Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CEO4720 Advanced Environmental Engineering
CEO4720 Advanced Environmental Engineering
Uploaded by
maazmahboob2Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CEO4720 Advanced Environmental Engineering
CEO4720 Advanced Environmental Engineering
Uploaded by
maazmahboob2Copyright:
Available Formats
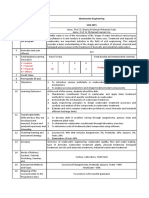
+Departmen Course Course Course Pre- Course Credit Contact Total
t No. Title Designation Requisites Type Hours Hours Contact
L T P Hours
Advanced
Civil
CEO4720 Environmental OE None Theory 4 3 1 0 4
Engineering
Engineering
Course Assessment Method
1. Assignments and Oral Quizzes (15%)
2. Mid-Semester Examination (25%)- 1 Hour
3. End Semester Examination (60%)- 2 Hour
Course Objective
1. To impart fundamental training and knowledge about this coveted field of engineering & sciences for
students of other disciplines as well (like Electrical, Electronics, Mechanical, Petro-Chemical,Architecture
etc.)
2. To develop basic understanding about the pollution control measures for water, air and land coupled with
application in the industry of any nature.
3. To provide students an in-depth importance and understanding of the physical, chemical, and biological
processes involved in the treatment of water, wastewater, air pollution control and disposal of solid wastes.
4. To develop a basic foundation for higher studies and research in both basic and applied environmental
disciplines and provides a direct transition to the post-graduate engineering programmes.
Course Outcomes
Upon successful completion of this course, it is expected that students will be able to:
1. Differentiate between environmental sciences and engineering
2. Address the importance of the environment in general and may apply fundamental concepts of
Environmental Engineering & Sciences in any field of their career.
3. Capable to face challenges and apply their knowledge in the areas of infrastructure development schemes,
industry, and environmental remediation.
4. Hands-on basic design procedure, field studies, and trips provide an understanding of the problems at
hand and thus make them capable to undertake any relevant task independently or as a team.
Topics Covered
Unit 1 Fundamentals of chemistry concept in environmental engineering: Water and Wastewater Quality
Parameters, their units, laboratory techniques for measurement, significance and adverse impact on
environment and human health
Unit 2 Fundamentals of microbiology in environmental engineering: Role of microorganisms in
environmentally relevant processes including bioremediation of pollutants, biological treatment systems
like activated sludge process, UASB etc.
Unit 3 Fundamentals of physio-chemical and biological processes of water and wastewater treatment:
Screening, Grit Removal, Coagulation & Flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, biological systems,
sludge treatment.
Unit 4 Mass balance and energy balance approach: Material Balance, Types of Reactors, Reactor Kinetics,
Steady-State Condition, Introduction to Air Pollution, their sources, standards, health effects,
Introduction to Solid Waste Management and Noise Pollution and its control.
