Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MH Kia 2.9
MH Kia 2.9
Uploaded by
Trương HàoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MH Kia 2.9
MH Kia 2.9
Uploaded by
Trương HàoCopyright:
Available Formats
199°C(282.2°F) Dom SPECIFICATION Temper: | ~40(-40) | -20(-4) (32) 2068) | i104) | so(r40) | 800176) Resistance | 4a | ta4-1e8| 574 | 29-26] 115 | o58 | ose FLB -42 FUEL SYSTEM (J3 TCI) [SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM] [CIRCUIT DIAGRAM] [CONNECTION INFORMATION) ors cou a inion 2 608-2) 150 - ECTS Signal 1 ‘ECM E03-2 (51) ‘Sensor Ground ee z str : ‘ster 3 ‘ECM E03-2 (50) ECTS Signal gee (2202) ono [HARNESS CONNECTORS] no 43, EoTs ECM DTC TROUBLESHOOTING PROCEDURES FLB -43, INSPECTION PROCEDURE 1. CHECK ECTS AND ECM CONNECTORS: 1. Thoroughly check connectors for looseness, poor connection, bending, corrosion, contamination, deterioration, or damage. + Refer to "CONNECTOR INSPECTION PROCEDURE" in BASIC INSPECTION PROCEDURE. Are all connectors good? Yes No. | Repair or replace it. . CHECK REFERENCE VOLTAGE TO ECTS ‘Tum ignition switch to OFF and disconnect ECTS connector. ‘Turn ignition switch to ON. Measure voltage in harness between terminal 3 of ECTS harness connector and chassis ground + Specification: approximately SV eRap Is(Are) voltage(s) within specification? [vs] No | Repair open or short circuit in harness. 3. CHECK FOR OPEN IN HARNESS Ss 1. Tum ignition switch to OFF, and then disconnect ECM and ECTS "| ects connector. a 2, Measure resistance between terminal 3 of ECTS harness connector i and terminal E03-2(50) of ECM harness connector. 3. Measure resistance between terminal 1 of ECTS harness connector cuter <4 1] 3] @) and terminal E03-2(51) of ECM hamess connector. sid 50) * Specification: below 19 . 03-2 Is(Are) resistance(s) within specification? Yes No | Repair open circuit in harness. FLB -44 4. CHECK FOR SHORT TO GROUND IN HARNESS 1. Tum ignition switch to OFF, and then disconnect ECM and ECTS connector. 2. Measure resistance between terminal 3 of ECTS hamess connector and chassis ground. 3. Measure resistance between terminal 3 and 1 of ECTS hamess connector. © Specification: infinite Is(Are) resistance(s) within specification? oO” ECTS @ ~d: 3 ED cose : ECM FUEL SYSTEM (J3 TCI) Yes No | Repair short or short to chassis ground in harness. 5. CHECK FOR SHORT TO POWER IN HARNESS 4, Tum ignition switch to OFF, and then disconnect ECM and ECTS connector, 2, Turn ignition switch to ON. 3. Measure voltage between terminal 3 of ECTS hamess connector land chassis ground. * Specification: below 0.5V ls(Are) vottage(s) within specification? @ on Sf e032 ECM ECTS so) f Yes No_ | Repair short to power in harness. 6. CHECK ECTS RESISTANCE 1. Tum ignition switch to OFF and disconnect ECTS connector. 2. Measure resistance between terminal 3 and 1 of ECTS connector. * Refer to "SPECIFICATION" for more information. Is(Are) resistance(s) within specification? o” 03-2 ECTS 2 51 ECM a No | Replace the ECTS. Proceed with "ECM PROBLEM INSPECTION PROCEDURE" in BASIC INSPECTION PROCEDURE. DTC TROUBLESHOOTING PROCEDURES TROUBLESHOOTING FOR DTC prc P0120 __| Accelerator Position Sensor (APS) 1 Circuit Malfunction ] 0a Signal low (Open circuit or short circuit to ground) cc-CODE Ob Signal high (Short circuit to battery tine) 06 | Value incoherent DTC P0220 _| Accelerator Position Sensor (APS) 2 Circuit Malfunction 0a Signal low (Open circuit or short circuit to ground) ob Signal high (Short circuit to battery i ee cone ignal high ( battery line) aa 02 Signal low 03 Signal high vowing) DESCRIPTION distinct and different power sources so there is built in re~ ‘dundaney of information giving reliable driver's request in- formation. ‘A voltage is generated across the potentiometer in the On electronic injection systems, there is