Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trans 5 - Frog Organogenesis
Uploaded by
angelica sherinnCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trans 5 - Frog Organogenesis
Uploaded by
angelica sherinnCopyright:
Available Formats
DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY (LABORATORY)
Frog Organogenesis
Mr. Rainier Ulrich D. Velasco
OUTLINE
I. Organogenesis
II. 4mm frog
A. Whole Mount
B. Transverse Section
III. 7mm frog
A. Whole Mount
B. Transverse Section
IV. 10mm frog
A. Whole Mount
B. Transverse Section
I. ORGANOGENESIS
● The formation of the various organs
● Causes the differentiation of the interacting embryonic tissues that takes place.
● Start of the specification of tissues and organ primordia.
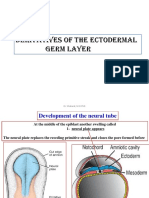
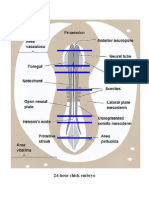
Table 5.1 Neurulation
Neural Plate Stage Neural Fold Stage Neural Tube Stage
● the earliest stage in neurulation ● stage where the neural folds are prominently ● neural folds have already fused at the
● Neural Plate (Medullary Plate) – A region of elevated. mid-dorsal region forming the closed structure
embryonic ectodermal cells that lie directly ● Neural Fold – portion of the neural plate that has called “neural tube” with a cavity, the neurocoel.
above the notochord called neuroectoderm. depresses and a laterally elevated margin ● Observe the cilia and pigment granules of the
During neurulation, an infolding of the neural ● Neural Groove – depression formed in the midline embryo in this stage. Additional structures:
plate occurs that then seals to form the neural as the neural folds meet at the mid-dorsal region of ● Neural Crest Cells –group of cells found at the
tube. the embryo and will also give rise the neurocoele. edges of the neural plate and lies above the
● Presumptive Epidermis – remainder of the ● Hypochordal (subnotochordal rod) – temporary neural tube after its formation. These cells
ectoderm after the formation of the neural plate. group of cells that may be present between the migrate throughout the embryo to form the
This is also the forerunner of the outer layer of notochord and the archenteric roof. May not be ganglia, sympathetic nervous system, pigment
the integument. visible. cells, parts of the gill arches, and etc.
● Notochord – oval mass of cells that originate ● Mesoderm–has differentiation in the following:
from the mesoderm below the neural plate. May → Epimere(somites) – segmented
have formed from the dorsal region of the mesodermal blocks that are located on either
archenteric roof.Temporary structure that sides of the notochord and lying beneath the
provides a skeletal support for early epidermal ectoderm. This will differentiate
development. into: sclerotome which forms the axial
skeleton, the myotome which forms muscles,
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 1 of 32
● Mesoderm – middle germ layer. Found both and the dermatome which forms the dermal
sides of the notochord and dorsal to the layer skin.
archenteric roof. In the early stages of → Mesomere (intermediate mesoderm,
organogenesis, 3 regions are visible: nephrotome, nephromere) –stalk-like
→ epimere (dorsal mesoderm) that will form connection between the epimere and
the somites, hypomere. Anteriorly forms the pronephros
→ mesomere (intermediate mesoderm or and posteriorly forms the mesenchyme which
nephrotome) that will form the excretory develops into the mesonephros and
system metanephros.
→ hypomere (lateral plate mesoderm) which → Hypomere – region of the mesoderm
delaminates into the inner splanchnic and the posterior to the mesomere. During this stage,
outer somatic mesoderm. the hypomere has split into two regions: the
● Endoderm – surrounds the gastrocoel outer somatic mesoderm and an interior
composed of large, yolk-laden cells splanchnic mesoderm. The cavity formed
between the two is called the coelom. During
the early neural stages, the demarcation of
the hypomere and epimere is not clear.
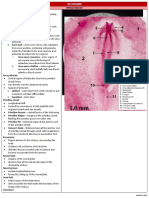
II. 4MM FROG
A. WHOLE MOUNT
● clearly recognizable tail, neural tube, notochord, and segmented mesoderm and fin folds.
