Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SE Patho
SE Patho
Uploaded by
Angel Mikaela CilladoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SE Patho
SE Patho
Uploaded by
Angel Mikaela CilladoCopyright:
Available Formats
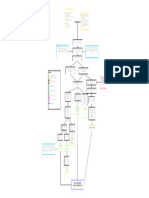
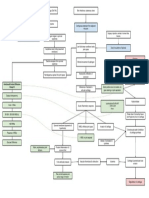
Crossover of infection (via Bacteria, most commonly
medical care worker, visitor, Escherichia coli, but also
medical instrument) other pathogens, enter the
urinary tract.
Bacterial Bacteria adhere to the
Inhalation Aspiration epithelial cells lining the
Translocation
urinary tract
Colonization in Colonization in
gastrointestinal Bacterial adherence is
nasopharynx facilitated by specific
track
virulence factors such as
fimbriae or pili.
Bacterial invasion triggers an
inflammatory response in the lungs.
Bacterial invasion triggers an
inflammatory response, leading to the
release of cytokines, chemokines, and
other inflammatory mediators.
Inflammation leads to the recruitment
of immune cells, release of
inflammatory mediators, and increased
vascular permeability.
Inflammation can cause damage to the
alveoli, leading to consolidation
(solidification) of lung tissue.
Impair gas exchange
Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factors
Bacteria enters the
Age bloodstream vausing systemic Hemodynamic Instability
Vascular Conditions spread Bacterial Infection
Comorbidities Microbial Toxins
Presence of an infection triggers a
systemic inflammatory response.
Infection activates immune cells
leading to the release of Body Malaise
pro-inflammatory mediators.
Pro-inflammatory cytokine causes
endothelial cell avctivation and
dysfunction.
Increased vascular permeability
leading to leakage of fluid and proteins Edema
into tissues.
Systemic inflammatory response
affects microvascular function.
Uneven blood distribution and tissue
perfusion.
Inflammatory mediators and
microvascular dysfunction can
compromise the integrity of
blood-brain-barrier (BBB).
Entry of immune cells and
pro-inflammatory mediators into the Alteration of Sleep-Wake Cycle
brain trigers a localized inflmmatory
response within the CNS.
If Treated
Microglial cells activated.
Laboratory and Diagnostic Medications:
citicholine Activated microglial release additional
telmisartan + amlodipine cytokines and inflammatory mediators
cilostazol within the brain.
Sputum GS CT Scan Urinalysis Arterial Blood Gas Complete Blood Serum Electrolytes atorvastatin
Count Lumbar Tap KCl
Epithelial Cells: >10/LPF Consider acute infarct right Yellow PCO2: 31 mmHg (L) K: 2.40 mmol/L (L) febuxostat
Gram (+) cocci: -1+ lobe and Slightly Cloudy PO2: 109 mmHg (H) RBC: 4.48 (L) Mg: 1.10 mmol/L (H) CSF Glucose: 5.07 colchine
Gram (-) rods: -1+ thalamocapsuloganglionic Specific Gravity: 1.036 HCO3: 21.1 mmol/L (L) WBC: 16.4 (H) Crea: 111.8 umol/L (H) piperacillin + Sepsis-induced inflammation and
Fungus: Few area. (H) tCO2: 22.1 (L) Segmenters: 0.85 (H) (H) CSF Protein: 42.8 (H) tazobactam oxidative stress
Periventricular hypodensity Protein (+) BEecf: -3.1 (L) Lymphocytes: 0.11 (L) RBC: 19.3 (H) mannitol
changes can be due to WBC: 104.8 (H) Eosinophils: 0.00 (L) ceftazidime
microangiopathy. RBC: 23.8 (H) RESPIRATORY Platelet Count: 431 (H) vancomycin
Cerebral atrophy can be Epithelial Cells: 21.9 (H) ALKALOSIS
age related with ex vacuo Bacteria: 3968.5 (H) Mitochondrial dysfunction in various
dilation of the anterior horn tissues.
of the right lateral ventricle.
