderator: DR Ramesh K NBharath Kumar PamulapatiNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia Algorhythm Concept MapDocument2 pagesHyponatremia Algorhythm Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Emergency Nephrology - Hyponatremia Approach & ManagementDocument1 pageEmergency Nephrology - Hyponatremia Approach & ManagementEarn PhongpetraNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Notes 1Document55 pagesHypertension Notes 1Chunnie JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Labs - BMP Panel & ElectrolytesDocument1 pageLabs - BMP Panel & ElectrolytesTori RolandNo ratings yet
- Fluid Resuscitation Algorithm For Adults With SepsisDocument1 pageFluid Resuscitation Algorithm For Adults With SepsisSorina BiliutaNo ratings yet
- Ped501 Hypernatremia NewDocument7 pagesPed501 Hypernatremia NewMisoo KimNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes PresentationDocument35 pagesFluid and Electrolytes PresentationJoe WildNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia2010 (2014 - 09 - 24 18 - 08 - 47 UTC)Document181 pagesHyponatremia2010 (2014 - 09 - 24 18 - 08 - 47 UTC)rnsharmasNo ratings yet
- Map DkaDocument1 pageMap DkaSH PrageethNo ratings yet
- HiponatremiaDocument6 pagesHiponatremiaRaka PrazastaNo ratings yet
- RCPCH TAS Renal Anatomy and Physiology Patrick DaviesDocument25 pagesRCPCH TAS Renal Anatomy and Physiology Patrick DaviesWaleed abdul hayeeNo ratings yet
- Icu Journal ClubDocument19 pagesIcu Journal Clubapi-649066372No ratings yet
- Intra and Intradialytic Hypotension and Hypertension InrigDocument29 pagesIntra and Intradialytic Hypotension and Hypertension InrigMonica HerreraNo ratings yet
- De Methaq L2 HyponatreamiaDocument11 pagesDe Methaq L2 Hyponatreamiaزين العابدين محمد عويش مشريNo ratings yet
- Fluid TherapyDocument56 pagesFluid TherapyHabibie El RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical 1 PDFDocument19 pagesMedical Surgical 1 PDFheyyymeeeNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Quick Reference GuideDocument1 pageSepsis Quick Reference GuideRavin DebieNo ratings yet
- SX Fumc - BurnDocument30 pagesSX Fumc - BurnJamee Lorraine Dela Rosa - TanteoNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid Management: DR Andrew Stein Consultant Nephrologist, UHCWDocument37 pagesIV Fluid Management: DR Andrew Stein Consultant Nephrologist, UHCWJosh BurkeNo ratings yet
- Lipasa PDFDocument3 pagesLipasa PDFIcathiu CardosoNo ratings yet
- Management of ShockDocument12 pagesManagement of ShockMuhamad HilmiNo ratings yet
- Guideline For The Management of Adults Patients With DKA or HHSDocument3 pagesGuideline For The Management of Adults Patients With DKA or HHSJonard GiloNo ratings yet
- Sodium and Water Need To KnowDocument48 pagesSodium and Water Need To KnowkartikaparamitaNo ratings yet
- Hyperchloremia PDFDocument2 pagesHyperchloremia PDFChezer KiethNo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy: Presenter: Chew Zi Qi Supervisor: Dr. Tan KWDocument43 pagesFluid Therapy: Presenter: Chew Zi Qi Supervisor: Dr. Tan KWaslanNo ratings yet
- Terapi Cairan Resusitasi: Iyan DarmawanDocument29 pagesTerapi Cairan Resusitasi: Iyan DarmawanalwiNo ratings yet
- HyponatremiaDocument40 pagesHyponatremiaarchana p sNo ratings yet
- I STAT Alinity V Utilization Guide ABX 00075R1Document8 pagesI STAT Alinity V Utilization Guide ABX 00075R1DrAlaa ZidanNo ratings yet
- ATOTW 136 Major Haemorrhage Part 1 2009Document6 pagesATOTW 136 Major Haemorrhage Part 1 2009viaereaNo ratings yet
- Siadh - Patho, Signs, Causes, TreatmentDocument1 pageSiadh - Patho, Signs, Causes, TreatmentVishalNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument4 pagesShockKristine Violon SecorinNo ratings yet
