0% found this document useful (0 votes)
213 views10 pagesGas Meter
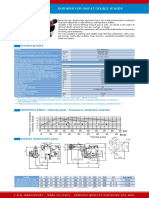
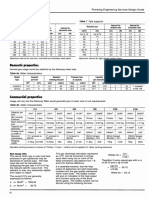
The document discusses gas meter selection and reading for measuring gas consumption. It provides information on gas meter types, technical specifications for diaphragm gas meters, how to convert gas volume measurements to mass using correction factors accounting for temperature and pressure, and energy content values for different gases.
Uploaded by
cadtechnologiesdesignCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
213 views10 pagesGas Meter
The document discusses gas meter selection and reading for measuring gas consumption. It provides information on gas meter types, technical specifications for diaphragm gas meters, how to convert gas volume measurements to mass using correction factors accounting for temperature and pressure, and energy content values for different gases.
Uploaded by
cadtechnologiesdesignCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd