Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EARLY DEVELOPMENT-2nd 3rd Week
Uploaded by
Najah HanimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EARLY DEVELOPMENT-2nd 3rd Week
Uploaded by
Najah HanimCopyright:
Available Formats
2ND & 3RD WEEK : EARLY DEVELOPMENT
CHANGES IN SECOND WEEK OF DEVELOPMENT
CHANGE IN TROPHOBLAST
2 layers Inner cytotrophoblast
The cytotrophoblast is mitotically active.
The new cells migrate to the syncytiotrophoblast.
Outer syncytiotrophoblast
The cells don’t divide and the new cells are formed from the
cytotrophoblast.
Erodes maternal tissues
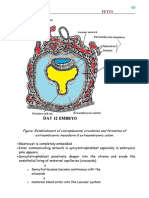
Lacunae (cavities) Spaces (cavities) called lacunae appear in the syncytiotrophoblast.
Filled with maternal blood from eroded capillaries of
endometrium.
Establishment of lacunae become continuous with the blood capillaries of the mother.
uteroplacental
circulation
Primary chorionic villi cells of the cytotrophoblast extend into the syncytiotrophoblast
forming the primary chorionic villi.
The spaces between the villi are called intervillous spaces which
are filled with maternal blood.
CHANGE IN INNER CELL MASS
Bilaminar germ disc Epiblast: the superior layer, formed of columnar cells.
Hypoblast: the inferior layer, formed of cuboidal cells facing the
blastocyst cavity.
Amniotic cavity Amniotic cavity appears in the epiblast. It has:
Amnioblasts = roof of amniotic cavity.
2ND & 3RD WEEK : EARLY DEVELOPMENT
Epiblast = floor of amniotic cavity.
Primary yolk sac cavity A thin membrane called exocoelomic (Heuser’s) membrane is
formed the margin of the hypoblast.
It surrounds a new cavity called the primary yolk sac.
Extraembryonic Formed from the exocoelomic membrane and fills the space between
mesoderm the cytotrophoblast and the exocoelomic membrane.
Extraembryonic coelom Cavities appear in the extraembryonic mesoderm, which fuse to
form a single cavity called the extraembryonic coelom.
It surrounds the yolk sac & the amniotic cavity except at the
connecting stalk (the future umbilical cord).
2 layers:
Extraembryonic somatic mesoderm: covering the amnion.
Extraembryonic splanchnic mesoderm: covering the yolk sac.
Chorion It is formed by:
The trophoblast.
The lining extraembryonic somatic mesoderm.
Chorion is formed of 3 layers:
Syncytiotrophoblast: outer layer.
Cytotrophoblast: middle layer.
Extraembryonic somatic mesoderm: inner layer.
Secondary yolk sac Hypoblast cells migrate along the inner surface of the exocoelomic
membrane surrounding a new cavity
2ND & 3RD WEEK : EARLY DEVELOPMENT
CHANGE IN THIRD WEEK OF DEVELOPMENT
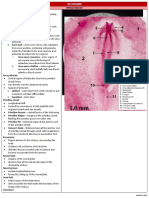
GASTRULATION
Bilaminar plate becomes trilaminar with the formation of the 3 germ layers
Formation of the:-
Prechordal plate
Primitive streak.
Primitive node (Hensen’s node).
Notochord.
Formation of the 3 germ layers:
Ectoderm, endoderm & mesoderm.
Allantois.
Prechordal plate cranial end of the hypoblast where the cuboidal cells
become columnar
Primitive Streak area of proliferation of the epiblast in the midline of the
caudal part of the embryonic disc
epiblast and hypoblast fuse behind the primitive streak
to form the cloacal membrane (future site of the anal
canal).
Primitive node (Hensen’s Node) area of proliferation of the epiblast at the cranial end of
the primitive streak
forms a midline cord of cells called the notochordal
process which grows cranially between the epiblast and
the hypoblast (primary endoderm).
2ND & 3RD WEEK : EARLY DEVELOPMENT
Notochord grows from the primitive node between the epiblast
* Remnant of the notochord in the and hypoblast till it reaches the prechordal plate.
intervertebral disk forms the nucleus Functions of the Notochord:
pulposus 1. Forms the axis for the formation of the vertebral
column.
2. Induces the development of the CNS.
Fate of the Notochord: it degenerates except 2 parts:
1. Upper part: forms part of the skull (basilar part of
the occipital bone).
2. Central part of the intervertebral disc: forms the
nucleus pulposus.
