Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment 3 General Reactions of Carbohydrates Biochem Lab .Docx Removed
Experiment 3 General Reactions of Carbohydrates Biochem Lab .Docx Removed
Uploaded by
Miki Cantavieja0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesExperiment 3 General Reactions of Carbohydrates Biochem Lab .Docx Removed
Experiment 3 General Reactions of Carbohydrates Biochem Lab .Docx Removed
Uploaded by
Miki CantaviejaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Name: Peligres, Pornela, Portugal, Saito, Tomas, Tulayba Rating:
Course, Year and Section: BSMT2H Instructor: Prof. Ranola
Group Number: 5 Date: November 9, 2023
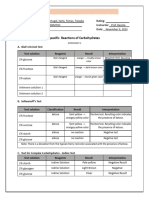
Reactions of Carbohydrates
EXPERIMENT 2
I. General Reactions of Carbohydrates
A. Reaction with Acids - Molisch Test
Test solution Reagents Result Interpretation
Molisch Reagent purple ring/color Positive
1% glucose
Molisch Reagent dark purple ring/color Positive
1% xylose
Molisch Reagent dark yellow ring/color Negative
1% sucrose
Molisch Reagent purple ring/color Positive
1% starch
B. Reducing Property
B.1. Fehling’s Test
Test solution Reagents Result Interpretation
1% glucose Fehling's A and Had a red precipitate Positive result which
Fehling's B when heated after an indicates the presence
ample amount of time of reducing sugars
1% xylose Fehling's A and Had a red precipitate Positive result which
Fehling's B when heated after an indicates the presence
ample amount of time of reducing sugars
1% sucrose Fehling's A and The product was a hazy Negative result
Fehling's B yellow brown liquid
1% starch Fehling's A and After being heated it Negative result
Fehling's B did not change, the
color was still blue
B2. Nylander’s Test
Test solution Reagents Result Interpretation
1% glucose
1% xylose
1% sucrose
1% starch
B3. Benedict’s Test
Test solution Reagents Result Interpretation
1% glucose Benedict’s Reagent yellow/orange when it An orange color
1% glucose is heated → brownish indicates that 1 - 1.5
orange with brownish percent of reducing
black precipitate sugar is present.
Therefore It is a
positive result.
1% xylose Benedict’s Reagent brick red with brownish Brick red indicates
1% xylose precipitate positive results and it
has a presence of more
than 2% of reducing
sugar
1% sucrose Benedict’s Reagent Blue-ish yellow when it It turns blue-ish yellow
1% sucrose is heated → brownish upon heating which
red with brown indicates a negative
precipitate results
1% starch Benedict’s Reagent Blue Negative results - no
1% starch reaction at all or
remains the same
because starch do not
react with benedict’s
reagent because starch
has small number of
reducing sugar
B4. Moore’s Test
Test solution Reagents Result Interpretation
You might also like
- Isolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesIsolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesMiguel Sabillena100% (4)
- PharmacognosyDocument7 pagesPharmacognosyNxxx33% (3)
- DRD - Dedini Direct Refined - AustcaneDocument55 pagesDRD - Dedini Direct Refined - AustcaneFernando Cesar BoscariolNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q4 SLM7Document13 pagesScience 10 Q4 SLM7Kennedy Fieldad Vagay100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Grade 8 - BiomuleculesDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Grade 8 - BiomuleculesRoxanne Reglos67% (3)
- Experiment 3 General Reactions of Carbohydrates: NH OHDocument16 pagesExperiment 3 General Reactions of Carbohydrates: NH OHAl Cris BarroNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Specific Reactions of Carbohydrates Biochem Lab - Docx RemovedDocument1 pageExperiment 4 Specific Reactions of Carbohydrates Biochem Lab - Docx RemovedMiki CantaviejaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 7 Laboratory Report DRAFT 1Document4 pagesGROUP 7 Laboratory Report DRAFT 1Leah Mae TomasNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATES LabDocument22 pagesCARBOHYDRATES LabJan Leanne OrbigosoNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Test For Amino Acids and ProteinDocument7 pagesQualitative Test For Amino Acids and ProteinShamarie Love MaribaoNo ratings yet
- Color Reaction of ProteinsDocument28 pagesColor Reaction of ProteinsKae ArturiaNo ratings yet
- Metodos de CarbohidratosDocument19 pagesMetodos de CarbohidratosMelissa DiliaNo ratings yet
- Solution Observatio N Interpretation 1% Albumin 1% Casein 1% Peptone Solution Observation Interpretation Urea With Distilled WaterDocument8 pagesSolution Observatio N Interpretation 1% Albumin 1% Casein 1% Peptone Solution Observation Interpretation Urea With Distilled WatershakesNo ratings yet
- Exp. 8 WorksheetDocument11 pagesExp. 8 WorksheetChristina mikaela CabusaoNo ratings yet
- Activity No 21 Carbohydratesdocx PDF FreeDocument13 pagesActivity No 21 Carbohydratesdocx PDF FreeDorotheè PartridgeNo ratings yet
