Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6613b19a1e5d830018ae7da9 - ## - Lecture Planner - Maths
Uploaded by
redlegend6060 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views9 pagesOriginal Title
6613b19a1e5d830018ae7da9_##_Lecture Planner _ Maths
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views9 pages6613b19a1e5d830018ae7da9 - ## - Lecture Planner - Maths
Uploaded by
redlegend606Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
VP LIVE: Arjuna 1.
0 | Target JEE 2026 | (Hindi+English)
Maths
S No Chapter Lec No Topics Sub - Topics
1 Basic Maths 1 Modulus Equation Quadratic modulus functions
2 Basic Maths 2 Modulus Inqualities Linear modulus functions
3 Basic Maths 3 Logarithm Properties of Logarithms
4 Basic Maths 4 Logarithm Logarithmic Equations
5 Basic Maths 5 Logarithm Logarithmic Inequalities
Introduction of set
Roster Or Tabular Form
Set-Builder Form
Empty Set
Singleton Set
Sets and Their Finite Set
Representation, Kinds Infinite Set
6 Set Theory 1 of Set Cardinal Number Or Order of A Finite Set
Equal Sets
Equivalent Sets
Subsets ( proper )
Subsets ( improper )
Power Set
Universal Set
Subsets of set of real numbers
Intervals as subsets of R
Venn diagram
Union of Sets
Intersection of Sets
Disjoint Sets
Differences of Two Sets
Analysis of Two Sets, Symmetric Difference of Two Sets
7 Set Theory 2 Operations On Sets
De Morgans Law
Algebra On Sets
Properties of Operation of Intersection
Properties of the operation of union
Complement of a Set
Complement laws
Law of double complementation
Practical Problems On Laws of empty set
Union and Intersection Idempotent laws
of Two Sets, Practical Identity laws
Problems On Union Commutative laws
and Intersection of Associate laws
8 Set Theory 3 Two Sets Distributive laws
Analysis of Two Sets,
Operations On
Setsand Problem
based on venn
9 Set Theory 4 diagram Practice Problems
Radian or Circular measure
Arc-angle relation
Systems For Relation between degree and radian measure
Trigonometric Measurement of An
10 Functions 1 Angle
Values of Trigonometric Functions For Some Specific Angles
Sign of Trigonometric Functions
Range and domain of trigonometric functions
Trigonometric Ratios of Allied Angles.
compound angles
Graph of standard trigonometric function
Trigonometric Trigonometric Trigonometric Ratios of Allied Angles.
11 Functions 2 Functions Trigonometric identities
Transformation Formulae
Trigonometric Trigonometric Ratios Trigonometric Ratio of An Angle 2A In Terms of An Angle A
12 Functions 3 of Multiple Angles Trigonometric Ratio of An Angle 3A In Terms of An Angle A
Trigonometric Ratios
Trigonometric In Sub-Multiple Angles Trigonometric Ratios In Sub-Multiple Angles In Their Domain
13 Functions 4 In Their Domain Analysis of The Form Y = A Sin X ± B Cos X
Conditional
Trigonometric Trigonometrical
14 Functions 5 Identities Conditional Trigonometrical Identitie
Conditional
Trigonometric Trigonometrical
15 Functions 6 Identities Sum of Some Trigonometric Series
Conditional
Trigonometric Trigonometrical
16 Functions 7 Identities Practice Problems
Trigonometric
17 Functions 8 ?? ??
Trigonometric Principal Value
18 Equation 1 General Solution general solutions of Basic Trigonometric Equations
Trigonometric
19 Equation 2 Inequalities Inequalities in Trigonometric Equation
Number Of Solutions
Trigonometric of Trigonometric
20 Equation 3 Equations Number Of Solutions of Trigonometric Equations
Number Of Solutions
Trigonometric of Trigonometric
21 Equation 4 Equations Number Of Solutions of Trigonometric Equations
Condition For One Common Root Between Two Quadratic Equations
Condition For Condition For Two Quadratic Equations To Have Both Roots Common
Quadratic Common Root(S) of Formation of equation with given roots
22 Equations 1 Quadratic Equations Symmetric function of the roots
Quadratic Expression
Sign of Quadratic Expression
Quadratic Sign of Quadratic Graphs of Quadratic Expressions
23 Equations 2 Expression,
Formation of New Relation Between Roots and Coefficients of A Polynomial Equation
Equations With The Analysis of Cubic Equation
Quadratic Help of Given Formation of New Equations With The Help of Given Equations
24 Equations 3 Equations nature of graphs of cubic
Quadratic Expression In Two Variables
Quadratic Expression MAX AND MIN VALUE
Quadratic In Two Variables, Position of A Number With Respect To Roots of An Equation
