Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical Assignment
Uploaded by
SKANDAN BHARADWAJOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Assignment
Uploaded by
SKANDAN BHARADWAJCopyright:
Available Formats
ACTIVITY-1
DC REGULATED POWER SUPPLY
BY:
SKANDAN BHARADWAJ K – 4NI22EC104
SOMANTH GOWDA H D – 4NI22EC105
SHREYAS B BALAGAVI – 4NI22EC101
SINCHANA GANAPATHI HEGDE – 4NI22EC103
SHRINIDHI S GADA – 4NI22EC102
ECE DEPT, NIE SOUTH CAMPUS PAGE- 1
ACTIVITY-1
DC REGULATED POWER SUPPLY
GENERAL BLOCK DIAGRAM OF POWER SUPPLY:
The general block diagram for this project is given below. It is very
simple. It has the following four main sub-blocks.
• The Transformer
• The Rectifier Circuit
• The Filter
• The Regulator
INPUT TRANSFORMER:
A transformer is a device that can step up or step down voltage levels,
following the law of conversation of energy. 9-0-9 step down
Transformer is used.
Input voltage from Transformer = 230V
Frequency = 50Hz
We need the input transformer to step down the incoming AC to our
required lower level such that output is 5V (DC).
ECE DEPT, NIE SOUTH CAMPUS PAGE- 1
ACTIVITY-1
RECTIFIER CIRCUIT:
The stepped-down voltage is still AC. To convert it into DC, we need
a good rectifier circuit .A bridge rectifier is used in the following
circuit. We can define bridge rectifiers as a type of full-wave rectifier
that uses four or more diodes in a bridge circuit configuration to
efficiently convert alternating (AC) current to a direct (DC) current.
Diode’s used: IN4007
Voltage required to turn on the Diode: 0.7V
When an AC signal is applied across the bridge rectifier:
terminal A becomes positive during the positive half cycle while
terminal B becomes negative. This results in diodes D1 and D3
becoming forward biased while D2 and D4 becoming reverse biased.
During the negative half-cycle, terminal B becomes positive while
terminal A becomes negative. This causes diodes D2 and D4 to become
forward biased and diode D1 and D3 to be reverse biased.
THE FILTER:
The rectifier circuit converts the incoming AC to DC but unluckily it
does not make it a pure DC. The output of the rectifier is pulsating and
is called pulsating DC. A filter circuit in which the first element is a
capacitor connected in parallel with the output of the rectifier in a linear
power supply. The capacitor increases the DC voltage and decreases
the ripple voltage components of the output.
THE REGULATOR:
A regulator is the linear integrated circuit used to provide a regulated
constant output voltage. It consists of a Zener diode and a load resistor.
Voltage regulators keep the voltages from a power supply within a
range that is compatible with the other electrical components. It
maintains a fixed output voltage.
ECE DEPT, NIE SOUTH CAMPUS PAGE- 1
ACTIVITY-1
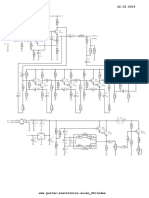
CIRCUIT DESIGN:
THEORITICAL VALUES BY CALCULATION:
Vout = 5V
ILmax = 10mA
RLmin = 500 Ohm
Is = 12mA
VCD = 11.382V
Rs = 530 Ohm
R’L = 1030 Ohm
We have considered the repel factor to be 0.01.
C = 0.000280 Farad
We have considered the minimum current through Zener as:
Izmin = 2mA
We have considered VDon as 0.7V
ECE DEPT, NIE SOUTH CAMPUS PAGE- 1
ACTIVITY-1
EXPERIMENTAL VALUES:
ECE DEPT, NIE SOUTH CAMPUS PAGE- 1
ACTIVITY-1
CONCLUSION:
In conclusion, a DC regulated supply plays a crucial role in providing
consistent and reliable power to various electronic devices and systems.