- Activity No 21 Carbohydratesdocx PDF FreeDocument13 pagesActivity No 21 Carbohydratesdocx PDF FreeDorothy AtilanoNo ratings yet
- MC2.Experiment5.Proteins - Group 2Document11 pagesMC2.Experiment5.Proteins - Group 2beannaladera04No ratings yet
- POLYSACCHARIDESDocument2 pagesPOLYSACCHARIDESYholzManioNo ratings yet
- Test For Carbohydrates, Proteins and LipidsDocument5 pagesTest For Carbohydrates, Proteins and LipidsEBWong100% (1)
- Biochemistry Laboratory: Seliwanoff's Test S Eliwanoff's Reagent: Add Positive ResultDocument7 pagesBiochemistry Laboratory: Seliwanoff's Test S Eliwanoff's Reagent: Add Positive ResultAllejah Jane CantaNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 RasheedDocument26 pagesBio 1 RasheedRaghad AlNo ratings yet
- Primary Products of PhotosynthesisDocument32 pagesPrimary Products of PhotosynthesisMerrene Bright Divino JudanNo ratings yet
- Experiment-9-Properties-of-Protein-Schematic-Diagram Group 2Document9 pagesExperiment-9-Properties-of-Protein-Schematic-Diagram Group 2Bee Anne BiñasNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate EstimationDocument19 pagesCarbohydrate EstimationAjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Reactions Unknown Carbohydrates AnnotatedDocument19 pagesReactions Unknown Carbohydrates AnnotatedKkc KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Act 9Document3 pagesAct 9Rei Deller TagiobonNo ratings yet
- Test Result Discussion/Explanation: CarbohydratesDocument11 pagesTest Result Discussion/Explanation: CarbohydratesAnnapril TasicNo ratings yet
- Practical Report 1: FHSC1214 Fundamentals of Cell Biology Foundation in ScienceDocument3 pagesPractical Report 1: FHSC1214 Fundamentals of Cell Biology Foundation in ScienceEngNo ratings yet
- Food TestsDocument4 pagesFood Testsrchataika863No ratings yet
- Lab Report 5Document9 pagesLab Report 5Krizia Corrine St. PeterNo ratings yet
- Experiment #1 - Food TestDocument5 pagesExperiment #1 - Food TestZachary MedwinterNo ratings yet
- Practial No 2 Identification Reaction, Testand Sceheme For CarbohydrateeDocument5 pagesPractial No 2 Identification Reaction, Testand Sceheme For CarbohydrateemitalNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Module 2Document4 pagesWorksheet Module 2YuraNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 Reduction Test (Benedict's Test)Document2 pagesActivity 6 Reduction Test (Benedict's Test)Corpus, Irene Zen P.No ratings yet
- Post Lab Experiment 3 Carbohydrates Group Work PDFDocument8 pagesPost Lab Experiment 3 Carbohydrates Group Work PDFJeff MarianoNo ratings yet
- Experiment B: Qualitative Test For Protein: Chemical Equation For Biuret ReactionDocument11 pagesExperiment B: Qualitative Test For Protein: Chemical Equation For Biuret ReactionElla Nicole TaljaNo ratings yet
- Chem Data AnalysiDocument2 pagesChem Data Analysilbmartinez4574pamNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Proteins Group 1Document7 pagesActivity 2 Proteins Group 1Althea Aubrey AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates LabDocument21 pagesCarbohydrates LabBernardMarkMateoNo ratings yet
- Biochem Moving Exam Reviewer 2Document19 pagesBiochem Moving Exam Reviewer 2gyleveloso21No ratings yet
- Expt 2: Estimation of Glucose by Benedict's Quantitative ReagentDocument21 pagesExpt 2: Estimation of Glucose by Benedict's Quantitative ReagentMuhammad Hanif100% (1)
- Biochemistry Laboratory - Carbohydrate Lab ReportDocument2 pagesBiochemistry Laboratory - Carbohydrate Lab Reportminkcd51No ratings yet
- LAB REPORT EXP 1 G3 Dalila - Faris - Imannina - Farhana Sabuddin - ElianaDocument9 pagesLAB REPORT EXP 1 G3 Dalila - Faris - Imannina - Farhana Sabuddin - ElianaKhairul Salam HasinorNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Unknown SugarDocument3 pagesAnalysis of Unknown SugarsasmithaNo ratings yet
- Food Tests 1. Carbohydrates (Sugars and Starches)Document3 pagesFood Tests 1. Carbohydrates (Sugars and Starches)nmrasaNo ratings yet
- Benedict'S Test: Qualitative Tests For CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesBenedict'S Test: Qualitative Tests For Carbohydrateskatherine m. superioridadNo ratings yet
- Test For Glucose and Albumin Laboratory in BiochemistryDocument10 pagesTest For Glucose and Albumin Laboratory in BiochemistryJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Chem 528 - Activity 3Document8 pagesChem 528 - Activity 3Aries Jay ReyesNo ratings yet
- Test For CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesTest For CarbohydratesBriar Rose BausingNo ratings yet
- Task 1 - Carbohydrates - Legario, M PDFDocument5 pagesTask 1 - Carbohydrates - Legario, M PDFMeddy LegarioNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab Report (G2) PDFDocument10 pagesBio Lab Report (G2) PDFAina NabihaNo ratings yet
- Lab Exp 3Document4 pagesLab Exp 3erin.134340No ratings yet
