Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brakes Formula
Brakes Formula
Uploaded by
20mec06sriram0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesOriginal Title
brakes formula
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesBrakes Formula
Brakes Formula
Uploaded by
20mec06sriramCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
REVIEW AND SUMMARY
Drake S a mechanical device by neans of which motion of a body is
retarded for
Slowmg down or to bring it to rest, by applying artificial frictional
I he main (ypes of mechanical brakes are block or resistance.
shoe brakes, band brakes, band and
block brakes, internal expamding shoe brakes, and external
Three types of brake linings used are contracting brakes.
organic. semi-metallic and metallic limingS
Braking torque in Block or shoe brake is given by
(a)
a- C fwhen the rotation of drum is clockwise]
(b)
at lC when the rotation of drum is anticlockvise]
where T7 = Braking torque,
r = Radius of drum,
F = Force applied at lever end,
u = Coefficient offriction, and
a, c&l = Dinnensions of lever.
Eguivalentcoefficient of friction (u) used when 20> 40is given by
tu sin O
20 sin 20
where 20 = Angle of contact
Braking torgue in Double block or double shoe brake is given by
I = ur (Ryy Ry)
where r = Radius of drun,
Ryy & Ry = Normal reaction on the lefi and right hand side shoes
respectively.
In Band brake system.
Tension ratio, and
Braking torque, IB =(1-Tyr
where T, and T, = Tension in the band on tight and siack sides respectively.
0 - Angle of lap. and
=
r = Rudius of the drum.
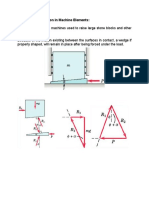
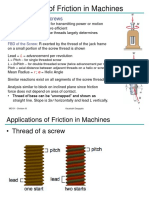
Force applied on the lever in Simple band brake is given by
b
(i) F= 11a [For clockwise rotation of the drun]
b
(i) [For anticlockw ise rotation of the drum]
For notations a, b, T,and T, refer Fig. l1. 11.
Tension ratioin Band and block brake is given by
I+ utan
To I- utan 0
where T, Tension in the band on tight side (maxinmum lension).
To = Tension in the band on slack side (mininnuntension),
20 = Angle subtended by each block at the drum centre, and
n = Number of wooden blocks.
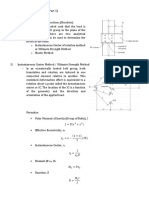
Internal expanding shoe brake (Refer Fig ll 22)
Moment of nornal force, M. 5P,b r 00, 10,- 0,)
9) 5 (sin 20, -sin 28)
Moment offrictional force, M, - PI br
4
(cos 2 , - cos
20)|
M Mr
Actuating force on leading (or left hund) shoc, F
M+ M:
and Actuating force on trailing (or right hand, shoe, F,
where the notations have usual eanings
Energy considerations :
() Total energy absorhed by brake E,
(i) Heut generated in brakes : H, - l xR. xv p.1
(iuy lleut dissipated in brakes : H, = CxAx At =CxA x(t, -I)
where the notulions have usual meanilngs.
Temperature rise: A1 Cx
You might also like
- QAQC References 2Document138 pagesQAQC References 2Mohd SharainiNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- BrakesDocument62 pagesBrakesTarun Surya KatreddyNo ratings yet
- Brakes & ClutchesDocument16 pagesBrakes & ClutchesNeil RubsNo ratings yet
- Fired Heater - 2013 FW TalkDocument38 pagesFired Heater - 2013 FW TalkSong Hoe100% (2)
- Komatsu Training Aid (Heavy Equipment)Document849 pagesKomatsu Training Aid (Heavy Equipment)RenzoDT100% (1)
- TorsionDocument58 pagesTorsionAizat Sera SuwandiNo ratings yet
- Types of BrakesDocument12 pagesTypes of Brakesذوالفقار علي حسينNo ratings yet
- 35 Design of Shoe BrakesDocument10 pages35 Design of Shoe BrakesPRASAD326100% (1)
- Physical Geodesy: Martin VermeerDocument520 pagesPhysical Geodesy: Martin VermeerreflectiondarkNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 LectureDocument48 pagesChapter3 LectureAlaaNo ratings yet
- Dodi Mulyadi, MTDocument54 pagesDodi Mulyadi, MTAdiwahyu NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Design of Curved BeamsDocument42 pagesDesign of Curved Beamsananth k r80% (25)