● Neural system differentiates from a closed tube into several distinct parts of the brain that is indicated by the appearance of thickening and constrictions
Continued on the next page…
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 2 of 32
Table 5.2 4mm Frog Whole Mount
Figure Parts Description/Location Fate
Prosencephalon foremost part of the brain differentiates into Telencephalon
and Diencephalon
Mesencephalon middle part of the brain
Rhombencephalon hindpart of the brain differentiates into Myelencephalon
and Metencephalon
Epiphysis slight mid-dorsal evagination of the brain vesicle pineal body
Olfactory placode thickenings on the lateral surface of the head
anterior
Evaginated to form cavities called olfactory pits
Lens placode paired thickening of the head ectoderm anterior lens vesicle
to the olfactory placode
evaginate to form the lens vesicle → eye lens
Notochord extends from midbrain to the posterior of the
body which has somites flanking on each side
Stomodeum ectodermal rudiment of the mouth Mouth
formed by invagination of the antero-ventral
ectoderm of the head that is in contact with the
anterior wall of the foregut but is separated from
the endodermal foregut by an oropharyngeal
membrane which ruptures and forms the mouth
Proctodeum ectodermal invagination at the tail base Anus
Oral suckers ectodermal thickenings ventrolateral to the oral
region
Heart formed due to the loose mesodermal cells
beneath the floor of the foregut and the anterior
yolk
Liver median posteroventrally directed diverticulum of
the foregut
Yolky endoderm serve as nutrition
Continued on the next page…
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 3 of 32
B. TRANSVERSE SECTION
Table 5.3 4mm frog transverse section
Figure Parts Description Origin Fate
Level of the Prosencephalon and Nasal Rudiments
Prosencephalon anterior part of the embryonic brain ectoderm Differentiates into
prosocoel - cavity of Telencephalon and
prosencephalon Diencephalon
*In the figure, the brain regions are
already specified but you can still
answer prosencephalon
Mesenchyme embryonic connective tissue neural crest cells and forms predominantly
mesoderm connective tissues and
differentiate into
epithelial, muscular, and
nervous tissue
Head mesenchyme fill the spaces between the neural crest cells and
presumptive epidermis (skin mesoderm
ectoderm) and the walls of the
A prosencephalon
Olfactory placodes paired pigmented invaginations on ectoderm
either side of the prosocoel found in
the head mesenchyme.
Epidermis outermost skin layer derived from ectoderm
the ectoderm
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 4 of 32
Level of the Mesencephalon and Optic Cups
Mesencephalon mid part of the embryonic brain ectoderm
cavity called mesocoel
dorsal to the infundibulum
Prosencephalon anterior part of the embryonic brain ectoderm
prosocoel - cavity of
prosencephalon
*In the figure, the brain regions are
already specified
Infundibulum funnel-like depression in the floor of posterior portion of
the prosencephalon pituitary gland
Hypophysis small knot of tissue ventral to the anterior portion of the
infundibulum pituitary gland
In growth or in nodular aggregation
of cells lying between the oral and
brain cavity.
This term may be used in two
different manners:
B
1.) the invagination of the
stomodeum which fuses with the
infundibulum to form the pituitary
gland
2.) endocrine gland form from an
ingrowth from the stomodeum and
the infundibulum
Oral evagination a cavity that is ventral to the
infundibulum and hypophysis
the walls surrounding the cavity are
composed of endoderm
Oral cavity cavity at the cranial end of the
alimentary canal
Oral plate thickened region where the cranial
(pharyngeal plate, portion of the alimentary canal
oropharyngeal comes in contact with the
membrane) ectodermal portion of the head
Stomodeum ectodermal rudiment of the mouth ectoderm Mouth
formed by invagination of the
ectoderm at the anteroventral
C region of the head
Mandibular Arch Most cranial branchial arch pharynx the coddle border of the
stomodeum and also the
maxillary process cranial
to the stomodeum
Adhesive glands Third ectodermal thickenings found ectoderm
(Oral suckers, in the ventral surface of anuran
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 5 of 32
mucous glands, (frog) embryos that secrete
cement glands) adhesive mucus for attachment to
floating objects
Optic cups double walled structure ectoderm inner layer: retina
invagination of the distal portion of outer layer: pigmented
the optic vesicle. epithelium
Optic vesicle evagination from the lateral wall of ectoderm walls will give rise to the
the prosencephalon. First indication ectodermal parts of the
of the formation of the eye eye except the lens and
the cornea
Optic stalk connection of the optic cup with the ectoderm
brain.
E
*to better understand the difference between
the optic cup and optic vesicle
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 6 of 32
Level of the Rhombencephalon (Section through the anterior pharynx)
Rhombencephalon most caudal region of the brain with Neural ectoderm Metencephalon and
a cavity called rhombocoel. Myelencephalon
Notochord round structure originating from the Chordamesoderm
mesoderm. Defines the
anterior/posterior axis in the
developing embryo.
Pharynx Broad region of the foregut and its Endoderm
paired evagination corresponds to
the pharyngeal pouch
Otic (auditory paired invagination of the otic Ectoderm Inner ear
vesicle) placode that is ventrolateral to the
brain that forms the inner ear when
it separates from the head
ectoderm
F
Level of the Rhombencephalon (Section through the embryonic heart)
Heart located beneath the enlarged Loose mesenchymal
foregut, suspended within the cells
pericardial coelom by the dorsal
mesocardium
Pericardial coelom cavity of the heart
Pericardium thin layer of somatic mesoderm that somatic mesoderm
delimits the pericardial coelom
Formed by the heart mesoderm to
the midventral region of the
pericardial cavity.
Endocardium a continuous endothelial lining of Loose mesenchymal Inner endocardium -
the heart arise from loose cells lining of the heart wall
mesenchymal cells of the Outer epimyocardium -
mesoderm of the heart mesoderm muscle
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 7 of 32
H
Level of the Rhombencephalon (Section through the liver diverticulum)
Mesomeres Presence of paired bulges of tissue pronephric tubules;
below horizontal level of notochord collectively called
pronephros or pronephric
kidney
Liver diverticulum rudiment of the liver seen as an liver
extremely deep groove below the
pharynx.