By maintaining a stable output voltage regardless of fluctuations in
input voltage or load variations, it ensures the proper functioning and
longevity of sensitive components. This technology finds extensive
application in industries such as electronics, telecommunications,
automation, and more. The ability to deliver precise and controlled DC
power not only enhances the efficiency of devices but also contributes
to overall system safety and performance. As technology continues to
advance, DC regulated supplies will likely remain an integral part of
powering modern electronics and driving innovation across various
sectors.
ECE DEPT, NIE SOUTH CAMPUS PAGE- 1
You might also like
- Wi-Fi Home AutomationDocument23 pagesWi-Fi Home Automationchandru_8No ratings yet
- LCD Led Screen Panel Repair Guide 2016 PDFDocument278 pagesLCD Led Screen Panel Repair Guide 2016 PDFAsus X45577% (13)
- Lecture On Power SupplyDocument81 pagesLecture On Power SupplyMATE0100% (2)
- Step Timing Control Electronic Control UnitDocument9 pagesStep Timing Control Electronic Control Unitricardolechuga100% (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Project Report of A Variable Power SupplyDocument21 pagesProject Report of A Variable Power SupplyTalha Saeed100% (3)
- DC Regulated Power SupplyDocument15 pagesDC Regulated Power SupplyMegha Projects100% (1)
- AC To DC Project ReportDocument2 pagesAC To DC Project ReportAryaan Revs0% (1)
- Project Report Regulated Power SupplyDocument36 pagesProject Report Regulated Power SupplyPeerzada Wahid75% (12)
- Schneider NS800Document64 pagesSchneider NS800Anonymous Lh3Yh8basINo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply DocumentationDocument4 pagesDC Power Supply DocumentationAashi BhawsarNo ratings yet
- DC Regulated Power SupplyDocument14 pagesDC Regulated Power SupplyMegha Projects100% (2)
- 01m Adaptation Basic SettingDocument4 pages01m Adaptation Basic SettingEmma MummyNo ratings yet
- Regulated Power Supply Made by - Rajat AggarwalDocument37 pagesRegulated Power Supply Made by - Rajat AggarwalSONUAGGARWAL23338871% (35)
- Lic Report 14 - 4 Final2Document12 pagesLic Report 14 - 4 Final2Harshvardhan MishraNo ratings yet
- Variablepowersupply MICRO-PROJECT ORGDocument21 pagesVariablepowersupply MICRO-PROJECT ORGAbhishek HatagaleNo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply CircuitDocument7 pagesDC Power Supply CircuitEhtasham Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- SCE-Hardware Configuration S7-1500 (2016)Document256 pagesSCE-Hardware Configuration S7-1500 (2016)Jorge_Andril_5370No ratings yet
- Indian Power Market, Power Exchange - Bangladesh PerspectiveDocument50 pagesIndian Power Market, Power Exchange - Bangladesh PerspectiveSanuwar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument14 pagesPower Supplyapi-314840968No ratings yet
- 5V Power SupplyDocument20 pages5V Power SupplyAnujNo ratings yet
- DC Power SUPPLY BUILDING COMPETITIONDocument15 pagesDC Power SUPPLY BUILDING COMPETITIONHafsa aminNo ratings yet
- 0-12v Variable Power SupplyDocument19 pages0-12v Variable Power Supplygirigtr2010100% (1)
- Febrication of Remote Control Gantry CraneDocument46 pagesFebrication of Remote Control Gantry CraneDebashishParidaNo ratings yet
- Power Supply ProjectDocument16 pagesPower Supply ProjectMichal ValakovičNo ratings yet
- Project Engineering Workshop Report 2045125Document10 pagesProject Engineering Workshop Report 2045125Talha HashmiNo ratings yet
- Adjustable DC Power Supply 0-30V: Laboratory Project Report Semiconductors Devices LabDocument5 pagesAdjustable DC Power Supply 0-30V: Laboratory Project Report Semiconductors Devices LabMISHAL FATIMANo ratings yet