3 germ layers Endoderm: cells from the epiblast migrate to replace
the hypoblast forming the endoderm.
Mesoderm: other cells migrate between the epiblast and
the newly formed endoderm to form the
intraembryonic mesoderm.
Ectoderm: the remaining epiblast cells form the
ectoderm.
Intraembryonic Mesoderm Origin: from the epiblast through the:
1. Primitive streak: main source
2. Primitive node
Distribution:
Between the ectoderm and endoderm
Divisions: divided by a groove into 3 parts:
Paraxial mesoderm: on each side of the notochord
Intermediate mesoderm: in the floor of the groove
Lateral plate mesoderm: lateral to the groove
Allantois It is a diverticulum arising from the caudal part of the
yolk sac.
It extends into the connecting stalk (umbilical cord).
It forms the apex of the urinary bladder.
You might also like
- Universal Embryology SummaryDocument6 pagesUniversal Embryology SummaryJason TonioloNo ratings yet
- GA&E 14 - Bilaminar Germ DiscDocument34 pagesGA&E 14 - Bilaminar Germ DiscSu ZikaiNo ratings yet
- Jus 3 F 2003Document32 pagesJus 3 F 2003Abedur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Embryology in Weeks SimpleDocument38 pagesEmbryology in Weeks SimpleFrancesca vitaleNo ratings yet
- Embryology Notes emDocument25 pagesEmbryology Notes emAnonymous IwWT90VyNo ratings yet
- Development of Cardiovascular System PDFDocument58 pagesDevelopment of Cardiovascular System PDFVizhiNo ratings yet
- Gas Tru LationDocument53 pagesGas Tru LationSam MumoNo ratings yet
- Safari - 6 Nov 2018 at 4:57 PMDocument1 pageSafari - 6 Nov 2018 at 4:57 PMAfnan AdelNo ratings yet
- Embryology 1 Asr 3eny New 2024 (1)Document9 pagesEmbryology 1 Asr 3eny New 2024 (1)Hassan AwadNo ratings yet
- Gastrulation in BirdsDocument20 pagesGastrulation in Birdskashif manzoor75% (4)
- Embryonic Period: Dr. Khin Ma MADocument34 pagesEmbryonic Period: Dr. Khin Ma MAIbrahim Foondun100% (1)
- Embryonic Period Development Gastrulation MesodermDocument40 pagesEmbryonic Period Development Gastrulation MesodermAliya Batrisya AliyaNo ratings yet
- 24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabDocument3 pages24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabIvy Cruz50% (2)
- 0 Review Embryoloby 2024.3 2Document34 pages0 Review Embryoloby 2024.3 2sh.farangissNo ratings yet
- Gastrulationin MammalsDocument16 pagesGastrulationin MammalsHarsha MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Embrology 14 Jan FinalDocument16 pagesEmbrology 14 Jan FinalBhumi Chouhan100% (1)
- Bilaminar Germinal DiscDocument53 pagesBilaminar Germinal Discapi-261507800No ratings yet
- 5.1 Frog Embryology SlidesDocument10 pages5.1 Frog Embryology SlidesChandan kumar MohantaNo ratings yet
- Third To Eigth WeekDocument13 pagesThird To Eigth WeekKyla CalsoNo ratings yet
- Development of The NSDocument7 pagesDevelopment of The NSJean Pierre Chastre LuzaNo ratings yet
- Frog Embryology PDFDocument17 pagesFrog Embryology PDFHohai ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Weeks 3 - 8Document32 pagesWeeks 3 - 8Stefan HutsonNo ratings yet
- Embryology Notes emDocument32 pagesEmbryology Notes emSavita HanamsagarNo ratings yet
- Embryology 2020Document8 pagesEmbryology 2020A-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- The Third Week of Development: TH THDocument8 pagesThe Third Week of Development: TH THbarbacumlaudeNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal DevelopmentDocument40 pagesMusculoskeletal DevelopmentMajd HusseinNo ratings yet
- 2 AND 3 WEEKS OF DEVELOPMENTDocument40 pages2 AND 3 WEEKS OF DEVELOPMENTjabirNo ratings yet
- Embryology Notes emDocument18 pagesEmbryology Notes emLuqman AfifNo ratings yet
- 3rd Week of Development 2022Document36 pages3rd Week of Development 2022aameena nadaNo ratings yet
- Embryology of the Muscular and Respiratory SystemsDocument26 pagesEmbryology of the Muscular and Respiratory SystemsLiz NGALEUNo ratings yet