Arteriosclerotic internal
Urine GS
carotid and vertebral
arteries. Mitochondrial impairment disrupts Generation of reactive oxygen
cellular energy production and species.
contributes to cellular injury.
Increased ROS production, coupled
with reduced antioxidant defenses, Cognitive Impairment
results in oxidative stress.
Altered Mental Status
Disrupt neurotransmitter balance
in the brain.
Anorexia
Cellular injury and dysfunction can
lead to the accumulation of fluid Increased intracranial
within brain cells, known as pressure.
cytotoxic edema.
Microglia becomes activated in
response to inflammmation
Dysregulation of cerebral blood
flow autoregulation occurs.
Cumulative effects of the
inflammatory response and
cellular dysfunction
If untreated
Shock Coma
Poor Prognosis
You might also like
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesCommunity-Acquired Pneumonia PathophysiologyFrancis Adrian83% (12)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY-PTB - FinalDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGY-PTB - FinaliamMye100% (1)
- BMI1014: Chapter 2 - Bacteria-Morphology and ClassificationDocument6 pagesBMI1014: Chapter 2 - Bacteria-Morphology and ClassificationAkmal Adib FadzilNo ratings yet
- Latina 2009 06 LoveAndSexDocument1 pageLatina 2009 06 LoveAndSexDorkys RamosNo ratings yet
- Lower Respiratory Tract Infection (Pneumonia)Document4 pagesLower Respiratory Tract Infection (Pneumonia)krvpriya0No ratings yet
- 3rd Lect (Systemic Infections) OCRDocument4 pages3rd Lect (Systemic Infections) OCRHussainNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Vaginosis A Practical Review.3 PDFDocument7 pagesBacterial Vaginosis A Practical Review.3 PDFyayangNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Antibiotic AgentsDocument13 pagesAntibacterial Antibiotic AgentsEmmanuel coleteNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PneumoniaDocument1 pagePathophysiology PneumoniaMaythresha GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Sensitivity FINAL V4 Sheet1Document1 pageAntibiotic Sensitivity FINAL V4 Sheet1JHNo ratings yet
- Virus Multiplication 4Document16 pagesVirus Multiplication 4Ananya TomerNo ratings yet
- Affiche Infection MFA BRDocument1 pageAffiche Infection MFA BRcynthiaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AmoxicillinDocument1 pageDrug Study AmoxicillinMarjorie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- 1000 Pyq BioDocument554 pages1000 Pyq Bioishani.gupta2006No ratings yet
- Pcap Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesPcap Pathophysiology PDFMikaela RamosNo ratings yet
- AtlasRespiratorioPorcino IngDocument6 pagesAtlasRespiratorioPorcino IngEduardo ViolaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Classification PDFDocument8 pagesBacterial Classification PDFdenportillo12No ratings yet
- ARP Antibiotics Currently in Global Clinical Development Data Table v2Document10 pagesARP Antibiotics Currently in Global Clinical Development Data Table v2tanishtarun06No ratings yet
- Ab SensitivityDocument5 pagesAb Sensitivityliashuban29No ratings yet
- Microbiology and Management of Peritonsillar, Retropharyngeal, and Parapharyngeal AbscessesDocument6 pagesMicrobiology and Management of Peritonsillar, Retropharyngeal, and Parapharyngeal AbscessesVenter CiprianNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Sensitivity December 2015Document1 pageAntibiotic Sensitivity December 2015Ali MehdiNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Sensitivity December 2015Document1 pageAntibiotic Sensitivity December 2015Jeffery WangNo ratings yet
- Vancogenx LineDocument5 pagesVancogenx LineMahsaNo ratings yet