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 8 of 32
Level of the Rhombencephalon (Section through the pronephros)
Spinal cord cavity that replaces the hindbrain
Pronephros paired structure located on the Initial excretory organ
lateral side of the specimen. found in developing
Spherical structures clustered vertebrate embryos.
together. Functional in larval
amphibians and fish.
Degenerates and
replaced by the
mesonephric kidney in
adults.
Somites Segmented mesodermal blocks dorsal mesoderm sclerotome - forms the
located on either side of the spinal axial skeleton (located
cord which arises from the dorsal above the neural tube
mesoderm. and notochord)
myotome - forms the
muscle
dermatome - forms the
dermis
I
Level of the Rhombencephalon (Section through the midgut)
Subnotochordal Presence of small knot of cells
rod wedged between the notochord and
midgut
*spinal cord and notochord are
approximate in size
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 9 of 32
Level of the Rhombencephalon (Section through the hindgut)
Cloacal membrane Presence of a delicate strand of posterior opening of the
tissues that will become perforated digestive tract
to form the posterior opening of the
digestive tract
Dorsal fin flat extension of the body,
degenerates during the
metamorphosis of the tadpole
Hindgut Posterior most region of the cloaca, colon, small
embryonic gut. intestine, and rectum
Proctodeum ectodermal invagination on the anus
ventral side of the trunk which later
breaks into the hindgut forming the
anus.
Continued on the next page…
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 10 of 32
III. 7MM FROG
A. WHOLE MOUNT
● Well formed external gills and a functional heart
● Presence of tail for swimming with lateral segmented somites and fin folds on the dorsal and ventral side
Table 5.4 Sample Table for Sana Makagraduate Tayong Lahat.
Figure Parts Description/Location Origin Fate
Tail for swimming;
with lateral segmented
somites and fin folds on the
dorsal and ventral side
Forebrain two hemispheres:
telencephalon and
diencephalon
Stomodeum deeply invaginated and large
pigmented cells surrounding
the olfactory pit
Epiphysis circular knob of cells that are
separated from the brain
Notochord extends to the tail
Hindgut does not lose its cavity but urinary bladder (ventral
persists as the cloaca evagination; not visible in
the slides)
Post anal gut dorsal wall of the hindgut breaks up and
extending into the tail disappears in later
rudiment embryonic development
Continued on the next page…
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 11 of 32
B. TRANSVERSE SECTION
Note: Sagittal section of 10 mm frog was used since the parts observed in the specimen match those of the 10 mm
Table 5.5 7mm frog transverse section
Figure Parts Description/Location Origin Fate
Level of the Telencephalon and Olfactory Pits
Olfactory pits ventral portion; olfactory placodes that nasal passages with
cavity in the lateral surface of invaginated and olfactory receptors
the head lengthened
Oral cavity large indentation on the
ventral surface marks its
beginning
Oral plate perforates and has an open
mouth
Telencephalon paired hemispheres that
occupies the anterior region
of the forebrain
Diencephalon posterior division of the
prosencephalon
Epiphysis slight middorsal evagination will form the pineal body
of the brain vesicle of the adult
Head mesenchyme loose cells of mesenchyme
that formed between the
head ectoderm and brain
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 12 of 32
A
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 13 of 32
Level of the Diencephalon and Optic Cups
Oral cavity visible and surrounded by
presumptive jaw cartilages
Adhesive glands present on the ventral
surface
Diencephalon deep, laterally compressed
region to which the optic
stalks, infundibulum, and
epiphysis attach
Mesencephalon brain is located posterior to
the eye;
center for reflexes
associated with vision,
hearing, and movement of
the head.
Optic cup outer pigmented layer and
inner retinal potion can be
distinguished;
lens vesicle lies in its
concavity.
Pharynx large and rounded; will give rise to the
clustered mass of cells in mandibular arch which is
each side the posterior border of
the stomodeum
Stomodeum deep invagination of the midventral ectoderm
pigmented, midventral
ectoderm at the anterior end
of the pharynx
Adhesive glands paired ectodermal
(aka cement thickenings of the ventral
glands, mucous surface of the head;
glands, oral secretes mucus for
suckers) adhesion..