- Week 6 - Day 1 - Development of Body CavitiesDocument46 pagesWeek 6 - Day 1 - Development of Body CavitiesNsikan GabrielNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Thorax ReviewDocument18 pagesAnatomy Thorax Reviewyachiru121No ratings yet
- Embryology Notes - emDocument18 pagesEmbryology Notes - emrigario80% (5)
- Gastrulation and Segmentation ofDocument20 pagesGastrulation and Segmentation ofAina AdesolaNo ratings yet
- Gastrulation - Week Three of Development: Dr. BarasaDocument37 pagesGastrulation - Week Three of Development: Dr. BarasaGrace NdutaNo ratings yet
- Gastrulation and Placental Development 3rd WeekDocument26 pagesGastrulation and Placental Development 3rd Weekaimi Batrisyia100% (1)
- 48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFDocument5 pages48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFSheanna May FuriaNo ratings yet
- Gastrulation and Neurulation Processes in Embryonic DevelopmentDocument74 pagesGastrulation and Neurulation Processes in Embryonic DevelopmentCynthiaNo ratings yet
- Elzatona Written 2023Document10 pagesElzatona Written 2023mahmoud ezzeldeenNo ratings yet
- 6 - 2nd Week of Devlt.-Dr - GosaiDocument22 pages6 - 2nd Week of Devlt.-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Seminar 2Document7 pagesSeminar 2gatorssoccer1313No ratings yet
- Trans 5 - Frog OrganogenesisDocument32 pagesTrans 5 - Frog Organogenesisangelica sherinnNo ratings yet
- Development of the Nervous SystemDocument45 pagesDevelopment of the Nervous SystemAbdimalik AliNo ratings yet
- 04 - Develpment Week 3Document12 pages04 - Develpment Week 3hiba jasimNo ratings yet
- Embryology-Nervous System DevelopmentDocument157 pagesEmbryology-Nervous System DevelopmentGheavita Chandra DewiNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Period 1Document35 pagesEmbryonic Period 1Riya SinghNo ratings yet
- Dumaguit (2021)Document12 pagesDumaguit (2021)Dimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- Development of CNSDocument84 pagesDevelopment of CNSSamuel frankNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Organ Plants (Botany)Document23 pagesMale Reproductive Organ Plants (Botany)kunalNo ratings yet
- 24 HR Chick ReviewerDocument4 pages24 HR Chick ReviewerGail AmuraoNo ratings yet
- Histology Practical PDF Bytom CnaanDocument65 pagesHistology Practical PDF Bytom CnaanMichel MunozNo ratings yet
- Development of FaceDocument19 pagesDevelopment of FaceAkhila ReddyNo ratings yet
- Gastrulation: Understanding Cell Movements That Occur During GastrulationDocument33 pagesGastrulation: Understanding Cell Movements That Occur During Gastrulationandreana kusumaNo ratings yet
- Embryology of The CNS 2022Document130 pagesEmbryology of The CNS 2022isicheipraise3No ratings yet
- ZL 124 Lecture 7 - Gastrulation in Birds & MammalsDocument36 pagesZL 124 Lecture 7 - Gastrulation in Birds & MammalsNestory MartineNo ratings yet
- 09 - Musculoskeletal DevelopmentDocument8 pages09 - Musculoskeletal DevelopmentAXA OFFICIALNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Development and OrganogenesisDocument33 pagesEmbryonic Development and OrganogenesisMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- L1-Development of male genital systemDocument25 pagesL1-Development of male genital systemAhmed AbdellaNo ratings yet
- Third To Eighth WeekDocument33 pagesThird To Eighth WeekGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip and Palate Management: A Comprehensive AtlasFrom EverandCleft Lip and Palate Management: A Comprehensive AtlasRicardo D. BennunNo ratings yet
- Quiz on the Chest Wall Anatomy by Dr Adel BondokDocument10 pagesQuiz on the Chest Wall Anatomy by Dr Adel BondokNajah Hanim100% (2)
- Quiz On The HeartDocument11 pagesQuiz On The HeartNajah HanimNo ratings yet