25 Equations 4 Location of roots Multiplicity Theorem
Quadratic Expression In Two Variables
Quadratic Quadratic Expression MAX AND MIN VALUE
26 Equations 5 In Two Variables and Conditions on Common roots.
Quadratic Expression In Two Variables
Quadratic Expression MAX AND MIN VALUE
Quadratic In Two Variables, Position of A Number With Respect To Roots of An Equation
27 Equations 6 Location of roots Multiplicity Theorem
Quadratic Expression
Quadratic In Two Variables,
28 Equations 7 Location of roots Problems Practice
Quadratic
29 Equations 8
Sequences ( definition )
Different type of sequence
General term of sequence
Series
Nth Term of A.P.
Properties of An A.P.
Sequences, Series, Sum To N Terms of An A.P.
Sequence & Arithmetic Progression Arithmetic Mean
30 Series 1 (A.P.) Important properties of arithmetic mean
Nth Term of a G.P.
Sum To N Terms of a G.P.
Sum of infinite terms of a G.P.
Properties of G.P.
Sequence & Geometic Progression Geometric Mean (G.M.)
31 Series 2 (G.P.) Important properties of Geometric mean
Arithmetic -Geometric Arithmetic -Geometric Series (Agp)
Sequence & Series (Agp), Nth Term
32 Series 3 Harmonic Progression Harmonic Mean(S)
A.M. and G.M. Inequality and Its Application
A.M.,G.M. and H.M. of two positive real numbers
A.M. and G.M. Sum To First N Natural Numbers
Inequality and Its Sum of Squares of The First N Natural Numbers
Application, Sum To N To Find The Sum of The Cubes of The First N Natural Numbers
Sequence & Terms of Special Special series
33 Series 4 Series Sum of series by method of difference
Sequence & Telescopic Sums and Telescopic Sums and Products
34 Series 5 Products,
Definition
General term of A.G.P.
Sum of n terms of A.G.P
Sequence & Sum of an infinite Arithmetic- Geometric sequence
35 Series 6 Miscellaneous series Sum of infinity of the series reducible A.G.P.
Definition
General term of A.G.P.
Sum of n terms of A.G.P
Sequence & Sum of an infinite Arithmetic- Geometric sequence
36 Series 7 Miscellaneous series Sum of infinity of the series reducible A.G.P.
Sequence & Sum of an infinite Arithmetic- Geometric sequence Sum of infinity of the
37 Series 8 Miscellaneous series series reducible A.G.P
Sequence &
38 Series 9 Miscellaneous series Sum of an Arithmetic Series using V-N method
Sequence &
39 Series 10 Miscellaneous series Special series
Definition of Binomial Expression
Pascals Triangle
Definition of Binomial Binomial Theorem For A Positive Integral Index
Expression, General Some Special Forms of Binomial Theorem
Binomial Term In The Problems Based On Direct Expansion
40 Theorem 1 Expansion of (A + X)N General Term In The Expansion of (A + X)N
Case-I : When N Is An Even Number
Case-Ii : When N Is An Odd Number
Binomial Middle Term In The Problems Based On General Term, Particular Terms and Middle Term In A