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 14 of 32
C
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 15 of 32
E
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 16 of 32
Level of the Rhombencephalon (Section through the thyroid)
Cranial nerve found lateral to the floor neural crest cells
ganglion mesencephalon;
(developing) part of the peripheral
nervous system derived from
the neural crest cells
Pharynx wider at this level
Thyroid arises as an evagination of endodermal cells from the
the endodermal cells from pharyngeal floor
the pharyngeal floor
*The brain region is already specified to
myelencephalon
Level of the Rhombencephalon (Section through the otic vesicle)
Rhombencephalon roof is composed of a single metenchepalon (anterior)
layer of flattened cells; and myelencephalon
third brain vesicle which (posterior)
expands anteriorly to form
the IV ventricle
Notochord visible and ventral to the mesoderm
brain;
lies dorsal to the gut and
ventral to the hindbrain;
it defines the
anterior/posterior axis in the
developing embryo as well
as providing temporary
skeletal support during early
development
Otic vesicle irregular, hollow organ on formed by the invagination
each side of the brain; of the otic placodes
closed chamber formed by
the invagination of the otic
placodes
Heart below the pharynx
Bulbus cordis anterior-most heart chamber
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 17 of 32
Pericardial coelom cavity that surrounds the
heart and is bounded by the
pericardium
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 18 of 32
Level of the Rhombencephalon (Section through the heart)
External gills evident on the outer surface
of the pharyngeal region and
look like fingerlike
projections that are
protruding on each sides of
the head;
filamentous respiratory
organ, arises from the
branchial arches 3 to 6, and
later replaced by inner gills
Esophageal plug mass of cells that temporarily
blocks the esophagus before
the amphibian larva begins
to feed
Atrium chamber of the heart that
receives blood from the
sinus venosus and delivers it
into the ventricle
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 19 of 32
I
Level of the Spinal Cord (Section through the pronephros and midgut)
● Frog tadpoles are filter feeders which require very long intestines
Glomus two triangular shaped
structures at the ventral
portion of the dorsal aorta
and hangs down into the
coelomic activity;
appears to be tufts of small
blood vessels surrounded on
both their lateral and ventral
surfaces of the pronephric
kidneys;
waste products diffuse from
the glomi into the coelomic
fluids
Spinal cord arises from the posterior-most region of
posterior-most region of the the neural tube
neural tube
Somites segmented mesodermal dorsal mesoderm differentiates into: the
blocks located on either side sclerotome (found
of the developing spinal cord above the neural tube
which arise from the dorsal and notochord, forms
mesoderm; part of the axial
skeleton), the myotome
(forms muscles), and the
dermatome (forms the
dermal layer of the skin)
Dorsal aorta primitive;
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 20 of 32
longitudinal arteries of the
trunk lying beneath the
notochord anterior to the gut.
Pronephros initial excretory organ;
nitrogenous wastes are
passed from the pronephric
tubules into the pronephric
ducts, from the ducts to the
cloaca, then to the exterior;
functional only in larval
amphibians and fish;
later replaced by the
mesonephric kidney
Nephrostomes funnel-shaped opening of the
pronephric tubules where the
coelomic fluid is swept
Midgut middle part of the gut with a archenteron small intestine
small lumen and a thick,
yolky floor
Dorsal fin extension of the body wall will degenerate in older
along the mid-dorsal side of specimens
the trunk and tail and will
degenerate in older
specimens
Cloaca posterior-most chamber in
the vertebrate digestive
system
Proctodeum ectodermal invagination on ectoderm anus
the ventral side of the trunk
at the base of the tail and will
give rise to the anus
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 21 of 32
J
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 22 of 32
K
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 23 of 32
M
Continued on the next page…
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 24 of 32
IV. 10MM FROG
A. WHOLE MOUNT
B. TRANSVERSE SECTION (SERIES 1)
Table 5.7 10mm Frog transverse section.
Figure Parts Description/Location Origin Fate
Level of the Telencephalon and Olfactory Organs
Telencephalon anterior and paired division of the Neuroectoderm Cerebrum
prosencephalon.
lateral ventricle/telocoel - cavity
- formed by the evagination
of the side of the neural
tube at the anterior end of
the neurocoel.
Ependymal Layer one-cell thick ciliated layer
surrounding the neurocoel. The cilia
aid in the movement of the
cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles
of the brain and in the central canal
of the spinal cord
Mantle Layer broad layer adjacent to the Gray matter of the
ependymal layer central nervous system
Marginal Layer outermost layer which contains White matter of the
neuroblasts from the inner layers central nervous system
and nerve fibers
Nasal/Olfactory region of the telencephalon and
organ lying ventrolateral to it. Formed by
the invagination of the ectoderm.
Olfactory nerve connecting the
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 25 of 32
olfactory lobes to the brain arises
from the olfactory epithelium.
External naris Opening of the nasal cavity on the
outside and marks the point of the
original ectodermal invagination
Internal naris Opening of the nasal cavity into the
(choana) buccal region
Frontal organ Arises as an invagination of the *epiphysis lang kayang
diencephalic roof together with the makita
epiphysis. Migrates forward from
the region of the diencephalon to
the region of the telencephalon
beneath the epidermis. This organ
contains photoreceptors and may
function as a “third eye”
Jacobson’s Organ Saccular structure formed by the
(vomeronasal org evagination of the nasal organ. it
an) may function in picking up the smell
of food from the buccal region.
Buccal cavity Where the nasal cavity and mouth
opens. lie to the coelom and is
derived from the stomodeum. jaws
are tipped with horny material and
tooth germs. External to the jaws
are lobose structures called the
oral papillae
Prechordal cartilage Hyaline cartilages beneath the chondrocranium -
telencephalon cartilaginous cranium
Melanocytes Stellate cells scattered over the neural crest cells
dorsolateral region of the brain and
lateral to the nasal organs.
