Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test To Pass
Test To Pass
Uploaded by
ayushbhardwaj1818200 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views7 pagesOriginal Title
test to pass
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views7 pagesTest To Pass
Test To Pass
Uploaded by
ayushbhardwaj181820Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
1) CT or hounsfield number depends upon
A. Mass density
B. Electron density
C. Atomic number
D. Atomic mass
2) Which of the following statement is true ?
A. By reducing kVp by 50% radiation dose is reduced to half
B. In pediatric patients dose should be reduced
C. CT dose index is not useful for control exposure in multi slice CT
D. kV has no control over CT dose index
3) Which artery is dissected most commonly following arteriography by
femoral route?
A. Celiac trunk
B. Superior mesenteric artery
C. Inferior mesenteric artery
D. Gastroduodenal artery
4) Earliest investigation for diagnosis of Ankylosing spondylitis
A. MRI STIR sequence
B. Bone scan
C. CT scan
D. X-ray
E. USG
5) How much area is covered by spiral CT in 30 second?
A. Entire organ
B. Entire abdomen
C. Entire trunk
D. Whole body
6) In CT scan, Hounsfield unit depends on
A. Electron density
B. Mass density
C. Effective atomic number
D. Linear attenuation number
7) X-ray view of choice for lumber spondylosis is/ are
A. PA view
B. Lateral view
C. Left oblique view
D. Right oblique view
High resolution CT of the lung is a specialized CT technique for a greater
detail of lung parenchyma and it utilizes
A. Special lung filter
B. Thick collimation
C. Bone algorithm for image reconstruction
D. Large field of view
9) Which of the following is non – ionizing radiation
A. X-ray
B. Beta Rays
C. Alpha rays
D. Microwave
E. Gamma rays
10) Time sector scanning of neonates is preferred because of the following
reason. Most practical reason
A. Open fontanelles
B. Inexpensive
C. Children more co – operative
D. Better resolution
11) PET stand for
A. Positive electron tomography
B. Proton electron therapy
C. Positron emission tomography
D. Photon emitting tomography
12) What modification is needed for proper radiographic image In a heavy
bony built person?
A. Increased mA
B. Increased kVp
C. Increased exposure time
D. Increased developing time
13) Maximum radiation exposure occurs in
A. Bone scan
B. X-ray
C. MRI
D. CT scan
14) USG is definitive investigation of
A. Vasa previa
B. Abruption placenta
C. Placenta previa
D. Imperforate hymen
15) Investigation of choice in whole body imaging in metastasis is
A. MRI
B. Angiography
C. Venography
D. PET scan
16) Gyromagnetic property of proton is seen in
A. MRI
B. CT
C. PET
D. USG
17) Most reliable test for spinal tuberculosis
A. Raised ESR
B. PPD skin test
C. CT guide biopsy
D. MRI
18) In MRI , paramagnetic substance cause
A. Shortening of both T1 and T2 relaxation times
B. Shortening T2 relaxation times only
C. Shortening of T1 relaxation time only
D. No effect on T1 or T2 relaxation times
19) SI unit of absorbed dose of radiation is
A. Roentgen
B. Gray
C. Sievert
D. Coulomb
20) Frequency of Ultrasound wave in Usg
A. 200 Hz
B. 500 Hz
C. <2 MHz
D. > 2 MHz
21) Which of the following is a non – iodine containing contrast?
A. Gadolinium
B. Visipaque
C. Iopamidol
D. Diatrizoate
22) In CT , the attenuation value are measured in Hounsfield unit . An
attenuation value of ‘0’ ( zero) HU corresponds to
A. Water
B. Very dense bone structure
C. Air
D. Fat
23) The best contrast to perform an IVU in the contemporary era is
A. Iodinated ionic water soluble contrast
B. Iodinated non ionic water soluble contrast
C. Gadolinium based contrast
D. Lipidol
24) All of the following are true about iodinated intravascular contrast
media
A. They are used in digital substraction angiography
B. They are radio – opaque
C. They can cause anaphylactic reaction
D. They are used in MRI
E. They are excreted mainly by the kidneys
25) BIRADS stand for
A. Breast imaging reporting and data system
B. Best imaging reporting and data system
C. Brain imaging reporting and data system
D. Breast investigation reporting and data system
26) Doppler effect is due to
A. Change in frequency in relation to the movement of source or observer
B. Change in attenuation
C. Change in absorption
D. Change in reverberation
27) Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism is primarily made by
A. Multidetector CT contrast
B. Angiography
C. Ventilation perfusion scan
D. CXR
28) Alpha is similar to
A. Electron
B. Proton
C. Neutron
D. Helium
29) Neural tube defects is best detected by
A. USG
B. Chromosomal analysis
C. Amniocentesis
D. Placentography
30) Light ray and x-ray have same
A. Velocity
B. Wavelength
C. Energy
D. Frequency
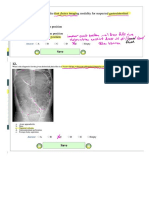
A patient comes in complaining of abdominal pain and the
doctor orders an x-ray of the abdomen. Afterwards, you
compare it to the last image the patient had taken and you
see this x-ray. What is the name of this x-ray position?
a. KUB
(Kidneys, ureter, and bladder) b. Lateral Decubitus c.