- Brakes: Presented By: Cerda, JoshuaDocument22 pagesBrakes: Presented By: Cerda, JoshuaJoshua100% (2)
- Diagnostic Check Answers: Part 1: Non-FictionDocument45 pagesDiagnostic Check Answers: Part 1: Non-FictionMay Youssef100% (2)
- Friction Clutches PDFDocument14 pagesFriction Clutches PDFamanmittal0850% (2)
- Beams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsFrom EverandBeams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Field Study 2 Learning Episode 7Document6 pagesField Study 2 Learning Episode 7Mc Dave Mendoza Mangurali II100% (6)
- Band BrakeDocument17 pagesBand Brakeocy12No ratings yet
- Flat-Plate Friction Clutches and ThrustDocument17 pagesFlat-Plate Friction Clutches and ThrustYuvaperiyasamy MayilsamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Shaft (Cont'd)Document47 pagesChapter 1 Shaft (Cont'd)Rayuth KEATNo ratings yet
- Power ScrewDocument7 pagesPower ScrewLeiyibot bayot ver.No ratings yet
- TortionDocument25 pagesTortionadamNo ratings yet
- 05 Mechanical and Structural Calculations Booklet ST PaulsDocument43 pages05 Mechanical and Structural Calculations Booklet ST PaulsGanesh VeluNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Shaft DesignDocument18 pagesLecture 1. Shaft DesignhasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Bolted Connections (Part 3)Document3 pagesChapter 4 - Bolted Connections (Part 3)John Philip NuñezNo ratings yet
- Band BrakeDocument19 pagesBand BrakeRioardhsyhNo ratings yet
- Torque Measurement... : Mechanical Dynamometers.. S.SANJAY (18P221)Document52 pagesTorque Measurement... : Mechanical Dynamometers.. S.SANJAY (18P221)vijay AmirtharajNo ratings yet
- Advanced Theory of Vibrations ME-742 CH 08Document51 pagesAdvanced Theory of Vibrations ME-742 CH 08CADCAM 2K14No ratings yet
- Gear TrainDocument8 pagesGear TrainP RAVI KUMARNo ratings yet
- Application of Friction in Machine ElementsDocument11 pagesApplication of Friction in Machine ElementsPrince QuimnoNo ratings yet
- Construction and Working of Simple Band BrakeDocument5 pagesConstruction and Working of Simple Band BrakeYT BoyNo ratings yet
- GY403 DynamicAnalysisDocument37 pagesGY403 DynamicAnalysissaira tahirNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Stresses & Strains PDFDocument48 pages1.introduction To Stresses & Strains PDFErNo ratings yet
- Friction ClutchesDocument10 pagesFriction ClutchesThế Nam VũNo ratings yet
- ME 6505 - Dynamics of Machines: Fifth Semester Mechanical Engineering (RegulationsDocument18 pagesME 6505 - Dynamics of Machines: Fifth Semester Mechanical Engineering (RegulationsshivendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Me6505 DM Mech VST Au Unit III PDFDocument18 pagesMe6505 DM Mech VST Au Unit III PDFMechanical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Application of FrictionDocument18 pagesApplication of FrictionManprita BasumataryNo ratings yet
- Design of ShaftDocument20 pagesDesign of ShaftPranav BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Machine Design 2013Document44 pagesMachine Design 2013cooLkiD1412No ratings yet
- CH 02Document118 pagesCH 02RODRIGO JAVIER BRIZUELA PADILLANo ratings yet
- ClutchDocument4 pagesClutchtisha revillaNo ratings yet
- D A M 03 Crankshaft Designt-04Document49 pagesD A M 03 Crankshaft Designt-04Twite_Daniel2No ratings yet
- N - CH 08 ME-742 s19 Final PDFDocument75 pagesN - CH 08 ME-742 s19 Final PDFCADCAM 2K14No ratings yet
- Apr May 2019Document6 pagesApr May 2019VenkadeshNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material1 PDFDocument80 pagesStrength of Material1 PDFPratik BajracharyaNo ratings yet
- TorsionDocument44 pagesTorsionPrabhjyot SinghNo ratings yet
- Dom - 2marks MinimumDocument4 pagesDom - 2marks MinimumRobinston Jeyasingh KNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1-sp24Document19 pagesTutorial 1-sp24islameslamoislam807No ratings yet