41 Theorem 2 Expansion of (A + X)N Given Binomial Expansion
Numerically Greatest
Binomial Term In The Binomial Greatest Binomial Coefficient
42 Theorem 3 Expansion Numerically Greatest Term In The Binomial Expansion
Sum of Binomial Coefficients
Use of Differentiation
Use of Integration
Bino-Arithmetic Series
Bino-Geometric Series
Binomial Properties of Binomial Bino-Harmonic Series
43 Theorem 4 Coefficients Bino-Binomial Series
Application of Binomial expansion (Finding remainder using Binomial
theorem
Expansion of (x+y)^n+-(x-y)^n
Binomial Use of complex number in Binomial theorem
44 Theorem 5 Multinomial Theorem Multinomial Theorem
An Important Concept of Binomial Theorem
Binomial Theorem For Any Index
Some Useful Binomial Expansion For Negative Indices
Binomial Theorem For Binomial inside Binomial
Binomial Any Index, Sum of Sum of series
45 Theorem 6 series Series from multiplication of two series
Multiplication Principle
Addition Rule
Factorial Notation
Permutation & Fundamental Principle Some results related to factorial n
46 Combinations 1 of Counting Exponent of prime n!
Permutation & Permutations of Things All Distinct
47 Combinations 2 Permutations Permutations of Things Not All Distinct
Number of Permutations Under Certain Restrictions
Number of Number of permutation of n different things taken r at a time when each
Permutation & Permutations Under thing can be repeated any number of times
48 Combinations 3 Certain Restrictions Clockwise and anti-clockwise arrangment.
Circular Permutation (Nqr Or Q(N, R))
Rank of A Word In Dictionary
Combinations
Circular Permutation properties of ncr
(Nqr Or Q(N, R)), Special Uses of Ncr
Permutation & Divisors, Divisibility Restricted Combination
49 Combinations 4 rule Divisors, Number Divisible By 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 11, 13
Sum of The Numbers Sum of The Numbers Formed By N-Digits
Permutation & Formed By N-Digits, Division Into Groups
50 Combinations 5 Division Into Groups Equal Division of Objects
Distribution Into Groups
Total number of sections of one or more things from p identical things of
one type
q identical things of another type, r identical things of the third type and n
different things
Permutation & Distribution Into Distribution of n distinct objects into r distinct boxes if in each box at least
51 Combinations 6 Groups one object is placed
Arrangement Into Groups
Number of Integral Solution of An Equation
Application of Multinomial Expansion
Multinomial theorem
Different Cases of multinomial theorem and its applications
Highest Power of A Prime P In N!
Highest Power of A Composite Number M In N!
Multinomial theorem, Highest Power of A Prime Number P In Ncr
Derangements, Highest Power of A Prime Number P In Npr
Exponent of A Prime Principle of inclusion and exclusion
Permutation & Number In N!, Ncr and Derangements
52 Combinations 7 Npr
Permutation &
53 Combinations 8 ?? ??
Analysis of Quadrants
Distance Formula
Section Formula (interior)
Section Formula( exterior)
Section Formula
Area of Polygon
Area of a triangle
Condition For Collinearly
Cartesian Coordinates, Centriod (G)
Area of Polygon, Incentre (I)
Condition For Excentres
Collinearly,Different Orthocentre (H)
Centres of A Triangle Circumcentre (O)
54 Straight Lines 1 Abc Having Vertices properties related to Different Centre
Some Important Points About The Quadrilateral
locus Problems
Slope of Line
Angle Between The Lines
Parallel To Axes
Point-Slope Form
Two-Point Form
Slope-Intercept Form
Locus, Slope of Line, Intercept-Form
Angle Between The Normal Form
Lines, Different Forms Parametric Form
55 Straight Lines 2 of Straight Lines General Form
Position of Two Points
56 Straight Lines 3 Relative To A Line Position of Two Points Relative To A Line
Position of A Point
Which Lies Inside A
57 Straight Lines 4 Triangle Position of A Point Which Lies Inside A Triangle
Image Reflection, Foot of Perpendicular, Perpendicular Distance of A Point
With Respect To A Line
Point of Intersection
Parallel Lines
Perpendicular Lines
Distance Between Two Parallel Lines
Image Reflection, Foot Image of One Line Through The Other Line Mirror
of Perpendicular, Family of Lines
Perpendicular Equations of Straight Line Passing Through A Given Point and Making A
Distance of A Point Given Angle With A Given Straight Line
With Respect To A Condition for the lines to be parallel
Line Condition for the lines to be perpendicular
58 Straight Lines 5 Analysis of Two Lines Angle between two straight lines when their equations are given
Working Rule For Finding The Equation of Bisector of The Angle Containing
The Origin
Working Rule For Finding Acute (Internal) and Obtuse (External) Angle
Bisectors
Working Rule To Find The Equations of The Internal Bisectors of A Triangle
Analysis of Three Lines
Concurrency of three lines
Analysis of Quadrilateral
Shifting of Origin
Rotation of Axis
Pair of Straight Lines Passing Through (0, 0)
Combined Equation of Lines
Separation of Lines Represented By S = 0
Equation of The Point of Intersection
Bisectors, Pair of Angle Between The Lines Represented By S = 0
Straight Lines,General Equation of Angle Bisector
Equation of The Parallel Lines
59 Straight Lines 6 Second Degree Homogenisation
Equation of The
Bisectors, Pair of Pair of Straight Lines Passing Through (0, 0) Combined Equation of Lines
Straight Lines,General Separation of Lines Represented By S = 0 Point of Intersection Angle
Equation of The Between The Lines Represented By S = 0 Equation of Angle Bisector