*melanocytes are darker compared
to mesenchyme
Mesenchyme Stellate, mesodermal cells filling up mesoderm forms a loose reticulum
the space between the organs and with the outermost cells
the epidermis forming the dermis of the
integument
Epidermis outer layer of the skin composed of ectoderm
the two strata of ectodermal cells
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 26 of 32
Level of the Diencephalon and the Eye
Diencephalon Posterior subdivision of the Thalamus and
prosencephalon and possesses a hypothalamus
cavity called the III ventricle
Infundibulum funnel-like invagination of the posterior pituitary gland
diencephalic floor together with
stomodeum
Mesencephalon middle region of the brain dorsal to
the diencephalon which bears the
3rd and 4th cranial nerves. it
possesses a cavity known as the
cerebral aqueduct
Pituitary body Oval mass beneath the thin floor of endocrine gland is
(Hypophysis) the infundibulum. derived from the
infundibulum in a
solid ingrowth from
the stomodeum
Optic cup lateral to the diencephalon
Retina thick inner layer of the optic cup. ectoderm
differentiated into the following
layers: ganglion cells, bipolar
neurons, rods and cones
Layer of Ganglian innermost sub layer of the retina ectoderm
cells and where are the axons of the
nerve cells in this sublayer form the
optic nerve.
optic chiasma - The region where
the optic nerves cross in the floor of
the diencephalon
Layer of Bipolar Middle layer of cells that will ectoderm
neurons synapse the receptor and the
ganglian cells
Rods and Cones Outermost sublayer of the retina ectoderm
where the photoreceptoral process
is formed.
Pigmented Outer wall of the optic cup formed ectoderm Iris of the eye
epithelium from the medial half of the optic
vesicle
Lens Spherical body and partly enclosed ectoderm
by the optic cup formed by the
thickenings of the inner wall of the
lens vesicle.
Lens epithelium One-cell thick outer layer ectoderm
Lens fibers Columnar cells at the core of the ectoderm long fibers arranged in
lens layers.
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 27 of 32
Cornea superficial covering of the eye
formed by an assembly of
ectodermal and mesodermal cells
between the ectoderm and lens
Choroid and Sclera Outer investments of the optic cup. Mesoderm
At this stage, they are represented
by the mesodermal cells
aggregating outside the pigmented
epithelium.
Pharynx The broad gut at this level which is
lined by the endodermal cells
Hypobranchial Long masses of cartilage under the
cartilage floor of the foregut that makes up
parts of the visceral skeleton and
supports the pharynx.
Thyroid Pair of small endocrine bodies
associated with the pharynx found
beneath the hypobranchial
cartilages
Skeletal muscle mesodermal masses lying on the Mesoderm
lateral and ventral side of the
pharynx.
Oral suckers Bear glandular structures, Ectoderm
(cement glands, composed of elongated columnar
mucous glands, cells, on the ventral surface of the
adhesive glands) tadpole that produces sticky slime
for attachment to floating objects.
Level of the Myelencephalon and Auditory Vesicle
Myelencephalon Most posterior region of the brain later development the
with a thick floor (basal plates). roof becomes
IV ventricle - cavity vascularized to form the
posterior choroid plexus
medulla oblongata
Auditory vesicle completely hollow organ on each
side of the medulla
Endolymphatic duct Thick wall tube between the
medulla and the ear vesicle and
marks the course of the
invagination of the auditory vesicle
from the ectoderm
Utriculus large dorsal chamber of the ear
vesicle
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 28 of 32
Semicircular canals Three mutually perpendicular folds
of the auditory vesicle observe only
in older specimens and the sensory
epithelium
is represented here by the
thickened horizontal canal.
Sacculus Ill-defined ventral chamber of the lagena - lower
auditory vesicle vertebrates
cochlea - higher
vertebrates
Auditory capsule Mesenchymal cells surrounding the cartilaginous ear capsule
auditory vesicle that surrounds and
protects the inner ear
Auditory ganglion Mass of nerve cells on the medial Neural crest cells
(acoustic ganglion) side of the auditory vesicle.
CNVIII
Notochord beneath the brain region Chordamesoderm Mesenchymal cells of
the notochord will give
rise to the notochordal
sheath
Parachordals Cartilages flanking the notochord
on each side
Heart lightly coiled tube twisted to the
right
Pericardial cavity chamber enclosing the heart
Conus arteriosus most anterior region of the heart
(bulbus cordis) connecting the ventricle with the
ventral aorta
Ventricle Thick muscular walled chamber
that follows and is connected to the
conus arteriosus
Sinus venosus posteriormost chamber lying on the
right, anterior to the liver
Opercular cavity (gill paired chamber continuous with the
chamber) gut and lying on each side of the
heart and it contains the internal
gills with branchial blood vessels
Dorsal aorta Blood vessel located above each
gill chamber. Receives venous
blood and delivers it to atrium
Aortic arches blood vessels lying within the
branchial arches and encircling the
pharynx and these structures
connect the dorsal aorta with the
ventral aorta.