Upright Abdominal x-ray d. IVP (Intra venous Pyelogram)
What condition does this patient have?
a. Broken rib b. Situs inversus c. Pleural effusion
d. Dislocated shoulder
You might also like
- Test Bank For Radiologic Science For Technologists 12th Edition by BushongDocument51 pagesTest Bank For Radiologic Science For Technologists 12th Edition by Bushongmarcuskenyatta275No ratings yet
- Comprehensive Radiographic Pathology 6th Edition Eisenberg Test BankDocument13 pagesComprehensive Radiographic Pathology 6th Edition Eisenberg Test BankCherylRandolphpgyre100% (13)
- Fixed Pitch Propeller Rev 6Document68 pagesFixed Pitch Propeller Rev 6Arturo Postigo HerranzNo ratings yet
- The Ultrasound BeamDocument9 pagesThe Ultrasound BeamFrancy100% (2)
- MCQ On CT and MriDocument42 pagesMCQ On CT and MriFathima Hiba100% (1)
- New MCQDocument129 pagesNew MCQAlhaji100% (1)
- MCQ (1) .UltrasoundDocument5 pagesMCQ (1) .UltrasoundFlorentino Edgar LLacma Sanchez80% (5)
- Cluster 5Document23 pagesCluster 5Robert JNo ratings yet
- ملف جديدDocument46 pagesملف جديدSalem AlnamshanNo ratings yet
- RS CoachingDocument201 pagesRS CoachingHalia MalicNo ratings yet
- Radiology FinalDocument37 pagesRadiology Finalmira bellaNo ratings yet
- Radiology, Anesthesia, Gynecology NeetDocument71 pagesRadiology, Anesthesia, Gynecology NeetDivya Joyce100% (1)
- BVRMIT-301Principles of CT and MammographyDocument10 pagesBVRMIT-301Principles of CT and MammographyShivani Yadav100% (2)
- 13Document7 pages13abdulfatahalhemeryNo ratings yet
- Exam 17 Urology 2Document9 pagesExam 17 Urology 2malaz.jaafarNo ratings yet
- جذومن -سويرولاكبلا ةلمحل يعاعشلإا ريوصتلا ناحتما E) ) Radiography Technology Bachelor Degree) Bsc Exam Number:) Bsc-E)Document9 pagesجذومن -سويرولاكبلا ةلمحل يعاعشلإا ريوصتلا ناحتما E) ) Radiography Technology Bachelor Degree) Bsc Exam Number:) Bsc-E)Nuhad Bou MoslehNo ratings yet
- سويرولاكبلا ةلمحل يعاعشلإا ريوصتلا ناحتما Radiography Technology Bachelor Degree (Bsc Exam Number: (Bsc-C)Document8 pagesسويرولاكبلا ةلمحل يعاعشلإا ريوصتلا ناحتما Radiography Technology Bachelor Degree (Bsc Exam Number: (Bsc-C)Nuhad Bou MoslehNo ratings yet
- Radiology PDFDocument81 pagesRadiology PDFrawaNo ratings yet
- General knowled-WPS OfficeDocument10 pagesGeneral knowled-WPS OfficeTeeNo ratings yet
- D. Cardiac EnlargementDocument10 pagesD. Cardiac EnlargementNuhad Bou Mosleh100% (1)
- Ests School of Thoracic SurgeryDocument8 pagesEsts School of Thoracic SurgerybasirNo ratings yet
- جذومن -سويرولاكبلا ةلمحل يعاعشلإا ريوصتلا ناحتما (B) Radiography Technology Bachelor Degree) Bsc Exam Number:) Bsc-B (Document9 pagesجذومن -سويرولاكبلا ةلمحل يعاعشلإا ريوصتلا ناحتما (B) Radiography Technology Bachelor Degree) Bsc Exam Number:) Bsc-B (Nuhad Bou MoslehNo ratings yet
- Mcqs Surgery RadiologyDocument7 pagesMcqs Surgery RadiologyAsif JielaniNo ratings yet
- جذومن -سويرولاكبلا ةلمحل يعاعشلإا ريوصتلا ناحتما D) ) Radiography Technology Bachelor Degree) Bsc Exam Number:) Bsc-D)Document9 pagesجذومن -سويرولاكبلا ةلمحل يعاعشلإا ريوصتلا ناحتما D) ) Radiography Technology Bachelor Degree) Bsc Exam Number:) Bsc-D)Nuhad Bou MoslehNo ratings yet
- الهيئة 3Document10 pagesالهيئة 3mohsenNo ratings yet
- IMM Feb 2023-1Document4 pagesIMM Feb 2023-1Ahmed NadeemNo ratings yet
- Radiology Final Study GuideDocument100 pagesRadiology Final Study GuideEric Case100% (4)
- Promortion Exam - Senior, July 2009Document16 pagesPromortion Exam - Senior, July 2009Ahmad AlnemareNo ratings yet