60 Straight Lines 7 Second Degree Parallel Lines Homogenisation
61 Straight Lines 8 ?? ??
62 Straight Lines 9 ?? ??
Equation of circle with centre (h,k) and Radius r
General equation of circle
Equation of circle passing through three given points
Equation of circle on a given diameter
Parametric form of a circle
63 Circle 1 Equation of circle Intercepts made on axes by a circle
Different forms of the equations of a circle
Different forms of the Position of a point with respect to a circle
equations of a circle, Maximum and minimum distance of a point from the circle
Intersection of a line Intersection of a line and a circle
64 Circle 2 and a circle Segment of secant chords and tangent
Tangent to a circle at a given point
Different forms of the equations of tangents
Points of contact
Tangent from a point outside the circle
Length of the tangent from a point to a circle
Pair of tangent
Tangent of a circle, Normal to a circle at a given point, Director circle and its Equation
Normal to a circle at a Intersection of two circles
given point, Director Angle of intersection of two circles
circle and its Equation, Radical axis
Intersection of two Properties of the radical axis
65 Circle 3 circles, Radical axis Radical centre
Common chord of two circles
Length of the common chord
Equation of the chord Bisected at a given point
Problem based on locus
Equation of The Circle Having Tangent T = 0 At (X1,Y1) Is Given By (X -
X1)2 + (Y - Y1)2 + L T = 0
Common chord and Circle and Point
chord of contanct, Pair
66 Circle 4 of tangents Line and Circle
Family of Circles
Position of Two Circles
Radical Axis
Radical Centre of Three Circles
Family of Circles,
Analysis of Two Coaxial System of Circles
67 Circle 5 Circles,
Family of Circles
Position of Two Circles
Family of Circles, Radical Axis
Analysis of Two Radical Centre of Three Circles
68 Circle 6 Circles, Coaxial System of Circles
Family of Circles,
Analysis of Two
69 Circle 7 Circles, Practice problems
70 Circle 8 ?? ??
Locus Problems
Standard Equation of Parabola
Conic Sections: General equation of a Position of A Point Relative To A Parabola
71 Parabola 1 parabola Position of A Line With Respect To A Parabola
Equation of Tangent In Different Form
Equation of Director Circle
Conic Sections: Point of Intersection of Tangents At T1,T2
72 Parabola 2 Tangent And Normal Normal
Point of Intersection of normals At T1,T2
Properties of parabola
Equation of Chord With Middle Point (X1,Y1)
Conic Sections: Chord and pair of Equation of Diameter
73 Parabola 3 tangents Equation of Pair of Tangent
Properties of focal chord
Parabolic curve
Conic Sections: Recognition of conics
74 Parabola 4 Pair of tangents
Equation of Parabola when vertex is (h,k) and axis is parallel to x- axis
Equation of Parabola when vertex is (h,k) and axis is parallel to y- axis
Properties of normal
Co-normal Points and Circle through conormal points
Standard Equation of Reflection property of parabola
Conic Sections: Parabola, property of Properties of tangent
75 Parabola 5 tangent and normal Locus of point of intersection of tangent under different conditions
Standard Equation of
Conic Sections: Parabola, property of Properties of tangent Locus of point of intersection of tangent under
76 Parabola 6 tangent and normal different conditions and practice problems
Standard Equation of Ellipse
Parametric Form and Auxiliary Circle, Eccentric angle
Position of A Point
Conic Sections: Standard Equation of Point of Intersection of A Straight Line and Ellipse
77 Ellipse 1 Ellipse Director Circle of An Ellipse
Equation of Tangent
Equation of The Normal
Equation of Chord Passing Through (A Cosa, B Sina), (A Cosb, B Sinb)
Conic Sections: Equation of The Equation of The Chord With Middle Point (X1,Y1)
78 Ellipse 2 Tangent and Normal Equation of Pair of Tangents Form External Point (X1,Y1)
Diameter and Conjugate Diameter of An Ellipse
Equation of The Chord of Contact
Cyclic points on ellipse
Important properties related to tangent
Conormal points
Conic Sections: Equation of The Chord
79 Ellipse 3 and properties Some properties of ellipse
Diameter and Conjugate Diameter of An Ellipse
Equation of The Chord of Contact
Cyclic points on ellipse
Important properties related to tangent
Conormal points
Conic Sections: Equation of The Chord
80 Ellipse 4 and properties Some properties of ellipse
Standard Equation of The Hyperbola
Conic Sections: Standard Equation of Parametric Form and Auxiliary Circle, Eccentric angle
81 Hyperbola 1 The Hyperbola Point of Intersection of A Straight Line and A Hyperbola
Equation of Tangent
Equation of Normal
Director Circle of A Hyperbola
Conic Sections: Equation of The Equation of A Chord Whose Middle Point Is (X1,Y1)
82 Hyperbola 2 Tangent and Normal Equation of The Pair of Tangents From (X1,Y1)
Diameter and Conjugate Diameter of A Hyperbola
Position of point with respect to hyperbola
Conjugate hyperbola
Some properties of circle
Conic Sections: Equation of The Chord Equation of hyperbola referred to two perpendicular lines