- Pleno Pakar Blok EmergencyDocument30 pagesPleno Pakar Blok EmergencyakhomanNo ratings yet
- What Is Fluid Therapy?Document42 pagesWhat Is Fluid Therapy?Mirel YdianNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in The Treatment of ShockDocument52 pagesRecent Advances in The Treatment of ShockasupicuNo ratings yet
- SGPTDocument2 pagesSGPTNeña Lozada TabinasNo ratings yet
- Post-Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm: Return of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC)Document1 pagePost-Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm: Return of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC)johndoe1995No ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument144 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesAileyIrvetteNo ratings yet
- H2S Treatment by Scavenger at Oil and Gas FieldDocument37 pagesH2S Treatment by Scavenger at Oil and Gas FieldguruhnurizalNo ratings yet
- SepsisDocument1 pageSepsisCharlie LeeNo ratings yet
- K (Anion Gap 12) (Anion Gap 12) Acute Asthma Hypovolemia: - Vomit - Pyloric StenosisDocument4 pagesK (Anion Gap 12) (Anion Gap 12) Acute Asthma Hypovolemia: - Vomit - Pyloric StenosisAhmad Asyraf AzmanNo ratings yet
- Jenis ShockDocument6 pagesJenis ShockMuhamad Pathu RohmanNo ratings yet
- i-STAT Alinity V: Utilization GuideDocument8 pagesi-STAT Alinity V: Utilization GuideTony ChenNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart For AquaponicsDocument4 pagesFlow Chart For AquaponicsFisher MadamNo ratings yet
- DKA GuidelineDocument1 pageDKA GuidelineIvonneRemigioNo ratings yet
- Clor Bsis68 02 2011Document2 pagesClor Bsis68 02 2011ventas2antonioNo ratings yet
- 136 Management of Major Haemorrhage Part 1Document6 pages136 Management of Major Haemorrhage Part 1fitrah fajrianiNo ratings yet
- DS PNSSDocument2 pagesDS PNSSCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Terapi Cairan Pada Pasien Shock HemooragikDocument41 pagesTerapi Cairan Pada Pasien Shock HemooragikNur Syifa FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Vsim Nursing WorksheetDocument1 pageBlood Transfusion Vsim Nursing Worksheetapi-688564858No ratings yet
- 4 Calcium Channel BlockersDocument16 pages4 Calcium Channel BlockersIman SaksoukNo ratings yet
- SIADH Vs DI SN Study GuideDocument1 pageSIADH Vs DI SN Study Guidehvera01No ratings yet
- Antihypertensive AgentsDocument97 pagesAntihypertensive AgentsL2 - MAKILALA, Zion joy B.No ratings yet
- Cardiac TamponadeDocument1 pageCardiac TamponadePaula BissetteNo ratings yet
- Burns - Types & Care For Minor BurnsDocument1 pageBurns - Types & Care For Minor BurnsPaula BissetteNo ratings yet
- Asthma Nur220 Student PowerpointDocument26 pagesAsthma Nur220 Student PowerpointPaula BissetteNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing SetDocument19 pagesPsychiatric Mental Health Nursing SetPaula BissetteNo ratings yet
- Aimee M. Abide, Catherine Margaret Kuza, Michael T. Vest - Self-Assessment in Adult Multiprofessional Critical Care (2022, Society of Critical Care Medicine) - Libgen - Li 2Document360 pagesAimee M. Abide, Catherine Margaret Kuza, Michael T. Vest - Self-Assessment in Adult Multiprofessional Critical Care (2022, Society of Critical Care Medicine) - Libgen - Li 2Gibran HolmesNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument102 pagesFluids and Electrolytesfelxhu50% (2)
- Lesson 4 - Electrolyte Imbalances Part 1Document74 pagesLesson 4 - Electrolyte Imbalances Part 1Clark SavageNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Disorders: Camiron L. Pfennig Corey M. SlovisDocument19 pagesElectrolyte Disorders: Camiron L. Pfennig Corey M. SlovisMayra Itzel Guerrero ChavezNo ratings yet