Text Books and/or Reference Materials
1. Howard S. Peavy, et al., 'Environmental Engineering’ Mc Graw- Hill Book Co.
2. Sawyer and Mc Carty, ‘Chemistry for Environmental Engineering’ Mc Graw- Hill Book Co.
Additional Learning Source
1. Ross E. McKinney, ‘Microbiology for Sanitary Engineers' Mc Graw- Hill Book Co.
2. NPTEL course material from IITs
131
You might also like
- Invocation of LilithDocument4 pagesInvocation of Liliths.bheeshmar100% (2)
- ATI Practice TestDocument6 pagesATI Practice TestMelissa Jaramillo66% (41)
- The Smoking GunDocument6 pagesThe Smoking Guneduardo castro roblesNo ratings yet
- CE195 Case StudyDocument7 pagesCE195 Case StudyRold BaldsNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument48 pagesSyllabusmoniraNo ratings yet
- Course Out Line For EIADocument2 pagesCourse Out Line For EIAAbdanur JihadNo ratings yet
- Syllabus M.tech 2nd SemDocument6 pagesSyllabus M.tech 2nd Semer.nazrulkhan430No ratings yet
- Wastewater SyllabusDocument5 pagesWastewater SyllabusRichard PekitpekitNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science, JU MSC - SyllabusDocument19 pagesEnvironmental Science, JU MSC - SyllabusFabiha Shafi MimNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Earth and Environmental Sciences Course Number: ENV 2205 Course Title: Introduction To Environmental Technology Credits: 3Document4 pagesFaculty of Earth and Environmental Sciences Course Number: ENV 2205 Course Title: Introduction To Environmental Technology Credits: 3michealNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument5 pagesCourse OutlineCatherine MasoudNo ratings yet
- VCB 3073 Wastewater Engineering - SyllabusDocument3 pagesVCB 3073 Wastewater Engineering - SyllabusRuben BenjaniNo ratings yet
- Pollution ControlDocument4 pagesPollution ControlDhwanikNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document4 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Hitesh PariharNo ratings yet
- SCHEME - G Fourth Semester CODocument37 pagesSCHEME - G Fourth Semester COAnsari SameerNo ratings yet
- Course Handout Ee Y18 2018-2019-SignedDocument14 pagesCourse Handout Ee Y18 2018-2019-SignedRajesh Chowdary TataNo ratings yet
- Eia Natural ResourcesDocument2 pagesEia Natural ResourcesAdiba ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 EIADocument86 pagesChapter 1 EIAMUHAMMAD LUQMAN IZZUDDIN BIN SUHAIMINo ratings yet
- ENVE206 SyllabusDocument2 pagesENVE206 Syllabusyasemin yılmazNo ratings yet
- Syllabus EVSDocument1 pageSyllabus EVSArbab 02No ratings yet
- CHBE370 Course SyllabusDocument5 pagesCHBE370 Course Syllabusjpcobucci58No ratings yet
- Chem 002 SyllabusDocument2 pagesChem 002 SyllabusJohn Cedric Satojeto100% (1)
- Course Guide: Environmental Science and Engineering: ESSU-ACAD-501 - Version 3page 1 of 2 Effectivity Date: June 10, 2021Document2 pagesCourse Guide: Environmental Science and Engineering: ESSU-ACAD-501 - Version 3page 1 of 2 Effectivity Date: June 10, 2021lupin balanayNo ratings yet
- Finalized Water Pollution Course Outline (OBE Based)Document3 pagesFinalized Water Pollution Course Outline (OBE Based)Rao Ahsan AttaNo ratings yet
- TCET FE Environmental Studies (2018-2019)Document219 pagesTCET FE Environmental Studies (2018-2019)KevinNo ratings yet
- Ecological PlanningDocument12 pagesEcological Planningy2kareinNo ratings yet
- Course Number ES 314 Descriptive Title Environmental Engineering Course DescriptionDocument2 pagesCourse Number ES 314 Descriptive Title Environmental Engineering Course DescriptionRegidor PetilunaNo ratings yet
- CE214 - FCH - Environmental Quality and ProcessesDocument4 pagesCE214 - FCH - Environmental Quality and ProcessesAayush SidanaNo ratings yet
- PG Level Subject: EIA LegislationDocument2 pagesPG Level Subject: EIA LegislationBalaKumar KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- HydrologyDocument4 pagesHydrologyRafia AbidNo ratings yet