83 Hyperbola 3 and properties Equation of chord joining two points
Asymptote
Rectangular Hyperbola
Rectangular Hyperbola Whose Asymptotes Are The Co-Ordinate Axes
Parametric Form
Equation of The Tangent
Conic Sections: Equation of The Normal
84 Hyperbola 4 Rectangular Hyperbola Asymptotes of hyperbola and its properties
Complex Definition of Complex Definition of Complex Numbers
85 Numbers - I 1 Numbers Real and Imaginary Part
Representation of Complex Numbers
Modulus of Complex Numbers
Properties of Modulus of Complex Numbers
Argument of A Complex Number
Properties of Argument of A Complex Number
Geometrical Representation
Complex Different Forms of Argument or Amplitude of z
86 Numbers - I 2 Complex Numbers..
Cartesian Form
Polar Form (R, Q)
Complex Different Forms of Euler Form
87 Numbers - I 3 Complex Numbers Vector representation of a complex number
Equality of Two Complex Numbers
Algebra of Complex Numbers
Geometrical Representation of Z1 + Z2
Subtraction
Multiplication
Division
Geometrical meaning of Algebric operations
Complex Algebra of Complex Triangle inequality
88 Numbers - I 4 Numbers Parallelogram law
conjugate of a complex number
Complex Conjugate of A Properties of Conjugate of A Complex Number
89 Numbers - II 1 Complex Number Logarithm of A Complex Number
Square Root of A
Complex Complex Number,
90 Numbers - II 2 Cube Roots of Unity Square Root of A Complex Number, Cube Roots of Unity
De-MoivreS Theorem
Complex nth roots of unity
91 Numbers - II 3 nth roots of unity
Section Formulae
Conditions For Quadrilateral
Rotation of Complex Numbers
Straight Line In Argand Plane
Complex Geometry of Complex Circle In Argand Plane
92 Numbers - II 4 Numbers Important Loci In The Argand Plane
nth roots of unity and
Complex Geometry of Complex
93 Numbers - II 5 Numbers Practice problems
Complex
94 Numbers - II 6 ?? ??
Determinate forms
Limits and ( Graphically)
95 Derivatives 1 Concept of limit Indeterminate forms
At infinity
Rationalisation
Limits and Factorisation
96 Derivatives 2 Methods to find a limit Trigonometric limit
By first principle
The sum of two function
Difference of two functions
Product of two functions
Limits and Quotient of two functions
97 Derivatives 3 Derivatives Chain rule
By first principle
The sum of two function
Difference of two functions
Product of two functions
Limits and Quotient of two functions
98 Derivatives 4 Derivatives Chain rule
Mean
Measure of central Median
99 Statistics 1 tendency Mode
Mean deviation of grouped and ungrouped data
Varience
100 Statistics 2 Standrard deviation Calculation of standard deviation
Coordinate Axes and Coordinate Planes In Three Dimensional Space
Coordinate Axes and Sign of Coordinates of A Point
Introduction to Coordinate Planes In Distance Between Two Points
Three Three Dimensional Internal Division
Dimensional Space External Division
101 Geometry 1 Section Formulae Collinearity of three points using section formula
Coordinate Axes and
Introduction to Coordinate Planes In
Three Three Dimensional
Dimensional Space
102 Geometry 2 Section Formulae Practice problems
Definition
Sample space
Sure and impossible events
Venn diagram ( 3 events A,B,C)
Exhaustive events
Exclusive events
Types of events and Complementary events
103 Probability 1 representation Equally likely events
De Morgan's Law
Addition theorems
At least one event of all
Simultaneous events
Neither of any event
Laws and Types of Geometrical problems
104 Probability 2 problems Continuous probability
Sine rule
Properties of Cosine rule
Triangle Projection formula
105 (Optional Topic) 1 Basic Properties Napier analogy
Half-Angles Formulae
Inradius , circumradius
Area of triangles
Pedal triangle
Circumcircle
Properties of Incircle
Triangle Exradius
106 (Optional Topic) 2 Triangular properties Circumradius
Regular Polygon
Properties of r1,r–R formula based
Triangle Regular Polygon, r1,r– Ambiguous case of triangle
107 (Optional Topic) 3 R formula based Distance between special points
Regular Polygon
Properties of r1,r–R formula based
Triangle Regular Polygon, r1,r– Ambiguous case of triangle
108 (Optional Topic) 4 R formula based Distance between special points
Height & Angle of Elevation and Depression
109 Distances 1 Heights and Distances Bearings of A Point
110
111
Ordered Pairs
Cartesian Product of Two Sets
Cartesian Product of Number of elements in cartesian product
112 Function 1 Sets Pictorial representation of cartesian product of two sets
Representation of Relation
Domain and Range of A Relation
113 Function 2 Relations Co-Domain of The Relation
Definition of A Function
Domain and Range
Graphical Transformation
Real Function
114 Function 3 Functions Features of A Mapping A To B
Rules For Finding Domain
Sign Scheme For Rational/Polynomial Function
115 Function 4 Domain Of Functions Domian of composite function
Method To Find The Range of A Function Y =F(X)