- Cholera Mindmap: Understanding The Disease, Symptoms, and PreventionDocument1 pageCholera Mindmap: Understanding The Disease, Symptoms, and PreventionUlysse BerraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System by AeyfkerDocument17 pagesRespiratory System by AeyfkerAfkar IshakNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument3 pagesDiarrheaChetan NaikNo ratings yet
- FILARIASISDocument1 pageFILARIASISJette Charmae OlboNo ratings yet
- Infographic The Race To Stop COVID 19Document1 pageInfographic The Race To Stop COVID 19Alfredo Martinez100% (1)
- Activity 1Document3 pagesActivity 1MANALANG JULIA ALEXISNo ratings yet
- LEC Gallery WalkDocument1 pageLEC Gallery WalkMaria ThereseNo ratings yet
- Can Existing Live Vaccines Prevent COVID-19?Document3 pagesCan Existing Live Vaccines Prevent COVID-19?lejuan0No ratings yet
- Ajr-Mucocele AppendixDocument4 pagesAjr-Mucocele AppendixOrlin Zlatarski100% (1)
- Drugs Inhibiting Cell Wall Synthesis - 2Document6 pagesDrugs Inhibiting Cell Wall Synthesis - 2NeelabhNo ratings yet
- History and Recent Advances in Coronavirus.Document5 pagesHistory and Recent Advances in Coronavirus.fendralulukNo ratings yet
- CFTR Protein: Cholera, Each Year. ItDocument2 pagesCFTR Protein: Cholera, Each Year. ItSiri Rao Student - EnloeHSNo ratings yet
- Pcap PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPcap PathophysiologyZandra Lyn AlundayNo ratings yet
- Biomérieux: Environmental Infection Control in HospitalsDocument25 pagesBiomérieux: Environmental Infection Control in HospitalsYohana Fransisca WapiniNo ratings yet
- AbdulrehmanDocument1 pageAbdulrehmanrabia buttNo ratings yet
- Anatomy ModelsDocument5 pagesAnatomy ModelstashanabrazhNo ratings yet
- Abas, Pathophysiology of CapDocument1 pageAbas, Pathophysiology of Capalexander abasNo ratings yet
- Classification of Medically Important BacteriaDocument2 pagesClassification of Medically Important BacteriaAUNG KHANT ZAWNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Book-Based) : CystitisDocument9 pagesPathophysiology (Book-Based) : CystitisIrish EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PresentationDocument2 pagesDrug Study PresentationKaren Joyce Costales MagtanongNo ratings yet
- DM, Glucocorticoid Therapy,: CRP & Esr FeverDocument1 pageDM, Glucocorticoid Therapy,: CRP & Esr FeverCJMALNo ratings yet
- Nutrition, Immunity and COVID-19Document10 pagesNutrition, Immunity and COVID-19W CnNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Anthracis: Microbiology and Parasitology - "Bacteria"Document5 pagesBacillus Anthracis: Microbiology and Parasitology - "Bacteria"stanihaNo ratings yet
- Community Medicine MindMapsDocument18 pagesCommunity Medicine MindMapsAhmed ShafikNo ratings yet
- Acquired Bronchiectasis: AbcessDocument14 pagesAcquired Bronchiectasis: AbcessAhmed GaberNo ratings yet
- Nutricia Advertorial 3Document1 pageNutricia Advertorial 3Nurul Falah KalokoNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman PneumoniaDocument6 pagesRangkuman PneumoniaHaikal MNo ratings yet
- M5 Post Task - AmoebiasisDocument1 pageM5 Post Task - Amoebiasisbing bongNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Pneumonia - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument1 pageBacterial Pneumonia - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfNang KhamNo ratings yet
- Bactera and FungiDocument17 pagesBactera and FungiGarvNo ratings yet
- Sperm A ToDocument16 pagesSperm A TogfujawatiNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell-1Document26 pagesProkaryotic Cell-1Sarah PavuNo ratings yet