- Public Health Engineering NotesDocument43 pagesPublic Health Engineering NotesTuray Abdullah FNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus Course DetailsDocument2 pagesCourse Syllabus Course Detailskujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Sewage Course OutlineDocument3 pagesSewage Course OutlineMuluken MelesseNo ratings yet
- L-1 IntroDocument18 pagesL-1 IntroMuhammad SajjadNo ratings yet
- CHE 611 Course Outline F2015Document4 pagesCHE 611 Course Outline F2015Waleed WaleedNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument7 pagesHydraulicsBernard PalmerNo ratings yet
- CE 110 Introduction To Environmental Engineering SyllabusDocument8 pagesCE 110 Introduction To Environmental Engineering SyllabusJohnclaude ChamandiNo ratings yet
- VAC 2 Environmental Studies 1Document4 pagesVAC 2 Environmental Studies 1pd62658mNo ratings yet
- Syllabus, Bioremediation W2019Document8 pagesSyllabus, Bioremediation W2019Waleed SulimanNo ratings yet
- Applied Chemistry (Non IT)Document5 pagesApplied Chemistry (Non IT)himanshuchawla654No ratings yet
- PCSM (3140509) Study MaterialsDocument22 pagesPCSM (3140509) Study MaterialsAkasH BinDNo ratings yet
- Chem 304 202210 2021 11 02Document6 pagesChem 304 202210 2021 11 02abrar jawad fardinNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 6611Document2 pagesSyllabus 6611Calin DiaconescuNo ratings yet
- 2018 - 2019 Environmental Engineering EnvirEng Syllabus IEDocument5 pages2018 - 2019 Environmental Engineering EnvirEng Syllabus IEImogen YstNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument4 pagesSyllabusIan HoldemanNo ratings yet
- Course ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENTDocument3 pagesCourse ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENTikhwanstorageNo ratings yet
- Environmental ChemistryDocument3 pagesEnvironmental Chemistryrlh2022No ratings yet
- Introduction To Environmental Engineering and Environmental SafetyDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Environmental Engineering and Environmental SafetyMichiko MatsuoNo ratings yet
- 1 CHEN401 - First Day Package - Prof. N.S. MainaDocument5 pages1 CHEN401 - First Day Package - Prof. N.S. Mainasaminumusa217No ratings yet
- Mapúa Institute of Technology: School of Chemical Engineering and Chemistry (Intramuros)Document5 pagesMapúa Institute of Technology: School of Chemical Engineering and Chemistry (Intramuros)Mikaella TambisNo ratings yet
- Environmental StudiesDocument3 pagesEnvironmental StudiespavanNo ratings yet
- Eem MinDocument59 pagesEem Minvishal bijiNo ratings yet
- CV7017 - Physico Chemical Treatment ProcessDocument6 pagesCV7017 - Physico Chemical Treatment ProcessHelly DesaiNo ratings yet
- L1 - SSC4353 Consumer Chemistry PDFDocument3 pagesL1 - SSC4353 Consumer Chemistry PDFlet's skip thisNo ratings yet
- ETZ C362 HandoutDocument4 pagesETZ C362 HandoutchetanursNo ratings yet
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani: Pilani Campus AUGS/ AGSR DivisionDocument3 pagesBirla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani: Pilani Campus AUGS/ AGSR DivisionrockNo ratings yet
- 2011-13 Cal Poly Catalog: Civil & Environmental Engineering DepartmentDocument3 pages2011-13 Cal Poly Catalog: Civil & Environmental Engineering DepartmentnedalmasaderNo ratings yet
- An Assignment For Awareness of Some Environmental Issues Related To ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesAn Assignment For Awareness of Some Environmental Issues Related To Thermodynamicshafsa AliNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesIrrigation Lesson PlanKAMALI R BITNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution and Its Control Technologies SyllabusDocument4 pagesWater Pollution and Its Control Technologies SyllabusOmkar ShindeNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education, Mumbai: W.E.F Academic Year 2012-13 G' SchemeDocument38 pagesMaharashtra State Board of Technical Education, Mumbai: W.E.F Academic Year 2012-13 G' Schemevikram kumarNo ratings yet