- جذومن -سويرولاكبلا ةلمحل يعاعشلإا ريوصتلا ناحتما A) ) Radiography Technology Bachelor Degree) Bsc Exam Number:) Bsc-A)Document9 pagesجذومن -سويرولاكبلا ةلمحل يعاعشلإا ريوصتلا ناحتما A) ) Radiography Technology Bachelor Degree) Bsc Exam Number:) Bsc-A)Nuhad Bou MoslehNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Computed Tomography and Principles of OperationsDocument6 pagesModule 1 Computed Tomography and Principles of OperationsWayne De Vergara PalaypayonNo ratings yet
- Stomach: 1. Spinous Process 2. BodyDocument27 pagesStomach: 1. Spinous Process 2. BodyAbdelkader SamehNo ratings yet
- Computed Tomography - An Increasing Source of Radiation ExposureDocument8 pagesComputed Tomography - An Increasing Source of Radiation ExposureMANUEL ALEJANDRO LEÓNNo ratings yet
- Radiology Mission NEETDocument130 pagesRadiology Mission NEETShibdatta DasNo ratings yet
- RadiologyDocument60 pagesRadiologynayejih371No ratings yet
- Us Mri Ct-ExamDocument68 pagesUs Mri Ct-ExamgetachewNo ratings yet
- Midterm Study GuideDocument8 pagesMidterm Study GuideAustin TroutNo ratings yet
- Computed Tomography HUDocument7 pagesComputed Tomography HUAnonymous 0XPHreGPNo ratings yet
- The Ultrasound BeamDocument5 pagesThe Ultrasound BeamSahadeb RoyNo ratings yet
- 4 5843476213649116596Document9 pages4 5843476213649116596خلدون سليمNo ratings yet
- Mid Exam 2010 Saudi Board SurgeryDocument16 pagesMid Exam 2010 Saudi Board SurgeryAhmad Alnemare100% (1)
- Aiims Nov 12 RadiologyDocument2 pagesAiims Nov 12 RadiologyNeelam VermaNo ratings yet
- ONCOLOGY MCQS PREPARATION FOR 5th Yr MBBSDocument21 pagesONCOLOGY MCQS PREPARATION FOR 5th Yr MBBSDrRaghavender Reddy100% (12)
- Radiology (FMGE)Document19 pagesRadiology (FMGE)Phani Pillarisetty100% (5)
- New Advances in Genitourinary Ultrasound: Jared D. Christensen, MD Vikram S. Dogra, MDDocument11 pagesNew Advances in Genitourinary Ultrasound: Jared D. Christensen, MD Vikram S. Dogra, MDkartikaNo ratings yet
- 50 Fmge Repeat Questions DiscussionDocument116 pages50 Fmge Repeat Questions DiscussionpalNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument3 pagesMCQYong Fang Yue100% (3)
- Radiography Mcqs Question: 1. Which of The Following Imaging Modalities Uses X - Rays?Document8 pagesRadiography Mcqs Question: 1. Which of The Following Imaging Modalities Uses X - Rays?Saurav MishraNo ratings yet
- Medical Physics Ib2 08Document22 pagesMedical Physics Ib2 08moez1122No ratings yet
- Radiology Teaching SurveyDocument3 pagesRadiology Teaching SurveyEvan O'FlahertyNo ratings yet
- Bladder & Prostate Cancer - 240514 - 070428Document31 pagesBladder & Prostate Cancer - 240514 - 070428Max TraderNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Computed Tomography and Principles of OperationsDocument6 pagesModule 1 Computed Tomography and Principles of OperationsWayne De Vergara PalaypayonNo ratings yet
- ST RD NDDocument7 pagesST RD NDALrasshida TanNo ratings yet
- Rad SciDocument11 pagesRad SciRaine SalvadorNo ratings yet
- امتحان التأهيل 2020Document21 pagesامتحان التأهيل 2020izat husseinNo ratings yet
- Modifications of X-RayDocument6 pagesModifications of X-Rayolajumokeojo9No ratings yet
- 2018 April DR TasnuvaDocument13 pages2018 April DR TasnuvaDr.Riashat azimNo ratings yet
- OSSSC Radiographer Medical Radiation Technology PaperDocument6 pagesOSSSC Radiographer Medical Radiation Technology PaperKeshav NishadNo ratings yet
- Radiology: Discussion PaperDocument12 pagesRadiology: Discussion PaperMadhu SowmithaNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic UltrasonographyFrom EverandEndoscopic UltrasonographyFrank G. GressNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument23 pagesAssignmentLadymae Barneso SamalNo ratings yet