no longer a load lever that mechanically controls the fuelling. The flow is calculated by the ECM depending on a number of param- eters, including pedal position, which is measured using a potentiometer. The absence of a mechanical link between the accelerator pedal and the injection system presents a risk of loss of control of the engine in the event of a failure ‘of the component in charge of providing the driver's re- ‘quest information to the injection system. The pedal sen- or therefore has two potentiometers whose slides areme- chanically soli. The two potentiometers are supplied from acceleration position sensor as a function of the accel- erator-pedal setting. Using a programmed characteristic curve, the pedal's position is then calculated from this volt- age. DTC DETECTING CONDITION (P0120) CC-CODE ___ Detecting Condition ee cispenlArea oa + Accelerator pedal angle (APS 1) < 4% | E 0b ‘+ Accelerator pedal angle (APS 1) > 95% ee eee * [Accelerator pedal angle (APS 1) - Accelerator + ECM ia pedal angle (APS 2) > 8% FLB -46 FUEL SYSTEM (J3 TCI) F846 EEO (P0220) ___ 6G-CODE Detecting Condition ‘Suspect Area 0a ~ Accelerator pedal angle (APS 2) < 2% ‘Ob * Accelerator pedal angle (APS 2) > 49.5% e noes or short in APS cirucit 02 ‘Sensor supply vollage < 3.17V Seca 03 * Sensor supply voltage > 4.63V SPECIFICATION i Condition CT = WOT Pedal Anglo at 106" EB [aps 1 14.66 ~ 18.34% 77.08 ~ 86.92% VouvVin (%) - a APS 2 7.36 ~ 7.85% 385 ~ 43.5% [SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ] [CIRCUIT DIAGRAM) [CONNECTION INFORMATION} APs com "Fermin | Connectedto Fonction ws: |e al * OM E09-1(1) | APS 2 Signal [5 Reference Votage 2 EM E00. (2) 7ABS 1 Signal 3] ECM E081 (10) | Referee Votage 2 cos | 5 (e001) | 3 ECM 05-1 (6) | Sensor Ground {3-cNo esa é eM E06" (6) | Reference Votage e S {05-1 HF netrence Vohage ( : (222-0 5 aps 2 sit 4 004 (08 Ip eno [HARNESS CONNECTORS] (a 2 [3+ GyisTe) Mo7 ECTS 03-1 OM DTC TROUBLESHOOTING PROCEDURES FLB -47 INSPECTION PROCEDURE 1. CHECK APS AND ECM CONNECTORS 1. Thoroughly check connectors for looseness, poor connection, bending, corrosion, contamination, deterioration, or damage. * Refer to "CONNECTOR INSPECTION PROCEDURE" in BASIC INSPECTION PROCEDURE. Are all connectors good? 2. CHECK REFERENCE VOLTAGE TO APS 1. Tumigniionevtch to OFF and disconnect APS connector, @) | apst_ | apse 2, Turn ignition switch to ON. -O—-0—0- 3, Measure voltage in harness between terminal 6 of APS harness ‘connector and chassis ground [APS 1} 4, Measure voltage in harness between terminal 2 of APS harness ‘connector and chassis ground [APS 2]. + Specification: approximately 5V Is(Are) voltage(s) within specification? Yes No | Repair open or short circuit in harness. 3, CHECK FOR OPEN IN HARNESS 1. Tum ignition switch to OFF, and then disconnect ECM and APS ee APS1 APS2 2, Measure resistance between terminal 2 of APS hamess connector and terminal E03-1(2) of ECM harness connector [APS 1], 8, Measure resistance between terminal 5 of APS harness connector and terminal E03-1(3) of ECM harness connector [APS 1] 4, Measure resistance between terminal 1 of APS hamess connector and terminal E03-1(11) of ECM harness connector [APS 2]. 5, Measure resistance between terminal 4 of APS hamess connector and terminal E03-1(12) of ECM hamess connector [APS 2] eos + Specification: below 19 ECM Is(Are) resistance(s) within specification? Yes No | Repair open circuit in hamess. FLB -48 FUEL SYSTEM (J3 TCI) 4, CHECK FOR SHORT TO GROUND IN HARNESS 1, Turn ignition switch to OFF, and then disconnect ECM and APS connector. 2, Measure resistance between terminal 2 of APS hamess connector and chassis ground (APS 1]. 3, Measure resistance between terminal 2 and 5 of APS harness connector [APS 1]. 4. Measure resistance between terminal 1 of APS hamess connector and chassis ground [APS 2]. 