- Project 1-Group 5Document14 pagesProject 1-Group 5Minh DangNo ratings yet
- Regulated DC Power Supply: A Presentation OnDocument24 pagesRegulated DC Power Supply: A Presentation OnRavinder SinghNo ratings yet
- DC Power SupplyDocument4 pagesDC Power SupplySohaib Ahmed100% (1)
- Reduction of AC MainsDocument3 pagesReduction of AC MainsFaizan NaeemNo ratings yet
- List of ComponentsDocument13 pagesList of ComponentsBenita AgbagwaraNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument36 pagesBasic Electronicswhatsapp status clipsNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Linear DC Power SupplyDocument56 pagesTopic 1 Linear DC Power SupplyKu AliyaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 - Creativity LabDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 1 - Creativity LabhloNo ratings yet
- PhysicsprojectDocument7 pagesPhysicsprojectgamerdk6577No ratings yet
- Asmat Ullah (70069423) Experiment:5: Circuit DiagramDocument11 pagesAsmat Ullah (70069423) Experiment:5: Circuit DiagramAsmat NiaziNo ratings yet
- 5v DC SupplyDocument19 pages5v DC SupplyDev Agarwal100% (1)
- 230v Ac To 12v DC and 5v DC Regulated Power ConverterDocument4 pages230v Ac To 12v DC and 5v DC Regulated Power ConvertershrianantNo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply ReporDocument19 pagesDC Power Supply ReporAbhay SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 12Document36 pagesUnit 12ahmed bashaNo ratings yet
- First Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorDocument9 pagesFirst Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorzaidNo ratings yet
- 12 Volt To 230 Volt Inverter Circuit Diagram Using IC 555Document26 pages12 Volt To 230 Volt Inverter Circuit Diagram Using IC 555Mohit Jatav0% (1)
- Mutual InducationDocument8 pagesMutual Inducationsibi johnNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument16 pagesAcknowledgementSourav MahariNo ratings yet
- Security Alarm For Doors, Almirah, Cupboards Using Opam Design in Protieus 4 1Document30 pagesSecurity Alarm For Doors, Almirah, Cupboards Using Opam Design in Protieus 4 1DebashishParida100% (1)
- Final ReviewDocument19 pagesFinal ReviewSanyam JainNo ratings yet
- Dav Cps Mandi: Physics Project ReportDocument17 pagesDav Cps Mandi: Physics Project Reportparasthakur.2007xNo ratings yet
- 2011 Important PDFDocument6 pages2011 Important PDFShaheer DurraniNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices and Circuit Lab ManualDocument46 pagesSemiconductor Devices and Circuit Lab ManualManu anand100% (1)
- ED REPORT (GRP 3)Document9 pagesED REPORT (GRP 3)Shreyas MarudwarNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Bridge RectifierDocument8 pagesFull Wave Bridge RectifierPurabi DasNo ratings yet
- Vishwa Physics Project New (1) (Repaired) - Vishwa SundarDocument21 pagesVishwa Physics Project New (1) (Repaired) - Vishwa Sundarcoolharini18102006No ratings yet
- Minor Project Repor1Document40 pagesMinor Project Repor1Manpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Lab Innovation Project DC DCDocument15 pagesLab Innovation Project DC DCAyush MittalNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and InstrumentationDocument15 pagesDepartment of Electronics and InstrumentationRajeshwariNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document18 pagesUnit 4H. ShekharNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering North South UniversityDocument12 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Computer Engineering North South UniversityFaria SharifNo ratings yet