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 29 of 32
The aortic arches that are involved
are 3-6 because they are gill
bearing
Facial ganglion (VII) Large mass of nerve cell bodies Neural crest cells
(Geniculate anterior to the auditory ganglion.
ganglion)
Acoustico-facialis fusion of the facial and auditory Neural crest cells
ganglion ganglia
Trigeminal ganglion Larger mass of nerve cell bodies Neural crest cells
(V) (Semilunar anterior and dorsal to the
ganglion) acoustico-facialis ganglion.
Glossopharyngeal Mass of nerve cell bodies below Neural crest cells
ganglion (IX) each auditory vesicle.
Operculum External wall of the opercular cavity
formed by a body fold
Metencephalon anterior subdivision of the Cerebellum and pons
rhombencephalon and lies behind
the optic lobes and medial to the V
ganglion.
Level of the Pronephros and the first spinal ganglion
Spinal cord Derived from the posterior region of
the neural tube.
Neural canal (central cavity that is laterally compressed
canal) by the thick lateral walls of the
spinal cord. Ependymal cells that
line the central canal possess cilia
and pigment granules.
Gray matter inner layer of the spinal cord close
to the ependymal layer and
composed of compact mass of
neuroblast and neuroglia.
White matter peripheral layer of the spinal cord
containing the axons of the neurons
in the gray matter.
Meninges Membranous covering of the
central nervous system which
begins to form at this
developmental stage
First spinal ganglia Masses of nerve cell bodies
ventrolateral to the spinal cord
Myotomes thickened primordia of skeletal
muscles on each side of the
notochord and the skeletal muscle
fibers are arranged longitudinally.
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 30 of 32
Pleuroperitoneal coelomic cavity containing the
cavity viscera except the heart
plural cavity - lungs
peritoneal cavity - digestive organs
Esophagus tubular organ with folded mucosal
lining below the notochord
Dorsal aorta paired blood vessel between the
notochord and the esophagus and
will fuse into a single blood vessel
posteriorly.
Pronephros paired excretory organ nephrotome
located at the ventrolateral region
of the body
Pronephric tubule ducts of the pronephros lined by
cuboidal epithelium
Posterior cardinal Blood vessels within the
veins pronephros and supplies the latter
with blood
Nephrostome Opening of the pronephric tubules
into the coelom.
Nephric duct Lone duct that can be observed at
the most caudal section of the
pronephros and when trace
posteriorly, it moves medially and
eventually joins the cloaca where it
empties its contents.
Glomus two triangular-shaped structures The glomi are functional
seen ventrally the dorsal aorta that components of the
hang down into the coelomic cavity. pronephric kidney. Waste
these structures are tufts of small products from the blood
blood vessels surrounded on their diffuse from the glomi
lateral and ventral surfaces by the into the coelomic fluid.
thin wall of the coelom.
Stomach Posterior continuation of the
esophagus with folded lining and
thick muscular walls. Evaginations
of the endodermal lining form the
rudiments of the gastric glands
Duodenum region of the gut between the
pyloric end of the stomach and the
intestine.
Intestine posterior to the duodenum and is
filled with the abundant yolk
platelets.
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 31 of 32
Liver highly vascularized and enlarged
organ to the right of the midline.
Sinusoids - spaces in the liver
Gallbladder one-cell thick, large vesicle
associated with the liver.
Bile duct thick-walled tube that appears in
the place of the gallbladder.
Pancreas large organ within the curvature of
the stomach. Located at the right of
the liver and bile duct and is
identified by the presence of the
nest of cells (alveoli) surrounding
small ducts.