- Presentation OptimizeDocument11 pagesPresentation Optimizexman4243No ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Module 1: Kinetic Molecular Theory of Liquids and Solids Pre-Learning HomeworkDocument1 pageQuarter 1 Module 1: Kinetic Molecular Theory of Liquids and Solids Pre-Learning HomeworkGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Design of Liquid Level Control System For Double TDocument6 pagesDesign of Liquid Level Control System For Double TSiddhartha MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument20 pagesAbstractRizky Thezacky SevenfoldismNo ratings yet
- BlasterDocument16 pagesBlasterCarpnado MasterNo ratings yet
- Feedback Control PID Control: HadiyantoDocument64 pagesFeedback Control PID Control: HadiyantoNuzul RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - 1.2 Materials - Edexcel IAL Physics A-LevelDocument35 pagesFlashcards - 1.2 Materials - Edexcel IAL Physics A-LevelNikitha SomaratneNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Cdi2Document42 pagesModule 1 Cdi2John Paul FernandezNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document4 pagesProblem Set 1kristine100% (1)
- Shri H.H.J.B. Polytechnic, Chandwad, Nashik: Project Title: Prepare A Model of Telescopic Hydraulic JackDocument13 pagesShri H.H.J.B. Polytechnic, Chandwad, Nashik: Project Title: Prepare A Model of Telescopic Hydraulic JackTejas PawarNo ratings yet
- Ditec Sector Reset - Product Specifications - ENDocument2 pagesDitec Sector Reset - Product Specifications - ENsistroyNo ratings yet
- Chen 801-T3Document28 pagesChen 801-T3hussainiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Pre-U: Further Mathematics 9795/01Document4 pagesCambridge Pre-U: Further Mathematics 9795/01charlesmccoyiNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging - Physical and Biological PrinciplesDocument529 pagesMagnetic Resonance Imaging - Physical and Biological PrinciplesThamiris Rosa100% (2)
- Calibre 150MM-0,05MM - Mitutoyo - 530-101Document1 pageCalibre 150MM-0,05MM - Mitutoyo - 530-101Cesar Eduardo NeiraNo ratings yet
- Chand Icse IxDocument70 pagesChand Icse IxDeepika MohanbabuNo ratings yet
- 01.technical Manual For Cus51dDocument20 pages01.technical Manual For Cus51dVIJAY KUMAR SAJJANo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Fundamentals of Solar Radiation Lucien Wald Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Fundamentals of Solar Radiation Lucien Wald Online Ebook All Chapter PDFwanita.craft341100% (10)
- 7 Electrical Technolgy - Electron TheoryDocument4 pages7 Electrical Technolgy - Electron TheoryGuyan GordonNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Mechanical Properties of MetalsDocument9 pagesExperiment 4 Mechanical Properties of MetalsDamien ManceraNo ratings yet
- OPT307 NAB G2 Addendum Template 2021 Group2 UPDATED (2664)Document6 pagesOPT307 NAB G2 Addendum Template 2021 Group2 UPDATED (2664)CLASH WORLDNo ratings yet
- D2937-10 Standard Test Method For Density of Soil in Place by The Drive-Cylinder MethodDocument7 pagesD2937-10 Standard Test Method For Density of Soil in Place by The Drive-Cylinder MethodFederico Montesverdes100% (1)
- Trigonometry Formulas Are Essential ForDocument5 pagesTrigonometry Formulas Are Essential ForIna Suelen PenalesNo ratings yet
- Tekla Structural Designer 2023 Us Codes ReferenceDocument264 pagesTekla Structural Designer 2023 Us Codes ReferenceKevin James BenitezNo ratings yet
- AssignQuiz2 141.417 23TP11Document9 pagesAssignQuiz2 141.417 23TP11Alex WhittakerNo ratings yet
- Elementsmark of Numerical Analysis of Numerical Analysis Second Edition Radhey SDocument16 pagesElementsmark of Numerical Analysis of Numerical Analysis Second Edition Radhey SUzomah TeslimNo ratings yet
- RUMUSDocument3 pagesRUMUSNURUL ASHIKIN AHMAD ASHRINo ratings yet
- The CurrentDocument5 pagesThe CurrentJoan BalendrezNo ratings yet