5. Measure resistance between terminal 1 and 4 of APS harness connector [APS 2). * Specification: infinite Is(Are) resistance(s) within specification? (SENSOR 1) Q) 3 2 140°C(284°F) ecm SPECIFICATION Tee ey. | 20022) | 2004) o(s2) 20168) | 40(104) | 60140) | 80(176) Resistance | 2o2-a18| 102-181 | 52-08 | 20-27 | 11-13 | o54~065| 090-82 DTC TROUBLESHOOTING PROCEDURES FLB-51 [SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM] [CIRCUIT DIAGRAM] [CONNECTION INFORMATION] fe Eom. 2 e034) [- Terminal | Connected to Function [ {55- ano 1 EOM £032 (54) FTS Signal 2 OM 03: ‘Sensor Ground i ©2821 signal 2 (65) [HARNESS CONNECTORS] 95 Fs. Sa [ela le lees [a7 aefaet 21] 1 |e [ee [se [7072] 70 3122 a [ar | [so for} ea 35] co] eos |e [35 [oo [oe [sa v2 [on 03-2 FLB -52 FUEL SYSTEM (J3 TCI) INSPECTION PROCEDURE Are all connectors good? 1. CHECK FTS AND ECM CONNECTORS 1. Thoroughly check connectors for looseness, poor connection, bending, corrosion, contamination, deterioration, or damage. * Refer to "CONNECTOR INSPECTION PROCEDURE" in BASIC INSPECTION PROCEDURE. Yes No Repair of replace it. eps CHECK REFERENCE VOLTAGE TO FTS ‘Tur ignition switch to OFF and disconnect FTS connector. “Turn ignition switch to ON. Measure voltage in harness between terminal 1 of FTS harness connector and chassis ground. «Specification: approximately 5V Is(Are) voltage(s) within specification? {yee} | m Repair open or short circuit in hamess. FTS connector. 3, CHECK FOR OPEN IN HARNESS 1. Tum ignition switch to OFF, and then disconnect ECM and 2. Measure resistance between terminal 1 of FTS harness connector and terminal £03-2(654) of ECM hamess connector. 3. Measure resistance between terminal 2 of FTS harness connector and terminal £03-2(55) of ECM hamess connector. + Specification: below 10. Is(Are) resistance(s) within specification? ©" |_-s F03-2| Yes No Repair open circuit in harness.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- SES-LHDDocument38 pagesSES-LHDTrương HàoNo ratings yet
- HL-LHDDocument11 pagesHL-LHDTrương HàoNo ratings yet
- General Information P1Document27 pagesGeneral Information P1Trương HàoNo ratings yet
- BDCDocument13 pagesBDCTrương HàoNo ratings yet
- Brake and Vehicle Dynamic Control Systems - Function and ComponentsDocument63 pagesBrake and Vehicle Dynamic Control Systems - Function and ComponentsTrương HàoNo ratings yet
- Tong HopDocument79 pagesTong HopTrương HàoNo ratings yet
- ABS GuideDocument57 pagesABS GuideTrương HàoNo ratings yet
- Automated IB5 Manual Transaxle - DiagnosisDocument62 pagesAutomated IB5 Manual Transaxle - DiagnosisTrương HàoNo ratings yet
- Vi SaiDocument7 pagesVi SaiTrương HàoNo ratings yet
- Combustion Engineering 1.en - VIDocument100 pagesCombustion Engineering 1.en - VITrương HàoNo ratings yet
- HDSD Thaco TowerDocument91 pagesHDSD Thaco TowerTrương HàoNo ratings yet
- Seat BeltsDocument15 pagesSeat BeltsTrương HàoNo ratings yet
- Bài Báo Cáo Máy Nén Cánh G T Ly TâmDocument16 pagesBài Báo Cáo Máy Nén Cánh G T Ly TâmTrương HàoNo ratings yet
- tháo phanh tang trốngDocument4 pagestháo phanh tang trốngTrương HàoNo ratings yet
- 05 Kia Un Air Con Gen VNDocument11 pages05 Kia Un Air Con Gen VNTrương HàoNo ratings yet
- Parking Distance System WiringDocument25 pagesParking Distance System WiringTrương HàoNo ratings yet
- Ngu N DB25 Ford Ranger 2002Document1 pageNgu N DB25 Ford Ranger 2002Trương HàoNo ratings yet
- Giáo Trình BDSC Đ NG CƠ PHUN XĂNG CĐ 120 GiDocument168 pagesGiáo Trình BDSC Đ NG CƠ PHUN XĂNG CĐ 120 GiTrương HàoNo ratings yet
- Lời Cảm Ơ1Document64 pagesLời Cảm Ơ1Trương HàoNo ratings yet
- Thiết bị KT áp suất phun xăngDocument1 pageThiết bị KT áp suất phun xăngTrương HàoNo ratings yet
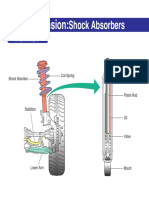
- SuspensionDocument4 pagesSuspensionTrương HàoNo ratings yet