ZOO 3202 Frog Organogenesis 32 of 32
You might also like
- 3rd Week of Development 2022Document36 pages3rd Week of Development 2022aameena nadaNo ratings yet
- Embryo If Embryonic Period PDFDocument12 pagesEmbryo If Embryonic Period PDFRyna Miguel MasaNo ratings yet
- 24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabDocument3 pages24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabIvy Cruz50% (2)
- Frog Embryology PDFDocument17 pagesFrog Embryology PDFHohai ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Development of CNSDocument84 pagesDevelopment of CNSSamuel frankNo ratings yet
- Dumaguit (2021)Document12 pagesDumaguit (2021)Dimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- Development of The Nervous System: Matt Velkey 454A Davison, Green Zone, Duke SouthDocument45 pagesDevelopment of The Nervous System: Matt Velkey 454A Davison, Green Zone, Duke SouthAbdimalik AliNo ratings yet
- 3RD To 8TH Week (I)Document31 pages3RD To 8TH Week (I)RaoulSusanto SusantoNo ratings yet
- 24 HR Chick ReviewerDocument4 pages24 HR Chick ReviewerGail AmuraoNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue Part 1Document25 pagesNervous Tissue Part 1nhcsmlmolNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Period 4-8weekDocument25 pagesEmbryonic Period 4-8weekaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Gastrulationin MammalsDocument16 pagesGastrulationin MammalsHarsha MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- EARLY DEVELOPMENT-2nd 3rd WeekDocument4 pagesEARLY DEVELOPMENT-2nd 3rd WeekNajah HanimNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Frog Embryology SlidesDocument10 pages5.1 Frog Embryology SlidesChandan kumar MohantaNo ratings yet
- Slides - 02-04 - Ectoderm Derivatives and NeurulationDocument14 pagesSlides - 02-04 - Ectoderm Derivatives and NeurulationSebastian RuaNo ratings yet
- 04 - Develpment Week 3Document12 pages04 - Develpment Week 3hiba jasimNo ratings yet
- OrganogenesisDocument6 pagesOrganogenesisnitesh.th15005No ratings yet
- 24-Hr Chick: Structure Description FateDocument18 pages24-Hr Chick: Structure Description FateDimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- Acrisologobsbio2 ADocument3 pagesAcrisologobsbio2 ACrisologo AllenNo ratings yet
- Gas Tru LationDocument53 pagesGas Tru LationSam MumoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13-Development of Skeletal & Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesLecture 13-Development of Skeletal & Muscular Systemtesfaye mekonnenNo ratings yet
- 262 - Embryology Physiology) EctodermDocument4 pages262 - Embryology Physiology) Ectodermarya409090No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal DevelopmentDocument40 pagesMusculoskeletal DevelopmentMajd HusseinNo ratings yet
- Derivatives of EctodermDocument22 pagesDerivatives of EctodermRagdha MehdawiNo ratings yet
- Embryo IDocument28 pagesEmbryo IggNo ratings yet
- Development of The NSDocument7 pagesDevelopment of The NSJean Pierre Chastre LuzaNo ratings yet
- Claire Bolalin - Quiz (Neurulation)Document1 pageClaire Bolalin - Quiz (Neurulation)Claire BolalinNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Organ Plants (Botany)Document23 pagesMale Reproductive Organ Plants (Botany)kunalNo ratings yet
- Jus 3 F 2003Document32 pagesJus 3 F 2003Abedur RahmanNo ratings yet
- 3 EmbryologyDocument19 pages3 EmbryologyKennVaneNo ratings yet
- 09 - Musculoskeletal DevelopmentDocument8 pages09 - Musculoskeletal DevelopmentAXA OFFICIALNo ratings yet
- Third To Eighth WeekDocument33 pagesThird To Eighth WeekGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- L1. Embryology of The LimbsDocument23 pagesL1. Embryology of The LimbsMahmoud AbdulahiNo ratings yet
- HDTD-E - 6 - Embryonic PeriodDocument33 pagesHDTD-E - 6 - Embryonic PeriodMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- MeningesDocument2 pagesMeningesDurga MadhuriNo ratings yet
- Do Not Delete (Chick-God)Document6 pagesDo Not Delete (Chick-God)Ricky Justin NgoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document7 pagesChapter 7Mia Kristhyn Calinawagan SabanalNo ratings yet
- 4mm Frog EmbryoDocument3 pages4mm Frog EmbryoIvy CruzNo ratings yet
- NeurulationDocument9 pagesNeurulationaesha890% (1)
- Neurulation, OrganogenesisDocument2 pagesNeurulation, OrganogenesisClaire BolalinNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Neural Development and Neurogenesis (Final)Document4 pages1.3 Neural Development and Neurogenesis (Final)Austin CabreraNo ratings yet
- Embryology 1 Asr 3eny New 2024Document9 pagesEmbryology 1 Asr 3eny New 2024Hassan AwadNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Period: Dr. Khin Ma MADocument34 pagesEmbryonic Period: Dr. Khin Ma MAIbrahim Foondun100% (1)
- 2 - Development of The Vertebrate Body PlanDocument66 pages2 - Development of The Vertebrate Body PlanRicarte FernandezNo ratings yet
- Gastrulation Somites and Folding TSRDocument27 pagesGastrulation Somites and Folding TSRAsia SattiNo ratings yet
- Universal Embryology SummaryDocument6 pagesUniversal Embryology SummaryJason TonioloNo ratings yet