Range of composite functions
116 Function 5 Range of Functions Range Using A.M > G.M., Calculus and Misc.
Identity function
Constant function
Polynomial function
Rational functions
Modulus function
Greatest integer function
Signum function
Fractional part function
Classification of Exponential function
117 Function 6 Functions Logarithmic function
Addition of Two Real Functions
Algebra of Real Subtraction of A Real Function From Another
Functions, Multiplication of Two Real Functions
Replacement Property Quotient of Two Real Functions
118 Function 7 of Function Replacement Property of Function
You might also like
- Comprehensive Revision Planner-Final (Both)Document8 pagesComprehensive Revision Planner-Final (Both)Naman HemrajaniNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Class 11 Mathematics & Marking Scheme: Chaper 1Document3 pagesSyllabus For Class 11 Mathematics & Marking Scheme: Chaper 1PrajeevNo ratings yet
- Jee Main 2024 Maths SyllabusDocument8 pagesJee Main 2024 Maths Syllabusbholu803201No ratings yet
- XII Syllabus With Deleted PartDocument5 pagesXII Syllabus With Deleted PartlalithNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 9 T0 12 Mathematics Session 2022-23Document30 pagesSyllabus 9 T0 12 Mathematics Session 2022-23ARCHITA DHARNo ratings yet
- Your Paragraph TextDocument1 pageYour Paragraph TextChrisha ClorinaNo ratings yet
- Notes Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument28 pagesNotes Mathematics in The Modern WorldICE ADRIENNE OCAMPO100% (1)
- Topics in Calculus: Integration byDocument24 pagesTopics in Calculus: Integration byparryamanNo ratings yet
- Math SyllabusDocument2 pagesMath SyllabusYana Rico100% (1)
- Matrices & Linear Algebra Module G-20 (Maths) : Day Date DAY Unit Topic Sub-Topics Exercise InstructionsDocument2 pagesMatrices & Linear Algebra Module G-20 (Maths) : Day Date DAY Unit Topic Sub-Topics Exercise InstructionssagarNo ratings yet
- 01 Paper 01 Linear AlgebraDocument2 pages01 Paper 01 Linear AlgebraAvinash PalaparthiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Basic Structures: Sets, Functions, Sequences, and SumsDocument74 pagesChapter 2. Basic Structures: Sets, Functions, Sequences, and SumsTrà Nguyễn LongNo ratings yet
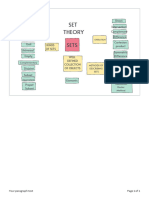
- Set TheoryDocument1 pageSet TheoryChrisha ClorinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Topic Review in Math Ed 809 by FUYONG BASILIO P1Document4 pagesLesson 1 Topic Review in Math Ed 809 by FUYONG BASILIO P1Jardy Gambong Fuentes IINo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS DIVISION For CLASS XII MATHEMATICS BY SUDHANSU JALI SIRDocument6 pagesSYLLABUS DIVISION For CLASS XII MATHEMATICS BY SUDHANSU JALI SIRsekharsudhansuNo ratings yet
- Math 241 Section 1.2 (3-2-2021)Document32 pagesMath 241 Section 1.2 (3-2-2021)H ANo ratings yet
- Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) in Python - Self PacedDocument4 pagesData Structures and Algorithms (DSA) in Python - Self PacedSakshamNo ratings yet
- 11th & 12th Math CBSE Se JEE Tak PDFDocument4 pages11th & 12th Math CBSE Se JEE Tak PDFHarsh Shah67% (3)
- Lecture Planner - MathsDocument11 pagesLecture Planner - Mathsadarahmittal123bariNo ratings yet
- Math 241 Section 2.2 (8-2-2021)Document25 pagesMath 241 Section 2.2 (8-2-2021)H ANo ratings yet
- JEE Main Most Asked Chapter and TopicsDocument59 pagesJEE Main Most Asked Chapter and TopicsMiss Rugvedha0% (1)
- Mste 1.0 Algebra Hand OutsDocument19 pagesMste 1.0 Algebra Hand OutsJasmine MartinezNo ratings yet
- Math 241 Section 1.1 (3-2-2021)Document21 pagesMath 241 Section 1.1 (3-2-2021)H ANo ratings yet
- Test TimetableDocument5 pagesTest TimetableVedant SangewarNo ratings yet