- ENV 107 Course Outline Summer 2020-MdoDocument3 pagesENV 107 Course Outline Summer 2020-MdoAl-Amin Khan FilmsNo ratings yet
- Key Questions in Environmental Toxicology: A Study and Revision GuideFrom EverandKey Questions in Environmental Toxicology: A Study and Revision GuideNo ratings yet
- Pollution Control and Resource Recovery: Industrial Construction and Demolition WastesFrom EverandPollution Control and Resource Recovery: Industrial Construction and Demolition WastesNo ratings yet
- PE - Module 3Document7 pagesPE - Module 3Princess Joana LamadridNo ratings yet
- Development of Adolescent Problem BehaviorDocument11 pagesDevelopment of Adolescent Problem BehaviorVisvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Stages of Grief After A Breakup 0Document1 pageStages of Grief After A Breakup 0Lovely Joy FiguerasNo ratings yet
- Irradiation Applications in Dairy Products: A ReviewDocument17 pagesIrradiation Applications in Dairy Products: A ReviewPravin Zine PatilNo ratings yet
- 3/2-Way Spool Valves With Solenoid Operation Type KKDER1Document8 pages3/2-Way Spool Valves With Solenoid Operation Type KKDER1nemi90No ratings yet
- Acasestudyfrom Mahan Coal Block Singrauli MPDocument5 pagesAcasestudyfrom Mahan Coal Block Singrauli MPSarah DanielNo ratings yet
- 1.3 - Social Identity and Changes - The ElderlyDocument4 pages1.3 - Social Identity and Changes - The ElderlySharik CheemaNo ratings yet
- FSW-Tech Handbook For Specialists and Engineers - enDocument172 pagesFSW-Tech Handbook For Specialists and Engineers - enkamal touilebNo ratings yet
- Queer Theory, Intersectionality, and LGBT-Parent FamiliesDocument21 pagesQueer Theory, Intersectionality, and LGBT-Parent Familiescarolscribd32No ratings yet
- India Energy Week 2023 Call For Papers BrochureDocument12 pagesIndia Energy Week 2023 Call For Papers BrochureaharnishaNo ratings yet
- People v. EchegarayDocument9 pagesPeople v. EchegarayJohn Soap Reznov MacTavishNo ratings yet
- 1103 1104FeaturesBenefitsDocument13 pages1103 1104FeaturesBenefitsjulio cesarNo ratings yet
- CommScope - RV4 65D R5 V6 - PentaDocument4 pagesCommScope - RV4 65D R5 V6 - PentaSana UllahNo ratings yet
- Pulidor DentalDocument16 pagesPulidor DentalAndre PereiraNo ratings yet
- Achilles Supply Chain Mapping Explained White PaperDocument12 pagesAchilles Supply Chain Mapping Explained White PaperGyaneshwar SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- Da Vinci S, Da Vinci Si Quick Reference Guide (Emergency Grip Release) (551979-05)Document2 pagesDa Vinci S, Da Vinci Si Quick Reference Guide (Emergency Grip Release) (551979-05)Juan RamirezNo ratings yet
- Datasheet of ACS730Document25 pagesDatasheet of ACS730Nguyên NghĩaNo ratings yet
- Narayana GT 5 QPDocument17 pagesNarayana GT 5 QPGowri Shankar100% (1)
- Indictment For Steven Mathew WallenDocument3 pagesIndictment For Steven Mathew WallenAnonymous 6Exo2J1No ratings yet
- Nurses LE 11-2022Document242 pagesNurses LE 11-2022PRC Baguio33% (3)
- VFD Design GuideDocument7 pagesVFD Design GuideKhaldoon AlnashiNo ratings yet
- COO Retail Restaurant Hospitality in Dallas FT Worth TX Resume Randall McGeeDocument2 pagesCOO Retail Restaurant Hospitality in Dallas FT Worth TX Resume Randall McGeeRandallMcGee100% (1)
- TDS Nitozinc Primer IndiaDocument3 pagesTDS Nitozinc Primer Indiasyed AffanNo ratings yet
- MG FCPS GuidelinesDocument23 pagesMG FCPS GuidelinesWajih FarhanNo ratings yet
- PRDS Valve: Different Options For UseDocument3 pagesPRDS Valve: Different Options For UseRahul GawaliNo ratings yet
- 1 Mechanical Behavior of MaterialsDocument7 pages1 Mechanical Behavior of MaterialsMohammed Rashik B CNo ratings yet