- Power Supply 1Document6 pagesPower Supply 1api-19786583No ratings yet
- Group I WorkDocument12 pagesGroup I WorkKalu SamuelNo ratings yet
- Types of Voltage Regulator and DC Power Supply NotesDocument23 pagesTypes of Voltage Regulator and DC Power Supply NotesSorry studyNo ratings yet
- Project PhysicsDocument19 pagesProject Physics84863755511No ratings yet
- UNIT 1-DC Power SupplyDocument30 pagesUNIT 1-DC Power SupplyMuizz ZainolNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operation Manual: Bt100 1 GHZ Broadband Telecommunications AmplifierDocument52 pagesInstallation and Operation Manual: Bt100 1 GHZ Broadband Telecommunications AmplifierLuis DiazNo ratings yet
- SIRADEL MMW Propagation 2Document11 pagesSIRADEL MMW Propagation 2Prabhakar SinghNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation PDFDocument1 pageInstrumentation PDFFerliemNo ratings yet
- Practical Application of Facts in Power SystemDocument5 pagesPractical Application of Facts in Power Systemshashi kishorNo ratings yet
- Ee 739 ProjectDocument11 pagesEe 739 ProjectTanuj KumarNo ratings yet
- SRAS GuidelinesDocument28 pagesSRAS GuidelinesJack ClarkeNo ratings yet
- CN202SR-Electrical Wiring Diagrams - 2019 - 10 - 18 NEW PDFDocument378 pagesCN202SR-Electrical Wiring Diagrams - 2019 - 10 - 18 NEW PDFLamro TambaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Audible Noise and Magnetic Fields: Vollmer Substation and Transmission Line ProjectDocument20 pagesAnalysis of Audible Noise and Magnetic Fields: Vollmer Substation and Transmission Line ProjecteNo ratings yet
- Ds Ruckus r320Document5 pagesDs Ruckus r320nothingtoloseNo ratings yet
- BEC Micro Project (Report)Document14 pagesBEC Micro Project (Report)roshni60% (5)
- IS 8783 (Part-4-Sec.1) - 1995 - HR PVC Insulated - Winding Wires For Submersible MotorsDocument10 pagesIS 8783 (Part-4-Sec.1) - 1995 - HR PVC Insulated - Winding Wires For Submersible Motorsshivam dwivediNo ratings yet
- Signal and Power Isolated RS-485 Transceiver With 15 KV ESD ProtectionDocument22 pagesSignal and Power Isolated RS-485 Transceiver With 15 KV ESD ProtectionAndryasDoniIraniNo ratings yet
- WLP Physics 2Document4 pagesWLP Physics 2RenlieLegaspiNo ratings yet
- PS18/28/35/38/48 Series Iii Bass Module Dsp/Amp Boardpcb P/N 309887 Rev 01 Sheet 1 of 12Document14 pagesPS18/28/35/38/48 Series Iii Bass Module Dsp/Amp Boardpcb P/N 309887 Rev 01 Sheet 1 of 12Sv KoNo ratings yet
- PSA Unit-3Document25 pagesPSA Unit-3yvkrishnareddyNo ratings yet
- QW 482 Suggested Format For Welding Procedure Specifications WPSDocument3 pagesQW 482 Suggested Format For Welding Procedure Specifications WPSmohamedqcNo ratings yet
- Creepage Distance For PCBs Handling Line Voltage AC - Electrical Engineering Stack ExchangeDocument5 pagesCreepage Distance For PCBs Handling Line Voltage AC - Electrical Engineering Stack ExchangeboisolivierNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesElectrical and Electronics EngineeringSrinivasaraoNo ratings yet
- Load Sharing Module: ApplicationsDocument2 pagesLoad Sharing Module: ApplicationsGonzalo Villalobos SanchezNo ratings yet
- 4-2 ECE R13 Syllabus TSSNDocument21 pages4-2 ECE R13 Syllabus TSSNnagaraniNo ratings yet
- Univibe ENGDocument5 pagesUnivibe ENGba3jarNo ratings yet
- Samsung Gcr26asa Chassis La26a450c1 LCD PDFDocument160 pagesSamsung Gcr26asa Chassis La26a450c1 LCD PDFkanakNo ratings yet
- Circular 1573640299117 - Tricolite Industry Project ReportDocument38 pagesCircular 1573640299117 - Tricolite Industry Project ReportLevelUp PresentsNo ratings yet
- 03 - Sensors - Sensor Input ManagementDocument14 pages03 - Sensors - Sensor Input ManagementLeca GeorgeNo ratings yet