- JMJ Notre Dame-Siena College of PolomolokDocument5 pagesJMJ Notre Dame-Siena College of PolomolokJea TaladroNo ratings yet
- Untitled DiagramDocument1 pageUntitled Diagramjb jbNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: Subject: Eco. BBA - 1207 Subject: (Basic Mathematics I) Semester: BBA 1Document3 pagesCourse Outline: Subject: Eco. BBA - 1207 Subject: (Basic Mathematics I) Semester: BBA 1Muhammad HameedNo ratings yet
- JMJ Notre Dame-Siena College of PolomolokDocument5 pagesJMJ Notre Dame-Siena College of PolomolokJea TaladroNo ratings yet
- Civl ENGG SyllabusDocument45 pagesCivl ENGG SyllabusKenneth Joy SorianoNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Math (India) : Con Nue Number SystemsDocument2 pagesClass 9 Math (India) : Con Nue Number Systemsavijitcu2007No ratings yet
- Afda Vocab Cards 2016Document141 pagesAfda Vocab Cards 2016Anderson Nascimento100% (1)
- Class - XII Subject-Mathematics SyllabusDocument3 pagesClass - XII Subject-Mathematics Syllabus043 HimanshuNo ratings yet
- CLASS: 8th Class: PHASE PLANNER-2019-20Document1 pageCLASS: 8th Class: PHASE PLANNER-2019-20SMNo ratings yet
- RPS T.S. XI Class ScheduleDocument3 pagesRPS T.S. XI Class ScheduleMohit YadavNo ratings yet
- 6613b15c23d4d90018f2a31e - ## - Lecture Planner - PhysicsDocument6 pages6613b15c23d4d90018f2a31e - ## - Lecture Planner - Physicsredlegend606No ratings yet
- Checklist c1Document3 pagesChecklist c1Arwa HamdiNo ratings yet
- Linear AlgebraDocument205 pagesLinear AlgebratebaaanNo ratings yet
- PH SheetDocument40 pagesPH SheetBassem KhalidNo ratings yet
- Course 1 Course 5 TopicsDocument1 pageCourse 1 Course 5 Topicsmadellekylenetabinas01No ratings yet
- AAI ATC Junior Executive 2023 Victory Live BatchDocument5 pagesAAI ATC Junior Executive 2023 Victory Live Batchcesurgaming07No ratings yet
- WINSEM2020-21 CSE3020 ETH VL2020210504780 Reference Material I 13-Apr-2021 Tables-AsyncDocument65 pagesWINSEM2020-21 CSE3020 ETH VL2020210504780 Reference Material I 13-Apr-2021 Tables-AsyncRaghu narayana RaaviNo ratings yet
- Math 241 Section 2.1 (3-2-2021)Document20 pagesMath 241 Section 2.1 (3-2-2021)H ANo ratings yet
- Class 11 MATHSDocument2 pagesClass 11 MATHSAbhimanyu AbhirajNo ratings yet
- Curriculum MapDocument16 pagesCurriculum MapCris John AgpalzaNo ratings yet
- Higher Paper SkillsDocument1 pageHigher Paper SkillsTahmid SiraziNo ratings yet
- Cur Map Sample 2Document3 pagesCur Map Sample 2GIL tabilingNo ratings yet
- Afda Vocab Cards 2016Document143 pagesAfda Vocab Cards 2016Hatice A. GürhanoğluNo ratings yet
- 2023 GCE O Level Add Math 4049 P2 (Possible Topics)Document2 pages2023 GCE O Level Add Math 4049 P2 (Possible Topics)ko2686284No ratings yet
- 1st Quarter - Curriculum Map - Math 8Document6 pages1st Quarter - Curriculum Map - Math 8Grace Perez0% (2)
- Grade 8 Cur MapDocument6 pagesGrade 8 Cur MapSir Charles PedrenaNo ratings yet
- Form Two PDFDocument3 pagesForm Two PDFTalatouremi FruNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2018 Mathematics Crash Course - MathonGoDocument1 pageJEE Advanced 2018 Mathematics Crash Course - MathonGoNameet JainNo ratings yet
- Physics Syl Lab UsDocument8 pagesPhysics Syl Lab UsABHINAV KUMAR SHUKLANo ratings yet
- Lists of IntegralsDocument9 pagesLists of IntegralsEfika Ikenna BruceNo ratings yet
- 15.5 Mathematics (Ma)Document1 page15.5 Mathematics (Ma)Sai Tejesh Reddy GurijalaNo ratings yet
- List of Math SymbolsDocument10 pagesList of Math SymbolsMax WolfNo ratings yet
- New Assessment Scheme 2021-22 Class 11-12 - MathematicsDocument1 pageNew Assessment Scheme 2021-22 Class 11-12 - MathematicsAditya Pratap Singh 12ANo ratings yet