- Bsp1a - Gr.a - ReportingDocument14 pagesBsp1a - Gr.a - ReportingannaMariaGracia EstardoNo ratings yet
- GA&E 14 - Bilaminar Germ DiscDocument34 pagesGA&E 14 - Bilaminar Germ DiscSu ZikaiNo ratings yet
- Gastrulation: Understanding Cell Movements That Occur During GastrulationDocument33 pagesGastrulation: Understanding Cell Movements That Occur During Gastrulationandreana kusumaNo ratings yet
- Development of Mesoderm-Derived Organs: 4BIO-4 / 4BIO - 8/ 4BIO-9 (Batch 2019)Document130 pagesDevelopment of Mesoderm-Derived Organs: 4BIO-4 / 4BIO - 8/ 4BIO-9 (Batch 2019)Samantha ArdaNo ratings yet
- Uni FileDocument10 pagesUni Filemuqadar khanNo ratings yet
- Embrology 14 Jan FinalDocument16 pagesEmbrology 14 Jan FinalBhumi Chouhan100% (1)
- Development of FaceDocument19 pagesDevelopment of FaceAkhila ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chick Embryo (Embryology Lab)Document9 pagesChick Embryo (Embryology Lab)humanupgrade100% (1)
- Skin and Its AppendagesDocument7 pagesSkin and Its AppendagesSheena PasionNo ratings yet
- Weeks 3 - 8Document32 pagesWeeks 3 - 8Stefan HutsonNo ratings yet
- Development of IntegumentaryDocument5 pagesDevelopment of IntegumentaryAkachukwu ObunikeNo ratings yet
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesFrom EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNo ratings yet
- Insulin Pump Therapy Vs InjectionsDocument6 pagesInsulin Pump Therapy Vs InjectionsHakan KüçükerNo ratings yet
- Peperomia PellucidaDocument8 pagesPeperomia PellucidajaninasuzetteNo ratings yet
- Pictures & Perspectives: Ophthalmology Volume 125, Number 2, February 2018Document1 pagePictures & Perspectives: Ophthalmology Volume 125, Number 2, February 2018SashaNo ratings yet
- Excerpt From A Journal of The Plague YearDocument3 pagesExcerpt From A Journal of The Plague YearErnez LaurenceNo ratings yet
- S 511 Anti Slip PDFDocument9 pagesS 511 Anti Slip PDFidealsentaNo ratings yet
- Unpicking The Link Between Smell and MemoriesDocument1 pageUnpicking The Link Between Smell and MemoriesMicheleFontanaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord InjuryDocument97 pagesSpinal Cord Injuryamoon1275% (4)
- Kramer 1992Document7 pagesKramer 1992Elite Dental AcademyNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Correction of Uterine Torsion in Cattle and BuffaloesDocument13 pagesDiagnosis and Correction of Uterine Torsion in Cattle and Buffaloesgnpoba100% (12)
- Hearing ImpairmentDocument26 pagesHearing ImpairmentMelody MejiaNo ratings yet
- Sarah S. Taupan, RN, MN, DPADocument33 pagesSarah S. Taupan, RN, MN, DPAKatri ArasaNo ratings yet
- Expt. 6 Biochemical Test of UrineDocument13 pagesExpt. 6 Biochemical Test of UrineMary Ella Mae PilaNo ratings yet
- Strain Counterstrain Handout March 26 2010Document3 pagesStrain Counterstrain Handout March 26 2010David MarcksNo ratings yet
- Myopathy - SujathaDocument83 pagesMyopathy - SujathaRancho Vaibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Aimpt - 2015Document41 pagesAimpt - 2015Vino PrabaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Minimal Access Surgery PDFDocument520 pagesPediatric Minimal Access Surgery PDFDiana PescaruNo ratings yet
- CSIR Life Sciences Paper 2 Model QuestionsDocument12 pagesCSIR Life Sciences Paper 2 Model QuestionsImmanuel VinothNo ratings yet
- Group 5 (HIV&AIDS - BPA1A)Document23 pagesGroup 5 (HIV&AIDS - BPA1A)CindyNo ratings yet
- JanuszKorczak - How To Love A ChildDocument262 pagesJanuszKorczak - How To Love A Childvasilisaburzia100% (1)
- Coping With More People With More Illness. Part 1 - The Nature of The Challenge and The Implications For Safety and QualityDocument5 pagesCoping With More People With More Illness. Part 1 - The Nature of The Challenge and The Implications For Safety and QualitySusi RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- AUBF Gastric AnalysisDocument3 pagesAUBF Gastric AnalysisRichelyn Grace B. VenusNo ratings yet
- VT CriteriaDocument8 pagesVT CriterianitipatNo ratings yet
- Systematic Review and Meta AnalysisDocument13 pagesSystematic Review and Meta AnalysisAndreas AdiwinataNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Care Protocol For Hospital PhysiciansDocument648 pagesNeonatal Care Protocol For Hospital PhysiciansИван Мельник100% (2)
- NCP Patient 3 Cervical CADocument8 pagesNCP Patient 3 Cervical CAFatima LabaoNo ratings yet
- Master of Arts (Psychology) Term-End Examination December, 2015 MPC-002Document35 pagesMaster of Arts (Psychology) Term-End Examination December, 2015 MPC-002Rajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- Referat Gangguan Psikotik AkutDocument8 pagesReferat Gangguan Psikotik AkutYoga Oktavian NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Scioly 2012 Microbe MissionDocument2 pagesScioly 2012 Microbe Missionedguchi19100% (3)
- Retinal Diseases George Pile, MD: RetinaDocument5 pagesRetinal Diseases George Pile, MD: RetinaPrincess Cate MercadoNo ratings yet
- Donning and Removing Sterile GlovesDocument20 pagesDonning and Removing Sterile GlovesRicky Dwi Cahyo50% (6)