- Legacy Carl Woesse 2013Document7 pagesLegacy Carl Woesse 2013NatiNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: Lesson 1 Second Semester, 2020 - 2021Document81 pagesMicrobiology: Lesson 1 Second Semester, 2020 - 2021Quezon, Michaella BSN1No ratings yet
- MCB 120 Microbial PhysiologyDocument98 pagesMCB 120 Microbial PhysiologyArianne ManuelNo ratings yet
- Bacteria (Unit I)Document22 pagesBacteria (Unit I)Muhammad KaleemNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Basic Study of BacteriaDocument3 pagesLab 1 - Basic Study of BacteriaElija Leigh MauricioNo ratings yet
- Uace Biology Classification Questions and AnswersDocument14 pagesUace Biology Classification Questions and Answersmoggadavid480No ratings yet
- GONORRHOEADocument23 pagesGONORRHOEADwi Fikha AprilyantiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Medical Microbiology 2023Document93 pagesIntroduction To Medical Microbiology 2023Samuel fikaduNo ratings yet
- Uncovering The Mechanisms of Acinetobacter Baumannii VirulenceDocument12 pagesUncovering The Mechanisms of Acinetobacter Baumannii VirulenceTony ChuNo ratings yet
- Burton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 3. Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument25 pagesBurton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 3. Cell Structure and TaxonomyLindsay SwanepeolNo ratings yet
- Basic Bacteriology: MunawirDocument50 pagesBasic Bacteriology: MunawirindahirmawatiNo ratings yet
- Geentic Transformation in BacteriaDocument4 pagesGeentic Transformation in Bacteriahimanshi singhNo ratings yet
- Science Magazine 5856 2007-12-07Document123 pagesScience Magazine 5856 2007-12-07sumersoft1100% (1)
- Download pdf Concise Review Of Veterinary Microbiology Second Edition Askews ebook full chapterDocument53 pagesDownload pdf Concise Review Of Veterinary Microbiology Second Edition Askews ebook full chapterannie.welle889100% (2)
- Microparasitology IntroDocument36 pagesMicroparasitology IntroLady DanielleNo ratings yet
- + Cell Strucutre and FunctionDocument116 pages+ Cell Strucutre and FunctionSandara PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Microbiology PDFDocument103 pagesMicrobiology PDFmedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Microbiology: Amit Kumar RaiDocument31 pagesUnit-I Microbiology: Amit Kumar RaiAmreen KhanNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Unit 1: Mansi Damani BNCPDocument73 pagesMicrobiology Unit 1: Mansi Damani BNCPSiddhant BanwatNo ratings yet
- Current Concepts in The Pathogenesis of Periodontitis: From Symbiosis To DysbiosisDocument20 pagesCurrent Concepts in The Pathogenesis of Periodontitis: From Symbiosis To DysbiosisgugicevdzoceNo ratings yet
- تخدير المحاضرة الاولىDocument7 pagesتخدير المحاضرة الاولىXcv FfgNo ratings yet
- Microbial EcologyDocument23 pagesMicrobial EcologyUsman SurajNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mechanisms of E.coli PathogenicityDocument13 pagesMolecular Mechanisms of E.coli PathogenicityJonatan SBNo ratings yet
- Sharma Et Al-2016-Journal of Applied MicrobiologyDocument11 pagesSharma Et Al-2016-Journal of Applied MicrobiologyJoanaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial PlasmidsDocument9 pagesBacterial PlasmidsspanishinqNo ratings yet
- SOCRANSKY 2002 - Dental Biofilms Difficult Therapeutic TargetsDocument44 pagesSOCRANSKY 2002 - Dental Biofilms Difficult Therapeutic TargetsLuiz Guilherme FiorinNo ratings yet
- Reproduction of Prokaryotic CellDocument29 pagesReproduction of Prokaryotic CellNurrazanahKarmanNo ratings yet
- Assoni2021 Article CurrentStageInTheDevelopmentOfDocument19 pagesAssoni2021 Article CurrentStageInTheDevelopmentOfSeksi IlmiahNo ratings yet