- Quiz On The Upper LimbDocument6 pagesQuiz On The Upper LimbNajah HanimNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Anomalies ExplainedDocument4 pagesChromosomal Anomalies ExplainedNajah HanimNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - Examples of Antibiotic ResistanceDocument1 pageAssignment 2 - Examples of Antibiotic ResistanceNajah HanimNo ratings yet
- Aswini - EmbryologyDocument16 pagesAswini - EmbryologyIssac Jerin MathewsNo ratings yet
- Embryonic InductionDocument11 pagesEmbryonic Inductionsourya jyoti dashNo ratings yet
- Stages of Human DevelopmentDocument18 pagesStages of Human DevelopmentElaine Galleros RosalitaNo ratings yet
- RINCIAN KASUS OBSTETRI DAN GINEKOLOGI RSUD ASY-SYIFA TALIWANGDocument11 pagesRINCIAN KASUS OBSTETRI DAN GINEKOLOGI RSUD ASY-SYIFA TALIWANGimamsantos1191No ratings yet
- MODULE 3 Lesson 1,2,3 Prof LanitDocument16 pagesMODULE 3 Lesson 1,2,3 Prof LanitCRING TVNo ratings yet
- General Embryology Ta7 Notes 2023Document14 pagesGeneral Embryology Ta7 Notes 2023ibraham mohammadNo ratings yet
- Stages of Prenatal DevelopmentDocument20 pagesStages of Prenatal DevelopmentKimay DanielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2B Developmental Stages According To SantrockDocument44 pagesChapter 2B Developmental Stages According To SantrockJheny Palamara100% (1)
- CleavageDocument4 pagesCleavageapi-38010390% (1)
- 18 HR 1Document5 pages18 HR 1bingchillingNo ratings yet
- 4 - Embryology Lecture 4 (Week 2 of Development A)Document31 pages4 - Embryology Lecture 4 (Week 2 of Development A)Mostafa MostafaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Comprehensive Perinatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care 4th Edition by Whitaker Isbn 10 1439059438 Isbn 13 9781439059432Document7 pagesTest Bank For Comprehensive Perinatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care 4th Edition by Whitaker Isbn 10 1439059438 Isbn 13 9781439059432trangdatif0No ratings yet
- Embyology UG Part II Note 2 - Development of Amphioxus Drprity Mam2Document8 pagesEmbyology UG Part II Note 2 - Development of Amphioxus Drprity Mam2Adwika DeoNo ratings yet
- Bronfenbrenner'S Ecological System TheoryDocument7 pagesBronfenbrenner'S Ecological System TheoryKeith SaratorioNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8: Embryology of The FrogDocument4 pagesExercise 8: Embryology of The FrogDaks ZabateNo ratings yet
- Grades Blastomere Size Fragmentation 4 3 2 1Document4 pagesGrades Blastomere Size Fragmentation 4 3 2 1easa_tNo ratings yet
- Indice CerebroplacentarioDocument10 pagesIndice CerebroplacentarioJose Octavio CastroNo ratings yet
- Stages of Fetal Development FinalDocument43 pagesStages of Fetal Development Finalsanthiyasandy100% (6)
- Rapid Review of Embryology, First PDFDocument137 pagesRapid Review of Embryology, First PDFmayurdadhaniya100% (1)
- Week Wise Pregnancy & Fetus DevelopmentDocument22 pagesWeek Wise Pregnancy & Fetus DevelopmentVirtue BabyNo ratings yet
- Forms of Embryonic Primordia: Prof. Anthony Obioma NwaoparaDocument32 pagesForms of Embryonic Primordia: Prof. Anthony Obioma NwaoparamatthewNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The Developing FetusDocument52 pagesNursing Care of The Developing FetusKyrriel CNo ratings yet
- Placentation: Structure, Type and Physiology of Placenta: Nimita KantDocument24 pagesPlacentation: Structure, Type and Physiology of Placenta: Nimita KantNikkNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument59 pagesPlacentaEdna Jenkins100% (9)
- DR - Suryadi Embriologi Prenatal PDFDocument64 pagesDR - Suryadi Embriologi Prenatal PDFHenry wijaya oeijNo ratings yet
- Embriologi 2022Document33 pagesEmbriologi 2022ikhlas maulanaNo ratings yet
- BoneDocument7 pagesBoneMarshallchiyan PhilipNo ratings yet
- Intra Embryonic MesodermDocument26 pagesIntra Embryonic MesodermEniola DaramolaNo ratings yet
- Embryo MCQ 9 ItemsDocument2 pagesEmbryo MCQ 9 ItemsBeda MalecdanNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and Implantation ProcessDocument16 pagesFertilization and Implantation ProcessIgnacio FelicityNo ratings yet