- Metabolic EmergenciesDocument48 pagesMetabolic EmergenciesKhanszarizennia Madany AgriNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology CardiovascularDocument86 pagesPharmacology Cardiovascularamasoud96 amasoud96No ratings yet
- NCBI Bookshelf-Diabetes InsipidusDocument44 pagesNCBI Bookshelf-Diabetes InsipidusDiah Pradnya ParamitaNo ratings yet
- Severe Hyponatremia and Water Intoxication - Diagnostic Challenge in Department of Emergency MedicineDocument7 pagesSevere Hyponatremia and Water Intoxication - Diagnostic Challenge in Department of Emergency MedicineNećeš SadaNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Hypernatremia in Adults - UpToDateDocument35 pagesTreatment of Hypernatremia in Adults - UpToDateJuLio Czar Carmona100% (1)
- In-Depth Review: Helbert Rondon-Berrios and Tomas BerlDocument11 pagesIn-Depth Review: Helbert Rondon-Berrios and Tomas BerlMuzaffar MehdiNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia in Cirrhosis: Pathogenesis, Clinical Significance, and ManagementDocument48 pagesHyponatremia in Cirrhosis: Pathogenesis, Clinical Significance, and ManagementrlagamNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes in BPHDocument74 pagesElectrolytes in BPHPreeti Gehlaut NaraNo ratings yet
- Med Surg Exam 3 Comprehensive Review of The Material Covered For Professor Martinez Medical PDFDocument53 pagesMed Surg Exam 3 Comprehensive Review of The Material Covered For Professor Martinez Medical PDFBirhanu Ayenew100% (1)
- Fluid Management in PediatricsDocument3 pagesFluid Management in PediatricsZiyadNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Pediatric SurgeryDocument30 pagesHandbook of Pediatric SurgeryMichelle Chia JungNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Fluid Therapy in ChildrenDocument4 pagesMaintenance Fluid Therapy in ChildrenNicole_0No ratings yet
- Central Diabetes InsipidusDocument8 pagesCentral Diabetes InsipidusasdwasdNo ratings yet
- Macro and Micro Minerals-1Document38 pagesMacro and Micro Minerals-1Ximay Mato100% (1)
- Med Surg BurnsDocument8 pagesMed Surg BurnsawuahbohNo ratings yet
- Quiz 8Document3 pagesQuiz 8DoctorSajid BuzdarNo ratings yet
- Lab Value Interpretation PDFDocument32 pagesLab Value Interpretation PDFDiky JuliantoNo ratings yet
- A Prospective Study On Therapeutic Management and Outcome Measures in Renal Failure PatientsDocument5 pagesA Prospective Study On Therapeutic Management and Outcome Measures in Renal Failure Patientsvathsalya porankiNo ratings yet
- What Are Electrolytes? What Causes Electrolyte Imbalance?: Fast Facts On ElectrolytesDocument11 pagesWhat Are Electrolytes? What Causes Electrolyte Imbalance?: Fast Facts On ElectrolytesL InfiniteNo ratings yet
- Review of The TheoryDocument8 pagesReview of The TheoryPriskaCliquersNo ratings yet
- Hiponatremia Acute ApendicitisDocument13 pagesHiponatremia Acute ApendicitisDeliciousNo ratings yet
- Reading Synthesis # 2: San Roque Extension, Roxas City, Capiz, Philippines 5800Document15 pagesReading Synthesis # 2: San Roque Extension, Roxas City, Capiz, Philippines 5800Jay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- SIADH, DI and Cerebral Salt Wasting: Karim Rafaat, MDDocument54 pagesSIADH, DI and Cerebral Salt Wasting: Karim Rafaat, MDMahendra PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, Usp: Visiv ContainerDocument13 pages0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, Usp: Visiv ContainerZelin Yair Chavez HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Salt Wasting Syndrome ReviewDocument6 pagesCerebral Salt Wasting Syndrome ReviewSoewira Sastra100% (1)