- Identification of Biological Molecules in FoodDocument13 pagesIdentification of Biological Molecules in FoodNurul Ain AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Biochem ProteinDocument40 pagesBiochem ProteinCharlene SibugNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 3Document11 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 3wmaximoff426No ratings yet
- Test Purpose Reagent Used Principle/Purpose of Reagent ResultDocument5 pagesTest Purpose Reagent Used Principle/Purpose of Reagent ResultAldren BeliberNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 Carbohydrates: Specific Reactions I. CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesActivity 4 Carbohydrates: Specific Reactions I. CarbohydratesAlih KathlyannNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates II NEW JaiDocument10 pagesCarbohydrates II NEW JaiNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- BendictDocument6 pagesBendictMg HNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Carbohydrates ExperimentDocument3 pagesReactions of Carbohydrates ExperimentAlyssa LumaadNo ratings yet
- Practical Sugar - Benedict's and Iodine TestsDocument6 pagesPractical Sugar - Benedict's and Iodine TestsAriyukiNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Lecture Sample ProblemsDocument4 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Lecture Sample ProblemsMiki CantaviejaNo ratings yet
- Gbm1 New (Autosaved) - 1Document39 pagesGbm1 New (Autosaved) - 1Miki CantaviejaNo ratings yet
- GBM3 RevDocument15 pagesGBM3 RevMiki CantaviejaNo ratings yet
- GB2M 1Document9 pagesGB2M 1Miki CantaviejaNo ratings yet
- MTLBDocument10 pagesMTLBMiki CantaviejaNo ratings yet
- Density of Sugar Factory ProductsDocument1 pageDensity of Sugar Factory ProductsJose GarciaNo ratings yet
- NCM 105-Macronutrients Carbohydrates ReviewerDocument6 pagesNCM 105-Macronutrients Carbohydrates ReviewerJustine AbongNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates OverviewDocument144 pagesCarbohydrates OverviewButz AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 6 Procedure - Hydrolysis of CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesActivity No. 6 Procedure - Hydrolysis of CarbohydratesMan Gal7No ratings yet
- Bio Chem Prelims Hand OutsDocument18 pagesBio Chem Prelims Hand Outsnina grace joyNo ratings yet
- 3006 14611 1 PBDocument6 pages3006 14611 1 PBWidiyantoNo ratings yet
- Hydrolysis of Starch DataDocument5 pagesHydrolysis of Starch DataWenn Joyrenz ManeclangNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides DisaccharidesDocument32 pages4.0 Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides DisaccharidesPikuNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules NotesDocument15 pagesBiomolecules NotesJatin KumarNo ratings yet
- Structure of MaltoseDocument2 pagesStructure of MaltoseBhavaniNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate PPT in PDFDocument23 pagesCarbohydrate PPT in PDFsadaf zaidiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 CarbohydratesDocument19 pagesChapter 13 CarbohydratesMADANNo ratings yet
- Allen Next Physiology NotesDocument5 pagesAllen Next Physiology NotesKailashNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry, As The Name Implies, Is The Chemistry of Living Organisms. LivingDocument7 pagesBiochemistry, As The Name Implies, Is The Chemistry of Living Organisms. LivingSaravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Swan Et Al, 2018Document3 pagesSwan Et Al, 2018Evan LauNo ratings yet
- 405 Method Not AllowedDocument5 pages405 Method Not AllowedNaji Mohamed AlfatihNo ratings yet
- Unit 10R - CarbohydratesDocument20 pagesUnit 10R - CarbohydratesGovind ManglaniNo ratings yet
- 05b Sweeteners Reading20161228 ENGDocument10 pages05b Sweeteners Reading20161228 ENGfransiscaNo ratings yet
- Flowsheet PG Pesantren Baru FixxDocument1 pageFlowsheet PG Pesantren Baru FixxAsafarid AndrianiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4:: Organic Components: CarbohydratesDocument20 pagesExercise 4:: Organic Components: CarbohydratespikachuzingungaNo ratings yet
- Biomass Liquefaction:: "Liquefaction" of Biomass Mainly Takes Place Through Two ProcessesDocument3 pagesBiomass Liquefaction:: "Liquefaction" of Biomass Mainly Takes Place Through Two Processeswasif karimNo ratings yet
- General Properties of CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesGeneral Properties of CarbohydratesShine GatilloNo ratings yet
- Worksheet of CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesWorksheet of CarbohydratesVita Ayu FatihahNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 2 - Analysis of Carbohdrates - 1Document5 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 2 - Analysis of Carbohdrates - 1Juliane JaynNo ratings yet
- Sugar in FoodDocument6 pagesSugar in FoodNelson MiraNo ratings yet