- SAT Scores AprilDocument4 pagesSAT Scores Apriljayvee armamentoNo ratings yet
- Item AnalysisDocument4 pagesItem Analysisangel rose medinaNo ratings yet
- 3 Square Root Spiral PDFDocument2 pages3 Square Root Spiral PDFAvinash WarkeNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics Trial SPM - Module 2 - Paper 2 PDFDocument20 pagesAdditional Mathematics Trial SPM - Module 2 - Paper 2 PDFJoanne WongNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- IB Mathematics HL Internal AssessmentDocument18 pagesIB Mathematics HL Internal AssessmentZinzan Gurney100% (20)
- Rational and Irrational NumbersDocument11 pagesRational and Irrational NumbersRoberta Gonzales SisonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Vector and Geometry SpaceDocument66 pagesChapter 10 - Vector and Geometry SpaceRiyad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics 1Document2 pagesEngineering Mathematics 1ofreneo_joshua4437No ratings yet
- Numerical Methods: Module 2 Part 2 by Carlos Hortinela IVDocument11 pagesNumerical Methods: Module 2 Part 2 by Carlos Hortinela IVBenj MendozaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics PracticeDocument2 pagesMathematics PracticeHishq DhimanNo ratings yet
- LAS Math9 Q3 Wk1 Quadrilaterals PDFDocument11 pagesLAS Math9 Q3 Wk1 Quadrilaterals PDFRodel EsparragoNo ratings yet
- Ms Bank 0606Document200 pagesMs Bank 0606crampingpaul50% (2)
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 9 Mathematics Kite and Its PropertiesDocument3 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 9 Mathematics Kite and Its PropertiesHazel LiwanagNo ratings yet
- 10 Sample Paper Chennai Region 2Document11 pages10 Sample Paper Chennai Region 2Illaya BharathiNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics in The Modern World: Submitted To: Genero BatocaelDocument14 pagesGeneral Mathematics in The Modern World: Submitted To: Genero BatocaelJoh Na AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Hints & Solutions: Jee Preparatory Test-2 (Jpt-2)Document20 pagesHints & Solutions: Jee Preparatory Test-2 (Jpt-2)pranjalNo ratings yet
- Computer Arithmetic 1. Addition and Subtraction of Unsigned NumbersDocument19 pagesComputer Arithmetic 1. Addition and Subtraction of Unsigned NumbersSai TrilokNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-9. DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONSDocument4 pagesHsslive-9. DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONSTeam Electrical inspectorNo ratings yet
- NSS Mathematics in Action - 4B08Document57 pagesNSS Mathematics in Action - 4B08Angel’s StudygramNo ratings yet
- TOS-Math 7 1st QuarterDocument2 pagesTOS-Math 7 1st QuarterAngelou Tingson100% (1)
- MMC 2018 10a SecDocument2 pagesMMC 2018 10a SecMark-Honey Boquiron Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Module 2 ActivityDocument4 pagesDigital Electronics Module 2 ActivityWilma NaderaNo ratings yet
- 2002 AMC 12A ProblemsDocument5 pages2002 AMC 12A ProblemsjabagaweeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 MATH13-1Document23 pagesLesson 3 MATH13-1akladffja100% (1)
- 9709 Y20-22 Sow Pure1 v1Document35 pages9709 Y20-22 Sow Pure1 v1James100% (1)
- Numerical Methods Roots of Equation Chapter OneDocument5 pagesNumerical Methods Roots of Equation Chapter Oneadnan-651358No ratings yet
- Work Sheet Class 9 PDFDocument12 pagesWork Sheet Class 9 PDFBurhan SyedNo ratings yet
- Reduced Syllabus of JEE Main Mathematics - MathonGo-1699082353228Document21 pagesReduced Syllabus of JEE Main Mathematics - MathonGo-1699082353228astrophysicistanantNo ratings yet
- IOQM 2022 Practice Test-07Document2 pagesIOQM 2022 Practice Test-07AkashNo ratings yet