- Torsion of Circular ShaftDocument12 pagesTorsion of Circular ShaftTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- MCQ Based On Force For Class-10Document9 pagesMCQ Based On Force For Class-10RedNo ratings yet
- MOM Module 4Document51 pagesMOM Module 4Ramesh Reddy B TNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 MOMDocument6 pagesExperiment 3 MOMHafiz HamzaNo ratings yet
- Dip 2nd UnitDocument31 pagesDip 2nd UnitSuresh BalamNo ratings yet
- Torsion of Circular Shaft: Torque or Turning Moment or Twisting MomentDocument13 pagesTorsion of Circular Shaft: Torque or Turning Moment or Twisting Momentmahmudul adilNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics A NotesDocument8 pagesEngineering Mechanics A NotesTourlêy MunroNo ratings yet
- Torsion of Circular ShaftsDocument45 pagesTorsion of Circular ShaftsRajNo ratings yet
- CE 382 L6 - Shear and Moment DiagramsDocument42 pagesCE 382 L6 - Shear and Moment DiagramsAydın Göğüş100% (2)
- Click Here: E6-201 Power Electronics Lab Tutorial On LtspiceDocument6 pagesClick Here: E6-201 Power Electronics Lab Tutorial On LtspiceAnonymous Fv6p6owhNo ratings yet
- What Changes Should Leclerc Incorporate in The Design and Architecture of A New Boot Camp?Document2 pagesWhat Changes Should Leclerc Incorporate in The Design and Architecture of A New Boot Camp?Anonymous vZUWVIRtNo ratings yet
- Home Health Aide Job Description ResumeDocument7 pagesHome Health Aide Job Description Resumezug0badej0n2100% (2)
- THSISES Updated 27-02-2024Document75 pagesTHSISES Updated 27-02-2024Abiola segunNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Successful Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) Implementation in Hypermarket StoresDocument15 pagesFactors Influencing Successful Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) Implementation in Hypermarket Storestiara dwi citraNo ratings yet
- M550 AC Drive User Manual enDocument112 pagesM550 AC Drive User Manual enVentas Indee S.A.CNo ratings yet
- Concrete Column DesignDocument3 pagesConcrete Column DesignLarisa Viorica FlorianNo ratings yet
- Whatfix - Sales Predictable Hiring MetricsDocument4 pagesWhatfix - Sales Predictable Hiring MetricsVignesh ManiNo ratings yet
- Six Approaches To Stylistic Analysis - WDocument5 pagesSix Approaches To Stylistic Analysis - WAdelNo ratings yet
- 645-1925-1-PB Intervensi PDFDocument25 pages645-1925-1-PB Intervensi PDFnicholasNo ratings yet
- Life Skills: Giving PresentationsDocument2 pagesLife Skills: Giving PresentationsВіта МоскаленкоNo ratings yet
- JGR Catalog 2021 HDocument47 pagesJGR Catalog 2021 HChandra Arief BudimanNo ratings yet
- Parts Catalogue For Pramac gx1009 - v1Document20 pagesParts Catalogue For Pramac gx1009 - v1ПетрNo ratings yet
- A Three-Edged SwordDocument5 pagesA Three-Edged SwordGYedwab100% (2)
- J Apenergy 2017 05 183Document10 pagesJ Apenergy 2017 05 183Firman Adi RifansyahNo ratings yet
- SCDL - Java ProgrammingDocument68 pagesSCDL - Java Programmingapi-3733148100% (1)
- Hive Advanced ConceptsDocument57 pagesHive Advanced ConceptsAditya RaoNo ratings yet
- Spelling Words For Adults PDFDocument7 pagesSpelling Words For Adults PDFluther jay astronomoNo ratings yet
- Chartered Project Professional (CHPP) Application GuidanceDocument53 pagesChartered Project Professional (CHPP) Application GuidancehardikNo ratings yet
- An Interview With Sensorband: Bert BongersDocument12 pagesAn Interview With Sensorband: Bert BongersTrisha JacksonNo ratings yet
- Case Study Transportation MGTDocument3 pagesCase Study Transportation MGTHải Đăng0% (1)
- 2075-Assembly Manual For FFF - FDMDocument115 pages2075-Assembly Manual For FFF - FDMCristo LBNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Lesson Preparation and Delivery On Student's PerformanceDocument22 pagesThe Influence of Lesson Preparation and Delivery On Student's PerformanceWhambi Enock75% (4)
- GSM Wireless-Wired Alarm System-2Document2 pagesGSM Wireless-Wired Alarm System-2Mada NafeaNo ratings yet